

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (06): 1064-1074.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0092
收稿日期:2024-05-27
出版日期:2024-12-15
发布日期:2024-11-28
作者简介:关莹,博士,主要从事史前考古学研究。E-mail: guanying@ivpp.ac.cn
基金资助:
GUAN Ying1( ), WANG Shejiang1, ZHOU Zhenyu2, GAO Xing1, ZHANG Xi1,3
), WANG Shejiang1, ZHOU Zhenyu2, GAO Xing1, ZHANG Xi1,3
Received:2024-05-27
Online:2024-12-15
Published:2024-11-28
摘要:
本项研究通过对陕西洛南张豁口遗址发现的淀粉粒进行分析,聚焦旧石器时代早期人类如何利用植物性食物资源。张豁口遗址出土的阿舍利工业产品上保存了微量的淀粉粒,尽管数量较低,但却为研究早期人类利用植物性资源提供了宝贵的证据,为解读人类早期历史提供了重要线索。此外,本研究深入探讨了早期人类对根茎类植物挖掘、采集和食用行为的可能性,指出根茎类植物不仅为早期人类提供了重要的营养价值,在人类饮食结构中占据核心地位,而且对于理解旧石器时代早期石制品使用方式、环境适应策略、古人类认知水平的演变等问题也具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
关莹, 王社江, 周振宇, 高星, 张茜. 洛南手斧上的淀粉粒与古人类使用石器的策略[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(06): 1064-1074.
GUAN Ying, WANG Shejiang, ZHOU Zhenyu, GAO Xing, ZHANG Xi. Starch grains on the Luonan handaxe and strategy of ancient humans using stone tools[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(06): 1064-1074.
| 标本号Specimen No. | 采样性质Sediment Type | 淀粉粒样号Starch Speciment No. |
|---|---|---|
| 4239 | 附着土 | SSP21 |
| 4239 | 湿洗 | SSP22 |
| 4239 | 超声 | SSP23 |
| 182 | 附着土 | SSP24 |
| 182 | 湿洗 | SSP25 |
| 182 | 超声 | SSP26 |
| 1156 | 附着土 | SSP27 |
| 1156 | 湿洗 | SSP28 |
| 1156 | 超声 | SSP29 |
| 963 | 附着土 | SSP30 |
| 963 | 湿洗 | SSP31 |
| 963 | 超声 | SSP32 |
| 230 | 湿洗 | SSP33 |
| 230 | 超声 | SSP34 |
| 8854 | 湿洗 | SSP35 |
| 8854 | 超声 | SSP36 |
| 1088 | 湿洗 | SSP37 |
| 1088 | 超声 | SSP38 |
| 1843 | 湿洗 | SSP39 |
| 1843 | 超声 | SSP40 |
| 2557 | 附着土 | SSP41 |
| 2557 | 湿洗 | SSP42 |
| 2557 | 超声 | SSP43 |
| 237 | 湿洗 | SSP44 |
| 237 | 超声 | SSP45 |
| 2056 | 湿洗 | SSP46 |
| 2056 | 超声 | SSP47 |
| 515 | 湿洗 | SSP48 |
| 515 | 超声 | SSP49 |
| 857 | 附着土 | SSP50 |
| 857 | 湿洗 | SSP51 |
| 857 | 超声 | SSP52 |
| 2030 | 湿洗 | SSP53 |
| 2030 | 超声 | SSP54 |
| 5316 | 湿洗 | SSP55 |
| 5316 | 超声 | SSP56 |
| 1171 | 湿洗 | SSP57 |
| 1171 | 超声 | SSP58 |
| 1828 | 湿洗 | SSP59 |
| 1828 | 超声 | SSP60 |
| 1475 | 湿洗 | SSP61 |
| 1475 | 超声 | SSP62 |
| 1011 | 湿洗 | SSP63 |
| 1011 | 超声 | SSP64 |
| 830 | 湿洗 | SSP65 |
| 830 | 超声 | SSP66 |
| 1172 | 湿洗 | SSP67 |
| 1172 | 超声 | SSP68 |
| 3687 | 湿洗 | SSP69 |
| 3687 | 超声 | SSP70 |
| 2417 | 湿洗 | SSP71 |
| 2417 | 超声 | SSP72 |
| 1962 | 湿洗 | SSP73 |
| 1962 | 超声 | SSP74 |
| 356 | 附着土 | SSP75 |
| 356 | 湿洗 | SSP76 |
| 356 | 超声 | SSP77 |
| 295 | 湿洗 | SSP78 |
| 295 | 超声 | SSP79 |
| 965 | 附着土 | SSP80 |
| 965 | 湿洗 | SSP81 |
| 965 | 超声 | SSP82 |
| 1593 | 湿洗 | SSP83 |
| 1593 | 超声 | SSP84 |
| 1792 | 湿洗 | SSP85 |
| 1792 | 超声 | SSP86 |
| 235 | 附着土 | SSP87 |
| 235 | 湿洗 | SSP88 |
| 235 | 超声 | SSP89 |
表1 张豁口遗址石制品植物残留物分析采样登记表
Tab.1 Sampled specimen from Zhanghuokou site
| 标本号Specimen No. | 采样性质Sediment Type | 淀粉粒样号Starch Speciment No. |
|---|---|---|
| 4239 | 附着土 | SSP21 |
| 4239 | 湿洗 | SSP22 |
| 4239 | 超声 | SSP23 |
| 182 | 附着土 | SSP24 |
| 182 | 湿洗 | SSP25 |
| 182 | 超声 | SSP26 |
| 1156 | 附着土 | SSP27 |
| 1156 | 湿洗 | SSP28 |
| 1156 | 超声 | SSP29 |
| 963 | 附着土 | SSP30 |
| 963 | 湿洗 | SSP31 |
| 963 | 超声 | SSP32 |
| 230 | 湿洗 | SSP33 |
| 230 | 超声 | SSP34 |
| 8854 | 湿洗 | SSP35 |
| 8854 | 超声 | SSP36 |
| 1088 | 湿洗 | SSP37 |
| 1088 | 超声 | SSP38 |
| 1843 | 湿洗 | SSP39 |
| 1843 | 超声 | SSP40 |
| 2557 | 附着土 | SSP41 |
| 2557 | 湿洗 | SSP42 |
| 2557 | 超声 | SSP43 |
| 237 | 湿洗 | SSP44 |
| 237 | 超声 | SSP45 |
| 2056 | 湿洗 | SSP46 |
| 2056 | 超声 | SSP47 |
| 515 | 湿洗 | SSP48 |
| 515 | 超声 | SSP49 |
| 857 | 附着土 | SSP50 |
| 857 | 湿洗 | SSP51 |
| 857 | 超声 | SSP52 |
| 2030 | 湿洗 | SSP53 |
| 2030 | 超声 | SSP54 |
| 5316 | 湿洗 | SSP55 |
| 5316 | 超声 | SSP56 |
| 1171 | 湿洗 | SSP57 |
| 1171 | 超声 | SSP58 |
| 1828 | 湿洗 | SSP59 |
| 1828 | 超声 | SSP60 |
| 1475 | 湿洗 | SSP61 |
| 1475 | 超声 | SSP62 |
| 1011 | 湿洗 | SSP63 |
| 1011 | 超声 | SSP64 |
| 830 | 湿洗 | SSP65 |
| 830 | 超声 | SSP66 |
| 1172 | 湿洗 | SSP67 |
| 1172 | 超声 | SSP68 |
| 3687 | 湿洗 | SSP69 |
| 3687 | 超声 | SSP70 |
| 2417 | 湿洗 | SSP71 |
| 2417 | 超声 | SSP72 |
| 1962 | 湿洗 | SSP73 |
| 1962 | 超声 | SSP74 |
| 356 | 附着土 | SSP75 |
| 356 | 湿洗 | SSP76 |
| 356 | 超声 | SSP77 |
| 295 | 湿洗 | SSP78 |
| 295 | 超声 | SSP79 |
| 965 | 附着土 | SSP80 |
| 965 | 湿洗 | SSP81 |
| 965 | 超声 | SSP82 |
| 1593 | 湿洗 | SSP83 |
| 1593 | 超声 | SSP84 |
| 1792 | 湿洗 | SSP85 |
| 1792 | 超声 | SSP86 |
| 235 | 附着土 | SSP87 |
| 235 | 湿洗 | SSP88 |
| 235 | 超声 | SSP89 |
| 检测部位Examined location→ 样品类型Sediment→ 标本号Specimen No.↓ | 尖端point | 尾端end | 总计Total | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 淀粉粒Starch granule | 其他Other | 淀粉粒Starch granule | 其他Other | |||||||||
| 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | |||||
| 1806 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||
| 4239 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||||
| 3687 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 1618 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 6 | ||||||||
| 857 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||||||||
| 1962 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 7 | ||||||||
| 356 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 295 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 总计 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 14 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 27 | |||
表2 洛南张豁口出土标本各层次样品中的淀粉粒遗存数据
Tab.2 Starch granule data from Zhanghuokou artifacts per sediment sample
| 检测部位Examined location→ 样品类型Sediment→ 标本号Specimen No.↓ | 尖端point | 尾端end | 总计Total | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 淀粉粒Starch granule | 其他Other | 淀粉粒Starch granule | 其他Other | |||||||||
| 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | |||||
| 1806 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||
| 4239 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||||
| 3687 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 1618 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 6 | ||||||||
| 857 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||||||||
| 1962 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 7 | ||||||||
| 356 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 295 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 总计 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 14 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 27 | |||
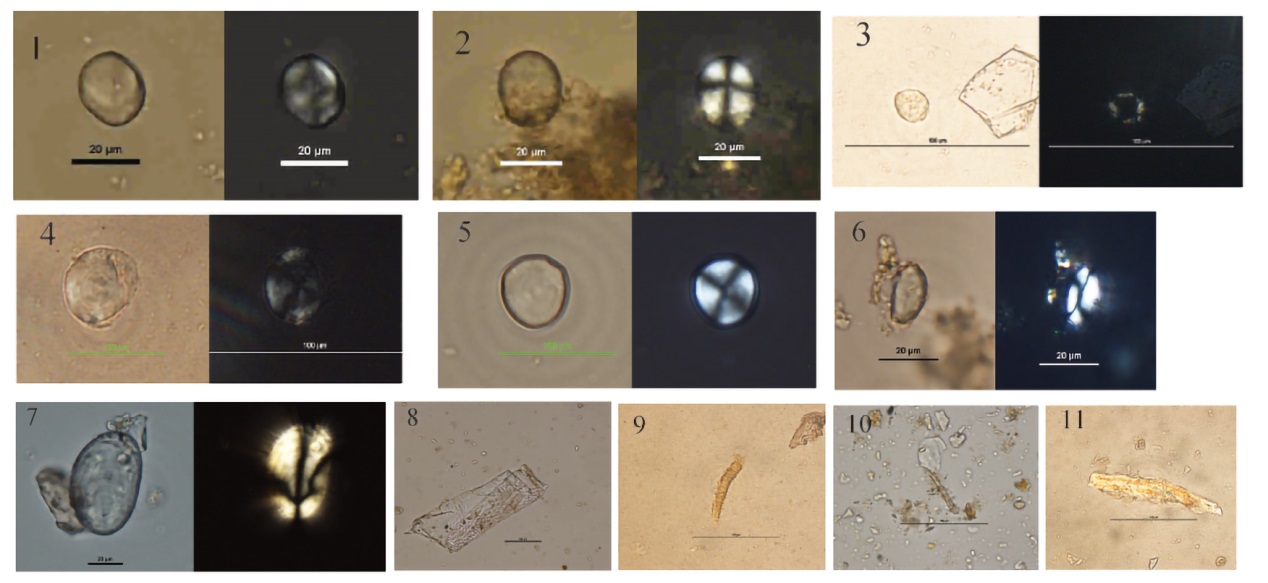
图3 张豁口遗址器物表面超声样品中发现植物微体残留 1-7为淀粉粒残留物,分别来自标本1806、1806、857、857、1962、356、4239; 8-11为纤维类植物残骸,分别来自标本1618、857、1962、857。比例尺:20 μm。
Fig.3 Plant residues from Sed3 samples in Zhanghuokou site
| [1] | Kibunjia M. Pliocene archaeological occurrences in the Lake Turkana basin[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 1994, 27(1): 159-171 |
| [2] | Semaw S. The World's Oldest Stone Artefacts from Gona, Ethiopia: Their Implications for Understanding Stone Technology and Patterns of Human Evolution Between 2.6-1.5 Million Years Ago[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2000, 27(12): 1197-1214 |
| [3] | Beyene Y, Katoh S, WoldeGabriel G, et al. The characteristics and chronology of the earliest Acheulean at Konso, Ethiopia[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(5): 1584-1591 |
| [4] | Toth N, Schick K. Why did the Acheulean happen? Experimental studies into the manufacture and function of Acheulean artifacts[J]. L'Anthropologie, 2019, 123(4): 724-768 |
| [5] | Keeley LH, Toth N. Microwear polishes on early stone tools from Koobi Fora, Kenya[J]. Nature, 1981, 293(5832): 464-465. |
| [6] |
Dominguez- Rodrigo M, Serrallonga J, Juan-Tresserras J, et al. Woodworking activities by early humans: a plant residue analysis on Acheulian stone tools from Peninj (Tanzania)[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2001, 40(4): 289-299
pmid: 11312582 |
| [7] | Gao X, Guan Y. Handaxes and the Pick-Chopper Industry of Pleistocene China[J]. Quaternary International, 2018, 480: 132-140 |
| [8] | Wang SJ, Lu JY. Taphonomic and paleoenvironmental issues of the Pleistocene loessic Paleolithic sites in the Qinling Mountains, central China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59: 1519-1528 |
| [9] | Norton CJ, Bae K. Erratum to “The Movius Line sensu lato (Norton et al., 2006) further assessed and defined” J. H. Evol. 55 (2008) 1148-1150[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2009, 57(3): 331-334 |
| [10] | 关莹, 高星. 旧石器时代残留物分析:回顾与展望[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(4): 418-429 |
| [11] | Leeuwenhoek A. Epistolae Physiologicae super Compluribus Naturae Arcanus: Epistolae 26[M]. Delphis: Apud Adrianum Beman, 1719 |
| [12] | Reichert ET. The differentiation and specificity of starches in relation to genera, species, etc.; stereochemistry applied to protoplasmic processes and products, and as a strictly scientific basis for the classification of plants and animals (Vol. Pt.2)[M]. Washington DC: Carnegie institution of Washington, 1913 |
| [13] | Fritzsche J. Ueber das Amylum[J]. Annalen der Pharmacie, 1834, 12(2-3): 263-276 |
| [14] | Guan Y, Pearsall DM, Gao X, et al. Plant use activities during the Upper Paleolithic in East Eurasia: Evidence from the Shuidonggou Site, Northwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 347: 74-83 |
| [15] |
Hardy BL, Kay M, Marks AE, et al. Stone tool function at the paleolithic sites of Starosele and Buran Kaya III, Crimea: Behavioral implications[J]. PNAS, 2001, 98(19): 10972-10977
pmid: 11535837 |
| [16] |
Liu L, Bestel S, Shi J, et al. Paleolithic human exploitation of plant foods during the last glacial maximum in North China[J]. PNAS, 2013, 110(14): 5380-5385
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217864110 pmid: 23509257 |
| [17] | Loy TH, Spriggs M, Wickler S. Direct evidence for human use of plants 28,000 years ago: starch residues on stone artefacts from the northern Solomon Islands[J]. Antiquity, 1992, 66(253): 898-912 |
| [18] | Langejans G. Micro-residue analysis on Early Stone Age Tools from Sterkfontein South Africa: A Methodological enquiry[J]. The South African Archaeological Bulletin, 2012, 67(196): 120-144 |
| [19] | Salleh A. Bloody stone tools tell hominids' tales[CP/OL]. Retrieved from http://www.abc.net.au/science/articles/2004/07/19/1156792.htm |
| [20] | Williamson. Prehistoric stone tool residue analysis from Rose Cottage Cave and other Southern Africa sites[D]. Johannesburg: University of Witwatersrand, 2000 |
| [21] |
Van Peer P, Fullagar R, Stokes S, et al. The Early to Middle Stone Age Transition and the Emergence of Modern Human Behaviour at site 8-B-11, Sai Island, Sudan[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2003, 45(2): 187-193
pmid: 14529653 |
| [22] | Marlize L. Distribution Patterns of Organic Residues on Middle Stone Age Points from Sibudu Cave, Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa[J]. The South African Archaeological Bulletin, 2004, 59(180): 37-44 |
| [23] | Williamson BS. Down the microscope and beyond: Microscopy and molecular studies of stone tool residues and bone samples from Rose Cottage Cave[J]. South African Journal of Science, 1997, 93(10) |
| [24] | Williamson BS. Middle Stone Age tool function from residue analysis at Sibudu Cave[J]. South African Journal of Science, 2004, 100(3) |
| [25] | Haslam M. The decomposition of starch granules in soils: implications for archaeological residue analyses[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2004, 31(12): 1715-1734 |
| [26] | Perry L. Starch analyses reveal the relationship between tool type and function: an example from the Orinoco valley of Venezuela[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2004, 31(8): 1069-1081 |
| [27] | Chandler-Ezell K, Pearsall DM. “Piggyback” microfossil processing: Joint starch and phytolith sampling from stone tools[J]. The Phytolitharien, 2003, 15: 2-8 |
| [28] | Duncan NA, Pearsall DM, Benfer RA. Gourd and squash artifacts yield starch granules of feasting foods from preceramic Peru[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2009, 106(32): 13202-13206 |
| [29] | Pearsall DM, Chandler-Ezell K, Zeidler JA. Maize in ancient Ecuador: results of residue analysis of stone tools from the Real Alto site[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2004, 31(4): 423-442 |
| [30] | 关莹, Pearsall DM, 高星, 等. 石制品残留物分析的实验室方法-以水洞沟石制品处理为例[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(4): 130-140 |
| [31] | Torrence R. Ancient Starch Research[M]. Walnut Creek, California: Left Coast Press Inc, 2006 |
| [32] | Pearsall DM. Paleoethnobotany[M]. California: Left Coast Press Inc, 2015 |
| [33] | Henry AG, Ungar PS, Passey BH, et al. The diet of Australopithecus sediba[J]. Nature, 2012, 487(7405): 90-93 |
| [34] | O'Connell JF. Tubers and human evolution[A]. In: TorrenceB, BartonH(Eds). Ancient starch research[M]. Walnut Creek, CA: Left Coast Press Inc, 2006, 20-21 |
| [35] |
Teaford MF, Ungar PS. Diet and the evolution of the earliest human ancestors[J]. PNAS, 2000, 97(25): 13506-13511
doi: 10.1073/pnas.260368897 pmid: 11095758 |
| [1] | 张乐, 张双权. 贵州普定穿洞遗址1981年出土的骨制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(06): 1048-1063. |
| [2] | 张晓凌, 王呈祥, 谭韵瑶, 靳英帅, 杨紫衣, 王社江. 青藏高原旧石器时代考古发现与研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(06): 967-978. |
| [3] | 李浩, 肖培源, 彭培洺, 王雨晴, 陈清懿, Ikram QAYUM, 贾真秀, 阮齐军, 陈发虎. 西南丝绸之路上的旧石器文化与人群交流[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(06): 979-992. |
| [4] | Evgeny P RYBIN, Arina M KHATSENOVICH. 旧石器时代晚期初段色楞格河人类的扩散路线[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 780-796. |
| [5] | 高黄文, 刘颖杰, 陆成秋, 孙雪峰, 黄旭初, 徐静玥. 湖北郧阳包包岭遗址2021年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 828-838. |
| [6] | 成楠, 夏文婷, 杨青, 吉学平, 字兴, 范斌, 邹梓宁, 余童, 张俞, 石林, 张吾奇, 郑洪波. 云南巍山三鹤洞地点的石制品及年代与环境[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 392-404. |
| [7] | 肖培源, 阮齐军, 高玉, 贾真秀, 张明, 杨李靖, 刘建辉, 李三灵, 李浩. 2022年云南宾川盆地旧石器遗址调查报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 448-457. |
| [8] | Hiroyuki SATO, Kazuki MORISAKI. 日本旧石器晚期石器技术起源的新考古学与人类学证据[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 470-487. |
| [9] | 王华, 李占扬, Thijs van KOLFSCHOTEN. 德国西宁根与中国灵井的骨器比较[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 214-232. |
| [10] | 赵清坡, 马欢欢. 河南灵宝旧石器考古调查报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 321-330. |
| [11] | 许竞文, 浣发祥, 杨石霞. 旧石器时代考古中出土的赭石及相关遗物的研究方法[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 331-343. |
| [12] | 高星, 张月书, 李锋, 陈福友, 王晓敏, 仪明洁. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址2016-2019年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 106-121. |
| [13] | 赵云啸, 仝广, 涂华, 赵海龙. 河北省泥河湾盆地石沟遗址C区发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 122-131. |
| [14] | 周士航, 何湘栋, 徐静玥, 李潇丽, 牛东伟. 蔚县盆地东沟遗址2017年度发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 132-142. |
| [15] | 张振, 王莹, 李月丛. 泥河湾盆地旧石器时代人类活动与环境关系的研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 184-198. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 252
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 306
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3