

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (06): 982-993.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0003cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0003
收稿日期:2021-04-20
修回日期:2021-09-01
出版日期:2022-12-15
发布日期:2022-12-19
通讯作者:
赵宇超
作者简介:侯哲,副研究员,主要从事旧石器时代考古学研究。E-mail: 基金资助:
HOU Zhe1( ), ZHAO Yuchao2(
), ZHAO Yuchao2( ), GAO Xing3,4,5, SEONG Chuntaek6
), GAO Xing3,4,5, SEONG Chuntaek6
Received:2021-04-20
Revised:2021-09-01
Online:2022-12-15
Published:2022-12-19
Contact:
ZHAO Yuchao
摘要:
本文以原料产地距离衰减效应为视角,根据目前中国东北地区和韩国旧石器时代晚期黑曜岩石制品的发现情况以及黑曜岩产源地研究成果,结合狩猎采集人群社交网络模型、民族学、考古学资料,对以长白山为核心的黑曜岩源产地对中韩两地的辐射影响作出了直接供应区(天池火山口为圆心辐射半径150~200 km)和接触区(距离天池火山口200 km以上)的划分。在此基础上对比研究两地的黑曜岩石制品,发现由于距离源头产地较远,韩国黑曜岩石制品的数量以及类型丰度均低于中国东北地区。而又由于原料的长距离损耗以及对于原料更加经济的开发利用,导致韩国典型遗址中黑曜岩细石核与完整石片的体积更小,原料缩减更甚。
中图分类号:
侯哲, 赵宇超, 高星, 成春泽. 原料产地对中国东北和韩国旧石器时代晚期黑曜岩石器工业的影响[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(06): 982-993.
HOU Zhe, ZHAO Yuchao, GAO Xing, SEONG Chuntaek. Impact of raw material source on the obsidian lithic industry of Northeast China and South Korea[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022, 41(06): 982-993.
| 遗址Site | 主要原料及占比 Major materials and their contents (%) | 黑曜岩占比 Obsidian content (%) | 数量(n) | BP 2σ (95.4%) | 分析法Method[ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 采集Surface | 地层Strata | p-XRF | LA-ICP-AES | ED-XRF | ||||
| 炮台山遗址 Paotaishan[ | 流纹岩46%; 角岩28.5% | 17.5% | 91 | 0 | √ | √ | √ | |
| 秦家东山Qinjia Dongshan[ | 角岩61% | 13.3% | 60 | 0 | ||||
| 杨林西山Yanglin Xishan[ | 角岩61.2%; 流纹岩31.8% | 3.1% | 55 | 30 | ||||
| 杨林南山Yanglin Nanshan[ | 角岩50.49%; 板岩21.36% | 6.8% | 84 | 13 | √ | √ | ||
| 珲春北山Hunchun Beishan[ | 86.5% | 51 | 1 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 桦甸仙人洞 Yedian Xianrendong[ | 角岩62.7% | 0.4% | 0 | 244 | 40589 ~37746 | √ | ||
| 辉南邵家店Huinan Shaojiaidian[ | 石英45.6% | 31.6% | 49 | 0 | √ | |||
| 新屯西山Xintun Xishan[ | 100% | 0 | 30 | √ | √ | |||
| 抚松东台Fusong Dongtai[ | — | — | — | √ | √ | |||
| 抚松枫林Fusong Fenglin[ | 96% | 2217 | 651 | 17000 | ||||
| 海沟金矿Haigou Jinkuang[ | 石英44.4%; 凝灰岩33.4% | 11.1% | 9 | 0 | √ | √ | ||
| 安图立新Antu Lixin[ | 21.1% | 65 | 6 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 安图沙金沟 Antu Shajingou[ | 90.2% | 77 | 5 | √ | √ | |||
| 两江石人沟Liangjiangzhen SRG[ | 75% | 28 | 0 | |||||
| 和龙青头Helong Qingtou[ | 84.3% | 197 | 19 | √ | √ | |||
| 和龙西沟Helong xigou[ | 69.6% | 102 | 0 | √ | √ | |||
| 和龙牛心村Helong niuxincun[ | 94% | 49 | 0 | |||||
| 和龙二水坪 Helong ershuiping[ | 98% | 51 | 0 | |||||
| 和龙广兴Helong guangxing[ | 87% | 23 | 0 | |||||
| 和龙柳洞Helong liudong[ | 93.66% | 138 | 4 | √ | √ | |||
| 和龙大洞 Helong dadong[ | 99.4% | 5752 | 4389 | 25916 ~25340 | √ | √ | √ | |
| 和龙林场Helong linchang[ | 97.42% | 30 | 86 | |||||
| 和龙石人沟 Helong shirengou[ | 99.9% | 115 | 1267 | √ | √ | |||
| 国东大穴 Guodong daxue[ | — | — | — | √ | √ | |||
表1 中国东北地区含黑曜岩的旧石器时代晚期遗址
Tab.1 Upper Paleolithic sites with obsidian artifacts in Northeast China
| 遗址Site | 主要原料及占比 Major materials and their contents (%) | 黑曜岩占比 Obsidian content (%) | 数量(n) | BP 2σ (95.4%) | 分析法Method[ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 采集Surface | 地层Strata | p-XRF | LA-ICP-AES | ED-XRF | ||||
| 炮台山遗址 Paotaishan[ | 流纹岩46%; 角岩28.5% | 17.5% | 91 | 0 | √ | √ | √ | |
| 秦家东山Qinjia Dongshan[ | 角岩61% | 13.3% | 60 | 0 | ||||
| 杨林西山Yanglin Xishan[ | 角岩61.2%; 流纹岩31.8% | 3.1% | 55 | 30 | ||||
| 杨林南山Yanglin Nanshan[ | 角岩50.49%; 板岩21.36% | 6.8% | 84 | 13 | √ | √ | ||
| 珲春北山Hunchun Beishan[ | 86.5% | 51 | 1 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 桦甸仙人洞 Yedian Xianrendong[ | 角岩62.7% | 0.4% | 0 | 244 | 40589 ~37746 | √ | ||
| 辉南邵家店Huinan Shaojiaidian[ | 石英45.6% | 31.6% | 49 | 0 | √ | |||
| 新屯西山Xintun Xishan[ | 100% | 0 | 30 | √ | √ | |||
| 抚松东台Fusong Dongtai[ | — | — | — | √ | √ | |||
| 抚松枫林Fusong Fenglin[ | 96% | 2217 | 651 | 17000 | ||||
| 海沟金矿Haigou Jinkuang[ | 石英44.4%; 凝灰岩33.4% | 11.1% | 9 | 0 | √ | √ | ||
| 安图立新Antu Lixin[ | 21.1% | 65 | 6 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 安图沙金沟 Antu Shajingou[ | 90.2% | 77 | 5 | √ | √ | |||
| 两江石人沟Liangjiangzhen SRG[ | 75% | 28 | 0 | |||||
| 和龙青头Helong Qingtou[ | 84.3% | 197 | 19 | √ | √ | |||
| 和龙西沟Helong xigou[ | 69.6% | 102 | 0 | √ | √ | |||
| 和龙牛心村Helong niuxincun[ | 94% | 49 | 0 | |||||
| 和龙二水坪 Helong ershuiping[ | 98% | 51 | 0 | |||||
| 和龙广兴Helong guangxing[ | 87% | 23 | 0 | |||||
| 和龙柳洞Helong liudong[ | 93.66% | 138 | 4 | √ | √ | |||
| 和龙大洞 Helong dadong[ | 99.4% | 5752 | 4389 | 25916 ~25340 | √ | √ | √ | |
| 和龙林场Helong linchang[ | 97.42% | 30 | 86 | |||||
| 和龙石人沟 Helong shirengou[ | 99.9% | 115 | 1267 | √ | √ | |||
| 国东大穴 Guodong daxue[ | — | — | — | √ | √ | |||
| 遗址Site | 主要原料 Major materials | 黑曜岩制品Obsidian artifacts | 年代Age (BP) | 产源分析法Sourcing method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量 (n) | 占比(%) | ICP-MS | LA-ICP-MS | PIXE | INAA | |||
| 上沙里Sangsa-ri | - | - | - | √ | ||||
| 长兴里Jangheung-ri | 石英55% | 178 | 26.5% | 29796~27361 30007~27595 | √ | |||
| 抱川中里Youngsujaeyul | 石英55.93% | 607 | 8.65% | 21240±150 | √ | |||
| 通贤里 Tonghyeon-ri | 石英75.5% | - | 4% | |||||
| 奇窟B Gigok B | 脉石英-石英岩92.3% | 19 | 0.4% | 12429~11412 14802~13314 | √ | |||
| 上舞龙里 Sangmuryong-ri | 石英99.1% | 268 | 0.2% | √ | ||||
| 富坪里 Bupyeong-ri | √ | |||||||
| 民乐洞 Minrak-dong | 40 | - | √ | |||||
| 禾垈里 Hwadae-ri | 脉石英-石英岩97.1% | - | 0.51% | 23950±100* | ||||
| 浦日洞 Poildong | 20 | |||||||
| 下花溪里 Hahwagae-ri | 脉石英-石英岩70.9% | 1306 | 21% | 16318~15904 | √ | |||
| 三里 Sam-ri | 石英91% | 67 | 4% | √ | ||||
| 昌内 Changnae | 4 | - | ||||||
| 垂杨介Suyanggae | 106 | - | 18630; 16400 | √ | ||||
| 好坪洞 Hopyeong-dong | 脉石英54.2% | 1074 | 21.6% | 25852~25013 27716~25352 | √ | |||
| 石壮里Seokjang-ri | 6 | - | 30781~21265 | √ | ||||
| 月城洞Wolseong-dong | 角页岩82% | 357 | 2.76% | 32300±3200* | √ | √ | ||
| 新北Sinbuk | 28 | 0.8% | 29700~19400 | √ | ||||
表2 韩国含黑曜岩的旧石器时代晚期主要遗址
Tab.2 Upper Paleolithic sites with obsidian artifacts in South Korea[34,35]
| 遗址Site | 主要原料 Major materials | 黑曜岩制品Obsidian artifacts | 年代Age (BP) | 产源分析法Sourcing method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量 (n) | 占比(%) | ICP-MS | LA-ICP-MS | PIXE | INAA | |||
| 上沙里Sangsa-ri | - | - | - | √ | ||||
| 长兴里Jangheung-ri | 石英55% | 178 | 26.5% | 29796~27361 30007~27595 | √ | |||
| 抱川中里Youngsujaeyul | 石英55.93% | 607 | 8.65% | 21240±150 | √ | |||
| 通贤里 Tonghyeon-ri | 石英75.5% | - | 4% | |||||
| 奇窟B Gigok B | 脉石英-石英岩92.3% | 19 | 0.4% | 12429~11412 14802~13314 | √ | |||
| 上舞龙里 Sangmuryong-ri | 石英99.1% | 268 | 0.2% | √ | ||||
| 富坪里 Bupyeong-ri | √ | |||||||
| 民乐洞 Minrak-dong | 40 | - | √ | |||||
| 禾垈里 Hwadae-ri | 脉石英-石英岩97.1% | - | 0.51% | 23950±100* | ||||
| 浦日洞 Poildong | 20 | |||||||
| 下花溪里 Hahwagae-ri | 脉石英-石英岩70.9% | 1306 | 21% | 16318~15904 | √ | |||
| 三里 Sam-ri | 石英91% | 67 | 4% | √ | ||||
| 昌内 Changnae | 4 | - | ||||||
| 垂杨介Suyanggae | 106 | - | 18630; 16400 | √ | ||||
| 好坪洞 Hopyeong-dong | 脉石英54.2% | 1074 | 21.6% | 25852~25013 27716~25352 | √ | |||
| 石壮里Seokjang-ri | 6 | - | 30781~21265 | √ | ||||
| 月城洞Wolseong-dong | 角页岩82% | 357 | 2.76% | 32300±3200* | √ | √ | ||
| 新北Sinbuk | 28 | 0.8% | 29700~19400 | √ | ||||
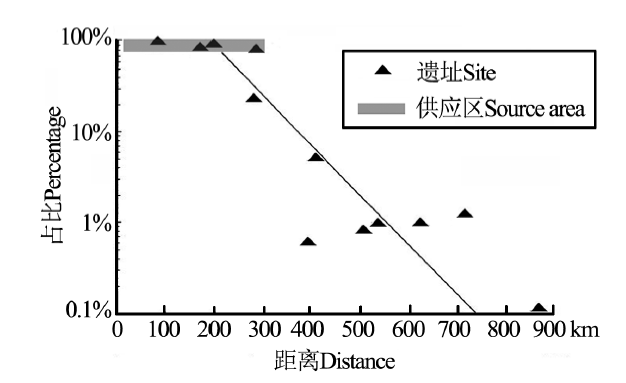
图1 近东地区新石器时代遗址中黑曜岩占比和与原产地距离的关系
Fig.1 Percentage of obsidian in the total chipped stone industry plotted against obsidian source distance for Near Eastern Early Neolithic sites[41]
| 遗址 Site | 普通石核 Cores | 石叶石核Blade cores | 细石核 Micro-blade cores | 石叶和细石叶Blades & Microblades | 石器 Retouched tools | 废片 Debitage | 断块 Chunks | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珲春北山 Beishan[ | 2; 4.4% | - | - | 4; 8.9% | 2; 4.4% | 37; 82.2% | - | 43; 100% |
| 辉南邵家店Shaojiadian[ | - | - | - | - | 5; 35.7% | 9; 64.3% | - | 14; 100% |
| 和龙柳洞Liudong[ | 6; 4.5% | - | 2; 1.5% | 11; 8.4% | 13; 9.8% | 77; 58.4% | 23; 17.4% | 132; 100% |
| 和龙大洞Dadong[ | 29; 0.5% | - | 24; 0.4% | 156; 2.8% | 548; 9.8% | 4026; 72.4% | 784; 14.1% | 5567; 100% |
| 和龙大洞Dadong 2007[ | - | - | - | - | 20; 28.6% | 45; 64.3% | 5; 7.1% | 70; 100% |
| 和龙大洞Dadong[ | - | 1; 0.02% | 14;0.3% | 201; 4.58% | 106; 2.4% | 3598; 82% | 469; 10.7% | 4389; 100% |
| 和龙青头Qingtou[ | - | - | - | 18; 9.8% | 39; 21.4% | 104; 56.8% | 22; 12% | 183; 100% |
| 安图沙金沟Shajingou[ | 1; 1.3% | - | 2;2.7% | 7; 9.3% | 15; 20% | 50; 66.7% | - | 75; 100% |
| 新屯西山遗址Xintun xishan[ | - | 1; 3.35% | - | 1; 3.35% | - | 28; 93.3% | - | 30; 100% |
| 和龙林场Linchang[ | - | - | 1;0.9% | 13; 11.5% | 5; 4.4% | 94; 83.2% | - | 113; 100% |
| 和龙西沟 Xigou[ | - | - | - | 9; 12.7% | 28; 39.4% | 34; 47.9% | - | 71; 100% |
| 和龙石人沟Shirengou[ | 1; 2.5% | 1; 2.5% | - | 6; 15% | 8; 20% | 24; 60% | - | 40; 100% |
| 和龙石人沟Shirengou[ | 1; 0.1% | - | 11; 0.9% | 297; 23% | 98; 7.6% | 793; 61.4% | 91; 7% | 1291; 100% |
| 和龙石人沟Shirengou[ | 2; 3.9% | - | 1; 2% | 4; 7.8% | 22; 43.1% | 16; 31.4% | 6; 11.8% | 51; 100% |
| 杨林西山 Yanglinxishan[ | - | - | - | 2; 50% | - | 2; 50% | - | 4; 100% |
| 秦家东山Qinjiadongshan[ | - | - | - | 1; 12.5% | 7; 87.5% | - | - | 8; 100% |
| 炮台山遗址Paotaishan[ | - | - | 1; 6.2% | - | 4; 25% | 7; 43.8% | 4; 25% | 16; 100% |
| 牛心村遗址Niuxincun[ | - | - | 1; 2.2% | 2; 4.3% | 9; 19.6% | 31; 67.4% | 3; 6.5% | 46; 100% |
| 二水坪遗址Ershuiping[ | 1; 2% | - | 2; 4% | 2; 4% | 5; 10% | 31; 62% | 9; 18% | 50; 100% |
| 广兴遗址 Guangxing[ | 2; 9.5% | - | - | 1; 4.8% | 5; 23.8% | 13; 61.9% | - | 21; 100% |
| 桦甸仙人洞Xianrendong[ | - | - | - | - | 1; 100% | - | - | 1; 100% |
| 海沟金矿Jinkuang[ | - | - | - | - | - | 1; 100% | - | 1; 100% |
| 两江镇石人沟LJZ Shirengou[ | - | - | 1; 5% | 8; 40% | 2; 10% | 9; 45% | - | 20; 100% |
| 总计/Total | 45; 0.37% | 3; 0.02% | 60; 0.49% | 743; 6.07% | 942; 7.7% | 9029; 73.78% | 1416; 11.67% | 12338; 100% |
表3 中国东北地区各类黑曜岩石制品的数量与比例
Tab.3 Quantity and proportion of various types of obsidian lithics in Northeast China
| 遗址 Site | 普通石核 Cores | 石叶石核Blade cores | 细石核 Micro-blade cores | 石叶和细石叶Blades & Microblades | 石器 Retouched tools | 废片 Debitage | 断块 Chunks | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珲春北山 Beishan[ | 2; 4.4% | - | - | 4; 8.9% | 2; 4.4% | 37; 82.2% | - | 43; 100% |
| 辉南邵家店Shaojiadian[ | - | - | - | - | 5; 35.7% | 9; 64.3% | - | 14; 100% |
| 和龙柳洞Liudong[ | 6; 4.5% | - | 2; 1.5% | 11; 8.4% | 13; 9.8% | 77; 58.4% | 23; 17.4% | 132; 100% |
| 和龙大洞Dadong[ | 29; 0.5% | - | 24; 0.4% | 156; 2.8% | 548; 9.8% | 4026; 72.4% | 784; 14.1% | 5567; 100% |
| 和龙大洞Dadong 2007[ | - | - | - | - | 20; 28.6% | 45; 64.3% | 5; 7.1% | 70; 100% |
| 和龙大洞Dadong[ | - | 1; 0.02% | 14;0.3% | 201; 4.58% | 106; 2.4% | 3598; 82% | 469; 10.7% | 4389; 100% |
| 和龙青头Qingtou[ | - | - | - | 18; 9.8% | 39; 21.4% | 104; 56.8% | 22; 12% | 183; 100% |
| 安图沙金沟Shajingou[ | 1; 1.3% | - | 2;2.7% | 7; 9.3% | 15; 20% | 50; 66.7% | - | 75; 100% |
| 新屯西山遗址Xintun xishan[ | - | 1; 3.35% | - | 1; 3.35% | - | 28; 93.3% | - | 30; 100% |
| 和龙林场Linchang[ | - | - | 1;0.9% | 13; 11.5% | 5; 4.4% | 94; 83.2% | - | 113; 100% |
| 和龙西沟 Xigou[ | - | - | - | 9; 12.7% | 28; 39.4% | 34; 47.9% | - | 71; 100% |
| 和龙石人沟Shirengou[ | 1; 2.5% | 1; 2.5% | - | 6; 15% | 8; 20% | 24; 60% | - | 40; 100% |
| 和龙石人沟Shirengou[ | 1; 0.1% | - | 11; 0.9% | 297; 23% | 98; 7.6% | 793; 61.4% | 91; 7% | 1291; 100% |
| 和龙石人沟Shirengou[ | 2; 3.9% | - | 1; 2% | 4; 7.8% | 22; 43.1% | 16; 31.4% | 6; 11.8% | 51; 100% |
| 杨林西山 Yanglinxishan[ | - | - | - | 2; 50% | - | 2; 50% | - | 4; 100% |
| 秦家东山Qinjiadongshan[ | - | - | - | 1; 12.5% | 7; 87.5% | - | - | 8; 100% |
| 炮台山遗址Paotaishan[ | - | - | 1; 6.2% | - | 4; 25% | 7; 43.8% | 4; 25% | 16; 100% |
| 牛心村遗址Niuxincun[ | - | - | 1; 2.2% | 2; 4.3% | 9; 19.6% | 31; 67.4% | 3; 6.5% | 46; 100% |
| 二水坪遗址Ershuiping[ | 1; 2% | - | 2; 4% | 2; 4% | 5; 10% | 31; 62% | 9; 18% | 50; 100% |
| 广兴遗址 Guangxing[ | 2; 9.5% | - | - | 1; 4.8% | 5; 23.8% | 13; 61.9% | - | 21; 100% |
| 桦甸仙人洞Xianrendong[ | - | - | - | - | 1; 100% | - | - | 1; 100% |
| 海沟金矿Jinkuang[ | - | - | - | - | - | 1; 100% | - | 1; 100% |
| 两江镇石人沟LJZ Shirengou[ | - | - | 1; 5% | 8; 40% | 2; 10% | 9; 45% | - | 20; 100% |
| 总计/Total | 45; 0.37% | 3; 0.02% | 60; 0.49% | 743; 6.07% | 942; 7.7% | 9029; 73.78% | 1416; 11.67% | 12338; 100% |
| 遗址Site | 细石核 Microblade cores | 石叶和细石叶 Blades & Microblades | 石器 Retouched tools | 废片Debitage | 总计Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长兴里 Jangheung-ri | 4; 2.2% | 34; 19.1% | 21; 11.8% | 119; 66.9% | 178; 100% |
| 上舞龙里 Sangmuryong-ri | 0 | 23; 8.6% | 45; 16.8% | 200; 74.6% | 268; 100% |
| 下花溪里 Hahwagae-ri | 16; 1.2% | 575; 44.2% | 56; 4.3% | 655; 50.3% | 1306; 100% |
| 奇窟B Gigok B | - | 1; 5.3% | 1; 5.3% | 17; 89.5% | 19; 100% |
| 民乐洞 Minrak-dong | 1; 2.5% | 2; 5.0% | 3; 7.5% | 34; 85.0% | 40; 100% |
| 好坪洞 Hopyeong-dong | 4; 0.4% | 370; 34.5% | 24; 2.2% | 676; 62.9% | 1074; 100% |
| 三里 Sam-ri | - | 11; 16.4% | 4; 6.0% | 52; 77.6% | 67; 100% |
| 昌内 Changnae | - | - | 1; 25.0% | 3; 75.0% | 4; 100% |
| 垂杨介 Suyanggae | 2; 1.9% | 26; 24.5% | 16; 15.1% | 62; 58.5% | 106; 100% |
| 石壮里 Seokjang-ri | - | 6; 100.0% | - | - | 6; 100% |
| 月城洞 Wolseong-dong | - | 150; 42.0% | 14; 3.9% | 193 54.1% | 357 100% |
| 新北 Sinbuk | 1; 3.6% | 10; 35.7% | 3; 10.7% | 14; 50.0% | 28; 100% |
| 浦日洞 Poildong | - | 4; 20.0% | 2;10.0% | 14; 70.0% | 20; 100% |
| 抱川中里 Youngsujaeyul | 5; 0.8% | 553 91.1% | 31; 5.1% | 18; 3.0% | 607; 100% |
| 总计Total | 33; 0.81% | 1765; 43.30% | 221; 5.42% | 2057; 50.47% | 4076; 100% |
表4 韩国黑曜岩石制品的类型及占比
Tab.4 Obsidian lithic class inventories of Upper Paleolithic sites in South Korea[35]
| 遗址Site | 细石核 Microblade cores | 石叶和细石叶 Blades & Microblades | 石器 Retouched tools | 废片Debitage | 总计Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长兴里 Jangheung-ri | 4; 2.2% | 34; 19.1% | 21; 11.8% | 119; 66.9% | 178; 100% |
| 上舞龙里 Sangmuryong-ri | 0 | 23; 8.6% | 45; 16.8% | 200; 74.6% | 268; 100% |
| 下花溪里 Hahwagae-ri | 16; 1.2% | 575; 44.2% | 56; 4.3% | 655; 50.3% | 1306; 100% |
| 奇窟B Gigok B | - | 1; 5.3% | 1; 5.3% | 17; 89.5% | 19; 100% |
| 民乐洞 Minrak-dong | 1; 2.5% | 2; 5.0% | 3; 7.5% | 34; 85.0% | 40; 100% |
| 好坪洞 Hopyeong-dong | 4; 0.4% | 370; 34.5% | 24; 2.2% | 676; 62.9% | 1074; 100% |
| 三里 Sam-ri | - | 11; 16.4% | 4; 6.0% | 52; 77.6% | 67; 100% |
| 昌内 Changnae | - | - | 1; 25.0% | 3; 75.0% | 4; 100% |
| 垂杨介 Suyanggae | 2; 1.9% | 26; 24.5% | 16; 15.1% | 62; 58.5% | 106; 100% |
| 石壮里 Seokjang-ri | - | 6; 100.0% | - | - | 6; 100% |
| 月城洞 Wolseong-dong | - | 150; 42.0% | 14; 3.9% | 193 54.1% | 357 100% |
| 新北 Sinbuk | 1; 3.6% | 10; 35.7% | 3; 10.7% | 14; 50.0% | 28; 100% |
| 浦日洞 Poildong | - | 4; 20.0% | 2;10.0% | 14; 70.0% | 20; 100% |
| 抱川中里 Youngsujaeyul | 5; 0.8% | 553 91.1% | 31; 5.1% | 18; 3.0% | 607; 100% |
| 总计Total | 33; 0.81% | 1765; 43.30% | 221; 5.42% | 2057; 50.47% | 4076; 100% |
| 地区Area | 遗址Site | 标本Sample | 高h(mm) | 长l(mm) | 厚d(mm) | 体积V(mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国东北Northeast China | 和龙柳洞 Liudong[ | HLP.04001 | 33.01 | 29.38 | 11.69 | 11337 |
| HLP.04027 | 29.68 | 16.16 | 6.14 | 2945 | ||
| 和龙大洞 Dadong[ | 07DD.C935 | 22.4 | 41.2 | 13.2 | 12182 | |
| 07DD.C111 | 15.8 | 29.1 | 12.5 | 5747 | ||
| 07DD.C1529 | 22.8 | 31.7 | 14.1 | 10191 | ||
| 07DD.C899 | 22.9 | 42.6 | 13.5 | 13170 | ||
| 07DD.C1175 | 46.8 | 34.7 | 12.8 | 20787 | ||
| 07DD.37 | 26.09 | 22.77 | 7.12 | 4230 | ||
| 07DD.3651 | 35.81 | 9.09 | 14.45 | 4704 | ||
| 07DD.3814 | 44.88 | 29.97 | 9.79 | 13168 | ||
| 07DD.2481 | 40.91 | 13.99 | 6.31 | 3611 | ||
| 沙金沟 Shajingou[ | 06ASC:10 | 18 | 35.2 | 18.1 | 11468 | |
| 06ASC:32 | 20 | 43.1 | 19.1 | 16464 | ||
| 和龙林场 Linchang[ | 07.LC.C:1 | 35.28 | 42.95 | 18.31 | 27745 | |
| 和龙石人沟 Shirengou[ | 05SRG.C:18 | 14.9 | 17.2 | 5.1 | 1307 | |
| 07SRG.C:40 | 31.2 | 58.2 | 11.6 | 21064 | ||
| 炮台山 Paotaishan[ | 08PTS.C:89 | 11.84 | 36.62 | 12.62 | 5472 | |
| 牛心村 Niuxincun[ | HNX:06 | 21.5 | 27.9 | 6.7 | 4019 | |
| 二水坪 Ershuiping[ | HEP:1 | 30.9 | 48.3 | 13.9 | 20745 | |
| HEP:2 | 20.3 | 36.4 | 11.2 | 8276 | ||
| 枫林遗址 Fenglin[ | 15JFMF:122 | 20 | 41.3 | 6.3 | 5204 | |
| 15JFMF:123 | 13.2 | 27.5 | 6.1 | 2214 | ||
| 2016FFLDSP-163 | 31.86 | 50.1 | 9.75 | 15563 | ||
| 2016FFL-53 | 14.49 | 25.64 | 9.84 | 3656 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-543 | 14.09 | 21.92 | 11.96 | 3694 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-550 | 29.42 | 50.65 | 9.64 | 14365 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-559 | 28.38 | 36.39 | 8.67 | 8954 | ||
| 2016FFLDSP-95 | 27.74 | 81.36 | 11.23 | 25345 | ||
| 2016FFL-194 | 11.47 | 21.6 | 9.33 | 2312 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-545 | 22.25 | 18.76 | 8.78 | 3665 | ||
| 2016FFLDSP-194 | 13.11 | 26.92 | 6.62 | 2336 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-549 | 26.19 | 18.47 | 11.6 | 5611 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-546 | 19.66 | 27.56 | 14.85 | 8046 | ||
| 平均值Ave | 24.8 | 33.2 | 11.0 | 9684.7 | ||
| 韩国South Korea | 下花溪里 Hahwagyae-ri[ | 13 | 19 | 11 | 2717 | |
| 14 | 28 | 15 | 5880 | |||
| 43 | 10 | 8.6 | 3698 | |||
| 29 | 15 | 9 | 3915 | |||
| 14.7 | 22.4 | 7.7 | 2535 | |||
| 25.7 | 20.5 | 9 | 4742 | |||
| 23.4 | 28.5 | 7 | 4668 | |||
| 16.6 | 23 | 11 | 4200 | |||
| 24 | 19 | 10 | 4560 | |||
| 韩国South Korea | 下花溪里 Hahwagyae-ri[ | 30 | 9.5 | 10 | 2850 | |
| 48 | 13.7 | 8 | 5261 | |||
| 10 | 20 | 8 | 1600 | |||
| 15 | 25.6 | 10 | 3840 | |||
| 24 | 16 | 13 | 4992 | |||
| 21.3 | 6.7 | 6.3 | 899 | |||
| 17 | 18.7 | 8.3 | 2639 | |||
| 垂杨介 Suyanggae[ | 18.5 | 21 | 12.3 | 4779 | ||
| 平均值Ave | 22.8 | 18.6 | 9.7 | 3751.4 | ||
| 中韩对比T test between China and South Korea | P=0.4 | P<0.001 | P=0.12 | |||
表5 典型细石核标本测量值
Tab.5 Measurements of microblade cores
| 地区Area | 遗址Site | 标本Sample | 高h(mm) | 长l(mm) | 厚d(mm) | 体积V(mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国东北Northeast China | 和龙柳洞 Liudong[ | HLP.04001 | 33.01 | 29.38 | 11.69 | 11337 |
| HLP.04027 | 29.68 | 16.16 | 6.14 | 2945 | ||
| 和龙大洞 Dadong[ | 07DD.C935 | 22.4 | 41.2 | 13.2 | 12182 | |
| 07DD.C111 | 15.8 | 29.1 | 12.5 | 5747 | ||
| 07DD.C1529 | 22.8 | 31.7 | 14.1 | 10191 | ||
| 07DD.C899 | 22.9 | 42.6 | 13.5 | 13170 | ||
| 07DD.C1175 | 46.8 | 34.7 | 12.8 | 20787 | ||
| 07DD.37 | 26.09 | 22.77 | 7.12 | 4230 | ||
| 07DD.3651 | 35.81 | 9.09 | 14.45 | 4704 | ||
| 07DD.3814 | 44.88 | 29.97 | 9.79 | 13168 | ||
| 07DD.2481 | 40.91 | 13.99 | 6.31 | 3611 | ||
| 沙金沟 Shajingou[ | 06ASC:10 | 18 | 35.2 | 18.1 | 11468 | |
| 06ASC:32 | 20 | 43.1 | 19.1 | 16464 | ||
| 和龙林场 Linchang[ | 07.LC.C:1 | 35.28 | 42.95 | 18.31 | 27745 | |
| 和龙石人沟 Shirengou[ | 05SRG.C:18 | 14.9 | 17.2 | 5.1 | 1307 | |
| 07SRG.C:40 | 31.2 | 58.2 | 11.6 | 21064 | ||
| 炮台山 Paotaishan[ | 08PTS.C:89 | 11.84 | 36.62 | 12.62 | 5472 | |
| 牛心村 Niuxincun[ | HNX:06 | 21.5 | 27.9 | 6.7 | 4019 | |
| 二水坪 Ershuiping[ | HEP:1 | 30.9 | 48.3 | 13.9 | 20745 | |
| HEP:2 | 20.3 | 36.4 | 11.2 | 8276 | ||
| 枫林遗址 Fenglin[ | 15JFMF:122 | 20 | 41.3 | 6.3 | 5204 | |
| 15JFMF:123 | 13.2 | 27.5 | 6.1 | 2214 | ||
| 2016FFLDSP-163 | 31.86 | 50.1 | 9.75 | 15563 | ||
| 2016FFL-53 | 14.49 | 25.64 | 9.84 | 3656 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-543 | 14.09 | 21.92 | 11.96 | 3694 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-550 | 29.42 | 50.65 | 9.64 | 14365 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-559 | 28.38 | 36.39 | 8.67 | 8954 | ||
| 2016FFLDSP-95 | 27.74 | 81.36 | 11.23 | 25345 | ||
| 2016FFL-194 | 11.47 | 21.6 | 9.33 | 2312 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-545 | 22.25 | 18.76 | 8.78 | 3665 | ||
| 2016FFLDSP-194 | 13.11 | 26.92 | 6.62 | 2336 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-549 | 26.19 | 18.47 | 11.6 | 5611 | ||
| 2016FFLCJ-546 | 19.66 | 27.56 | 14.85 | 8046 | ||
| 平均值Ave | 24.8 | 33.2 | 11.0 | 9684.7 | ||
| 韩国South Korea | 下花溪里 Hahwagyae-ri[ | 13 | 19 | 11 | 2717 | |
| 14 | 28 | 15 | 5880 | |||
| 43 | 10 | 8.6 | 3698 | |||
| 29 | 15 | 9 | 3915 | |||
| 14.7 | 22.4 | 7.7 | 2535 | |||
| 25.7 | 20.5 | 9 | 4742 | |||
| 23.4 | 28.5 | 7 | 4668 | |||
| 16.6 | 23 | 11 | 4200 | |||
| 24 | 19 | 10 | 4560 | |||
| 韩国South Korea | 下花溪里 Hahwagyae-ri[ | 30 | 9.5 | 10 | 2850 | |
| 48 | 13.7 | 8 | 5261 | |||
| 10 | 20 | 8 | 1600 | |||
| 15 | 25.6 | 10 | 3840 | |||
| 24 | 16 | 13 | 4992 | |||
| 21.3 | 6.7 | 6.3 | 899 | |||
| 17 | 18.7 | 8.3 | 2639 | |||
| 垂杨介 Suyanggae[ | 18.5 | 21 | 12.3 | 4779 | ||
| 平均值Ave | 22.8 | 18.6 | 9.7 | 3751.4 | ||
| 中韩对比T test between China and South Korea | P=0.4 | P<0.001 | P=0.12 | |||
| [1] | Kuzmin YV. Long-distance obsidian transport in prehistoric northeast Asia[J]. Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association, 2012, 32: 1-5 |
| [2] |
Kuzmin YV. Obsidian as a commodity to investigate human migrations in the Upper Paleolithic, Neolithic, and Paleometal of Northeast Asia[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 442, Part B: 5-11
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.03.021 URL |
| [3] |
Kuzmin YV. Obsidian provenance studies in the far eastern and northeastern regions of Russia and exchange networks in the prehistory of Northeast Asia[J]. Documenta Praehistorica, 2019, 46: 296-307
doi: 10.4312/dp.46.18 URL |
| [4] | 刘爽. 中国东北地区旧石器时代晚期遗址黑曜岩制品原料来源探索[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019 |
| [5] |
Jwa YJ, Yi S, Jin ME, et al. Two contrasting provenances of prehistoric obsidian artifacts in South Korea: Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics[J]. Open Archaeology, 2019, 5(1): 106-120
doi: 10.1515/opar-2019-0008 URL |
| [6] | Carter T. The contribution of obsidian characterization studies to early prehistoric archaeology[A]. In Yamada M, Ono A (Eds.). Lithic Raw Material Exploitation and Circulation in Prehistory: A Comparative Perspective in Diverse Palaeoenvironments[C]. Liège: ERAUL, 2014: 23-33 |
| [7] | 陈全家, 田禾, 陈晓颖, 等. 海林炮台山旧石器遗址发现的石器研究[A].见: 边疆考古研究(第9辑)[C]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 9-24 |
| [8] | 陈全家, 田禾, 陈晓颖, 等. 秦家东山旧石器地点发现的石器研究[J]. 北方文物, 2014(2): 3-11 |
| [9] | 陈全家, 田禾, 王欢, 等. 黑龙江省海林市杨林西山旧石器遗址(2008)石器研究[J]. 北方文物, 2013(2): 3-14 |
| [10] | 田禾, 陈全家, 李有骞. 黑龙江省海林市杨林南山旧石器遗址石器研究[J]. 北方文物, 2010(3): 3-12 |
| [11] | 陈全家, 张乐. 吉林延边珲春北山发现的旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 2004, 23(2): 138-145 |
| [12] | 陈全家, 李其泰. 吉林桦甸寿山仙人洞旧石器遗址试掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 1994, 13(1): 12-19 |
| [13] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 王法岗. 吉林桦甸仙人洞旧石器遗址1993 年发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2007, 26(3): 222-236 |
| [14] | 陈全家, 李有骞, 赵海龙, 等. 吉林辉南邵家店发现的旧石器[J]. 北方文物, 2006(1): 3-9 |
| [15] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 王春雪. 抚松新屯西山旧石器遗址试掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(2): 147-153 |
| [16] | 徐廷. 吉林抚松发现枫林旧石器遗址[N]. 中国文物报, 2016-10-21(8) |
| [17] | 李万博, 陈全家, 张福有. 吉林枫林旧石器遗址发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(2): 191-199 |
| [18] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 卢悦. 吉林两江镇旧石器地点发现的石器研究[J]. 草原文物, 2001(2): 1-10 |
| [19] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 方启, 等. 延边安图立新发现的砾石石器[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(1): 45-50 |
| [20] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 方启, 等. 吉林安图沙金沟发现的石器研究[J]. 华夏考古, 2008(4): 51-58 |
| [21] | 陈全家, 方启, 李霞, 等. 吉林和龙青头旧石器遗址的新发现及初步研究[J]. 考古与文物, 2008(2): 3-9 |
| [22] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 方启, 等. 吉林省和龙西沟发现的旧石器[J]. 北方文物, 2010(2): 3-9 |
| [23] | 吉林省文物考古研究所, 和龙市文物管理所. 吉林省和龙市新发现三处旧石器时代遗址[A].见:边疆考古研究(第23辑)[C]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 1-9 |
| [24] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 霍东峰. 和龙市柳洞旧石器地点发现的石制品研究[J]. 华夏考古, 2005(3): 51-59 |
| [25] | 陈全家, 王春雪, 方启, 等. 吉林和龙柳洞2004年发现的旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 2006, 25(3): 208-219 |
| [26] | 李霞. 和龙崇善大洞旧石器遗址2007年发掘的石器研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008, 1-56 |
| [27] | 李万博, 陈全家, 方启, 等. 延边和龙大洞旧石器遗(2007)试掘简报[A].见:边疆考古研究(第20辑)[C]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016, 1-11 |
| [28] | 万晨晨, 陈全家, 方启, 等. 吉林和龙大洞遗址的调查与研究[J]. 考古学报, 2017(1): 1-30 |
| [29] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 方启, 等. 石人沟林场旧石器地点试掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(4): 373-382 |
| [30] | 陈全家, 王春雪, 方启, 等. 延边地区和龙石人沟发现的旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 2006, 25(2): 106-114 |
| [31] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 方启, 等. 延边和龙石人沟旧石器遗址2005年试掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(2): 105-114 |
| [32] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 王晓阳. 石人沟石器遗址2007年发现的石器研究[J]. 华夏考古, 2014(4): 50-58 |
| [33] |
Jia PW, Doelman T, Chen CJ, et al. Moving sources: A preliminary study of volcanic glass artifact distributions in northeast China using PXRF[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2010, 37(7): 1670-1677
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2010.01.027 URL |
| [34] | 侯哲. 旧石器时代晚期黑曜岩石器研究—以中国东北地区与南韩地区比较为中心[D]. 首尔: 韩国庆熙大学, 2015 |
| [35] | 崔哲慜, 高星, 夏文婷, 等. 晚更新世东北亚现代人迁移与交流范围的初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(1): 12-27 |
| [36] |
Chang YJ, Kim JC. Provenance of obsidian artifacts from the Wolseongdong Paleolithic site, Korea, and its archaeological implications[J]. Quaternary International, 2018, 467, Part B: 360-368
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2017.11.034 URL |
| [37] | Kuzmin YV, Glascock YV. The neutron activation analysis of volcanic glasses in the Russian Far East and neighbouring Northeast Asia:A summary of the first 20 years of research[A]. In: Ono MD, Glascock YV, Kuzmin YV(Eds.). Methodological Issues for Characterisation and Provenance Studies of Obsidian in Northeast Asia[C]. Oxford: Archaeopress, 2014: 85-93 |
| [38] |
Popov VK, Kuzmin YV, Grebennikov AV, et al. The “puzzle” of the primary obsidian source in the region of Paektusan (China/DPR Korea)[J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 519: 192-199
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.12.028 URL |
| [39] | Lee GK, Kim JC. Obsidians from the Sinbuk archaeological site in Korea - Evidences for strait crossing and long-distance exchange of raw material in Paleolithic age[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, Reports, 2015(2): 458-466 |
| [40] | Kim JC, Kim DK, Yoon M, et al. PIXE provenancing of obsidian artefacts from Paleolithic sites in Korea[J]. Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association, 2007(27): 122-128 |
| [41] |
Renfrew C, Dixon JE, Cann JR. Further analysis of Near Eastern obsidians[J]. Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society, 1968, 34: 319-331
doi: 10.1017/S0079497X0001392X URL |
| [42] |
Whallon R. Social networks and information: Non-“utilitarian” mobility among hunter-gatherers[J]. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, 2006, 25(2): 259-270
doi: 10.1016/j.jaa.2005.11.004 URL |
| [43] | Moutsiou T. Changing scales of obsidian movement and social networking[A]. In: Ruebens K, Romanowska I, Bynoe R(Eds.). Unravelling the Palaeolithic: Ten Years of Research at the Centre for the Archaeology of Human Origins (CAHO, University of Southampton)[C]. Southampton: University of Southampton, Series in Archaeology No. 8, 2012: 85-96 |
| [44] | Ambrose SH. Obsidian hydration dating and source exploitation studies in Africa[A]. In: Liritzis I, Stevenson CM (Eds.). The Dating and Provenance of Obsidian and Ancient Manufactured Glasses[C]. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, 2012: 56-72 |
| [45] | 林景胤, 董佩信. 长白山黑曜岩地质特征与成因浅析[J]. 地质与资源, 2016(4): 204-207 |
| [46] | Renfrew C. Alternative models for exchange and spatial distribution[A]. In: Earle TK, Ericson JE (Eds.). Exchanges Systems In Prehistory[C]. London: Academic, 1977: 71-90 |
| [47] | 中国新闻网. 专家谈黑曜岩石叶石核:遗址可能存在多期文化遗存[N]. 中国新闻网, 2021-03-24 |
| [48] | 田川, 徐廷, 关莹, 等. 吉林抚松枫林遗址细石核研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(1): 19-32 |
| [49] | Choe B, Kim YB, Kim ND. Excavation report on the Hahwagye Mesolithic site, Hongcheon[R]. In: Research Report on the Jrmgang Highway Construction Area[C]. Chuncheon: Kangwon-do, 1992, 13-260 |
| [50] | Lee YJ. Boat-shaped stone artifact from Suyanggae Upper Palaeolithic site[J]. Komunhwa, 1989, 35: 3-77 |
| [51] | Seong CT. Microblade technology in Korea and adjacent northeast Asia[J]. Asian Perspectives, 1998, 37(2): 245-278 |
| [52] | 王春雪, 陈全家, 赵海龙, 等. 试析东北地区东部与朝鲜半岛旧石器时代晚期细石叶工业之间的文化关系[J]. 内蒙古文物考古, 2009(2): 34-49 |
| [1] | Evgeny P RYBIN, Arina M KHATSENOVICH. 旧石器时代晚期初段色楞格河人类的扩散路线[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 780-796. |
| [2] | 李尧, 陈虹, 徐廷. 黑曜岩实验打制品使用后的痕迹特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 727-743. |
| [3] | 高黄文, 刘颖杰, 陆成秋, 孙雪峰, 黄旭初, 徐静玥. 湖北郧阳包包岭遗址2021年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 828-838. |
| [4] | 崔祚文, 王春雪, 陈全家, 曾庆硕, 张楠. 2021年河南南召新发现的旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 853-864. |
| [5] | 王家琪, 张雪微, 王春雪, 盛立双. 天津蓟州区太子陵旧石器地点2021年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 440-447. |
| [6] | Hiroyuki SATO, Kazuki MORISAKI. 日本旧石器晚期石器技术起源的新考古学与人类学证据[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 470-487. |
| [7] | 魏天旭, 王春雪, 张雪微, 王家琪, 盛立双. 天津蓟州区朝阳洞遗址2号地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 314-320. |
| [8] | 赵清坡, 马欢欢. 河南灵宝旧石器考古调查报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 321-330. |
| [9] | 高星, 张月书, 李锋, 陈福友, 王晓敏, 仪明洁. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址2016-2019年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 106-121. |
| [10] | 周士航, 何湘栋, 徐静玥, 李潇丽, 牛东伟. 蔚县盆地东沟遗址2017年度发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 132-142. |
| [11] | 刘连强, 蒲昱晓, 侯佳岐, 王法岗. 泥河湾盆地马圈沟遗址鱼咀沟1号地点2017-2018年发掘出土的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 40-54. |
| [12] | 周振宇, 王法岗, 关莹. 河北泥河湾盆地西白马营遗址1985-1986年出土的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 55-66. |
| [13] | 仝广, 李锋, 赵海龙, 闫晓蒙, 高星. 泥河湾盆地火山角砾岩原料的热处理实验[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 81-90. |
| [14] | 加藤真二. 旧石器时代晚期人类在欧亚东部地区的扩散和文化传播[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(06): 842-856. |
| [15] | 侯佳岐, 王法岗. 泥河湾盆地山兑东旧石器地点初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(06): 742-750. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 409
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 607
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3