

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (04): 731-748.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0029cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0029
收稿日期:2022-04-06
修回日期:2022-05-20
出版日期:2022-08-12
发布日期:2022-08-10
作者简介:吕厚远,研究员,主要从事第四纪地质和环境考古研究。Email: 基金资助:Received:2022-04-06
Revised:2022-05-20
Online:2022-08-12
Published:2022-08-10
摘要:
从古至今,气候变化特别是周期性气候变化,一直深刻影响着人类社会的变革和发展,从旧石器时代人类起源迁移、新石器时代文化文明演变、历史时期王朝兴衰更替,到工业化以来社会经济发展动荡等,无不留下周期性气候变化影响的烙印。本文依据近年来古气候、古人类、环境考古等研究的新证据、新进展,从周期性气候变化的角度审视人类社会各个发展阶段、关键节点的气候特征;通过典型案例,介绍和分析旧石器、新石器、历史时期不同时空尺度周期性气候变化和人类活动之间复杂的相互作用关系,讨论自然科学和人文社会科学对气候变化与人类活动关系认识的异同,阐述在学科交叉背景下研究气候与人类活动关系的新范式。
中图分类号:
吕厚远. 周期性气候变化与人类适应[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(04): 731-748.
LYU Houyuan. Periodic climate change and human adaptation[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022, 41(04): 731-748.
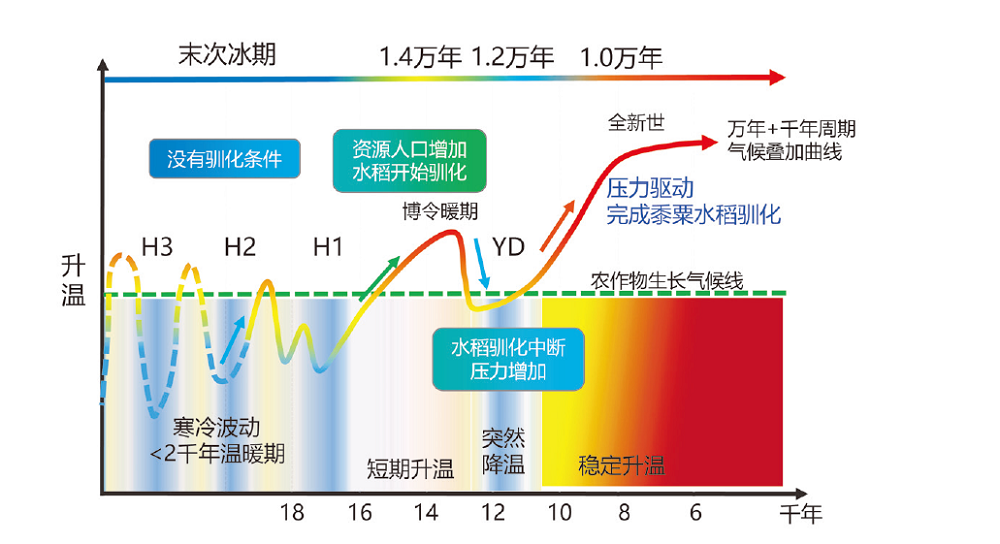
图2 东亚农业起源气候周期叠加驱动的可能机制[15,16,75-78,83]
Fig.2 Possible mechanism of climate cycle superposition driving the origin of agriculture in East Asia[15,16,75-78,83]
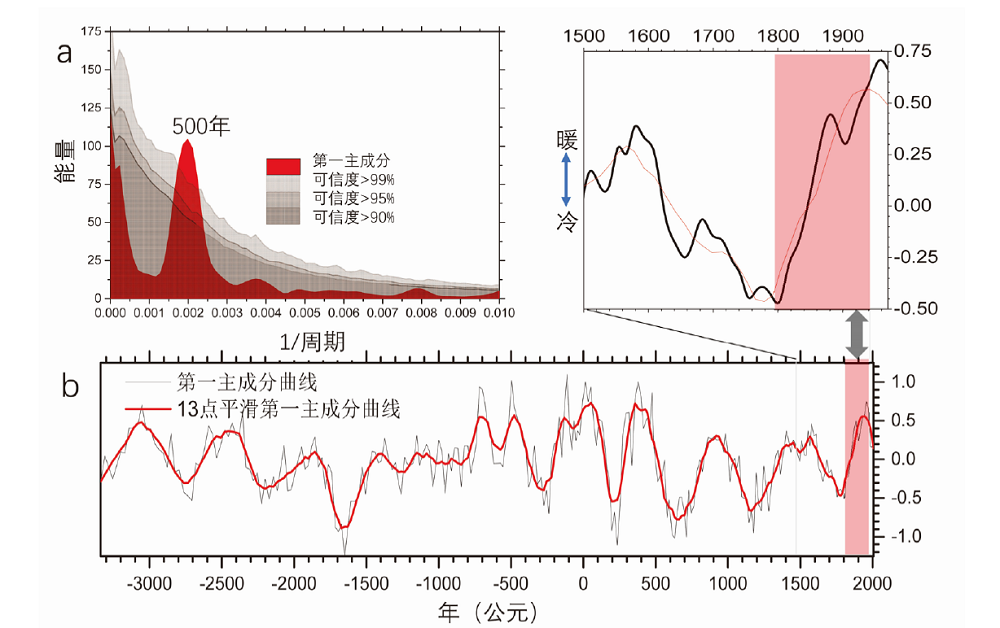
图3 中国东部小龙湾年纹层孢粉分析揭示的5350年以来的温度变化示意图 该图显示,近100年升温过程位于500年自然周期的变暖相位上;a.谱分析结果;b.气候变化曲线(据[103])。
Fig.3 Temperature changes since 5350 years ago revealed by annual stratigraphy pollen analysis in Xiaolongwan Lake, Eastern China indicating a warming process in the last 100 years, which is located in the warming phase of the 500-year natural cycle. a. spectrum analysis results; b. Climate change curve (by [103])
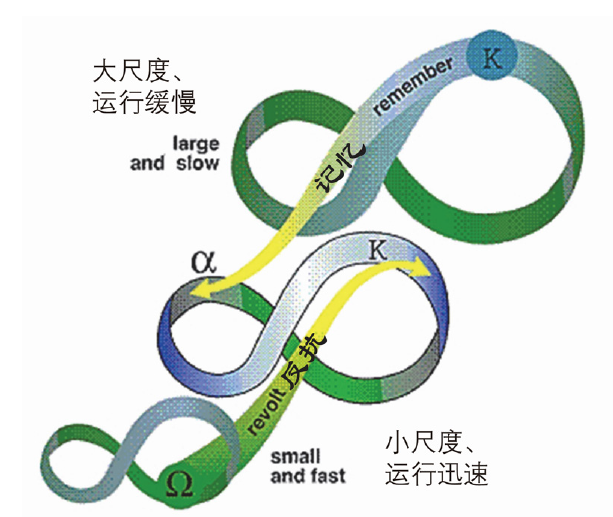
图4 扰沌(panarchy)连接,多个尺度上的关联适应循环[23] 图中r、K、Ω和α解释:r阶段(生长)系统的连接度和稳定性增加,并且开始积累自然资源和社会资本;K阶段(积累)聚集的资源越来越为系统所固持,随着系统的连接度增加、控制力也越来越强;Ω阶段(重组)随着K状态过度连接和僵硬的控制,导致系统的恢复力(resilience)降低,积累变得十分微弱,在微不足道的干扰下,会导致系统出现巨大危机和转变;α阶段(更新)系统进行重新组织,过程具有高度不确定性,有可能重复上一循环,也可能进入新的不同的循环。
Fig.4 Panarchy connections, linked adaptive cycles at multiple scales[23] Originally published in Panarchy: Understanding transformations in human and natural systems, Edited by Lance H. Gunderson and C.S. Holling 2002. Permission Island Press[23]). r, K, Ω and α Explanation: r stage (growth), the connectivity and stability of the system increase in r stage, and begin to accumulate natural resources and social capital; K-stage (accumulation), the resources gathered in stage K are increasingly fixed by the system, and the control force becomes increasingly stronger with the increase of the connection degree of the system; Ω stage (reorganization) with the over connection and rigid control in K state, the resilience of the system decreases and the accumulation becomes very weak, under insignificant interference, it will lead to great crisis and transformation of the system; α stage (update) system is reorganized, and the process is highly uncertain, it is possible to repeat the previous cycle or enter a new and different cycle.
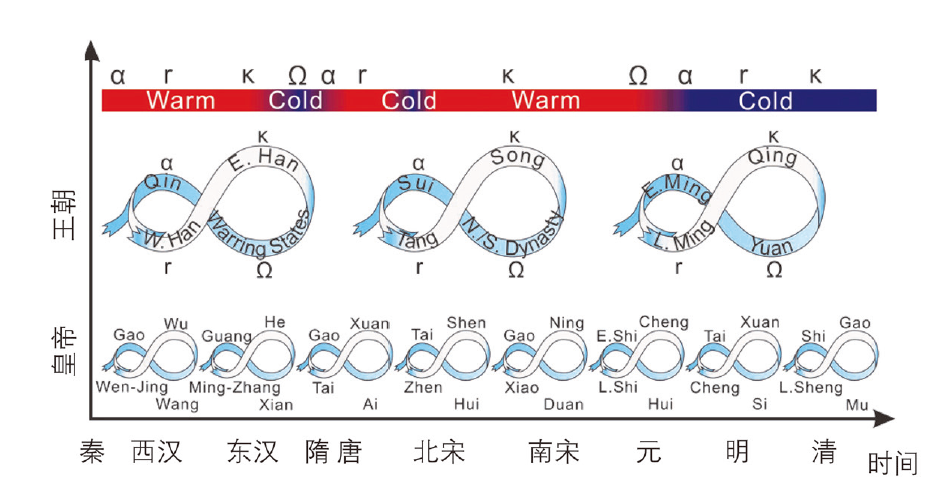
图5 自适应循环模型分析气候变化在中国近2000年以来宏观经济周期和朝代周期中的作用[22] 从上到下: 1)α、r、K和Ω分别代表自适应周期的4个阶段[23];它们同时也对应图中第2排的不同王朝; 2)彩色条表示中国百年尺度的暖/冷期[18];3)适应周期中每个主要王朝的阶段;4)各朝代皇帝在适应周期中所处的阶段;这8个圆圈代表8个漫长的朝代:西汉(公元前206年至公元25年)、东汉(公元25年至220年);唐(公元618-907年);北宋(北公元960-1127年);南宋(公元1127-1279年);元(公元1234-1368年);明代(公元1368-1644年);清朝(公元1644-1911年)。
Fig.5 The adaptive cycle model used to analyze the role of climate in the macro-economic and dynastic cycles in China over the past 2000 a[22] From top to bottom: 1) α, r, K, and Ω represent four phases of the adaptive cycle, respectively[23]; here, they also refer to the dynasties identified in the second row of the figure; 2) the colored bar indicates centennial-scale warm/cold periods in China[18]; 3) the phase of each major dynasty in the adaptive cycle; 4) the phase of Emperor in each dynasty in the adaptive cycle; the eight loops represent eight long dynasties: the Western Han(W. Han, 206 BC-AD 25), Eastern Han(E. Han, AD 25-220); Tang(AD 618-907); Northern Song(N. Song, AD 960-1127); Southern Song(S. Song, AD 1127-1279); Yuan(AD 1234-1368); Ming(AD 1368-1644); and Qing(AD 1644-1911)
| [1] | Burke A, Peros MC, Wren CD, et al. The archaeology of climate change: The case for cultural diversity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(30): e2108537118 |
| [2] | 周佰铨, 翟盘茂. IPCC第六次气候变化评估中的气候约束预估方法[J]. 气象学报, 2021, 79(6): 1063-1070 |
| [3] | Doblas-Reyes FJ, Srensson AA, Almazroui M, et al. IPCC AR6 WGI Chapter 10: Linking global to regional climate change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021 |
| [4] | 吴新智. 人类起源与进化简说[J]. 自然杂志, 2010, 32(2): 63-66 |
| [5] | 郭正堂, 任小波, 吕厚远, 等. 过去2万年以来气候变化的影响与人类适应-中国科学院战略性先导科技专项"应对气候变化的碳收支认证及相关问题"之影响与适应任务群研究进展[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2016, 31(1): 142-151 |
| [6] | Gowdy J. Our hunter-gatherer future: Climate change, agriculture and uncivilization[J]. Futures, 2020, 115: 2488 |
| [7] | Gornitz V. Ancient Cultures and Climate Change[A]. In: Gornitz V(Eds.). Encyclopedia of Paleoclimatology and Ancient Environments[M]. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series. Dordrecht: Springer, 2009 |
| [8] | 陈星灿. 考古学对于认识中国早期历史的贡献--中外考古学家的互动及中国文明起源范式的演变[J]. 南方文物, 2011, 2: 85-88 |
| [9] | 汪品先, 田军, 黄恩清, 等. 地球系统与演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018 |
| [10] |
Zeder MA. Central questions in the domestication of plants and animals[J]. Evolutionary Anthropology, 2006, 15(3): 105-117
doi: 10.1002/evan.20101 URL |
| [11] | 达尔文. 达尔文进化论全集·第三卷·物种起源[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996 |
| [12] | Gao X, Zhang X, Yang D, et al. Revisiting the origin of modern humans in China and its implications for global human evolution[J]. Sci China Earth Sci, 2010, 40(9): 1287-1300 |
| [13] | Keighren IM. Environmental Determinism (2nd Edition)[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2015 |
| [14] | Rabie M. Cultural Determinism[A]. In: Rabie M. Global Economic and Cultural Transformation: The Making of World History[M]. New Tork: Palgrave Macmillan, 2013 |
| [15] |
Wang C, Lu HY, Zhang JP, et al. Prehistoric demographic fluctuations in China inferred from radiocarbon data and their linkage with climate change over the past 50,000 years[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 98: 45-59
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.05.015 URL |
| [16] |
Lu HY, Wu NQ, Liu KB, et al. Modern pollen distributions in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and the development of transfer functions for reconstructing Holocene environmental changes[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30: 947-966
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.01.008 URL |
| [17] |
Miller DS, Gingerich J. Regional variation in the terminal Pleistocene and early Holocene radiocarbon record of eastern North America[J]. Quaternary Research, 2013, 79(2): 175-188
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2012.12.003 URL |
| [18] |
Ge QS, Hao ZX, Zheng JY, et al. Temperature changes over the past 2000 yr in China and comparison with the Northern Hemisphere[J]. Climate of the Past, 2013, 9(3): 1153-1160
doi: 10.5194/cp-9-1153-2013 URL |
| [19] | 裴卿. 历史气候变化和社会经济发展的因果关系实证研究评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017, 13(4): 375-382 |
| [20] | 李峯, 章典, 裴卿, 等. 中国近五百年旱涝灾害与内乱关系的定量分析[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2017, 47(12): 1395-1405 |
| [21] |
Zhang DD, Lee HF, Wang C, et al. The causality analysis of climate change and large-scale human crisis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108(42): 17296-17301
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1104268108 URL |
| [22] |
Wei ZD, Rosen AM, Fang XQ, et al. Macro-economic cycles related to climate change in dynastic China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2015, 83(1): 13-23
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2014.11.001 URL |
| [23] | Gunderson LH, Holling CS. Panarchy: Understanding Transformations In Human And Natural Systems[M]. Washington, DC: Island Press, 2003 |
| [24] |
Wu WX, Liu TS. Possible role of the "Holocene Event 3" on the collapse of Neolithic Cultures around the Central Plain of China[J]. Quaternary International, 2004, 117(1): 153-166
doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(03)00125-3 URL |
| [25] | Zhang DD, Pei Q, Lee HF, et al. The pulse of imperial China: a quantitative analysis of long-term geopolitical and climatic cycles[J]. Global Ecology & Biogeography, 2015, 24(1): 87-96 |
| [26] | 许靖华. 太阳、气候、饥荒与民族大迁移[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 1998, 28(4): 366-384 |
| [27] | 贾雷德·戴蒙德. 枪炮、病菌与钢铁:人类社会的命运[M]. 上海: 上海译文出版社, 2014 |
| [28] |
Wu QL, Zhao ZJ, Liu L, et al. Outburst flood at 1920 BCE supports historicity of China's Great Flood and the Xia dynasty[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6299): 579-582
doi: 10.1126/science.aaf0842 URL |
| [29] |
Xu DK, Lu HY, Chu GQ, et al. Synchronous 500-year oscillations of monsoon climate and human activity in Northeast Asia[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1-10
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07882-8 URL |
| [30] | 吕厚远. 新石器以来的北温带草原文化与气候变迁[J]. 文物保护与考古科学, 1991, 3(2): 43-50 |
| [31] | Catto N, Catto G. Climate change, communities, and civilizations: driving force, supporting player, or background noise?[J]. Quaternary International, 2004, 123: 7-10 |
| [32] | 章典, 詹志勇, 林初升, 等. 气候变化与中国的战争、社会动乱和朝代变迁[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(23): 2468-2474 |
| [33] |
Griffiths S, Robinson E. The 8.2 ka BP Holocene climate change event and human population resilience in northwest Atlantic Europe[J]. Quaternary International, 2018, 465: 251-257
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2017.10.017 URL |
| [34] | Blockley S, Candy I, Matthews I, et al. The resilience of postglacial hunter-gatherers to abrupt climate change[J]. Ecology & Evolution, 2018, 2(5): 810-818 |
| [35] |
Rosen AM, Rivera-Collazo I. Climate change, adaptive cycles, and the persistence of foraging economies during the late Pleistocene/Holocene transition in the Levant[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2012, 109(10): 3640-3645
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1113931109 URL |
| [36] | 舒展. 气候与中国北方游牧族群南侵再探[J]. 黄河黄土黄种人, 2021, 33: 41-48 |
| [37] |
拓守廷, 刘志飞. 始新世-渐新世界线的全球气候事件:从“温室”到“冰室”[J]. 地球科学进展, 2003, 18(5): 691-696
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2003.05.0691 |
| [38] |
Zachos J, Pagani M, Sloan L, et al. Trends, Rhythms, and Aberrations in Global Climate 65 Ma to Present[J]. Science, 2001, 292(5517): 686-693
pmid: 11326091 |
| [39] |
Callaway E. Femur findings remain a secret[J]. Nature, 2018, 553(7689): 391-392
doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-00972-z URL |
| [40] |
Carotenuto F, Tsikaridze N, Rook L, et al. Venturing out safely: The biogeography of Homo erectus dispersal out of Africa[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2016, 95: 1-12
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2016.02.005 pmid: 27260171 |
| [41] |
Leo G, Abesalom V, David L, et al. Earliest Pleistocene Hominid Cranial Remains from Dmanisi, Republic of Georgia: Taxonomy, Geological Setting, and Age[J]. Science, 2000, 288(5468): 1019-1025
doi: 10.1126/science.288.5468.1019 URL |
| [42] | Hadjouis D. Migration and Paleogeographic Distribution of the Homininae[A]. In: Hadjouis D. The Skull of Quadruped and Bipedal Vertebrates[M]. Hoboken: Wiley-ISTE, 2021 |
| [43] | 李潇丽. 气候波动频率与古人类演化[J]. 化石, 2016(2): 18-22 |
| [44] |
Potts R, Faith T. Alternating high and low climate variability: The context of natural selection and speciation in Plio-Pleistocene hominin evolution[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2015, 87: 5-20
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2015.06.014 URL |
| [45] |
Potts R. Hominin evolution in settings of strong environmental variability[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 73: 1-13
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.04.003 URL |
| [46] | Veldhuis D, Kjærgaard P, Maslin M. Human Evolution: Theory and Progress[M]. New York: Springer, 2014 |
| [47] |
Potts R. Evolution and climate variability[J]. Science, 1996, 273(5277): 922-922
doi: 10.1126/science.273.5277.922 URL |
| [48] | 丁仲礼. 米兰科维奇冰期旋回理论:挑战与机遇[J]. 第四紀研究, 2006, 26(5): 710-717 |
| [49] | 裴树文, 李潇丽, 刘德成, 等. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址古人类生存环境探讨[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54(19): 2895-2901 |
| [50] |
吴文祥, 刘东生. 泥河湾与黄土高原地层对比及其旧石器文化序列[J]. 地球科学进展, 2002, 17(1): 33
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2002.01.0033 |
| [51] | 汪品先, 田军, 成鑫荣. 第四纪冰期旋回转型在南沙深海的记录[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2001, 31(10): 793-799 |
| [52] |
Hao QZ, Wang L, Oldfield F, et al. Extra-long interglacial in Northern Hemisphere during MISs 15-13 arising from limited extent of Arctic ice sheets in glacial MIS 14[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 12103
doi: 10.1038/srep12103 URL |
| [53] |
Templeton A. Out of Africa again and again[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6876): 45-51
doi: 10.1038/416045a URL |
| [54] | Templeton AR. Haplotype trees and modern human origins[A]. In: Stinson S(Ed.). Yearbook of Physical Anthropology[C]. Washington: Washington University, 2005, 33-59 |
| [55] |
Timmermann A, Friedrich T. Late Pleistocene climate drivers of early human migration[J]. Nature, 2016, 538(7623): 92-95
doi: 10.1038/nature19365 URL |
| [56] |
Lambeck K, Rouby H, Purcell A, et al. Sea level and global ice volumes from the Last Glacial Maximum to the Holocene[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2014, 111(43): 15296-15303
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411762111 URL |
| [57] | Dietrich T. The Origin of Culture and Civilization[M]. Austin: Turnkey Press, 2005 |
| [58] | 严文明. 文明起源研究的回顾与思考[J]. 文物, 1999, 10: 27-34 |
| [59] | Feynman J, Ruzmaikin A. Climate Stability and the Origin of Agriculture[A]. In: Hussain S(Ed.). Climate Change and Agriculture[M]. London: IntechOpen, 2018 |
| [60] |
葛全胜, 方修琦, 郑景云. 中国历史时期气候变化影响及其应对的启示[J]. 地球科学进展, 2014, 29(1): 23-29
doi: 1001-8166(2014)01-0023-07 |
| [61] |
Munoz SE, Gajewski K, Peros MC. Synchronous environmental and cultural change in the prehistory of the northeastern United States[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010, 107(51): 22008-22013
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005764107 URL |
| [62] | Benati G, Guerriero C. Climate change and state evolution[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(14) |
| [63] | Hinsch B. Climatic change and history in China[J]. Journal of Asian History, 1988, 22(2): 131-159 |
| [64] | 韩建业. 论新石器时代中原文化的历史地位[J]. 江汉考古, 2004(1): 59-64 |
| [65] | Rawat V, Rawat S, Srivastava P, et al. Middle Holocene Indian summer monsoon variability and its impact on cultural changes in the Indian subcontinent[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2021, 255: 1-15 |
| [66] |
Williams AN. The use of summed radiocarbon probability distributions in archaeology: a review of methods[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2012, 39(3): 578-589
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2011.07.014 URL |
| [67] | 安怀志. 希尔伯特黄变换理论和应用的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2008 |
| [68] | 郭正堂. 《地球系统与演变》:未来地球科学的脉络简[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(9): 883-884 |
| [69] | 荣平平, 刘式达. 不同时间尺度下气候变化基本特征的探索[J]. 气候与环境研究, 1997, 2(1): 78-83 |
| [70] | 王绍武. D/O循环与H事件[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2011, 7(6): 458-460 |
| [71] |
Clark PU, Bartlein PJ. Correlation of late Pleistocene glaciation in the western United States with North Atlantic Heinrich events[J]. Geology, 1995, 23(6): 483-486
doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0483:COLPGI>2.3.CO;2 URL |
| [72] | Bond GC, Showers W, Elliot M, et al. The North Atlantic's 1-2 Kyr Climate Rhythm: Relation to Heinrich Events, Dansgaard/Oeschger Cycles and the Little Ice Age[M]. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union, 1999 |
| [73] | Bar-Yosef O. From foraging to farming in Western and Eastern Asia[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012 |
| [74] |
Belfer-Cohen BY. The Origins of Sedentism and Farming Communities in the Levant[J]. Journal of World Prehistory, 1989, 3(4): 447-498
doi: 10.1007/BF00975111 URL |
| [75] |
Lu HY, Liu ZX, Wu NQ, et al. Rice domestication and climatic change: phytolith evidence from East China[J]. Boreas, 2002, 31(4): 378-385
doi: 10.1111/j.1502-3885.2002.tb01081.x URL |
| [76] |
Lu HY, Zhang JP, Liu KB, et al. Earliest domestication of common millet (Panicum miliaceum) in East Asia extended to 10,000 years ago[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2009, 106(18): 7367-7372
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900158106 URL |
| [77] | Lu HY. New methods and progress in research on the origins and evolution of prehistoric agriculture in China[J]. Science China(Earth Sciences), 2017, 60(12): 2141-2159 |
| [78] |
Zuo XX, Lu HY, Jiang LP, et al. Dating rice remains through phytolith carbon-14 study reveals domestication at the beginning of the Holocene[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2017, 114(25): 6486-6491
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1704304114 URL |
| [79] |
He KY, Lu HY, Zhang JP, et al. Prehistoric evolution of the dualistic structure mixed rice and millet farming in China[J]. The Holocene, 2017, 27(12): 1885-1898
doi: 10.1177/0959683617708455 URL |
| [80] |
Xu DK, Lu HY, Wu NQ, et al. Asynchronous marine-terrestrial signals of the last deglacial warming in East Asia associated with low- and high-latitude climate changes[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(24): 9657-9662
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300025110 URL |
| [81] | Lu HY, Zhang JP, Wu NQ, et al. Phytoliths Analysis for the Discrimination of Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) and Common Millet (Panicum miliaceum)[J]. PLoS One, 2009, 4(2): 1-15 |
| [82] | Lu HY, Wu NQ, Liu KB, et al. Phytoliths as quantitative indicators for the reconstruction of past environmental conditions in China II: palaeoenvironmental reconstruction in the Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary ence Reviews, 2007, 26(5-6): 759-772 |
| [83] |
Yang XY, Wan ZW, Perry L, et al. Early millet use in northern China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(10): 3726-3730
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115430109 URL |
| [84] | Wang WY, Liu JQ, Liu TS, et al. The two-step monsoon changes of the last deglaciation recorded in tropical Maar Lake Huguangyan, Southern China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 16(16): 1529-1532 |
| [85] |
Huan X, Lu H, Jiang L, et al. Spatial and temporal pattern of rice domestication during the early Holocene in the lower Yangtze region, China[J]. The Holocene, 2021, 31(9): 1366-1375
doi: 10.1177/09596836211019090 URL |
| [86] | 吕厚远. 中国史前农业起源演化研究新方法与新进展[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2018, 48(2): 181-199 |
| [87] |
Shakun JD, Carlson AE. A global perspective on Last Glacial Maximum to Holocene climate change[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(15-16): 1801-1816
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.03.016 URL |
| [88] | Kaplan J. Late Quaternary-Holocene Vegetation Modeling[A]. In: Gornitz V(Eds.). Encyclopedia of Paleoclimatology and Ancient Environments[M]. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series. Dordrecht: Springer, 2009: 507-514 |
| [89] | 张修龙, 吴文祥, 周扬. 西方农业起源理论评述[J]. 中原文物, 2010(2): 36-45 |
| [90] | Anderson DG, Maasch KA, Sandweiss DH, et al. Climate and Culture Change: Exploring Holocene Transitions[M]. San Diego: Academic Press, 2007 |
| [91] | 吕厚远, 张健平. 关中地区的新石器古文化发展与古环境变化的关系[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(6): 1050-1060 |
| [92] | Tan M, Liu TS, Hou JZ, et al. Cyclic rapid warming on centennial-scale revealed by a 2650-year stalagmite record of warm season temperature[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30(12): 1617 |
| [93] | 陈强. 气候冲击、王朝周期与游牧民族的征服[J]. 经济学(季刊), 2015, 14(1): 373-394 |
| [94] | 安田喜宪, 刘绩生. 五千年前的气候变化与古代文明[J]. 世界科学, 1991, 13(2): 40-42 |
| [95] |
Lee HF, Zhang DD, Pei Q, et al. Demographic impact of climate change on northwestern China in the late imperial era[J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 425(15): 237-247
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.06.029 URL |
| [96] | 许倬云. 许倬云观世变[M]. 桂林: 广西师范大学出版社, 2008 |
| [97] | 范伶俐, 徐峰, 徐华, 等. 春季/夏季型El Nino对中国夏季降水变化的影响[J]. 大气科学学报, 2018, 41(6): 819-828 |
| [98] |
Ge QS, Zheng JY, Hao QZ, et al. Recent advances on reconstruction of climate and extreme events in China for the past 2000 years[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2016, 26(7): 827-854
doi: 10.1007/s11442-016-1301-4 URL |
| [99] | Straalen V, Roelofs NM, Straalen D, et al. An introduction to ecological genomics[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2011 |
| [100] | Cui AN, Lu HY, Liu XQ, et al. Tibetan Plateau Precipitation Modulated by the Periodically Coupled Westerlies and Asian Monsoon[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(7) |
| [101] | 葛全胜, 华中, 郑景云, 等. 过去2000年全球典型暖期的形成机制及其影响[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(18): 1728-1735 |
| [102] | 赵红军. 气候变化是否影响了我国过去两千年间的农业社会稳定?--一个基于气候变化重建数据及经济发展历史数据的实证研究[J]. 经济学(季刊), 2012, 11(2): 691-722 |
| [103] |
Xu DK, Lu HY, Chu GQ, et al. 500-year climate cycles stacking of recent centennial warming documented in an East Asian pollen record[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 4: 3611
doi: 10.1038/srep03611 URL |
| [104] | 施雅风, 沈永平, 胡汝骥. 西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的信号、影响和前景初步探讨[J]. 冰川冻土, 2002, 24(3): 219-226 |
| [105] | 张天宇, 陈正洪, 孙佳, 等. 三峡库区近百年来气温变化特征[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2012, 21(Z2): 138-144 |
| [106] | 潘蔚娟, 吴晓绚, 何健, 等. 基于均一化资料的广州近百年气温变化特征研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(4): 444-454 |
| [107] | 李黎, 崔研, 王浩宇, 等. 营口市百年气温变化特征研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2021, 37(3): 73-80 |
| [108] | 尼古拉斯·斯特恩. 气候变化经济学(上)[J]. 经济社会体制比较, 2009 |
| [109] | 王遥. 气候金融[M]. 北京: 中国经济出版社, 2013 |
| [110] | 于鹏. 贸易与气候变化[J]. 国际贸易译丛, 2010, 4: 6 |
| [111] | Dalio R. Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed and Fail[M]. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2021 |
| [112] | 王恩涌. “人地关系”的思想从“环境决定论”到“和谐”[J]. 北京大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 1992, 1: 84-90 |
| [113] | 王兴成. 社会生态学与社会发展问题[J]. 国外社会科学, 1988, 1: 18-21 |
| [114] | 成海鹰, 成芳. 唯意志论哲学在中国(第2版)[M]. 北京: 首都师范大学出版社, 2002 |
| [115] | 韩东屏. 审视文化决定论[J]. 探索与争鸣, 2016, 6: 79-84 |
| [116] |
Peet R. The Social Origins of Environmental Determinism[J]. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 1985, 75(3): 309-333
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8306.1985.tb00069.x URL |
| [1] | 张振, 王莹, 李月丛. 泥河湾盆地旧石器时代人类活动与环境关系的研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 184-198. |
| [2] | 芦永秀, 董广辉. 西北不同降水区域新石器至青铜时代人类活动与环境变化的关系[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(04): 749-763. |
| [3] | 杜雨薇, 丁馨, 裴树文. 浅议古人类活动遗址的动物埋藏学研究方法[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(03): 523-534. |
| [4] | 裴树文. 中国古人类活动遗址形成过程研究的进展与思考[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(03): 349-362. |
| [5] | 陈国科, 杨谊时, 张山佳, 王辉. 张掖西城驿遗址新石器时代晚期-青铜时代人类冶金活动的元素地球化学记录[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(01): 87-96. |
| [6] | 包易格, 李小强, 刘汉斌, 赵克良, John Dodson, 沈慧, 张贵林, 王建, 周新郢. 中国黄土高原北部地区新石器-青铜时代农业结构演变及其对区域生态环境的适应[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(03): 461-472. |
| [7] | 杨诗雨;张全超. 《古病理学指南》评介[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(04): 667-668. |
| [8] | 高星. 朝向人类起源与演化研究的共业:古人类学、考古学与遗传学的交叉与整合[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(01): 131-140. |
| [9] | 裴树文. 泥河湾盆地南部(蔚县盆地)发现一处重要古人类活动遗址群[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(01): 26-26. |
| [10] | 王法岗. 泥河湾盆地南山边遗址发现的旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 2016, 35(03): 331-342. |
| [11] | 陈全家; 赵海龙; 王法岗; 王春雪. 桦甸仙人洞遗址出土的动物化石与孢粉[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(01): 52-62. |
| [12] | 刘德成;夏正楷;王幼平;宝文博. 河南织机洞旧石器遗址的洞穴堆积和沉积环境分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(01): 71-78. |
| [13] | 李传令,薛祥煦. 陕西蓝田锡水洞遗址大型哺乳动物保存特征与古人类行为分析[J]. 人类学学报, 1999, 18(04): 282-290. |
| [14] | 刘泽纯. 北京猿人洞穴堆积反映的古气候变化及气候地层上的对比[J]. 人类学学报, 1983, 2(02): 172-183. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 1437
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 875
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3