

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (03): 427-435.doi: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0081cstr: 32091.14.j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0081
姬昊1,2( ), 刘春茹1(
), 刘春茹1( ), 宋为娟1, 魏传义1, 敖红3, 李建平1, 尹功明1
), 宋为娟1, 魏传义1, 敖红3, 李建平1, 尹功明1
收稿日期:2020-11-06
修回日期:2020-12-22
出版日期:2021-06-15
发布日期:2021-06-24
通讯作者:
刘春茹
作者简介:姬昊(1996.10-),男,中国地质大学(北京)2018级硕士研究生,主要从事ESR年代学研究。Email: 基金资助:
JI Hao1,2( ), LIU Chunru1(
), LIU Chunru1( ), SONG Weijuan1, WEI Chuanyi1, AO Hong3, LI Jianping1, YIN Gongming1
), SONG Weijuan1, WEI Chuanyi1, AO Hong3, LI Jianping1, YIN Gongming1
Received:2020-11-06
Revised:2020-12-22
Online:2021-06-15
Published:2021-06-24
Contact:
LIU Chunru
摘要:
泥河湾盆地因发育良好的晚新生代湖相地层、丰富的旧石器遗址和哺乳动物化石而广受关注。盆地内已发现旧石器遗址100余处,被学术界称为“东方奥杜韦(Olduvai)峡谷”。由于缺乏合适的年代测定方法,许多重要的遗址,尤其是中更新世时间段的遗址缺乏年龄数据,如三棵树遗址,使得旧石器遗址研究少了时间轴合理的年代学框架。电子自旋共振(ESR)测年技术是上世纪60年代发展起来的一种测年技术,并在实践中得到了地质学界的广泛认可。对于中更新世遗址年龄的测定,ESR测年法具有明显的优势。本文利用石英Ti-Li心ESR法对三棵树遗址沉积物样品进行了独立年代测定,得到三棵树遗址文化层的年龄为599±70 kaBP。该年龄对于了解泥河湾盆地古人类的生存演化提供了必要的年代学依据。
中图分类号:
姬昊, 刘春茹, 宋为娟, 魏传义, 敖红, 李建平, 尹功明. 泥河湾盆地三棵树遗址ESR年代学[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(03): 427-435.
JI Hao, LIU Chunru, SONG Weijuan, WEI Chuanyi, AO Hong, LI Jianping, YIN Gongming. ESR chronology of the Sankeshu Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021, 40(03): 427-435.
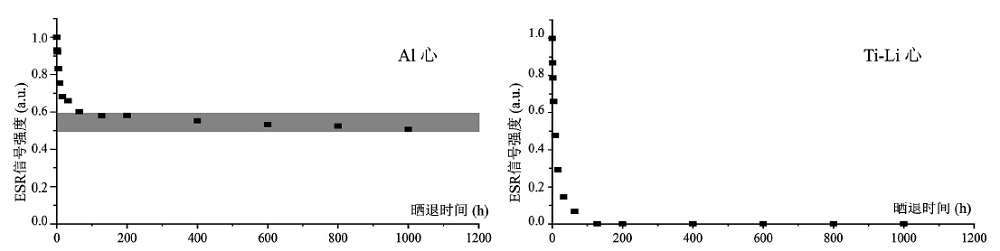
图4 三棵树遗址样品SKS-2石英Al心和Ti-Li心ESR信号光晒退特征
Fig.4 Sunlight bleaching characteristics of quartz Al and Ti-Li centers for the SKS-2 sample of the Sankeshu site
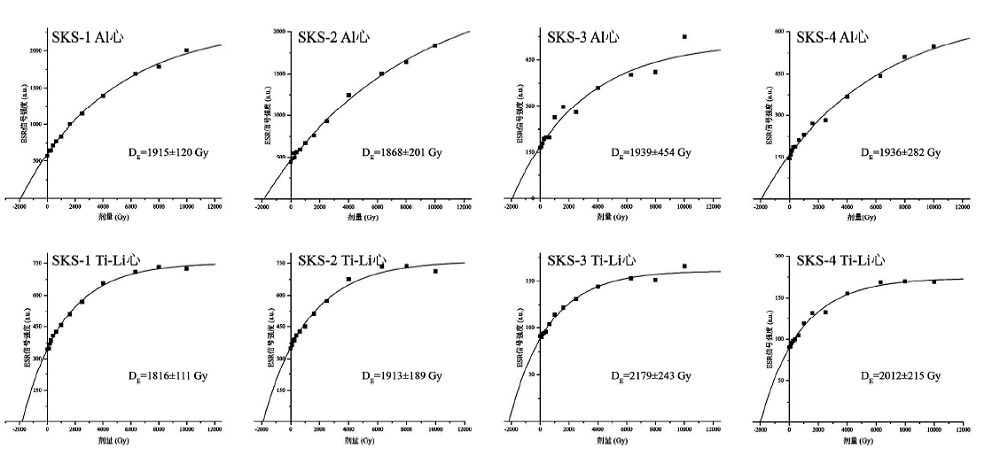
图5 三棵树遗址4个样品(SKS-1、SKS-2、SKS-3和SKS-4)的Al心和Ti-Li心附加剂量曲线
Fig.5 Additive dose curves of Al and Ti-Li centers for the four samples (SKS-1、SKS-2、SKS-3 and SKS-4) of the Sankeshu site
| 编号 No. | 含水量 water content | U (μg/g) | Th (μg/g) | K百分含量 K content | 环境剂量率 Dose rate (Gy/ka) | Al心等效剂量Al center DE (Gy) | Ti-Li心等效剂量 Ti-Li center DE (Gy) | 年龄 Age (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SKS-1 | 10±5% | 2.4±0.3 | 9.8±0.1 | 2.25±0.03% | 3.03±0.3 | 1915±120 | 1816±111 | 599±37 |
| SKS-2 | 10±5% | 2.8±0.4 | 11.2±0.1 | 2.33±0.04% | 3.26±0.3 | 1868±201 | 1913±189 | 587±58 |
| SKS-3 | 10±5% | 3.9±0.4 | 11.9±0.1 | 2.42±0.04% | 3.62±0.4 | 1939±454 | 2179±243 | 602±67 |
| SKS-4 | 10±5% | 3.3±0.4 | 10.8±0.1 | 2.25±0.03% | 3.28±0.3 | 1936±282 | 2012±215 | 610±65 |
表1 三棵树遗址4个样品的环境剂量率、Al和Ti-Li心等效剂量以及Ti-Li心ESR信号的年龄结果
Tab.1 Dose rates, equivalent doses of the Al and Ti centers, and age results obtained from the Ti-Li center for four samples of the Sankeshu site
| 编号 No. | 含水量 water content | U (μg/g) | Th (μg/g) | K百分含量 K content | 环境剂量率 Dose rate (Gy/ka) | Al心等效剂量Al center DE (Gy) | Ti-Li心等效剂量 Ti-Li center DE (Gy) | 年龄 Age (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SKS-1 | 10±5% | 2.4±0.3 | 9.8±0.1 | 2.25±0.03% | 3.03±0.3 | 1915±120 | 1816±111 | 599±37 |
| SKS-2 | 10±5% | 2.8±0.4 | 11.2±0.1 | 2.33±0.04% | 3.26±0.3 | 1868±201 | 1913±189 | 587±58 |
| SKS-3 | 10±5% | 3.9±0.4 | 11.9±0.1 | 2.42±0.04% | 3.62±0.4 | 1939±454 | 2179±243 | 602±67 |
| SKS-4 | 10±5% | 3.3±0.4 | 10.8±0.1 | 2.25±0.03% | 3.28±0.3 | 1936±282 | 2012±215 | 610±65 |
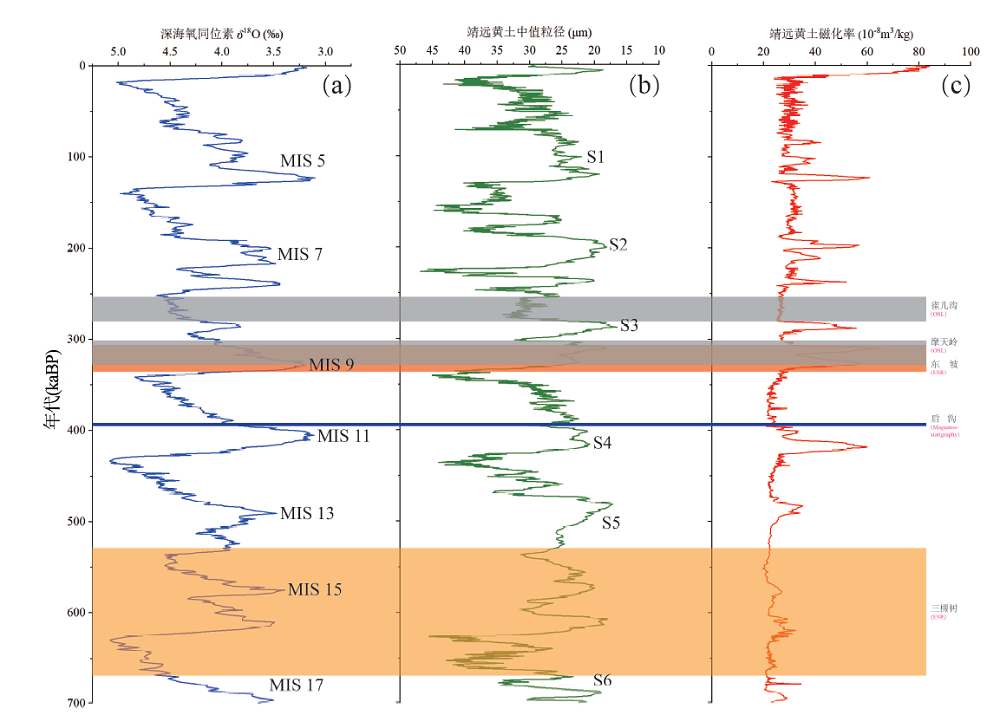
图6 三棵树遗址年龄以及泥河湾盆地其他已知的中更新世遗址年龄 雀儿沟Queergou(268±13 kaBP)[22],摩天岭Motianling(315±13 kaBP)[22],东坡Dongpo(321±15 kaBP)[23],后沟Hougou(395 kaBP)[21]和三棵树Sankeshu(599±70 kaBP)。(a)LR04钻孔深海氧同位素曲线Oxygen isotope record of marine benthos (Marine Isotope Stages) from LR04 drill[39];(b)&(c)分别为靖远黄土中值粒径和磁化率曲线the mean grain-size and the magnetic suscepitility (SUS) curves respectively from the Jingyuan loess section[40]
Fig.6 Age of the Sankeshu site and other known ages of the Middle Pleistocene sites in the Nihewan Basin
| [1] | Barbour GB. Preliminary observation in the Kalgan Area[M]. Bulletin of Geological Society of China, 1924,3(2):167-168 |
| [2] | Barbour GB. The deposits of the Sankanho Valley[M]. Bulletin of Geological Society of China, 1925,4(1):53-55 |
| [3] | 卫奇. 在泥河湾层中发现纳玛象头骨化石[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1976,14(1):53-58 |
| [4] | 卫奇. 泥河湾盆地发现177万年前的旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 2008,27(1):70-70 |
| [5] | 邓成龙, 郝青振, 郭正堂, 等. 中国第四纪综合地层和时间框架[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2019,49(1):330-352 |
| [6] |
Zhu RX, Hoffman KA, Potts R, et al. Earliest presence of humans in northeast Asia[J]. Nature, 2001,413(6854):413-417
pmid: 11574886 |
| [7] |
Zhu RX, Potts R, Xie F, et al. New evidence on the earliest human presence at high northern latitudes in northeast Asia[J]. Nature, 2004,431(7008):559-562
pmid: 15457258 |
| [8] |
Deng CL, Wei Q, Zhu RX, et al. Magnetostratigraphic age of the Xiantai Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin and implications for early human colonization of Northeast Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006,244(1-2):336-348
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.02.001 URL |
| [9] | Deng CL, Xie F, Liu CC, et al. Magnetochronology of the Feiliang Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin and implications for early human adaptability to high northern latitudes in East Asia[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007,34(14):1-6 |
| [10] |
Deng CL, Zhu RX, Zhang R, et al. Timing of the Nihewan formation and faunas[J]. Quaternary Research, 2008,69(1):77-90
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2007.10.006 URL |
| [11] | 谢飞, 李珺, 刘连强. 泥河湾旧石器文化[M]. 石家庄: 花山文艺出版社, 2005: 1-278 |
| [12] | 裴树文. 泥河湾盆地大长梁旧石器地点[J]. 人类学学报, 2002,21(2):116-125 |
| [13] | 裴树文, 李潇丽, 刘德成, 等. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址古人类生存环境探讨[J]. 科学通报, 2009,54(19):2895-2901 |
| [14] |
Pei SW, Li XL, Liu DC, et al. Preliminary study on the living environment of hominids at the Donggutuo site, Nihewan Basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009,54(21):3896
doi: 10.1007/s11434-009-0646-9 URL |
| [15] |
Pei SW, Deng CL, Torre DL, et al. Magnetostratigraphic and archaeological records at the Early Pleistocene site complex of Madigou (Nihewan Basin): Implications for human adaptations in North China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019,530:176-189
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.05.014 URL |
| [16] |
Wang HQ, Deng CL, Zhu RX, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the Donggutuo and Maliang Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2005,64(1):1-11
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2005.04.001 URL |
| [17] |
Wang HQ, Deng CL, Zhu RX, et al. Paleomagnetic dating of the Cenjiawan Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, northern China[J]. Science in China Series D, 2006,49(3):295-303
doi: 10.1007/s11430-006-0295-7 URL |
| [18] |
Liu P, Deng CL, Li SH, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the Huojiadi Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010,298(3-4):399-408
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.10.027 URL |
| [19] |
Ao H, Deng CL, Dekkers MJ, et al. Astronomical dating of the Xiantai, Donggutuo and Maliang Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin (North China) and implications for early human evolution in East Asia[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010,297(1):129-137
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.07.022 URL |
| [20] |
Ao H, An ZS, Dekkers MJ, et al. Pleistocene magnetochronology of the fauna and Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin: Significance for environmental and hominin evolution in North China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2013,18:78-92
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2013.06.004 URL |
| [21] | 左天文, 成洪江, 刘平, 等. 泥河湾盆地后沟旧石器遗址的磁性地层学定年[J]. 中国科学, 2012,42(1):94-102 |
| [22] |
Guo YJ, Li B, Zhang JF, et al. Luminescence ages for three ‘Middle Palaeolithic’ sites in the Nihewan Basin, northern China, and their archaeological and palaeoenvironmental implications[J]. Quaternary Research, 2016,85(3):456-470
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2016.03.002 URL |
| [23] | 刘春茹, 尹功明, 高璐, 等. 泥河湾盆地东坡遗址ESR年代学初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2009,29(1):166-170 |
| [24] |
Yang SX, Deng CL, Zhu RX, et al. The Paleolithic in the Nihewan Basin, China: Evolutionary history of an Early to Late Pleistocene record in Eastern Asia[J]. Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews, 2020,29(3):125-142
doi: 10.1002/evan.v29.3 URL |
| [25] |
Liu CR, Yin GM, Gao L, et al. ESR dating of Pleistocene archaeological localities of the Nihewan Basin, North China-Preliminary results[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2010,5(2-3):385-390
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2009.05.006 URL |
| [26] |
Liu CR, Yin GM, Fang F, et al. ESR dating of the Donggutuo Palaeolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, northern China[J]. Geochronometria, 2013,40(4):348-354
doi: 10.2478/s13386-013-0127-4 URL |
| [27] |
Liu CR, Yin GM, Deng CL, et al. ESR dating of the Majuangou and Banshan Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Journal of human evolution, 2014,73:58-63
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2014.05.012 URL |
| [28] | 侯亚梅, 刘扬, 李英华, 等. 泥河湾盆地三棵树旧石器遗址2008年试掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2010,29(3):227-240 |
| [29] | 刘春茹, 尹功明, 高璐, 等. 第四纪沉积物ESR年代学研究进展[J]. 地震地质, 2011,33(2):490-494 |
| [30] |
Toyoda S, Voinchet P, Falguères C, et al. Bleaching of ESR signals by the sunlight: A laboratory experiment for establishing the ESR dating of sediments[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2000,52(5):1357-1362
doi: 10.1016/S0969-8043(00)00095-6 URL |
| [31] |
Tissoux H, Falgurès C, Voinchet P, et al. Potential use of Ti center in ESR dating of fluvial sediment[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2007,2(1-4):367-372
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.04.006 URL |
| [32] |
Walther R, Zilles D. ESR studies on bleached sedimentary quartz[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1994,13(5-7):611-614
doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(94)90086-8 URL |
| [33] |
Voinchet P, Falguères C, Laurent M, et al. Artificial optical bleaching of the Aluminium center in quartz implications to ESR dating of sediments[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003,22(10-13):1335-1338
doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(03)00062-3 URL |
| [34] |
Liu CR, Grün R. Fluvio-mechanical resetting of the Al and Ti centres in quartz[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2010,46(10), 1038-1042
doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2011.06.076 URL |
| [35] | Toyoda S, Falguères C. The method to represent the ESR signal intensity of the aluminium hole center in quartz for the purpose of dating[J]. Advances in ESR applications, 2003,20:7-10 |
| [36] |
Liu CR, Yin GM, Han F. Effects of grain size on quartz ESR dating of Ti-Li center in fluvial and lacustrine sediments[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015,30:513-518
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.02.007 URL |
| [37] | Aitken MJ. Introduction to optical dating: the dating of Quaternary sediments by the use of photon-stimulated luminescence[M]. Clarendon Press, 1998 |
| [38] |
Duval M, Guilarte V. ESR dosimetry of optically bleached quartz grains extracted from Plio-Quaternary sediment: Evaluating some key aspects of the ESR signals associated to the Ti-centers[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2015,78:28-41
doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2014.10.002 URL |
| [39] | Lisiecki LE, Raymo ME. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ 18O records [J]. Paleoceanography, 2005,20:1-17 |
| [40] |
Sun YB, Yin QZ, Crucifix M, et al. Diverse manifestations of the mid-Pleistocene climate transition[J]. Nature communications, 2019,10(1):1-11
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07882-8 URL |
| [1] | Evgeny P RYBIN, Arina M KHATSENOVICH. 旧石器时代晚期初段色楞格河人类的扩散路线[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 780-796. |
| [2] | 任进成, 李锋, 陈福友, 高星. 泥河湾盆地板井子遗址2015年出土石制品的剥片技术[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 712-726. |
| [3] | 高黄文, 刘颖杰, 陆成秋, 孙雪峰, 黄旭初, 徐静玥. 湖北郧阳包包岭遗址2021年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 828-838. |
| [4] | 崔祚文, 王春雪, 陈全家, 曾庆硕, 张楠. 2021年河南南召新发现的旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 853-864. |
| [5] | 成楠, 夏文婷, 杨青, 吉学平, 字兴, 范斌, 邹梓宁, 余童, 张俞, 石林, 张吾奇, 郑洪波. 云南巍山三鹤洞地点的石制品及年代与环境[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 392-404. |
| [6] | 肖培源, 阮齐军, 高玉, 贾真秀, 张明, 杨李靖, 刘建辉, 李三灵, 李浩. 2022年云南宾川盆地旧石器遗址调查报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 448-457. |
| [7] | Hiroyuki SATO, Kazuki MORISAKI. 日本旧石器晚期石器技术起源的新考古学与人类学证据[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 470-487. |
| [8] | 王华, 李占扬, Thijs van KOLFSCHOTEN. 德国西宁根与中国灵井的骨器比较[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 214-232. |
| [9] | 赵清坡, 马欢欢. 河南灵宝旧石器考古调查报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 321-330. |
| [10] | 许竞文, 浣发祥, 杨石霞. 旧石器时代考古中出土的赭石及相关遗物的研究方法[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 331-343. |
| [11] | 高星, 张月书, 李锋, 陈福友, 王晓敏, 仪明洁. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址2016-2019年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 106-121. |
| [12] | 赵云啸, 仝广, 涂华, 赵海龙. 河北省泥河湾盆地石沟遗址C区发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 122-131. |
| [13] | 周士航, 何湘栋, 徐静玥, 李潇丽, 牛东伟. 蔚县盆地东沟遗址2017年度发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 132-142. |
| [14] | 王法岗, 杨石霞, 葛俊逸, 岳健平, 赵克良, Andreu Ollé, 李文艳, 杨海勇, 刘连强, 关莹, 谢飞, Francesco d’Errico, Michael Petraglia, 邓成龙. 泥河湾盆地下马碑遗址2013年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 143-156. |
| [15] | 张振, 王莹, 李月丛. 泥河湾盆地旧石器时代人类活动与环境关系的研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 184-198. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 214
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 619
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3