

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (05): 757-766.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0048cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0048
收稿日期:2023-09-19
修回日期:2024-01-19
出版日期:2024-10-15
发布日期:2024-10-10
通讯作者:
周亚威
作者简介:刘驷统,硕士研究生,主要从事人骨考古研究。E-mail: 17684352214@163.com
基金资助:
LIU Sitong1( ), GU Wanfa2, WU Qian2, ZHOU Yawei1(
), GU Wanfa2, WU Qian2, ZHOU Yawei1( )
)
Received:2023-09-19
Revised:2024-01-19
Online:2024-10-15
Published:2024-10-10
Contact:
ZHOU Yawei
摘要:
起止点形态改变是人体长期使用肌肉的累积性变化,能够在一定程度上反映个体生前的行为模式,被认为是复原古代人群活动强度或日常习惯性行为动作的重要指标。本文对仰韶文化中晚期巩义双槐树遗址70例个体的肱骨肩胛下肌止点、冈上肌和冈下肌止点、小圆肌止点、伸肌总腱起点和屈肌总腱起点5处纤维软骨型起止点的形态进行观测,并与明清万花组对比。结果显示,双槐树女性的4处起止点患病率高于男性,表明女性可能承担了更多的日常劳动,遗址内大于30岁和未超过30岁个体在三处起止点得分上均有显著差异(p<0.05),可能存在上肢行为模式的不同。相比于明清万花组,双槐树人群上肢承受机械应力负荷较重,特别是肩关节活动较多。鉴于起止点形态改变易受到多种因素的影响,对于古代人群上肢起止点形态变化与其行为模式关系仍需进一步探讨。
中图分类号:
刘驷统, 顾万发, 吴倩, 周亚威. 河南双槐树遗址人群肱骨肌腱的起止点形变[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 757-766.
LIU Sitong, GU Wanfa, WU Qian, ZHOU Yawei. Deformation of the starting and ending points of the humeral tendon in the population from the Shuanghuaishu site in Henan Province[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(05): 757-766.
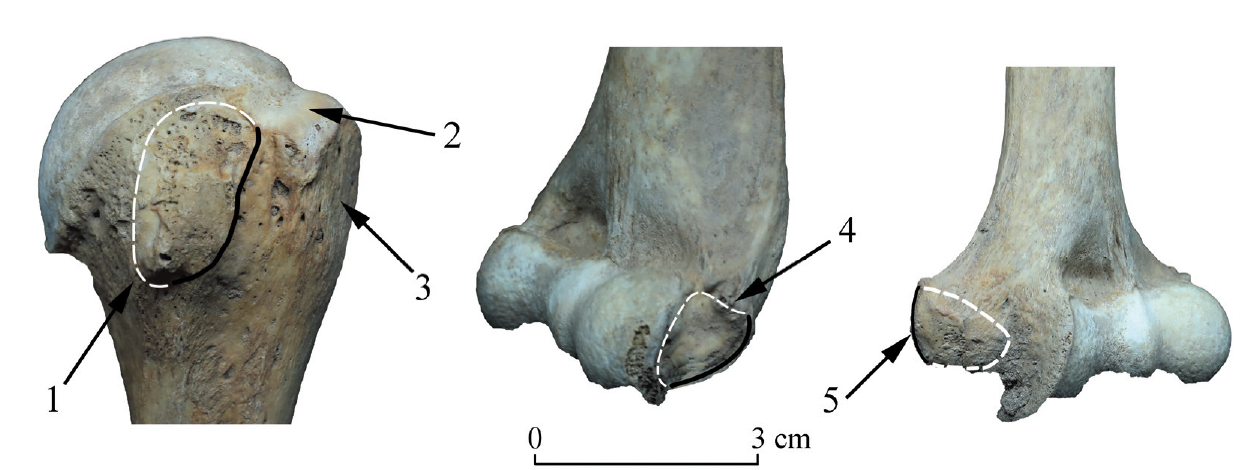
图1 肱骨五处起止点位置示意图 1.肩胛下肌止点M.subscapularis;2.冈上肌和冈下肌止点M. supra + infraspinatus;3.小圆肌止点M. teres minor; 4.伸肌总腱起点Extensor;5.屈肌总腱起点Flexor。线条框内区域为Zone 2,白色虚线为Zone 1。
Fig.1 Position of humeral entheses of M. subscapularis, extensor and flexor
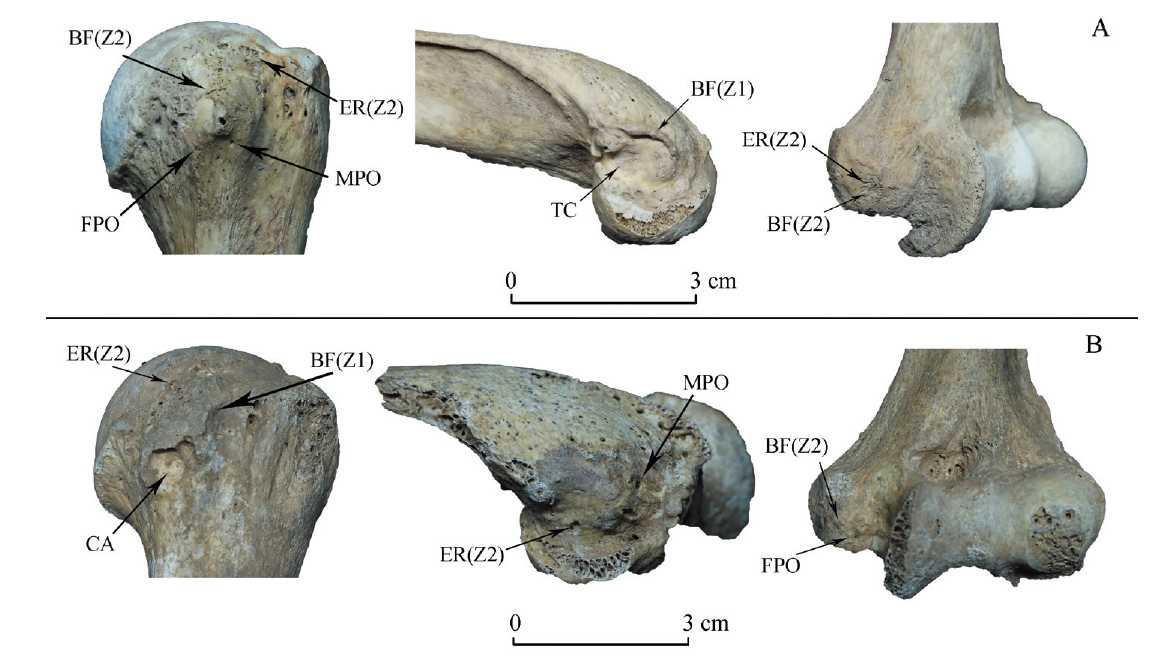

图2 双槐树遗址和万花遗址个体的肱骨起止点形态改变示意图 A.万花M4东个体的三处起止点three enthesis of M4: East in Wanhua site;B.双槐树M36个体的三处起止点three enthesis of M36 in Shuanghuaishu site。BF(Z1).起止点边缘的骨生成Bone formation (Zone 1);BF(Z2).起止点表面的骨生成Bone formation (Zone 2);ER(Z2).起止点表面的侵蚀Erosion (Zone 2);CA.起止点表面的骨质改变Textural change;FPO.起止点表面的小孔Fine-porosity;MPO.起止点表面的大孔Macro-porosity
Fig.2 Entheseal Changes of humerus of Shuanghuaishu and Wanhua sites
| 遗址Site → 测量项目Measurement items ↓ | 万花Wanhua | 双槐树Shuanghuaishu | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性Male | 女性Female | >30岁over 30 | ≤30岁under 30 | 男性Male | 女性Female | >30岁over 30 | ≤30岁under 30 | |||
| 肩胛下肌止点L/The left M.subscapularis | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 18 | 17 | 23 | 11 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 3 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 18 | 14 | 22 | 9 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 60.00% | 64.30% | 77.80% | 50.00% | 100.00% | 82.40% | 95.70% | 81.80% | ||
| 肩胛下肌止点R/The right M. subscapularis | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 8 | 10 | 16 | 12 | 18 | 8 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 4 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 15 | 11 | 17 | 7 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 80.00% | 64.30% | 87.50% | 60.00% | 93.80% | 91.70% | 94.40% | 87.50% | ||
| 冈上肌和冈下肌止点L/The left M. supra + infraspinatus | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 17 | 13 | 19 | 10 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 1 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 2 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 20.00% | 42.90% | 55.60% | 20.00% | 29.40% | 30.80% | 36.80% | 20.00% | ||
| 冈上肌和冈下肌止点R/The right M. supra + infraspinatus | 可观测个体数(n) | 4 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 17 | 13 | 19 | 9 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 1 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 2 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 25.00% | 57.10% | 66.70% | 30.00% | 29.40% | 38.50% | 42.10% | 22.20% | ||
| 小圆肌止点L/The left M. teres minor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 15 | 13 | 17 | 10 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 2 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 6 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 40.00% | 64.30% | 66.70% | 50.00% | 60.00% | 92.30% | 88.20% | 60.00% | ||
| 小圆肌止点R/The right M. teres minor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 15 | 9 | 14 | 8 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 4 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 11 | 9 | 13 | 5 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 80.00% | 50.00% | 77.80% | 40.00% | 73.30% | 100.00% | 92.90% | 62.50% | ||
| 伸肌总腱起点L/The left extensor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 23 | 17 | 26 | 14 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 3 | 9 | 6 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 17 | 5 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 60.00% | 64.30% | 66.70% | 60.00% | 52.20% | 58.80% | 65.40% | 35.70% | ||
| 伸肌总腱起点R/The right extensor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 23 | 15 | 24 | 12 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 3 | 10 | 8 | 5 | 16 | 11 | 21 | 4 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 60.00% | 71.40% | 88.90% | 50.00% | 69.60% | 73.30% | 87.50% | 33.30% | ||
| 屈肌总腱起点L/The left flexor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 25 | 15 | 26 | 14 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 5 | 11 | 8 | 8 | 13 | 8 | 15 | 5 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 100.00% | 78.60% | 88.90% | 80.00% | 52.00% | 53.30% | 57.70% | 35.70% | ||
| 屈肌总腱起点R/The right flexor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 29 | 16 | 27 | 15 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 3 | 9 | 8 | 4 | 15 | 9 | 19 | 3 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 60.00% | 64.30% | 88.90% | 40.00% | 51.70% | 56.30% | 70.40% | 20.00% | ||
表1 Villotte方法下双槐树遗址和万花遗址个体的起止点患病率
Tab.1 Morbidity of humeral enthesis in Villotte method of Shuanghuaishu and Wanhua sites
| 遗址Site → 测量项目Measurement items ↓ | 万花Wanhua | 双槐树Shuanghuaishu | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性Male | 女性Female | >30岁over 30 | ≤30岁under 30 | 男性Male | 女性Female | >30岁over 30 | ≤30岁under 30 | |||
| 肩胛下肌止点L/The left M.subscapularis | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 18 | 17 | 23 | 11 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 3 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 18 | 14 | 22 | 9 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 60.00% | 64.30% | 77.80% | 50.00% | 100.00% | 82.40% | 95.70% | 81.80% | ||
| 肩胛下肌止点R/The right M. subscapularis | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 8 | 10 | 16 | 12 | 18 | 8 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 4 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 15 | 11 | 17 | 7 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 80.00% | 64.30% | 87.50% | 60.00% | 93.80% | 91.70% | 94.40% | 87.50% | ||
| 冈上肌和冈下肌止点L/The left M. supra + infraspinatus | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 17 | 13 | 19 | 10 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 1 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 2 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 20.00% | 42.90% | 55.60% | 20.00% | 29.40% | 30.80% | 36.80% | 20.00% | ||
| 冈上肌和冈下肌止点R/The right M. supra + infraspinatus | 可观测个体数(n) | 4 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 17 | 13 | 19 | 9 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 1 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 2 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 25.00% | 57.10% | 66.70% | 30.00% | 29.40% | 38.50% | 42.10% | 22.20% | ||
| 小圆肌止点L/The left M. teres minor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 15 | 13 | 17 | 10 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 2 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 6 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 40.00% | 64.30% | 66.70% | 50.00% | 60.00% | 92.30% | 88.20% | 60.00% | ||
| 小圆肌止点R/The right M. teres minor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 15 | 9 | 14 | 8 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 4 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 11 | 9 | 13 | 5 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 80.00% | 50.00% | 77.80% | 40.00% | 73.30% | 100.00% | 92.90% | 62.50% | ||
| 伸肌总腱起点L/The left extensor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 23 | 17 | 26 | 14 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 3 | 9 | 6 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 17 | 5 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 60.00% | 64.30% | 66.70% | 60.00% | 52.20% | 58.80% | 65.40% | 35.70% | ||
| 伸肌总腱起点R/The right extensor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 23 | 15 | 24 | 12 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 3 | 10 | 8 | 5 | 16 | 11 | 21 | 4 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 60.00% | 71.40% | 88.90% | 50.00% | 69.60% | 73.30% | 87.50% | 33.30% | ||
| 屈肌总腱起点L/The left flexor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 25 | 15 | 26 | 14 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 5 | 11 | 8 | 8 | 13 | 8 | 15 | 5 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 100.00% | 78.60% | 88.90% | 80.00% | 52.00% | 53.30% | 57.70% | 35.70% | ||
| 屈肌总腱起点R/The right flexor | 可观测个体数(n) | 5 | 14 | 9 | 10 | 29 | 16 | 27 | 15 | |
| 发生形变个体数ns | 3 | 9 | 8 | 4 | 15 | 9 | 19 | 3 | ||
| 发生形变的比率ratio | 60.00% | 64.30% | 88.90% | 40.00% | 51.70% | 56.30% | 70.40% | 20.00% | ||
| 起止点Enthesis | 遗址site | 侧别Sides | 男性Male | 女性Female | 年龄>30 a | 年龄≤30 a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 左侧Left | 右侧Right | 左侧Left | 右侧Right | 左侧Left | 右侧Right | 左侧Left | 右侧Right | 左侧Left | 右侧Right | ||
| 肩胛下肌止点M.subscapularis | 双槐树Shuanghuaishu | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.67 | 1.5 | 1.41 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.61 | 1.25 | 1.2 |
| 万花Wanhua | 1.11 | 1.06 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 0.93 | 1.08 | 1.54 | 1.39 | 0.8 | 0.89 | |
| 伸肌总腱起点Extensor | 双槐树Shuanghuaishu | 0.76 | 1.13 | 0.91 | 1.22 | 0.82 | 1 | 1.18 | 1.69 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
| 万花Wanhua | 1.16 | 1.59 | 1 | 2 | 1.07 | 1.43 | 1.44 | 2.11 | 0.9 | 1 | |
| 屈肌总腱起点Flexor | 双槐树Shuanghuaishu | 0.56 | 0.8 | 0.56 | 0.76 | 0.6 | 0.81 | 0.65 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| 万花Wanhua | 1.37 | 1.24 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.36 | 1.14 | 1.78 | 1.89 | 1 | 0.56 | |
表2 两个遗址各起止点在不同分组模式下使用Coimbra方法所得的分数统计
Tab.2 Score of humeral entheses in Coimbra method under different grouping modes of two sites
| 起止点Enthesis | 遗址site | 侧别Sides | 男性Male | 女性Female | 年龄>30 a | 年龄≤30 a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 左侧Left | 右侧Right | 左侧Left | 右侧Right | 左侧Left | 右侧Right | 左侧Left | 右侧Right | 左侧Left | 右侧Right | ||
| 肩胛下肌止点M.subscapularis | 双槐树Shuanghuaishu | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.67 | 1.5 | 1.41 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.61 | 1.25 | 1.2 |
| 万花Wanhua | 1.11 | 1.06 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 0.93 | 1.08 | 1.54 | 1.39 | 0.8 | 0.89 | |
| 伸肌总腱起点Extensor | 双槐树Shuanghuaishu | 0.76 | 1.13 | 0.91 | 1.22 | 0.82 | 1 | 1.18 | 1.69 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
| 万花Wanhua | 1.16 | 1.59 | 1 | 2 | 1.07 | 1.43 | 1.44 | 2.11 | 0.9 | 1 | |
| 屈肌总腱起点Flexor | 双槐树Shuanghuaishu | 0.56 | 0.8 | 0.56 | 0.76 | 0.6 | 0.81 | 0.65 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| 万花Wanhua | 1.37 | 1.24 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.36 | 1.14 | 1.78 | 1.89 | 1 | 0.56 | |
| 分组模式Grouping mode → 起止点Enthesis ↓ | 性别Gender | 年龄Ages | 侧别Sides | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量n | 标准差σ | 检验Z | 检验P | 数量n | 标准差σ | 检验Z | 检验P | 数量n | 标准差σ | 检验Z | 检验P | |||
| 肩胛下肌止点M.subscapularis | 63 | 0.893 | -0.861 | 0.389 | 60 | 0.873 | -2.41 | 0.016 | 64 | 0.881 | -0.6 | 0.656 | ||
| 伸肌总腱起点Extensor | 80 | 0.974 | -0.323 | 0.747 | 52 | 0.882 | -3.054 | 0.002 | 75 | 8.074 | -1.2 | 0.303 | ||
| 屈肌总腱起点Flexor | 85 | 0.746 | -0.298 | 0.766 | 82 | 0.709 | -3.241 | 0.001 | 79 | 14.062 | -1.1 | 0.137 | ||
表3 双槐树遗址各起止点观测数量、标准差及秩和检验结果统计
Tab.3 Number of individuals, standard deviation and Rank Sum Test of Shuanghuaishu site
| 分组模式Grouping mode → 起止点Enthesis ↓ | 性别Gender | 年龄Ages | 侧别Sides | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量n | 标准差σ | 检验Z | 检验P | 数量n | 标准差σ | 检验Z | 检验P | 数量n | 标准差σ | 检验Z | 检验P | |||
| 肩胛下肌止点M.subscapularis | 63 | 0.893 | -0.861 | 0.389 | 60 | 0.873 | -2.41 | 0.016 | 64 | 0.881 | -0.6 | 0.656 | ||
| 伸肌总腱起点Extensor | 80 | 0.974 | -0.323 | 0.747 | 52 | 0.882 | -3.054 | 0.002 | 75 | 8.074 | -1.2 | 0.303 | ||
| 屈肌总腱起点Flexor | 85 | 0.746 | -0.298 | 0.766 | 82 | 0.709 | -3.241 | 0.001 | 79 | 14.062 | -1.1 | 0.137 | ||
| 起止点Enthesis | 数量n | 标准差σ | 检验Z | 检验P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肩胛下肌止点M.subscapularis | 99 | 0.959 | -2.076 | 0.038 |
| 伸肌总腱起点Extensor | 116 | 1.048 | -1.442 | 0.149 |
| 屈肌总腱起点Flexor | 118 | 0.860 | -3.627 | 0.000 |
表4 两个遗址各起止点的观测数量、标准差及秩和检验结果统计
Tab.4 Number of individuals, standard deviation and Rank Sum Test of two sites
| 起止点Enthesis | 数量n | 标准差σ | 检验Z | 检验P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肩胛下肌止点M.subscapularis | 99 | 0.959 | -2.076 | 0.038 |
| 伸肌总腱起点Extensor | 116 | 1.048 | -1.442 | 0.149 |
| 屈肌总腱起点Flexor | 118 | 0.860 | -3.627 | 0.000 |
| [1] | 郑州市文物考古研究院. 河南巩义市双槐树新石器时代遗址[J]. 考古, 2021, 7: 27-48 |
| [2] | 中国考古网. 第三届中国考古学大会人类骨骼考古专业委员会研讨会纪要[EB/OL]. URL: http://kaogu.cssn.cn/zwb/xsdt/xsdt_3347/xsdt_3348/202111/t20211115_5374508.shtml. Released on: 2021-11-15 |
| [3] | 周贝. 郑州地区仰韶文化居民的肢骨研究[D]. 硕士研究生毕业论文,郑州大学, 2020, 26 |
| [4] | 侯侃. 山西榆次高校园区先秦墓葬人骨研究[D]. 博士研究生毕业论文,吉林大学, 2017, 291-319 |
| [5] | Iscan MY, Kennedy K. Reconstruction of Life from the Skeleton[M]. New York: Alan R Liss, 1989, 129-160 |
| [6] | Hawkey DE, Merbs CF. Activity-induced musculoskeletal stress markers (MSM) and subsistence strategy changes among ancient Hudson Bay Eskimos[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 1995, 5(4): 324-338 |
| [7] | Mariotti V, Facchini F, Giovanna Belcastro M. Enthesopathies-proposal of a standardized scoring method and applications[J]. Collegium Antropologicum, 2004, 28(1): 145-159 |
| [8] |
Mariotti V, Facchini F, Belcastro MG. The study of entheses: Proposal of a standardised scoring method for twenty-three entheses of the postcranial skeleton[J]. Collegium antropologicum, 2007, 31(1): 291-313
pmid: 17598416 |
| [9] |
Villotte S, Castex D, Couallier V, et al. Enthesopathies as occupational stress markers: Evidence from the upper limb[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2010, 142(2): 224-234
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.21217 pmid: 20034011 |
| [10] | Santos AL, Alves-Cardoso F, Assis S, et al. The Coimbra workshop in musculoskeletal stress markers (MSM): An annotated review[C]. Antropologia Portuguesa, Centro de Investigação em Antropologia e Saúde (CIAS), 2011, 28: 135-161 |
| [11] | Benjamin M, Evans EJ, Copp L. The histology of tendon attachments to bone in man.[J]. Journal of Anatomy, 1986, 149(4): 89 |
| [12] | Benjamin M, Kumai T, Milz S, et al. The skeletal attachment of tendons--tendon “entheses”[J]. Comparative Biochemistry & Physiology Part A Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 2002, 133(4): 931-945 |
| [13] | 何嘉宁. 军都山古代人群股骨肌腱附着位点初步分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(3): 384-392 |
| [14] | 魏兴涛. 豫西晋西南地区新石器时代植物遗存的发现与初步研究[J]. 东方考古, 2014, 11: 343-364 |
| [15] | 罗运兵. 试论我国早期家猪饲养的方式与规模[J]. 农业考古, 2008, 4: 269-275 |
| [16] | 陈全家. 郑州西山遗址出土动物遗存研究[J]. 考古学报, 2006, 3: 385-418 |
| [17] | 雷帅, 等. 河南双槐树遗址仰韶文化居民的牙齿微磨耗形态研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2023, 43(5): 1417-1428 |
| [18] | 张雪莲, 等. 中原地区几处仰韶文化时期考古遗址的人类食物状况分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(2): 197-207 |
| [19] | 赵越云. 原始农业类型与中华早期文明研究[D]. 博士研究生毕业论文,西北农林科技大学, 2018, 58-60 |
| [20] | 钟华, 赵志军. 仰韶文化晚期中原地区农业生产模式初探[J]. 中国农史, 2023, 42(2): 52-61 |
| [21] | 郭云奇. 《武陟土产表》所见之清末武陟农业经济[J]. 新乡学院学报, 2020, 37(7): 59-63 |
| [22] | 李鹏飞. 环境史视野下的清代沁河流域农业开发研究[D]. 硕士研究生毕业论文,郑州大学, 2022, 55-66 |
| [23] | 张波, 樊志民. 中国农业通史·战国秦汉卷[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2007, 214-256 |
| [24] | 刘宸. 论明清时期河南棉花的商品化发展[D]. 硕士研究生毕业论文,西南大学, 2014, 6-9 |
| [25] | 唐纳德·A, 诺依曼. 骨骼肌肉功能解剖学(第2版)[M].译者:刘颖,师玉涛,闫琪,等. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2014, 157-197 |
| [26] | Henderson CY, Mariotti V, Pany-Kucera D, et al. Recording specific entheseal changes of fibrocartilaginous entheses: initial tests using the Coimbra method[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2013, 23(2): 152-162 |
| [27] | Henderson CY, Mariotti V, Pany-Kucera D, et al. The new ‘Coimbra Method’: A biologically appropriate method for recording specific features of fibrocartilaginous entheseal changes[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2015, 26(5): 926-932 |
| [28] | Henderson CY, Wilczak C, Mariotti V. Commentary: An update to the new Coimbra method for recording entheseal changes[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2016, 27(3): 522-523 |
| [29] | Jurmain R, Cardoso FA, Henderson C, et al. Bioarchaeology's Holy Grail: The Reconstruction of Activity[M]. Grauer AL. A companion to paleopathology. John Wiley & Sons, 2012, 531-552 |
| [30] | Davis CB, Shuler KA, Danforth ME, et al. Patterns of interobserver error in the scoring of entheseal changes[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2013, 23: 147-151 |
| [31] | Henderson CY, Mariotti V, Pany Kucera D, et al. The new ‘Coimbra method’: A biologically appropriate method for recording specific features of fibrocartilaginous entheseal changes[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2016, 26(5): 925-932 |
| [32] |
Milella M, Belcastro MG, Zollikofer CPE, et al. The effect of age, sex, and physical activity on entheseal morphology in a contemporary Italian skeletal collection[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2012, 148(3): 379-388
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.22060 pmid: 22460619 |
| [33] | Campanacho V, Santos AL. Comparison of the Entheseal Changes of the os coxae of Portuguese Males (19th-20th centuries) with Known Occupation[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2013, 23(2): 229-236 |
| [34] | Niinimäki S, Sotos LB. The relationship between intensity of physical activity and entheseal changes on the lower limb[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2013, 23(2): 221-228 |
| [35] | 王呼生, 常沛. 新编医学计算机信息应用[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2016, 333-337 |
| [36] | Jurmain R. Stories from the skeleton: behavioral reconstruction in human osteology[M]. Gordon and Breach, 1999, 149-157 |
| [37] | Michopoulou E, Nikita E, Henderson CY. A test of the effectiveness of the Coimbra method in capturing activity-induced entheseal changes[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2016, 27(3): 409-417 |
| [38] |
Villotte S, Churchill SE, Dutour OJ, et al. Subsistence activities and the sexual division of labor in the European Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic: Evidence from upper limb enthesopathies[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2010, 59(1): 35-43
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2010.02.001 pmid: 20602985 |
| [39] | 宋爱平. 郑州地区史前至商周时期聚落形态分析[J]. 东方考古, 2011, 1: 156-194 |
| [40] | 杨凡. 中原地区仰韶文化中晚期的农业与社会[D]. 博士研究生毕业论文,山东大学, 2021, 196-200 |
| [41] | 张明山. 明代农具设计研究[D]. 博士研究生毕业论文,南京艺术学院, 2014, 11-34 |
| [42] | Niinimäki S. What do muscle marker ruggedness scores actually tell us?[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2011, 21(3): 292-299 |
| [43] | 牛月明. 章丘焦家遗址史前体型和行为模式研究[D]. 硕士研究生毕业论文,山东大学, 2020, 49-52 |
| [1] | 周亚威, 王惠, 丁思聪, 陈博. 东周一例人体肱骨发育不对称的病理分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(01): 87-97. |
| [2] | 魏偏偏, 赵昱浩, 何嘉宁. 辽宁建平古人类肱骨形态结构分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(06): 943-954. |
| [3] | 赵昱浩, 周蜜, 魏偏偏, 邢松. 肱骨骨干骨密质厚度的二维可视化及其定量分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 632-647. |
| [4] | 仪明洁; 高星; Robert BETTINGER. 狩猎采集觅食模式及其在旧石器时代考古学中的应用[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(02): 156-168. |
| [5] | 陈胜前. 中国晚更新世—早全新世过渡期狩猎采集者的适应变迁[J]. 人类学学报, 2006, 25(03): 195-207. |
| [6] | 盛克标. 我国优秀划船运动员肱骨X线测量分析[J]. 人类学学报, 1984, 3(02): 126-131. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 169
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 230
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3