

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (06): 793-806.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2023.0048
李咏兰1,2,3( ), 于会新2, 张兴华4, 宇克莉4, 包金萍5, 郑连斌4(
), 于会新2, 张兴华4, 宇克莉4, 包金萍5, 郑连斌4( )
)
收稿日期:2023-01-17
接受日期:2023-03-31
出版日期:2023-12-15
发布日期:2023-12-14
通讯作者:
郑连斌,教授,主要研究方向为人类生物学。E-mail: 作者简介:李咏兰,教授,主要从事体质人类学与人类群体遗传学研究。E-mail: 基金资助:
LI Yonglan1,2,3( ), YU Huixin2, ZHANG Xinghua4, YU Keli4, BAO Jinping5, ZHENG Lianbin4(
), YU Huixin2, ZHANG Xinghua4, YU Keli4, BAO Jinping5, ZHENG Lianbin4( )
)
Received:2023-01-17
Accepted:2023-03-31
Online:2023-12-15
Published:2023-12-14
摘要:
本文对近年来测量的45254例(男19892例,女25362例)中国人的18项头面部测量数据,按地理分区进行统计与主成分分析,发现中国东北、华北人群男性耳较长,两眼外角距离较近、鼻较狭,头、面较宽;华南人群耳较短,眼、鼻较宽,头较狭,面较狭;东北、华北人群女性面较高,面较宽,两眼距离较大,耳较长;华南、西南人群女性面较低,面较狭,两眼距离较近,耳较短。对中国人群和外国人群头面部数据进行主成分分析和聚类分析,发现中国人群男性、女性头面部特征都相对接近于高加索人种的波斯人、北美白人,与尼格罗人种的非裔美国人差距较大,与南亚人差距也较大;中国男性容貌耳长,眼内角间宽、鼻宽、头宽、形态面高值多小于尼格罗人种的4个人群,形态面高值多小于高加索人种的波斯人;中国女性鼻宽、口宽值小于非裔美国人,容貌面高、眼内角间宽、面宽多大于北美白人、伊朗人。中国地理分区人群头面部特征的共性与人群间长期的融合、具有相似的遗传结构有关,环境因素是其存在差异的重要原因。
中图分类号:
李咏兰, 于会新, 张兴华, 宇克莉, 包金萍, 郑连斌. 中国不同地理分区人群的头面部特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(06): 793-806.
LI Yonglan, YU Huixin, ZHANG Xinghua, YU Keli, BAO Jinping, ZHENG Lianbin. Head and facial features of populations in different geographical regions of China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2023, 42(06): 793-806.
| 指标Index | 东北人群NE | 华北人群NC | 华东人群EC | 华南人群SC | 华中人群CC | 西北人群NW | 西南人群SW | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | |||||||
| 头长Lg-op | 178.8 | 10.5 | 179.1 | 11.6 | 184.0 | 8.6 | 186.4 | 7.2 | 188.9 | 6.9 | 182.2 | 10.5 | 188.4 | 7.9 | ||||||
| 头宽beu-eu | 154.2 | 11.6 | 152.6 | 10.3 | 151.1 | 9.3 | 150.2 | 6.9 | 154.3 | 6.3 | 151.6 | 9.4 | 152.5 | 6.8 | ||||||
| 额最小宽bft-ft | 111.8 | 10.7 | 105.8 | 8.7 | 109.4 | 7.3 | 106.6 | 8.4 | 108.0 | 6.0 | 108.6 | 9.3 | 109.5 | 6.5 | ||||||
| 面宽bzy-zy | 136.8 | 12.5 | 139.1 | 11.4 | 139.4 | 9.1 | 139.3 | 8.5 | 146.4 | 6.2 | 136.6 | 9.8 | 142.6 | 6.9 | ||||||
| 下颌角间宽bgo-go | 115.6 | 13.7 | 114.4 | 9.5 | 109.1 | 8.1 | 114.3 | 6.9 | 115.5 | 7.0 | 109.6 | 10.4 | 113.1 | 7.4 | ||||||
| 眼内角间宽ben-en | 32.2 | 4.4 | 32.1 | 4.5 | 32.7 | 3.4 | 34.1 | 3.6 | 34.2 | 3.6 | 34.1 | 4.3 | 33.3 | 3.6 | ||||||
| 眼外角间宽bex-ex | 93.6 | 7.0 | 89.9 | 10.2 | 93.7 | 6.5 | 94.9 | 6.6 | 93.1 | 5.8 | 96.3 | 6.5 | 93.1 | 6.3 | ||||||
| 鼻宽bal-al | 39.0 | 3.7 | 38.1 | 3.9 | 38.5 | 3.0 | 39.9 | 3.1 | 38.2 | 3.3 | 38.4 | 3.6 | 38.8 | 3.4 | ||||||
| 口宽bch-ch | 52.5 | 5.0 | 52.0 | 5.5 | 50.5 | 4.2 | 51.3 | 4.0 | 50.0 | 5.0 | 52.4 | 4.7 | 50.3 | 4.8 | ||||||
| 容貌面高Htr-gn | 189.2 | 9.5 | 196.4 | 9.5 | 186.7 | 9.7 | 188.8 | 8.8 | 189.1 | 8.5 | 189.7 | 10.7 | 189.9 | 8.6 | ||||||
| 形态面高Hn-gn | 127.5 | 13.7 | 125.4 | 9.4 | 123.4 | 7.9 | 122.0 | 8.1 | 120.8 | 6.6 | 126.3 | 15.2 | 120.5 | 7.7 | ||||||
| 鼻高Hn-sn | 55.1 | 6.1 | 54.8 | 8.6 | 54.9 | 4.8 | 50.6 | 4.0 | 52.2 | 4.9 | 56.8 | 6.5 | 51.6 | 5.0 | ||||||
| 上唇皮肤部高Hsn-ls | 17.4 | 3.2 | 17.4 | 3.4 | 16.8 | 3.1 | 17.6 | 2.9 | 16.5 | 3.0 | 17.5 | 3.3 | 16.0 | 2.8 | ||||||
| 唇高Hls-li | 14.9 | 4.1 | 15.0 | 4.3 | 16.2 | 3.9 | 16.1 | 4.1 | 15.7 | 3.8 | 14.6 | 4.3 | 15.7 | 3.9 | ||||||
| 红唇厚度Hls-sto | 7.6 | 1.8 | 7.4 | 2.8 | 8.2 | 1.9 | 8.6 | 1.9 | 7.6 | 2.1 | 7.0 | 2.3 | 7.9 | 2.0 | ||||||
| 容貌耳长Lsa-sba | 66.4 | 6.4 | 67.7 | 6.8 | 64.8 | 5.4 | 64.0 | 5.0 | 64.8 | 5.2 | 65.8 | 6.2 | 63.1 | 5.3 | ||||||
| 容貌耳宽bpra-pa | 31.8 | 3.4 | 31.1 | 4.0 | 31.7 | 3.7 | 30.5 | 2.8 | 31.4 | 3.8 | 33.4 | 8.9 | 31.9 | 3.8 | ||||||
| 耳上头高Hve-tr | 131.7 | 11.4 | 129.6 | 12.4 | 131.3 | 12.3 | 125.4 | 9.8 | 126.5 | 9.5 | 129.6 | 11.9 | 126.0 | 10.7 | ||||||
表1 7个地理分区男性头面部指标均值和标准差
Tab.1 Mean of male head and face measurements in 7 geographical regions
| 指标Index | 东北人群NE | 华北人群NC | 华东人群EC | 华南人群SC | 华中人群CC | 西北人群NW | 西南人群SW | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | |||||||
| 头长Lg-op | 178.8 | 10.5 | 179.1 | 11.6 | 184.0 | 8.6 | 186.4 | 7.2 | 188.9 | 6.9 | 182.2 | 10.5 | 188.4 | 7.9 | ||||||
| 头宽beu-eu | 154.2 | 11.6 | 152.6 | 10.3 | 151.1 | 9.3 | 150.2 | 6.9 | 154.3 | 6.3 | 151.6 | 9.4 | 152.5 | 6.8 | ||||||
| 额最小宽bft-ft | 111.8 | 10.7 | 105.8 | 8.7 | 109.4 | 7.3 | 106.6 | 8.4 | 108.0 | 6.0 | 108.6 | 9.3 | 109.5 | 6.5 | ||||||
| 面宽bzy-zy | 136.8 | 12.5 | 139.1 | 11.4 | 139.4 | 9.1 | 139.3 | 8.5 | 146.4 | 6.2 | 136.6 | 9.8 | 142.6 | 6.9 | ||||||
| 下颌角间宽bgo-go | 115.6 | 13.7 | 114.4 | 9.5 | 109.1 | 8.1 | 114.3 | 6.9 | 115.5 | 7.0 | 109.6 | 10.4 | 113.1 | 7.4 | ||||||
| 眼内角间宽ben-en | 32.2 | 4.4 | 32.1 | 4.5 | 32.7 | 3.4 | 34.1 | 3.6 | 34.2 | 3.6 | 34.1 | 4.3 | 33.3 | 3.6 | ||||||
| 眼外角间宽bex-ex | 93.6 | 7.0 | 89.9 | 10.2 | 93.7 | 6.5 | 94.9 | 6.6 | 93.1 | 5.8 | 96.3 | 6.5 | 93.1 | 6.3 | ||||||
| 鼻宽bal-al | 39.0 | 3.7 | 38.1 | 3.9 | 38.5 | 3.0 | 39.9 | 3.1 | 38.2 | 3.3 | 38.4 | 3.6 | 38.8 | 3.4 | ||||||
| 口宽bch-ch | 52.5 | 5.0 | 52.0 | 5.5 | 50.5 | 4.2 | 51.3 | 4.0 | 50.0 | 5.0 | 52.4 | 4.7 | 50.3 | 4.8 | ||||||
| 容貌面高Htr-gn | 189.2 | 9.5 | 196.4 | 9.5 | 186.7 | 9.7 | 188.8 | 8.8 | 189.1 | 8.5 | 189.7 | 10.7 | 189.9 | 8.6 | ||||||
| 形态面高Hn-gn | 127.5 | 13.7 | 125.4 | 9.4 | 123.4 | 7.9 | 122.0 | 8.1 | 120.8 | 6.6 | 126.3 | 15.2 | 120.5 | 7.7 | ||||||
| 鼻高Hn-sn | 55.1 | 6.1 | 54.8 | 8.6 | 54.9 | 4.8 | 50.6 | 4.0 | 52.2 | 4.9 | 56.8 | 6.5 | 51.6 | 5.0 | ||||||
| 上唇皮肤部高Hsn-ls | 17.4 | 3.2 | 17.4 | 3.4 | 16.8 | 3.1 | 17.6 | 2.9 | 16.5 | 3.0 | 17.5 | 3.3 | 16.0 | 2.8 | ||||||
| 唇高Hls-li | 14.9 | 4.1 | 15.0 | 4.3 | 16.2 | 3.9 | 16.1 | 4.1 | 15.7 | 3.8 | 14.6 | 4.3 | 15.7 | 3.9 | ||||||
| 红唇厚度Hls-sto | 7.6 | 1.8 | 7.4 | 2.8 | 8.2 | 1.9 | 8.6 | 1.9 | 7.6 | 2.1 | 7.0 | 2.3 | 7.9 | 2.0 | ||||||
| 容貌耳长Lsa-sba | 66.4 | 6.4 | 67.7 | 6.8 | 64.8 | 5.4 | 64.0 | 5.0 | 64.8 | 5.2 | 65.8 | 6.2 | 63.1 | 5.3 | ||||||
| 容貌耳宽bpra-pa | 31.8 | 3.4 | 31.1 | 4.0 | 31.7 | 3.7 | 30.5 | 2.8 | 31.4 | 3.8 | 33.4 | 8.9 | 31.9 | 3.8 | ||||||
| 耳上头高Hve-tr | 131.7 | 11.4 | 129.6 | 12.4 | 131.3 | 12.3 | 125.4 | 9.8 | 126.5 | 9.5 | 129.6 | 11.9 | 126.0 | 10.7 | ||||||
| 指标Index | 东北人群NE | 华北人群NC | 华东人群EC | 华南人群SC | 华中人群CC | 西北人群NW | 西南人群SW | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | |||||||
| 头长Lg-op | 171.2 | 15.2 | 169.2 | 11.8 | 176.5 | 8.3 | 178.2 | 6.8 | 18.00 | 6.7 | 173.5 | 15.3 | 180.6 | 7.9 | ||||||
| 头宽beu-eu | 145.0 | 12.4 | 144.6 | 10.3 | 146.2 | 7.7 | 145.2 | 6.8 | 147.6 | 5.6 | 144.2 | 10.7 | 147.1 | 6.4 | ||||||
| 额最小宽bft-ft | 107.1 | 12.5 | 101.3 | 8.9 | 106.2 | 7.6 | 102.5 | 8.7 | 105.3 | 5.3 | 106.3 | 13.3 | 107.0 | 6.8 | ||||||
| 面宽bzy-zy | 124.8 | 13.0 | 128.7 | 13.4 | 133.9 | 8.0 | 132.5 | 7.8 | 138.0 | 6.2 | 126.1 | 13.6 | 135.9 | 6.8 | ||||||
| 下颌角间宽bgo-go | 109.1 | 13.4 | 109.7 | 10.1 | 104.5 | 8.4 | 108.3 | 7.3 | 109.7 | 7.6 | 103.1 | 16.0 | 108.5 | 8.2 | ||||||
| 眼内角间宽ben-en | 28.6 | 6.2 | 30.7 | 4.6 | 31.5 | 4.2 | 32.9 | 3.7 | 33.8 | 3.4 | 32.1 | 5.1 | 32.4 | 3.4 | ||||||
| 眼外角间宽bex-ex | 93.4 | 9.1 | 89.0 | 11.6 | 89.0 | 6.6 | 91.1 | 6.7 | 90.3 | 5.3 | 94.8 | 8.3 | 89.6 | 6.3 | ||||||
| 鼻宽bal-al | 36.9 | 4.1 | 35.1 | 3.6 | 35.7 | 2.8 | 36.9 | 3.3 | 35.4 | 2.9 | 35.3 | 3.5 | 35.9 | 3.3 | ||||||
| 口宽bch-ch | 53.2 | 7.6 | 50.0 | 5.9 | 47.5 | 4.1 | 48.8 | 4.0 | 47.6 | 4.5 | 49.5 | 5.3 | 47.5 | 4.7 | ||||||
| 容貌面高Htr-gn | 184.7 | 9.8 | 188.9 | 10.1 | 178.5 | 9.3 | 179.2 | 7.9 | 181.6 | 8.2 | 182.1 | 11.3 | 181.1 | 8.6 | ||||||
| 形态面高Hn-gn | 116 | 13.1 | 117.6 | 10.2 | 116.1 | 7.6 | 113.8 | 7.9 | 112.3 | 8.5 | 118.1 | 9.9 | 111.6 | 7.8 | ||||||
| 鼻高Hn-sn | 50.1 | 6.7 | 51.1 | 8.3 | 51.6 | 4.9 | 47.2 | 4.4 | 49.2 | 5.5 | 53.0 | 6.9 | 47.0 | 4.9 | ||||||
| 上唇皮肤部高Hsn-ls | 16.8 | 3.6 | 16.2 | 3.4 | 15.4 | 2.9 | 16.0 | 2.9 | 15.0 | 2.7 | 16.3 | 3.4 | 14.6 | 2.9 | ||||||
| 唇高Hls-li | 14.6 | 4.0 | 14.3 | 3.9 | 15.7 | 3.4 | 15.6 | 3.7 | 15.4 | 3.6 | 14.4 | 4.2 | 14.8 | 3.7 | ||||||
| 红唇厚度Hls-sto | 7.1 | 1.8 | 7.3 | 2.4 | 7.8 | 1.7 | 8.1 | 1.6 | 7.7 | 1.8 | 6.8 | 2.5 | 7.5 | 1.7 | ||||||
| 容貌耳长Lsa-sba | 62.8 | 6.3 | 64.9 | 6.1 | 61.0 | 5.2 | 60.7 | 16.4 | 60.4 | 5.1 | 62.4 | 6.1 | 59.7 | 5.3 | ||||||
| 容貌耳宽bpra-pa | 30.1 | 3.9 | 30.6 | 3.7 | 30.5 | 3.4 | 29.3 | 2.9 | 29.8 | 3.1 | 29.4 | 3.7 | 30.3 | 3.3 | ||||||
| 耳上头高Hve-tr | 128.8 | 11.9 | 125.7 | 11.3 | 129.7 | 10.9 | 122.0 | 10.0 | 121.2 | 9.0 | 126.1 | 12.1 | 121.4 | 9.8 | ||||||
表2 7个地理分区女性头面部测量指标测量结果
Tab.2 Mean of female head and face measurements in 7 geographical regions
| 指标Index | 东北人群NE | 华北人群NC | 华东人群EC | 华南人群SC | 华中人群CC | 西北人群NW | 西南人群SW | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | $\bar{X}$ | σ | |||||||
| 头长Lg-op | 171.2 | 15.2 | 169.2 | 11.8 | 176.5 | 8.3 | 178.2 | 6.8 | 18.00 | 6.7 | 173.5 | 15.3 | 180.6 | 7.9 | ||||||
| 头宽beu-eu | 145.0 | 12.4 | 144.6 | 10.3 | 146.2 | 7.7 | 145.2 | 6.8 | 147.6 | 5.6 | 144.2 | 10.7 | 147.1 | 6.4 | ||||||
| 额最小宽bft-ft | 107.1 | 12.5 | 101.3 | 8.9 | 106.2 | 7.6 | 102.5 | 8.7 | 105.3 | 5.3 | 106.3 | 13.3 | 107.0 | 6.8 | ||||||
| 面宽bzy-zy | 124.8 | 13.0 | 128.7 | 13.4 | 133.9 | 8.0 | 132.5 | 7.8 | 138.0 | 6.2 | 126.1 | 13.6 | 135.9 | 6.8 | ||||||
| 下颌角间宽bgo-go | 109.1 | 13.4 | 109.7 | 10.1 | 104.5 | 8.4 | 108.3 | 7.3 | 109.7 | 7.6 | 103.1 | 16.0 | 108.5 | 8.2 | ||||||
| 眼内角间宽ben-en | 28.6 | 6.2 | 30.7 | 4.6 | 31.5 | 4.2 | 32.9 | 3.7 | 33.8 | 3.4 | 32.1 | 5.1 | 32.4 | 3.4 | ||||||
| 眼外角间宽bex-ex | 93.4 | 9.1 | 89.0 | 11.6 | 89.0 | 6.6 | 91.1 | 6.7 | 90.3 | 5.3 | 94.8 | 8.3 | 89.6 | 6.3 | ||||||
| 鼻宽bal-al | 36.9 | 4.1 | 35.1 | 3.6 | 35.7 | 2.8 | 36.9 | 3.3 | 35.4 | 2.9 | 35.3 | 3.5 | 35.9 | 3.3 | ||||||
| 口宽bch-ch | 53.2 | 7.6 | 50.0 | 5.9 | 47.5 | 4.1 | 48.8 | 4.0 | 47.6 | 4.5 | 49.5 | 5.3 | 47.5 | 4.7 | ||||||
| 容貌面高Htr-gn | 184.7 | 9.8 | 188.9 | 10.1 | 178.5 | 9.3 | 179.2 | 7.9 | 181.6 | 8.2 | 182.1 | 11.3 | 181.1 | 8.6 | ||||||
| 形态面高Hn-gn | 116 | 13.1 | 117.6 | 10.2 | 116.1 | 7.6 | 113.8 | 7.9 | 112.3 | 8.5 | 118.1 | 9.9 | 111.6 | 7.8 | ||||||
| 鼻高Hn-sn | 50.1 | 6.7 | 51.1 | 8.3 | 51.6 | 4.9 | 47.2 | 4.4 | 49.2 | 5.5 | 53.0 | 6.9 | 47.0 | 4.9 | ||||||
| 上唇皮肤部高Hsn-ls | 16.8 | 3.6 | 16.2 | 3.4 | 15.4 | 2.9 | 16.0 | 2.9 | 15.0 | 2.7 | 16.3 | 3.4 | 14.6 | 2.9 | ||||||
| 唇高Hls-li | 14.6 | 4.0 | 14.3 | 3.9 | 15.7 | 3.4 | 15.6 | 3.7 | 15.4 | 3.6 | 14.4 | 4.2 | 14.8 | 3.7 | ||||||
| 红唇厚度Hls-sto | 7.1 | 1.8 | 7.3 | 2.4 | 7.8 | 1.7 | 8.1 | 1.6 | 7.7 | 1.8 | 6.8 | 2.5 | 7.5 | 1.7 | ||||||
| 容貌耳长Lsa-sba | 62.8 | 6.3 | 64.9 | 6.1 | 61.0 | 5.2 | 60.7 | 16.4 | 60.4 | 5.1 | 62.4 | 6.1 | 59.7 | 5.3 | ||||||
| 容貌耳宽bpra-pa | 30.1 | 3.9 | 30.6 | 3.7 | 30.5 | 3.4 | 29.3 | 2.9 | 29.8 | 3.1 | 29.4 | 3.7 | 30.3 | 3.3 | ||||||
| 耳上头高Hve-tr | 128.8 | 11.9 | 125.7 | 11.3 | 129.7 | 10.9 | 122.0 | 10.0 | 121.2 | 9.0 | 126.1 | 12.1 | 121.4 | 9.8 | ||||||
| 人群 Population | 头长Lg-op | 头宽beu-eu | 面宽bzy-zy | 眼内角间宽ben-en | 眼外角间宽bex-ex | 鼻宽 bal-al | 形态面高 Hn-gn | 容貌耳长Lsa-sba |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东北人群NE | 179.9 | 158.0 | 139.3 | 34.1 | 93.6 | 37.9 | 128.4 | 64.8 |
| 华北人群NC | 180.2 | 154.2 | 140.7 | 32.0 | 89.9 | 36.8 | 124.0 | 64.8 |
| 华东人群EC | 185.4 | 153.6 | 141.5 | 33.0 | 93.7 | 38.6 | 123.0 | 63.1 |
| 华南人群SC | 185.4 | 152.7 | 141.7 | 34.8 | 94.9 | 39.4 | 120.8 | 61.3 |
| 华中人群CC | 188.5 | 155.5 | 147.1 | 35.2 | 93.1 | 38.0 | 120.1 | 63.9 |
| 西北人群NW | 179.6 | 152.6 | 136.5 | 33.9 | 96.3 | 37.7 | 123.7 | 63.3 |
| 西南人群SW | 188.7 | 153.8 | 143.5 | 33.6 | 93.1 | 38.3 | 120.0 | 61.4 |
| 波斯人Per | 194.4 | 158.7 | 141.2 | 32.8 | 94.7 | 36.7 | 127.4 | 63.3 |
| 北美白人NAW | 193.7 | 153.3 | 139.1 | 32.9 | 90.7 | 34.8 | 121.3 | 62.4 |
| 非裔美国人AfA | 199.1 | 148.0 | 139.0 | 35.8 | 96.8 | 44.1 | 125.6 | 60.5 |
| 尼日利亚人Nig | 193.8 | 149.2 | 127.1 | 34.1 | 99.1 | 42.4 | 117.4 | 60.0 |
| 乌干达人Uga | 195.2 | 149.6 | 126.7 | 34.5 | 101.4 | 42.8 | 126.5 | 59.4 |
| 肯尼亚人Ken | 195.5 | 153.3 | 127.5 | 35.1 | 101.8 | 40.1 | 130.7 | 59.9 |
表3 13个男性人群头面部测量指标值
Tab.3 Mean of male head and face measurements in 13 populations (mm)
| 人群 Population | 头长Lg-op | 头宽beu-eu | 面宽bzy-zy | 眼内角间宽ben-en | 眼外角间宽bex-ex | 鼻宽 bal-al | 形态面高 Hn-gn | 容貌耳长Lsa-sba |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东北人群NE | 179.9 | 158.0 | 139.3 | 34.1 | 93.6 | 37.9 | 128.4 | 64.8 |
| 华北人群NC | 180.2 | 154.2 | 140.7 | 32.0 | 89.9 | 36.8 | 124.0 | 64.8 |
| 华东人群EC | 185.4 | 153.6 | 141.5 | 33.0 | 93.7 | 38.6 | 123.0 | 63.1 |
| 华南人群SC | 185.4 | 152.7 | 141.7 | 34.8 | 94.9 | 39.4 | 120.8 | 61.3 |
| 华中人群CC | 188.5 | 155.5 | 147.1 | 35.2 | 93.1 | 38.0 | 120.1 | 63.9 |
| 西北人群NW | 179.6 | 152.6 | 136.5 | 33.9 | 96.3 | 37.7 | 123.7 | 63.3 |
| 西南人群SW | 188.7 | 153.8 | 143.5 | 33.6 | 93.1 | 38.3 | 120.0 | 61.4 |
| 波斯人Per | 194.4 | 158.7 | 141.2 | 32.8 | 94.7 | 36.7 | 127.4 | 63.3 |
| 北美白人NAW | 193.7 | 153.3 | 139.1 | 32.9 | 90.7 | 34.8 | 121.3 | 62.4 |
| 非裔美国人AfA | 199.1 | 148.0 | 139.0 | 35.8 | 96.8 | 44.1 | 125.6 | 60.5 |
| 尼日利亚人Nig | 193.8 | 149.2 | 127.1 | 34.1 | 99.1 | 42.4 | 117.4 | 60.0 |
| 乌干达人Uga | 195.2 | 149.6 | 126.7 | 34.5 | 101.4 | 42.8 | 126.5 | 59.4 |
| 肯尼亚人Ken | 195.5 | 153.3 | 127.5 | 35.1 | 101.8 | 40.1 | 130.7 | 59.9 |
| 人群 Population | 面宽 bzy-zy | 下颌角间宽 bgo-go | 眼内角间宽ben-en | 鼻宽 bal-al | 口宽 bch-ch | 容貌面高Htr-gn | 形态面高Hn-gn | 鼻高 Hn-sn | 容貌耳长Lsa-sba |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东北人群NE | 129.1 | 113.2 | 32.9 | 35.2 | 48.1 | 184.7 | 120.2 | 51.4 | 61.2 |
| 华北人群NC | 132.1 | 109.4 | 31.1 | 34.2 | 48.1 | 188.9 | 116.2 | 49.2 | 62.5 |
| 华东人群EC | 135.5 | 104.2 | 32.3 | 35.5 | 47.0 | 178.5 | 115.4 | 51.1 | 58.8 |
| 华南人群SC | 133.9 | 108.7 | 33.4 | 36.4 | 48.2 | 179.2 | 112.7 | 47.1 | 57.8 |
| 华中人群CC | 139.3 | 109.5 | 34.7 | 34.7 | 46.0 | 181.6 | 111.6 | 48.5 | 58.6 |
| 西北人群NW | 125.0 | 100.4 | 31.5 | 34.6 | 48.8 | 182.1 | 115.4 | 51.8 | 60.1 |
| 西南人群SW | 136.6 | 108.6 | 32.6 | 35.1 | 46.5 | 181.1 | 111.5 | 46.5 | 57.7 |
| 波斯人Per | 131.5 | 101.0 | 32.2 | 32.8 | 47.0 | 180.1 | 120.1 | 56.8 | 59.5 |
| 北美白人NAW | 131.1 | 94.5 | 32.5 | 31.9 | 49.8 | 173.3 | 112.0 | 49.2 | 59.0 |
| 非裔美国人AfA | 130.5 | 96.7 | 34.4 | 40.1 | 53.6 | 179.9 | 116.5 | 48.8 | 57.2 |
| 南亚人SAs | 116.2 | 101.6 | 23.8 | 33.8 | 46.5 | 163.0 | 107.6 | 43.7 | 54.6 |
| 伊朗人Ira | 127.1 | 97.2 | 28.7 | 30.1 | 49.1 | 176.2 | 122.7 | 46.1 | 58.5 |
| 印度裔美国人IAW | 125.9 | 95.2 | 31.2 | 35.6 | 51.1 | 169.4 | 102.3 | 45.6 | 58.6 |
表4 13个女性人群头面部测量指标值
Tab.4 Mean of female head and face measurements in 13 populations (mm)
| 人群 Population | 面宽 bzy-zy | 下颌角间宽 bgo-go | 眼内角间宽ben-en | 鼻宽 bal-al | 口宽 bch-ch | 容貌面高Htr-gn | 形态面高Hn-gn | 鼻高 Hn-sn | 容貌耳长Lsa-sba |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东北人群NE | 129.1 | 113.2 | 32.9 | 35.2 | 48.1 | 184.7 | 120.2 | 51.4 | 61.2 |
| 华北人群NC | 132.1 | 109.4 | 31.1 | 34.2 | 48.1 | 188.9 | 116.2 | 49.2 | 62.5 |
| 华东人群EC | 135.5 | 104.2 | 32.3 | 35.5 | 47.0 | 178.5 | 115.4 | 51.1 | 58.8 |
| 华南人群SC | 133.9 | 108.7 | 33.4 | 36.4 | 48.2 | 179.2 | 112.7 | 47.1 | 57.8 |
| 华中人群CC | 139.3 | 109.5 | 34.7 | 34.7 | 46.0 | 181.6 | 111.6 | 48.5 | 58.6 |
| 西北人群NW | 125.0 | 100.4 | 31.5 | 34.6 | 48.8 | 182.1 | 115.4 | 51.8 | 60.1 |
| 西南人群SW | 136.6 | 108.6 | 32.6 | 35.1 | 46.5 | 181.1 | 111.5 | 46.5 | 57.7 |
| 波斯人Per | 131.5 | 101.0 | 32.2 | 32.8 | 47.0 | 180.1 | 120.1 | 56.8 | 59.5 |
| 北美白人NAW | 131.1 | 94.5 | 32.5 | 31.9 | 49.8 | 173.3 | 112.0 | 49.2 | 59.0 |
| 非裔美国人AfA | 130.5 | 96.7 | 34.4 | 40.1 | 53.6 | 179.9 | 116.5 | 48.8 | 57.2 |
| 南亚人SAs | 116.2 | 101.6 | 23.8 | 33.8 | 46.5 | 163.0 | 107.6 | 43.7 | 54.6 |
| 伊朗人Ira | 127.1 | 97.2 | 28.7 | 30.1 | 49.1 | 176.2 | 122.7 | 46.1 | 58.5 |
| 印度裔美国人IAW | 125.9 | 95.2 | 31.2 | 35.6 | 51.1 | 169.4 | 102.3 | 45.6 | 58.6 |
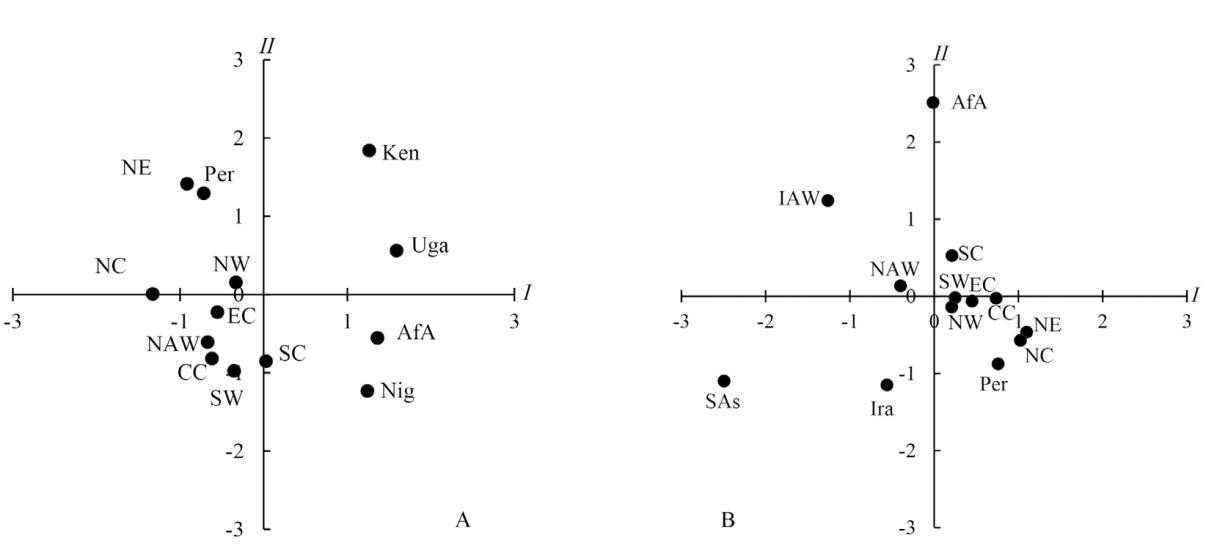
图1 13个人群头面部测量指标值的主成分分析 A.男性;B.女性。NE---东北人群;NC---华北人群;EC---华东人群;SC---华南人群;CC---华中人群;NW---西北人群;SW---西南人群;Per---波斯人;NAW---北美白人;AfA---非裔美国人;SAs---南亚人;Nig---尼日利亚人;Uga---乌干达人;Ken---肯尼亚人;Ira---伊朗人;IAW---印度裔美国人
Fig.1 Principal component analysis of head and face measurements in 13 populations
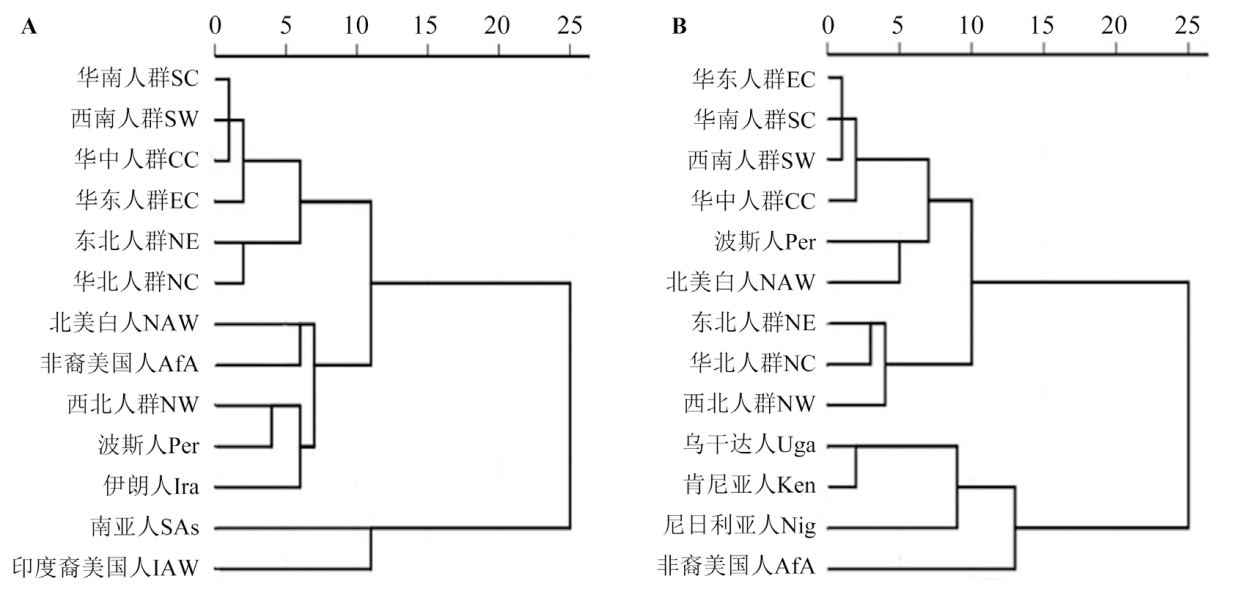
图2 13个人群头面部测量指标值的聚类分析 A.男性;B.女性。NE—东北人群;NC—华北人群;EC—华东人群;SC—华南人群;CC—华中人群;NW—西北人群;SW—西南人群;Per—波斯人;NAW—北美白人;AfA—非裔美国人;SAs—南亚人;Nig—尼日利亚人;Uga—乌干达人;Ken—肯尼亚人;Ira—伊朗人;IAW—印度裔美国人
Fig.2 Cluster analysis of head and face measurements in 13 populations
| 人群Population | 男头长Lg-op(Male) | 男头宽beu-eu(Male) | 女头长Lg-op(Female) | 女头宽beu-eu(Female) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\bar{X}$ | σ | u | $\bar{X}$ | σ | u | $\bar{X}$ | σ | u | $\bar{X}$ | σ | u | ||||
| 华北人群NC | 180.2 | 10.9 | — | 154.2 | 10.3 | — | 170.7 | 10.8 | — | 147.3 | 9.3 | — | |||
| 波斯人Per | 194.4 | 6.2 | 13.33** | 158.7 | 5.4 | 4.72** | 186.7 | 5.5 | 16.03** | 151.8 | 3.9 | 5.84** | |||
| 塞尔维亚人Ser[ | 190.4 | 7.4 | 16.21** | 157.9 | 7.6 | 5.90** | 178.4 | 6.5 | 12.01** | 150.2 | 6.2 | 5.18** | |||
| 韩国人Kor[ | 188.1 | 7.6 | 12.56** | 158.4 | 7.6 | 6.68** | — | — | — | — | |||||
表5 华北人群与外国人群头长、头宽值的u检验
Tab.5 U-test of head length and breadth between North China and foreign population
| 人群Population | 男头长Lg-op(Male) | 男头宽beu-eu(Male) | 女头长Lg-op(Female) | 女头宽beu-eu(Female) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\bar{X}$ | σ | u | $\bar{X}$ | σ | u | $\bar{X}$ | σ | u | $\bar{X}$ | σ | u | ||||
| 华北人群NC | 180.2 | 10.9 | — | 154.2 | 10.3 | — | 170.7 | 10.8 | — | 147.3 | 9.3 | — | |||
| 波斯人Per | 194.4 | 6.2 | 13.33** | 158.7 | 5.4 | 4.72** | 186.7 | 5.5 | 16.03** | 151.8 | 3.9 | 5.84** | |||
| 塞尔维亚人Ser[ | 190.4 | 7.4 | 16.21** | 157.9 | 7.6 | 5.90** | 178.4 | 6.5 | 12.01** | 150.2 | 6.2 | 5.18** | |||
| 韩国人Kor[ | 188.1 | 7.6 | 12.56** | 158.4 | 7.6 | 6.68** | — | — | — | — | |||||
| 性别Sex | 人群Population | $\bar{X}$ | σ | u |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性Male | 华北人群NC | 36.8 | 3.6 | — |
| 肯尼亚人Ken[ | 45.5 | 9.4 | 6.14** | |
| 尼日利亚人Nig[ | 42.4 | 4.0 | 6.91** | |
| 乌干达人Uga[ | 42.8 | 5.0 | 13.87** | |
| 女性Female | 华北人群NC | 34.2 | 3.2 | — |
| 肯尼亚人Ken[ | 44.7 | 6.5 | 10.65** | |
| 韩裔美国人KA[ | 35.5 | 3.4 | 2.94** | |
| 北美白人NAW[ | 31.4 | 2.0 | 12.01** | |
| 科索沃人Kso[ | 33.1 | 2.2 | 3.77** |
表6 华北人群与外国人群鼻宽值的u检验
Tab.6 U-test of nose breadth between North China and foreign population
| 性别Sex | 人群Population | $\bar{X}$ | σ | u |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性Male | 华北人群NC | 36.8 | 3.6 | — |
| 肯尼亚人Ken[ | 45.5 | 9.4 | 6.14** | |
| 尼日利亚人Nig[ | 42.4 | 4.0 | 6.91** | |
| 乌干达人Uga[ | 42.8 | 5.0 | 13.87** | |
| 女性Female | 华北人群NC | 34.2 | 3.2 | — |
| 肯尼亚人Ken[ | 44.7 | 6.5 | 10.65** | |
| 韩裔美国人KA[ | 35.5 | 3.4 | 2.94** | |
| 北美白人NAW[ | 31.4 | 2.0 | 12.01** | |
| 科索沃人Kso[ | 33.1 | 2.2 | 3.77** |
| 人群Population | 男性Male | 女性Female | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年均温度MAT(°C) | 年均降水量MAP(mm) | 年均光照MAS(h) | 年均温度MAT(°C) | 年均降水量MAP(mm) | 年均光照MAS(h) | ||
| 东北人群NE | 5.9 | 681.4 | 2383.6 | 6.3 | 706.4 | 2336 | |
| 华北人群NC | 2.3 | 384.1 | 2805.2 | 6.3 | 706.4 | 2336 | |
| 华东人群EC | 17.4 | 1181.4 | 1868.3 | 16.7 | 1131 | 1952.6 | |
| 华南人群SC | 20.5 | 1468.3 | 1660.4 | 21.1 | 1499.8 | 1599 | |
| 华中人群CC | 16.0 | 1007.9 | 1681.7 | 16.3 | 1054.4 | 1557.7 | |
| 西北人群NW | 9.5 | 377.4 | 2518.8 | 9.0 | 284.3 | 2582.4 | |
| 西南人群SW | 15.6 | 1279.5 | 1805.0 | 15.9 | 1295.5 | 1901.0 | |
表7 不同地理分区被测量者的地理指标均数
Tab.7 The mean of geographical indicators in different regions
| 人群Population | 男性Male | 女性Female | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年均温度MAT(°C) | 年均降水量MAP(mm) | 年均光照MAS(h) | 年均温度MAT(°C) | 年均降水量MAP(mm) | 年均光照MAS(h) | ||
| 东北人群NE | 5.9 | 681.4 | 2383.6 | 6.3 | 706.4 | 2336 | |
| 华北人群NC | 2.3 | 384.1 | 2805.2 | 6.3 | 706.4 | 2336 | |
| 华东人群EC | 17.4 | 1181.4 | 1868.3 | 16.7 | 1131 | 1952.6 | |
| 华南人群SC | 20.5 | 1468.3 | 1660.4 | 21.1 | 1499.8 | 1599 | |
| 华中人群CC | 16.0 | 1007.9 | 1681.7 | 16.3 | 1054.4 | 1557.7 | |
| 西北人群NW | 9.5 | 377.4 | 2518.8 | 9.0 | 284.3 | 2582.4 | |
| 西南人群SW | 15.6 | 1279.5 | 1805.0 | 15.9 | 1295.5 | 1901.0 | |
| 指标Index | 男性Male | 女性Female | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年均温度MAT (°C) | 年均降水量MAP(mm) | 年均光照MAS (h) | 年均温度MAT (°C) | 年均降水量MAP(mm) | 年均光照MAS (h) | ||
| 头长Lg-op | 0.128** | 0.181** | -0.195** | 0.136** | 0.198** | -0.166** | |
| 头宽beu-eu | -0.105** | -0.068** | 0.061** | -0.032** | 0.042** | -0.058** | |
| 额最小宽bft-ft | -0.046** | 0.022** | -0.016* | -0.102** | 0.012 | 0.01 | |
| 面宽bzy-zy | 0.024** | 0.091** | -0.156** | 0.191** | 0.236** | -0.320** | |
| 下颌角间宽bgo-go | -0.012 | 0.021** | -0.077** | -0.009 | 0.064** | -0.133** | |
| 眼内角间宽ben-en | 0.060** | 0.017* | -0.066** | 0.105** | 0.094** | -0.132** | |
| 鼻宽bal-al | 0.113** | 0.102** | 0.046** | 0.127** | 0.143** | 0.031** | |
| 口宽bch-ch | -0.079** | -0.095** | 0.090** | -0.117** | -0.096** | 0.117** | |
| 形态面高Hn-gn | -0.219** | -0.178** | 0.198** | -0.276** | -0.240** | 0.222** | |
| 鼻高Hn-sn | -0.277** | -0.264** | 0.302** | -0.278** | -0.291** | 0.285** | |
| 上唇皮肤部高度Hsn-ls | -0.091** | -0.159** | 0.156** | -0.140** | -0.174** | 0.174** | |
| 唇高Hls-li | 0.095** | 0.149** | -0.096** | 0.101** | 0.113** | -0.084** | |
| 容貌耳长Lsa-sba | -0.203** | -0.204** | 0.213** | -0.144** | -0.131** | 0.141** | |
| 耳上头高Hve-tr | -0.095** | -0.126** | 0.141** | -0.148** | -0.137** | 0.172** | |
表8 中国人头面部测量指标与地理环境指标的相关系数
Tab.8 Correlation coefficient between China’s head face measurement index and geographical environment index
| 指标Index | 男性Male | 女性Female | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年均温度MAT (°C) | 年均降水量MAP(mm) | 年均光照MAS (h) | 年均温度MAT (°C) | 年均降水量MAP(mm) | 年均光照MAS (h) | ||
| 头长Lg-op | 0.128** | 0.181** | -0.195** | 0.136** | 0.198** | -0.166** | |
| 头宽beu-eu | -0.105** | -0.068** | 0.061** | -0.032** | 0.042** | -0.058** | |
| 额最小宽bft-ft | -0.046** | 0.022** | -0.016* | -0.102** | 0.012 | 0.01 | |
| 面宽bzy-zy | 0.024** | 0.091** | -0.156** | 0.191** | 0.236** | -0.320** | |
| 下颌角间宽bgo-go | -0.012 | 0.021** | -0.077** | -0.009 | 0.064** | -0.133** | |
| 眼内角间宽ben-en | 0.060** | 0.017* | -0.066** | 0.105** | 0.094** | -0.132** | |
| 鼻宽bal-al | 0.113** | 0.102** | 0.046** | 0.127** | 0.143** | 0.031** | |
| 口宽bch-ch | -0.079** | -0.095** | 0.090** | -0.117** | -0.096** | 0.117** | |
| 形态面高Hn-gn | -0.219** | -0.178** | 0.198** | -0.276** | -0.240** | 0.222** | |
| 鼻高Hn-sn | -0.277** | -0.264** | 0.302** | -0.278** | -0.291** | 0.285** | |
| 上唇皮肤部高度Hsn-ls | -0.091** | -0.159** | 0.156** | -0.140** | -0.174** | 0.174** | |
| 唇高Hls-li | 0.095** | 0.149** | -0.096** | 0.101** | 0.113** | -0.084** | |
| 容貌耳长Lsa-sba | -0.203** | -0.204** | 0.213** | -0.144** | -0.131** | 0.141** | |
| 耳上头高Hve-tr | -0.095** | -0.126** | 0.141** | -0.148** | -0.137** | 0.172** | |
| [1] |
李咏兰, 郑连斌, 席焕久, 等. 中国北方、南方汉族体重的差异[J]. 解剖学报, 2015, 46(2): 270-274
doi: 10.16098/j.issn.0529-1356.2015.02.021 |
| [2] | 孙泽阳, 郑连斌, 宇克莉, 等. 中国藏缅语族未识别民族的体质特征[J]. 天津师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 42(1): 73-80 |
| [3] | 席焕久, 陈昭. 人体测量方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010 |
| [4] |
Amini F, Mashayekhi Z, Rahimi H, et al. Craniofacial morphologic parameters in a persian population: an anthropometric study[J]. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 2014, 25(5): 1874-1881
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000000902 pmid: 25203584 |
| [5] |
Farkas LG, Katic MJ, Forrest CR. Comparison of craniofacial measurements of young adult African-American and North American white males and females[J]. Annals of Plastic Surgery, 2007, 59(6): 692-698
doi: 10.1097/01.sap.0000258954.55068.b4 pmid: 18046155 |
| [6] |
Taura MG, Adamu LH, Gudaji A. Variation of facial features among three African populations: Body height match analyses[J]. Homo, 2017, 68(1): 69-79
doi: S0018-442X(16)30073-7 pmid: 28017294 |
| [7] |
Raveendran M. The South Asian facial anthropometric profile: a systematic review[J]. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery, 2019, 47(2): 263-272
doi: S1010-5182(18)30165-3 pmid: 30573375 |
| [8] |
Bayat M, Shariati M, Rajaeirad F, et al. Facial anthropometric norms of the young Iranian population[J]. Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery, 2018, 17(2): 150-157
doi: 10.1007/s12663-016-0897-3 pmid: 29618878 |
| [9] | Husein OF, Sepehr A, Garg R, et al. Anthropometric and aesthetic analysis of the Indian American woman’s face[J]. Journal of Plastic Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, 2010, 63(11): 1825-1831 |
| [10] |
Pavlica TM, Rakić RS, Božić-Krstić VS, et al. Secular trend of head and face shape in adult population of Vojvodina (Serbia)[J]. Annals of Human Biology, 2018, 45(4): 330-336
doi: 10.1080/03014460.2018.1452981 pmid: 29534623 |
| [11] |
Song WC, Kim JI, Kim SH, et al. Female-to-male proportions of the head and face in Koreans[J]. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 2009, 20(2): 356-361
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181843620 URL |
| [12] |
Sarna K, Sonigra K, Ngeow WC. A cross-sectional study to determine and compare the craniofacial anthropometric norms in a selected Kenyan and Chinese population[J]. Plastic Surgery, 2023, 31(1): 84-90
doi: 10.1177/22925503211024763 pmid: 36755821 |
| [13] |
Choe KS, Sclafani AP, Litner JA, et al. The Korean American woman's face[J]. Archives of Facial Plastic Surgery, 2004, 6(4): 244-252
doi: 10.1001/archfaci.6.4.244 URL |
| [14] |
Staka G, Asllani-Hoxha F, Bimbashi V. Facial anthropometric norms among Kosovo-Albanian adults[J]. Acta Stomatologica Croatica, 2017, 51(3): 195-206
doi: 10.15644/asc URL |
| [15] | 殷杏, 孙畅, 谭婧泽. 头面部测量特征证实汉族存在南北中地区差异[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2021, 44(S1): 11-11 |
| [16] | 马立广, 曹彦荣, 徐玖瑾, 等. 中国102 个人群的身高与地理环境相关性研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(3): 223-231 |
| [17] | 林琬生, 胡承康. 中国青年生长发育环境差异的研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1990, 9(2): 152-159 |
| [18] |
Meiri S, Yom-Tov Y, Geffen E. What determines conformity to Bergmann's rule?[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2007, 16(6): 788-794
doi: 10.1111/geb.2007.16.issue-6 URL |
| [19] | Leonard WR, Katzmarzyk PT. Body size and shape: Climatic and nutritional influences on human body morphology[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010 |
| [20] |
Arya R, Duggirala R, Comuzzie AG, et al. Heritability of anthropometric phenotypes in caste populations of Visakhapatnam, India[J]. Human biology, 2002, 74(3): 325-344
pmid: 12180759 |
| [21] | 杜利利, 兰亚佳, 王海椒, 等. 汉语族人头面部特征分析[J]. 工业卫生与职业病, 2010, 36(1): 13-17 |
| [22] |
Sero D, Zaidi A, Li J, et al. Facial recognition from DNA using face-to-DNA classifiers[J]. Nature communications, 2019, 10(1): 2557
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10617-y pmid: 31186421 |
| [23] | 宋春波, Macarena FG, Kaustubh A, 等. 秘鲁人面部形态特征的全基因组关联分析[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2021, 7: 2810-2818 |
| [24] | 曾雯, 李佳伟, 岳洪彬, 等. 2004年殷墟大司空遗址出土人骨线粒体DNA研究报告[J]. 华夏考古, 2018, 2: 100-105 |
| [25] | 朱思媚, 周亚威, 朱泓, 等. 华北民族融合进程中人群生存方式及对健康的影响:以北京延庆西屯村墓地为例[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(1): 127-134 |
| [26] | Li J, Zhang Y, Zhu H, et al. Genetic Research of Ancient Human Remains in the Central Plains during Yangshao Period[C]. NJ USA: WILEY, 2019, 168: 143-143 |
| [27] |
Yang MA, Fan X, Sun B, et al. Ancient DNA indicates human population shifts and admixture in northern and southern China[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6501): 282-288
doi: 10.1126/science.aba0909 pmid: 32409524 |
| [28] |
Wang CC, Yeh HY, Popov AN, et al. Genomic insights into the formation of human populations in East Asia[J]. Nature, 2021, 591(7850): 413-419
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03336-2 |
| [29] |
Xu S, Yin X, Li S, et al. Genomic dissection of population substructure of Han Chinese and its implication in association studies[J]. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 2009, 85(6): 762-774
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.10.015 URL |
| [30] |
Cao Y, Li L, Xu M, et al. The China MAP analytics of deep whole genome sequences in 10,588 individuals[J]. Cell Research, 2020, 30(9): 717-731
doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0322-9 |
| [31] |
He GL, Wang MG, Zou X, et al. Extensive ethnolinguistic diversity at the crossroads of North China and South Siberia reflects multiple sources of genetic diversity[J]. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 2023, 61(1): 230-250
doi: 10.1111/jse.12827 |
| [32] |
Wang MG, He GL, Zou X, et al. Reconstructing the genetic admixture history of Tai-Kadai and Sinitic people: Insights from genome-wide SNP data from South China[J]. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 2023, 61(1): 157-178
doi: 10.1111/jse.12825 |
| [33] | 康龙丽. 西藏各民族遗传多样性研究[M]. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 2020 |
| [34] |
He GL, Li YX, Wang MG, et al. Fine-scale genetic structure of Tuiia and central Han Chinese revealing massive genetic admixture under language borrowing[J]. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 2021, 59(1): 1-20
doi: 10.1111/jse.v59.1 URL |
| [35] | Pan Y, Wen J, Ning Z, et al. Comparative genomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal the impacts of genetic admixture in Kazaks, Uyghurs, and Huis[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2023, 40(3): 54 |
| [36] | Zhang G, Cui C, Wangdue S, et al. Maternal genetic history of ancient Tibetans over the past 4,000 years[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2023, Mar 16: S1673-8527(23)00071-1 |
| [37] |
Zhang MF, Wu SJ, Du SY, et al. Genetic variants underlying differences in facial morphology in East Asian and European populations[J]. Nature Genetics, 2022, 54(4): 403-411
doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01038-7 pmid: 35393595 |
| [38] | 李咏兰, 宇克莉, 张兴华, 等. 藏族的体质类型和人种学特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(4): 698-711 |
| [39] | 周大鸣. 从瑶族看中华民族共同体的形成[J]. 云南民族大学学报:哲学社会科学版, 2023, 40(1): 24-31 |
| [1] | 张咸鹏, 温有锋, 李文慧, 李欣, 曲泉颖, 徐国昌. 中国阿尔泰语系人群头面部的表型特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(03): 342-358. |
| [2] | 张明, 平婉菁, YANG Melinda Anna, 付巧妹. 古基因组揭示史前欧亚大陆现代人复杂遗传历史[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(03): 412-421. |
| [3] | 杜抱朴, 殷钰喆, 谭伊, 张宇格, 范博, 姚植正, 郭航. 中国现代人群两性身高差异分布及其影响因素[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(02): 191-200. |
| [4] | 叶芷, 杜雨薇, 裴树文, 丁馨, 徐哲, 马东东. 蔚县盆地吉家庄旧石器遗址的形成过程[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(01): 46-60. |
| [5] | 刘燕, 李玉玲. 遗传和环境因素对儿童青少年身体高度及其比例的影响[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(05): 875-882. |
| [6] | 李文琴, 覃大保, 熊健, 张惠娟, 黄大元. 腊尔山区苗族学生头面部形态特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(05): 862-874. |
| [7] | 李咏兰, 张兴华, 孙泽阳, 宇克莉, 包金萍, 郑连斌. 中国人的头面部形态特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(03): 450-462. |
| [8] | 刘晓敏, 乌云达来, 李玉玲. 双生子多巴胺D3受体基因多态性对儿童体成分的影响[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 274-281. |
| [9] | 李浩, 雷蕾, 李大伟, 张萌. 述评典型阿舍利遗址的石器技术及其蕴含的古人类行为[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 354-369. |
| [10] | 张金科, 董薇, 唐光峰, 黄晓亮, 杨振, 王晓军, 张杰, 赵英健, 朱奕卿, 江丽. 山东汉、回族男性人群父系遗传结构研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(01): 65-72. |
| [11] | 宇克莉, 向小雪, 李咏兰, 张洪明, 杜慧敏. 中国夏尔巴人的体质特征研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(05): 801-810. |
| [12] | 杜抱朴, 杜靖. 中国现代人群上、下肢形态与环境温度的相关性分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(04): 644-652. |
| [13] | 张兴华, 宇克莉, 郑连斌. 中国14个特殊旁系族群的头面部特征比较[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(02): 226-238. |
| [14] | 包金萍, 郑连斌, 宇克莉, 贾亚兰. 基诺族体质特征及35年来体质的变化[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(02): 261-271. |
| [15] | 张兴香, 李雍, 吴晓桐, 宋艳波, 栾丰实, 薛新明, 金正耀. 黄河流域出土龙山时期扬子鳄骨板的多种同位素分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(01): 75-86. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3