

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (02): 254-264.doi: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2019.0009cstr: 32091.14.j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2019.0009
收稿日期:2018-04-03
修回日期:2018-09-20
出版日期:2019-05-15
发布日期:2020-09-10
作者简介:惠家明 (1995-),男,汉族,江苏省苏州市人,中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所硕士研究生。Email: 基金资助:
HUI Jiaming1,2,3( ), HE Letian1,2,3, WANG Minghui4
), HE Letian1,2,3, WANG Minghui4
Received:2018-04-03
Revised:2018-09-20
Online:2019-05-15
Published:2020-09-10
摘要:
基于三维激光扫描的颅骨测量方法具有无接触、成像快速、易便携操作等优势,近年来在体质人类学与古人类学等领域发挥着日趋重要的作用。而在该测量技术普及的同时,其可靠性以及与手工测量的一致性问题也受到关注。本研究分别以手工方法与激光扫描建立模型法对考古出土颅骨进行测量,期望以实验手段探讨两种测量结果是否一致。实验结果显示,上述两种测量方法分别标定的两套测点相互之间吻合情况较好。其中,有易识别解剖学形态特征的测点吻合程度最优。而在两种测量手段的标点操作方式有所不同时,其标点位置间距会略有放大。从最终测量结果来看,两种测量手段所获数据的绝对差值和相对差异程度均较小。个别测量项在配对样本t检验中表现出了差异显著性,这应由两种测量结果大小差异的统一偏向性所致。在实际操作中,此类差异仍在可接受范围内,适宜混合同时使用。就差异的来源而言,测量操作方式的不同以及测点间的吻合程度是导致最终测量结果不同的主要原因之一,而仪器、颅骨表面的激光反射特性、扫描所获三维画面拼合情况等主客观因素也同样不可忽视。
中图分类号:
惠家明, 贺乐天, 王明辉. 基于三维激光扫描的颅骨测量与手工测量的比较[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(02): 254-264.
HUI Jiaming, HE Letian, WANG Minghui. A comparison between cranial measurements using three-dimensional laser scanning technology and manual measurements[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2019, 38(02): 254-264.
| 测点Landmarks | 平均距离 D(mm) | 标准差 σ(mm) | 个数 n | 测点Landmarks | 平均距离 D(mm) | 标准差 σ(mm) | 个数 n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 眉间点Glabella | 0.59 | 0.33 | 28 | 鼻棘点Nasospinale | 0.28 | 0.19 | 29 |
| 前囟点Bregma | 0.21 | 0.21 | 28 | 鼻棘下点Subspinale | 0.25 | 0.33 | 23 |
| 颅后点Opisthocranion | 0.74 | 0.43 | 29 | 上齿槽前点Prosthion | 0.29 | 0.29 | 28 |
| 大孔后缘点Opisthion | 0.16 | 0.26 | 29 | 左眶外缘点Ectoconchion(L) | 0.45 | 0.34 | 29 |
| 大孔前缘点Endobasion | 0.19 | 0.20 | 28 | 右眶外缘点Ectoconchion(R) | 0.50 | 0.33 | 28 |
| 颅底点Basion | 0.38 | 0.32 | 29 | 左颧颌点Zygomaxillare(L) | 0.28 | 0.26 | 28 |
| 左颅侧点Euryon(L) | 0.62 | 0.28 | 27 | 右颧颌点Zygomaxillare(R) | 0.32 | 0.23 | 28 |
| 右颅侧点Euryon(R) | 0.67 | 0.43 | 27 | 左颞额颧点Frontomalare temporal(L) | 0.48 | 0.19 | 28 |
| 左耳门上点Porion(L) | 0.39 | 0.30 | 29 | 右颞额颧点Frontomalare temporal(R) | 0.58 | 0.41 | 29 |
| 右耳门上点Porion(R) | 0.44 | 0.32 | 29 | 左眶额颧点Frontomalare orbitale(L) | 0.18 | 0.28 | 29 |
| 鼻根点Nasion | 0.17 | 0.25 | 29 | 右眶额颧点Frontomalare orbitale(R) | 0.33 | 0.26 | 29 |
| 左颌额点Maxillofrontale(L) | 0.33 | 0.22 | 29 | 左颧点Zygion(L) | 0.50 | 0.35 | 29 |
| 右颌额点Maxillofrontale(R) | 0.42 | 0.31 | 29 | 右颧点Zygion(R) | 0.50 | 0.30 | 29 |
表1 手工方法和激光扫描方法标定的测点间距
Tab.1 Distances between the landmarks set by laser scanning and manual measurements
| 测点Landmarks | 平均距离 D(mm) | 标准差 σ(mm) | 个数 n | 测点Landmarks | 平均距离 D(mm) | 标准差 σ(mm) | 个数 n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 眉间点Glabella | 0.59 | 0.33 | 28 | 鼻棘点Nasospinale | 0.28 | 0.19 | 29 |
| 前囟点Bregma | 0.21 | 0.21 | 28 | 鼻棘下点Subspinale | 0.25 | 0.33 | 23 |
| 颅后点Opisthocranion | 0.74 | 0.43 | 29 | 上齿槽前点Prosthion | 0.29 | 0.29 | 28 |
| 大孔后缘点Opisthion | 0.16 | 0.26 | 29 | 左眶外缘点Ectoconchion(L) | 0.45 | 0.34 | 29 |
| 大孔前缘点Endobasion | 0.19 | 0.20 | 28 | 右眶外缘点Ectoconchion(R) | 0.50 | 0.33 | 28 |
| 颅底点Basion | 0.38 | 0.32 | 29 | 左颧颌点Zygomaxillare(L) | 0.28 | 0.26 | 28 |
| 左颅侧点Euryon(L) | 0.62 | 0.28 | 27 | 右颧颌点Zygomaxillare(R) | 0.32 | 0.23 | 28 |
| 右颅侧点Euryon(R) | 0.67 | 0.43 | 27 | 左颞额颧点Frontomalare temporal(L) | 0.48 | 0.19 | 28 |
| 左耳门上点Porion(L) | 0.39 | 0.30 | 29 | 右颞额颧点Frontomalare temporal(R) | 0.58 | 0.41 | 29 |
| 右耳门上点Porion(R) | 0.44 | 0.32 | 29 | 左眶额颧点Frontomalare orbitale(L) | 0.18 | 0.28 | 29 |
| 鼻根点Nasion | 0.17 | 0.25 | 29 | 右眶额颧点Frontomalare orbitale(R) | 0.33 | 0.26 | 29 |
| 左颌额点Maxillofrontale(L) | 0.33 | 0.22 | 29 | 左颧点Zygion(L) | 0.50 | 0.35 | 29 |
| 右颌额点Maxillofrontale(R) | 0.42 | 0.31 | 29 | 右颧点Zygion(R) | 0.50 | 0.30 | 29 |
| 测量项 Variables | 手工测量 Manual measurements | 激光扫描模型测量 Measurements based on 3D laser scanning | 绝对差值均数(mm) Mean of absolute difference | 相对差异均数(%) Relative difference | 配对t检验(p值) Paired t-test | 个体数 n | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 (mm) | 标准差 σ(mm) | 平均值 (mm) | 标准差 σ(mm) | |||||
| 颅骨最大长Lmax of cranial | 178.51 | 8.22 | 178.6 | 8.14 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.063 | 29 |
| 颅底长L of Basis | 100.81 | 6.25 | 100.95 | 6.37 | 0.31 | 0.15 | 0.034* | 27 |
| 枕孔最大长L of Foramen magnum I | 36.57 | 2.59 | 36.76 | 2.58 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.405 | 28 |
| 颅骨最大宽bmax of cranial | 135.72 | 5.05 | 135.79 | 5.07 | 0.26 | 0.1 | 0.278 | 29 |
| 上面宽b of upper face | 102.62 | 4.04 | 102.63 | 4.16 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.879 | 28 |
| 面宽b of face | 103.84 | 7.12 | 103.81 | 7.07 | 0.23 | 0.09 | 0.568 | 29 |
| 中面宽b of Middle orbital I | 99.75 | 4.48 | 99.77 | 4.48 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.839 | 29 |
| 左眶宽b of left orbital | 40.64 | 1.46 | 40.70 | 1.63 | 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.449 | 29 |
| 右眶宽b of right orbital | 41.51 | 1.73 | 41.44 | 1.76 | 0.28 | 0.34 | 0.265 | 29 |
| 两眶宽b of biorbital | 96.10 | 3.35 | 95.82 | 3.31 | 0.42 | 0.22 | 0.001* | 29 |
| 前眶间宽b of vordere interorbital breite | 18.39 | 2.15 | 18.40 | 2.10 | 0.27 | 0.72 | 0.766 | 29 |
| 鼻宽b of Nasal | 26.26 | 1.68 | 26.35 | 1.74 | 0.27 | 0.51 | 0.208 | 29 |
| 颅高h of Basi-bregma | 135.09 | 9.88 | 135.07 | 9.86 | 0.28 | 0.1 | 0.676 | 29 |
| 耳上颅高h ofAuricular | 113.36 | 5.68 | 113.63 | 5.66 | 0.44 | 0.19 | 0.003* | 28 |
| 上面高h of upper facial | 71.50 | 4.05 | 71.48 | 4.05 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.288 | 27 |
| 左眶高h of left orbital | 34.15 | 1.26 | 34.38 | 1.27 | 0.40 | 0.58 | 0.001* | 29 |
| 右眶高h of right orbital | 34.04 | 1.17 | 34.44 | 1.21 | 0.47 | 0.69 | 0.005* | 29 |
| 鼻高h of nasal | 55.00 | 3.26 | 55.13 | 3.24 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.060 | 28 |
| 颅周C of horizontal | 509.51 | 19.08 | 511.66 | 19.32 | 0.93 | 0.09 | 0.085 | 26 |
| 颅矢状弧L of Total sagital arc | 363.46 | 16.38 | 364.27 | 16.07 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.532 | 28 |
表2 手工测量与激光扫描所得颅骨测量结果差异(直线、弧弦周长)
Tab.2 Comparison of measurement results of laser scanning and manual measurements (linear distances, circumferences and arc length )
| 测量项 Variables | 手工测量 Manual measurements | 激光扫描模型测量 Measurements based on 3D laser scanning | 绝对差值均数(mm) Mean of absolute difference | 相对差异均数(%) Relative difference | 配对t检验(p值) Paired t-test | 个体数 n | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 (mm) | 标准差 σ(mm) | 平均值 (mm) | 标准差 σ(mm) | |||||
| 颅骨最大长Lmax of cranial | 178.51 | 8.22 | 178.6 | 8.14 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.063 | 29 |
| 颅底长L of Basis | 100.81 | 6.25 | 100.95 | 6.37 | 0.31 | 0.15 | 0.034* | 27 |
| 枕孔最大长L of Foramen magnum I | 36.57 | 2.59 | 36.76 | 2.58 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.405 | 28 |
| 颅骨最大宽bmax of cranial | 135.72 | 5.05 | 135.79 | 5.07 | 0.26 | 0.1 | 0.278 | 29 |
| 上面宽b of upper face | 102.62 | 4.04 | 102.63 | 4.16 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.879 | 28 |
| 面宽b of face | 103.84 | 7.12 | 103.81 | 7.07 | 0.23 | 0.09 | 0.568 | 29 |
| 中面宽b of Middle orbital I | 99.75 | 4.48 | 99.77 | 4.48 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.839 | 29 |
| 左眶宽b of left orbital | 40.64 | 1.46 | 40.70 | 1.63 | 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.449 | 29 |
| 右眶宽b of right orbital | 41.51 | 1.73 | 41.44 | 1.76 | 0.28 | 0.34 | 0.265 | 29 |
| 两眶宽b of biorbital | 96.10 | 3.35 | 95.82 | 3.31 | 0.42 | 0.22 | 0.001* | 29 |
| 前眶间宽b of vordere interorbital breite | 18.39 | 2.15 | 18.40 | 2.10 | 0.27 | 0.72 | 0.766 | 29 |
| 鼻宽b of Nasal | 26.26 | 1.68 | 26.35 | 1.74 | 0.27 | 0.51 | 0.208 | 29 |
| 颅高h of Basi-bregma | 135.09 | 9.88 | 135.07 | 9.86 | 0.28 | 0.1 | 0.676 | 29 |
| 耳上颅高h ofAuricular | 113.36 | 5.68 | 113.63 | 5.66 | 0.44 | 0.19 | 0.003* | 28 |
| 上面高h of upper facial | 71.50 | 4.05 | 71.48 | 4.05 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.288 | 27 |
| 左眶高h of left orbital | 34.15 | 1.26 | 34.38 | 1.27 | 0.40 | 0.58 | 0.001* | 29 |
| 右眶高h of right orbital | 34.04 | 1.17 | 34.44 | 1.21 | 0.47 | 0.69 | 0.005* | 29 |
| 鼻高h of nasal | 55.00 | 3.26 | 55.13 | 3.24 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.060 | 28 |
| 颅周C of horizontal | 509.51 | 19.08 | 511.66 | 19.32 | 0.93 | 0.09 | 0.085 | 26 |
| 颅矢状弧L of Total sagital arc | 363.46 | 16.38 | 364.27 | 16.07 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.532 | 28 |
| 测量项 Variables | 手工测量 Manual measurements | 激光扫描模型测量 Measurements based on 3D laser scanning | 绝对差值均数 Mean of absolute difference(°) | 相对差异 Relative difference(%) | 配对t检验(p) Paired t-test | 例数 n | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值(°) | 标准差(°) σ | 平均值(°) | 标准差(°) σ | |||||
| 总面角Total prognathism | 85.09 | 2.92 | 85.23 | 2.62 | 0.51 | 0.3 | 0.731 | 28 |
| 中面角Middle prognathism I | 85.8 | 2.61 | 86.04 | 2.28 | 0.50 | 0.3 | 0.276 | 27 |
| 中面角Middle prognathism II | 86.43 | 2.97 | 86.70 | 2.21 | 0.73 | 0.42 | 0.769 | 26 |
| 齿槽面角Alveo prognathismⅠ | 80.48 | 6.41 | 80.01 | 6.37 | 0.43 | 0.25 | 0.786 | 27 |
| 齿槽面角Alveo prognathism II | 77.22 | 7.17 | 76.82 | 7.03 | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.292 | 27 |
| 鼻颧角naso-malar angle | 146.94 | 6.41 | 146.36 | 6.45 | 1.88 | 0.64 | 0.165 | 29 |
| 颧额角zygomaxillary angle | 131.30 | 7.31 | 131.13 | 7.01 | 1.34 | 0.52 | 0.592 | 29 |
表3 手工测量与激光扫描所得颅骨测量结果差异(角度)
Tab.3 Comparison of measurement results of laser scanning and manual measurements (angles)
| 测量项 Variables | 手工测量 Manual measurements | 激光扫描模型测量 Measurements based on 3D laser scanning | 绝对差值均数 Mean of absolute difference(°) | 相对差异 Relative difference(%) | 配对t检验(p) Paired t-test | 例数 n | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值(°) | 标准差(°) σ | 平均值(°) | 标准差(°) σ | |||||
| 总面角Total prognathism | 85.09 | 2.92 | 85.23 | 2.62 | 0.51 | 0.3 | 0.731 | 28 |
| 中面角Middle prognathism I | 85.8 | 2.61 | 86.04 | 2.28 | 0.50 | 0.3 | 0.276 | 27 |
| 中面角Middle prognathism II | 86.43 | 2.97 | 86.70 | 2.21 | 0.73 | 0.42 | 0.769 | 26 |
| 齿槽面角Alveo prognathismⅠ | 80.48 | 6.41 | 80.01 | 6.37 | 0.43 | 0.25 | 0.786 | 27 |
| 齿槽面角Alveo prognathism II | 77.22 | 7.17 | 76.82 | 7.03 | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.292 | 27 |
| 鼻颧角naso-malar angle | 146.94 | 6.41 | 146.36 | 6.45 | 1.88 | 0.64 | 0.165 | 29 |
| 颧额角zygomaxillary angle | 131.30 | 7.31 | 131.13 | 7.01 | 1.34 | 0.52 | 0.592 | 29 |
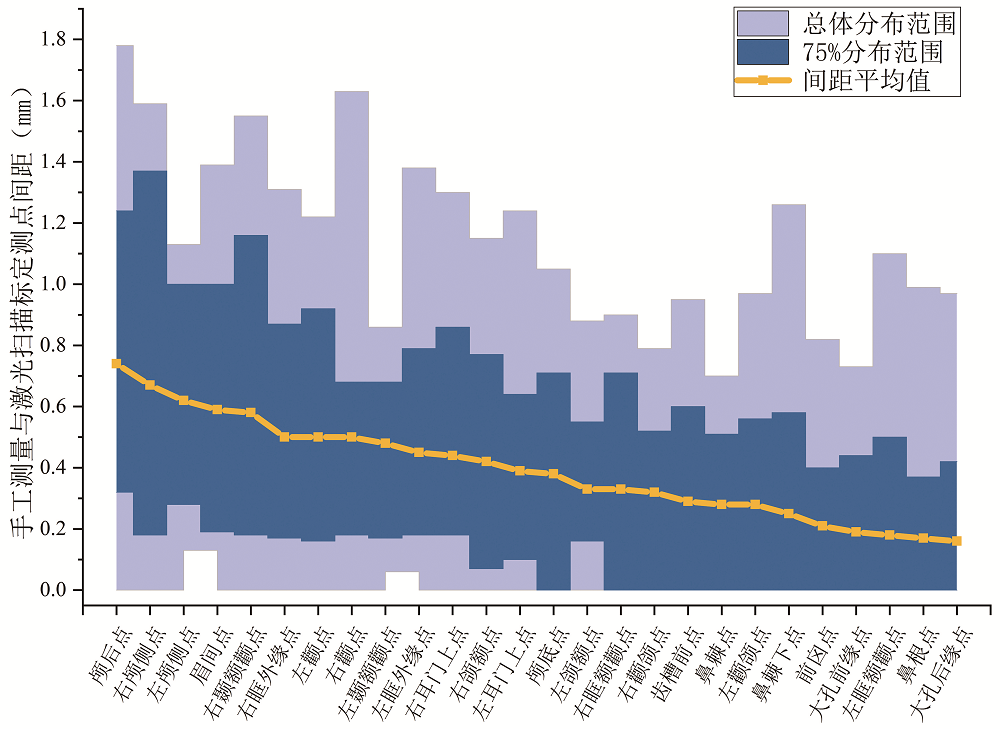
图2 各测点手工测量与三维激光扫描标点位置差异程度排序(按平均差值大小排序)
Fig.2 The goodness of fit of landmarks set by laser scanning and manual measurements ( ranked in order of mean values of distances )
| [1] |
Sla´dek V, Galeta P, Sosna D. Measuring human remains in the field: Grid technique, total station, or MicroScribe?[J]. Forensic Science International, 2012,221(1-3):16-22
doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2012.03.018 URL |
| [2] | 曾祥龙, 刘武. 颅骨测量与X线头影测量方法的比较研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1991,10(4):288-297 |
| [3] | 赵悦, 黄克强, 李春山. 西藏那曲地区藏族中小学生恒牙期颅面硬组织的结构特征:200例X射线头影测量[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2009,13(48):9541-9544 |
| [4] | Sholts SB, Flores LM, Walker PL, et al. Comparison of coordinate measurement precision of different landmark types on human crania using a 3D laser scanner and a 3D digitiser: Implications for applications of digital morphometrics International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2011,21(5):535-543 |
| [5] | 周文莲, 吴新智. 现代人头骨面部某些特征的投影栅相位法测量研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2001,20(2):81-92 |
| [6] | 惠增宏. 激光三维扫描、重建技术及其在工程中的应用[D]. 西安:西北工业大学, 2002 |
| [7] | 卢波. 激光三维扫描数据的表面重建技术研究[D]. 天津:天津大学, 2006 |
| [8] | 潘雷, 魏东, 吴秀杰. 现代人颅骨头面部表面积的纬度分布特点及其与温度的关系[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2014,44(8):1844-1853 |
| [9] | Wu XJ, Maddux SD, Pan L, et al. Nasal floor variation among Eastern Eurasian Pleistocene Homo[J]. Anthropological Sciences, 2012,120(3):217-226 |
| [10] | 吴秀杰, 潘雷. 利用3D激光扫描技术分析周口店直立人脑的不对称性[J]. 科学通报, 2011,56(16):1282-1287 |
| [11] | 吴秀杰, 范雪春, 李史明, 等. 福建漳平奇和洞发现的新石器时代早期人类头骨[J]. 人类学学报, 2014,33(4):448-459 |
| [12] | Friess M, Marcus LF, Reddy DP, et al. The use of 3D laser scanning techniques for the morphometric analysis of human facial shape variation[J]. BAR Int Series, 2002,1049:31-35 |
| [13] |
Deveci M, Oztürk S, Sengezer M, et al. Measurement of orbital volume by a 3-dimensional software program: an experimental study[J]. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 2000,58(6):645-648
doi: 10.1016/s0278-2391(00)90157-5 URL pmid: 10847286 |
| [14] | Slizewski A, Friess M, Semal P. Surface scanning of anthropological specimens: nominal-actual comparison with low cost laser scanner and high end fringe light projection surface scanning systems[J]. Quartar, 2010,57:179-187 |
| [15] |
Liu W, Jin CZ, Zhang YQ, et al. Human remains from Zhirendong, South China, and modern human emergence in East Asia[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010 , 107(45) : 19201-19206
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014386107 URL pmid: 20974952 |
| [16] | 魏偏偏, 邢松. 人类股骨断面面积与轮廓形状的不对称性——基于三维激光扫描的形态测量分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2013,32(3):354-364 |
| [17] | 魏偏偏. 周口店田园洞古人类股骨形态功能分析[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学, 2016 |
| [18] | 魏偏偏, 张全超, 邢松, 等. 内蒙古和林格尔县土城子遗址人群两侧股骨断面形态的不对称性[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2015,38(3):333-336 |
| [19] | 张亚盟, 魏偏偏, 吴秀杰. 现代人头骨断面轮廓的性别鉴定——基于几何形态测量的研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2016,35(2):172-180 |
| [20] | 邢松, 张银运, 刘武. 周口店直立人3号与5号头骨形态特征对比及其演化速率所反映的群体隔离[J]. 人类学学报, 2012,31(3):250-258 |
| [21] | 税午阳, 周明全, 杜国光, 等. 颅骨三维模型制作和数据库的构建[J]. 中国法医学杂志, 2016,31(1):1-4 |
| [22] | 宋杨, 孙玉春, 赵一姣, 等. 牙颌模型三维扫描仪精度定量评价[J]. 北京大学学报:医学版, 2013,45(1):140-144 |
| [23] | 陈俊, 吕培军, 冯海兰, 等. 牙颌模型三维激光扫描系统可靠性研究及与手工测量的比较[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2000,14(4):251-253 |
| [24] | Park HK, Chung JW, Kho HS. Use of hand-held laser scanning in the assessment of craniometry[J]. Forensic Science International, 160(2):200-206 |
| [25] |
Fourie Z, Damstra J, Peter O, et al. Evaluation of anthropometric accuracy and reliability using different three-dimensional scanning systems[J]. Forensic Science International, 207(1-3):127-134
doi: 10.1016/s0379-0738(00)00252-8 URL pmid: 10978613 |
| [26] |
Sholts SB, Wärmländer SK, Flores LM, et al. Variation in the Measurement of Cranial Volume and Surface Area Using 3D Laser Scanning Technology[J]. Journal of Forensic Sciences, 2010,55(4):871-876
doi: 10.1111/j.1556-4029.2010.01380.x URL pmid: 20384925 |
| [27] | 韩康信. 韩康信人类学文选[M]. 科学出版社, 北京, 2017 |
| [28] | 青海省文物管理处. 青海柳湾[M]. 文物出版社, 北京, 1984 |
| [29] | 任晓燕. 上孙家寨汉墓群族属初探[J]. 青海民族学院学报, 1988,4:28-31 |
| [30] | 蒲朝绂, 员安志. 甘肃永昌鸳鸯池新石器时代墓地[J]. 考古学报, 1982,2:199-227 |
| [31] | 席焕久, 陈昭. 人体测量方法[M]. 科学出版社, 北京, 2010 |
| [32] | 邵象清. 人体测量手册[M]. 上海辞书出版社, 上海, 1985 |
| [33] | John AR. Mathematical statistics and data analysis[M]. Thomson Brooks/Cole, 2007 |
| [34] |
Mustafa D, Serdar O, Mustafa S, et al. Measurement of Orbital Volume by a 3-Dimensional Software Program: An experimental study[J]. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 2000,58:645-648
doi: 10.1016/s0278-2391(00)90157-5 URL pmid: 10847286 |
| [35] | Kouchi M, Koizumi K. An analysis of errors in craniometry[J]. Anthropological Science, 2008,93:409-424 |
| [36] |
Utermohle CJ, Zegura SL. Intra and interobserver error in craniometry: A cautionary tale[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1982,57(3):303-310
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330570307 URL pmid: 7114195 |
| [37] |
Weinberg SM, Naidoo S, Govier DP, et al. Anthropometric precision and accuracy of digital three-dimensional photogrammetry: comparing the genex and 3dMD imaging systems with one another and with direct anthropometry[J]. The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 2006,17(3):477-483
doi: 10.1097/00001665-200605000-00015 URL pmid: 16770184 |
| [38] | Isheil A, Gonnet JP, Joannic D, et al. Fontaine Systematic error correction of a 3D laser scanning measurement device[J]. Optics & Lasers in Engineering, 2011,49(1):16-24 |
| [39] |
Fenga HY, Liua Y, Xi F. Analysis of digitizing errors of a laser scanning system[J]. Precision Engineering, 2001,25(3):185-191
doi: 10.1016/S0141-6359(00)00071-4 URL |
| [40] | 郑德华, 沈云中, 刘春. 三维激光扫描仪及其测量误差影响因素分析[J]. 测绘工程, 2005,14(2):32-34 |
| [41] | 李金海. 误差理论与测量不确定度评定[M]. 中国计量出版社, 北京, 2007 |
| [1] | 贺乐天, 王永强, 魏文斌. 新疆哈密拉甫却克墓地人的颅面部测量学特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(06): 1017-1027. |
| [2] | 张玄, 张亚盟, 吴秀杰. 3D虚拟复原精度的差异对头骨测量数值的影响——以Mimics软件为例[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(02): 270-281. |
| [3] | 魏偏偏, 邢松. 人类股骨断面面积与形状的不对称性——基于三维激光扫描的形态测量分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(03): 354-364. |
| [4] | 陈洪. 男性特小颅一例报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(04): 336-343. |
| [5] | 刘武,张银运. 中国直立人形态特征的变异——颅骨测量数据的统计分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2005, 24(02): 121-136. |
| [6] | 丁士海,阎锡光,法德华,任光金,薛良华,来现臣,武传德. 颅容积的测量与推算的改进[J]. 人类学学报, 1992, 11(03): 241-249. |
| [7] | 曾祥龙,刘武. 颅骨测量与X线头影测量方法的比较研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1991, 10(04): 288-297. |
| [8] | 孙尚辉,欧永章. 南京现代人颅骨的测量[J]. 人类学学报, 1988, 7(03): 215-218. |
| [9] | 欧永章. 男性巨颅一例报告[J]. 人类学学报, 1988, 7(02): 138-141、195. |
| [10] | 王汝信,鲍明新. 国人颅骨某些角度的测量[J]. 人类学学报, 1988, 7(02): 133-137. |
| [11] | 邵兴周,崔静,杨振江,王博,常喜恩. 洛浦县山普拉出土颅骨的初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1988, 7(01): 0-38、100. |
| [12] | 鲍明新,王汝信. 青岛汉族颅骨某些角度的测量(续)[J]. 人类学学报, 1984, 3(04): 330-333. |
| [13] | 王汝信,鲍明新. 青岛汉族颅骨某些角度的测量[J]. 人类学学报, 1984, 3(01): 32-36. |
| [14] | 丁士海. 颅骨某些角度的测量计算法[J]. 人类学学报, 1983, 2(04): 390-395. |
| [15] | 邵象清. 北京猿人头盖骨最大宽位置与高度测量的比较研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1983, 2(02): 116-208. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 211
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 635
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3