

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (01): 87-97.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0045cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0045
收稿日期:2021-07-09
修回日期:2021-12-23
出版日期:2023-02-15
发布日期:2023-02-20
通讯作者:
陈博,副教授,主要从事考古学方面的研究。E-mail: 作者简介:周亚威,教授,主要从事体质人类学研究。E-mail: 基金资助:
ZHOU Yawei( ), WANG Hui, DING Sicong, CHEN Bo(
), WANG Hui, DING Sicong, CHEN Bo( )
)
Received:2021-07-09
Revised:2021-12-23
Online:2023-02-15
Published:2023-02-20
摘要:
本文对东周时期一例肱骨发育不全的个体M45进行古病理学研究。经鉴定,M45为年龄在30岁左右的女性,其右侧肱骨短于左侧,肱骨头解剖颈上移且正面向上,小结节向前下方位移;三角肌粗隆处、解剖颈下方有骨质缺损现象;右侧骨髓腔相较于左侧略宽,右侧三角肌粗隆处骨松质较左侧明显,呈蜂窝状。通过肉眼观察、X射线影像和病理筛选等方法对其进行诊断,推测M45个体可能是分娩创伤导致肱骨近端生长点受损,或在儿童期生长板遭受创伤导致肱骨生长发育停滞。
中图分类号:
周亚威, 王惠, 丁思聪, 陈博. 东周一例人体肱骨发育不对称的病理分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(01): 87-97.
ZHOU Yawei, WANG Hui, DING Sicong, CHEN Bo. Pathological analysis of a case of human humeral asymmetry in Eastern Zhou Dynasty[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2023, 42(01): 87-97.
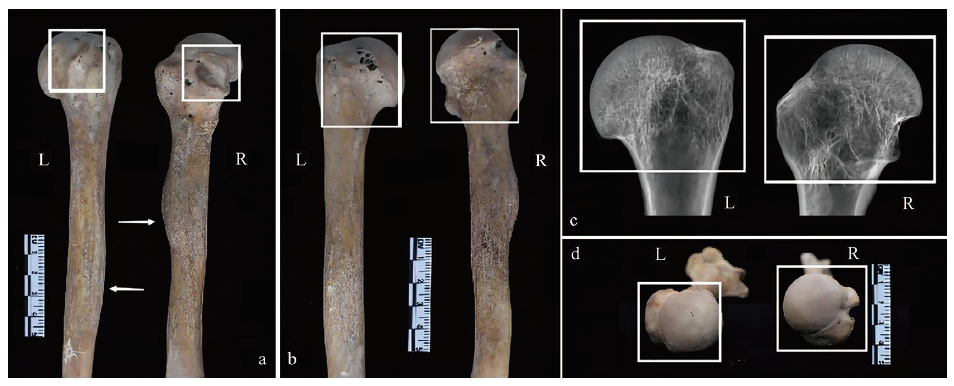
图2 M45两侧肱骨头主要变异部位及X光片对比 a.小结节位置对比contrast nodules location;b.冈上肌、冈下肌位置变化The position change of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus;c.X光骨密质比对X-ray bone density contrast;d.肱骨头位置 humerus head position. 白色箭头所指为三角肌粗隆处The white arrow refers to the trochanter of deltoid muscle
Fig.2 Comparison of main variation parts and X-ray films of humeral head on both sides of M45
| 骨骼Bone | 项目Item | 左侧L | 右侧R |
|---|---|---|---|
| 肱骨Humerus | 最大长Lmax | 284 | 216 |
| 全长L | 275.7 | 214 | |
| 中部最大径dmax | 18.88 | 17.95 | |
| 中部矢状径dmid | 18.18 | 18.44 | |
| 中部最小径dmin | 16.11 | 14.32 | |
| 中部横径dmid | 14.89 | 16.93 | |
| 最小周长Cmin | 55 | 55.7 | |
| 中部周长Cmid | 58 | 56 | |
| 上端宽btop | 41.52 | 42.36 | |
| 下端宽bbot | 50.36 | 53.14 | |
| 滑车宽b | 16.33 | 16.65 | |
| 滑车和小头宽b | 35.05 | 35.73 | |
| 滑车矢径d | 22.26 | 23.77 | |
| 头周长c | 11.2 | 11.2 | |
| 头横径d | 35.58 | 34.84 | |
| 头纵径d | 35.19 | 34.27 | |
| 横断面指数I | 0.856* | 0.794* | |
| 粗壮指数I | 0.187* | 0.257* | |
| 鹰嘴窝深d | 1.1 | 1.2 | |
| 鹰嘴窝宽b | 22.95 | 25.18 | |
| 关节盂长L | 32.59 | 30.55 | |
| 关节盂宽b | 22.77 | 25.10 | |
| 尺骨Ulna | 最大长Lmax | 234 | 237 |
| 生理长L | 201 | 203 | |
| 体最小周长Cmin | 37 | 37 | |
| 体横径d | 10.68 | 10.48 | |
| 体矢径d | 17.76 | 17.6 | |
| 上部横径dtop | 15.66 | 15.67 | |
| 上部矢径dtop | 17.76 | 17.60 | |
| 鹰嘴小头长L | 30.83 | 30.87 | |
| 鹰嘴宽b | 20.91 | 21.44 | |
| 鹰嘴深d | 18.59 | 2.83 | |
| 鹰嘴高h | 22.27 | 24.82 | |
| 鹰嘴冠突间距d | 30.22 | 29.97 | |
| 尺骨Ulna | 冠关桡前宽bant | 10.48 | 11.20 |
| 冠关桡后宽bpos | 9.85 | 9.84 | |
| 桡骨Radius | 最大长Lmax | 213 | 215 |
| 生理长L | 200 | 200 | |
| 中部周长Cmid | 39 | 40 | |
| 体最小周长Cmix | 38 | 38 | |
| 体横径d | 12.58 | 12.83 | |
| 体矢径d | 9.79 | 9.76 | |
| 中部横径dmid | 26.63 | 27.45 | |
| 中部矢径dmid | 8.71 | 8.83 | |
| 头横径d | 18.62 | 19.04 | |
| 头矢径d | 18.94 | 19.17 | |
| 颈横径d | 12.19 | 11.09 | |
| 颈矢径d | 12.77 | 11.16 | |
| 颈周长c | 48 | 48 | |
| 头周长c | 61 | 62 | |
| 下端宽bbot | 26.96 | 26.76 |
表1 M45两侧肱骨、尺骨和桡骨测量数据
Tab.1 Measured data of humerus, ulna and radius on both sides of M45
| 骨骼Bone | 项目Item | 左侧L | 右侧R |
|---|---|---|---|
| 肱骨Humerus | 最大长Lmax | 284 | 216 |
| 全长L | 275.7 | 214 | |
| 中部最大径dmax | 18.88 | 17.95 | |
| 中部矢状径dmid | 18.18 | 18.44 | |
| 中部最小径dmin | 16.11 | 14.32 | |
| 中部横径dmid | 14.89 | 16.93 | |
| 最小周长Cmin | 55 | 55.7 | |
| 中部周长Cmid | 58 | 56 | |
| 上端宽btop | 41.52 | 42.36 | |
| 下端宽bbot | 50.36 | 53.14 | |
| 滑车宽b | 16.33 | 16.65 | |
| 滑车和小头宽b | 35.05 | 35.73 | |
| 滑车矢径d | 22.26 | 23.77 | |
| 头周长c | 11.2 | 11.2 | |
| 头横径d | 35.58 | 34.84 | |
| 头纵径d | 35.19 | 34.27 | |
| 横断面指数I | 0.856* | 0.794* | |
| 粗壮指数I | 0.187* | 0.257* | |
| 鹰嘴窝深d | 1.1 | 1.2 | |
| 鹰嘴窝宽b | 22.95 | 25.18 | |
| 关节盂长L | 32.59 | 30.55 | |
| 关节盂宽b | 22.77 | 25.10 | |
| 尺骨Ulna | 最大长Lmax | 234 | 237 |
| 生理长L | 201 | 203 | |
| 体最小周长Cmin | 37 | 37 | |
| 体横径d | 10.68 | 10.48 | |
| 体矢径d | 17.76 | 17.6 | |
| 上部横径dtop | 15.66 | 15.67 | |
| 上部矢径dtop | 17.76 | 17.60 | |
| 鹰嘴小头长L | 30.83 | 30.87 | |
| 鹰嘴宽b | 20.91 | 21.44 | |
| 鹰嘴深d | 18.59 | 2.83 | |
| 鹰嘴高h | 22.27 | 24.82 | |
| 鹰嘴冠突间距d | 30.22 | 29.97 | |
| 尺骨Ulna | 冠关桡前宽bant | 10.48 | 11.20 |
| 冠关桡后宽bpos | 9.85 | 9.84 | |
| 桡骨Radius | 最大长Lmax | 213 | 215 |
| 生理长L | 200 | 200 | |
| 中部周长Cmid | 39 | 40 | |
| 体最小周长Cmix | 38 | 38 | |
| 体横径d | 12.58 | 12.83 | |
| 体矢径d | 9.79 | 9.76 | |
| 中部横径dmid | 26.63 | 27.45 | |
| 中部矢径dmid | 8.71 | 8.83 | |
| 头横径d | 18.62 | 19.04 | |
| 头矢径d | 18.94 | 19.17 | |
| 颈横径d | 12.19 | 11.09 | |
| 颈矢径d | 12.77 | 11.16 | |
| 颈周长c | 48 | 48 | |
| 头周长c | 61 | 62 | |
| 下端宽bbot | 26.96 | 26.76 |
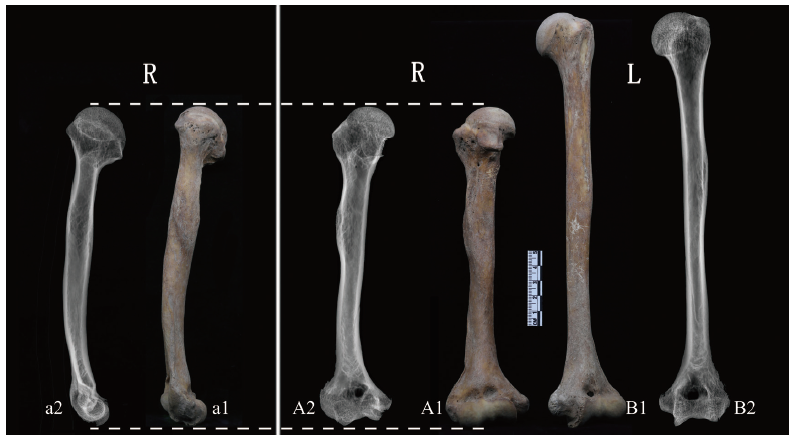
图4 M45右侧肱骨正面、侧面观及与左侧肱骨对比 A.右侧肱骨正面观anterior images of the right humerus;B.左侧肱骨正面观anterior images of the left humerus;a.右侧肱骨侧面观lateral images of the right humerus;A2, B2, a2. X光片X-ray film
Fig.4 Anterior and lateral images of the right humerus of the M45 comparing with the left humerus
| [1] | 夏洛特·罗伯茨. 疾病考古学(第三版)[M]. 济南: 山东画报出版社, 2010 |
| [2] | Amanda B. Bilateral Asymmetry of the Humerus During Growth and Development[J]. American Journal of Physical Antheropology, 2011, 145(4): 639-646 |
| [3] | Anna MK, Wioletta N, Antoine B, et al. Bilateral asymmetry of the humerus in Neandertals Australian aborigines and medieval humans[J]. American Journal of Physical Antheropology, 2018, 167(1): 46-60 |
| [4] |
Steven EC, Vincenzo F. A Case of Marked Bilateral Asymmetry in the Upper Limbs of an Upper Palaeolithic Male from Barma Grande (Liguria), Italy[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 1997, 7(1): 18-38
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1212(199701)7:1<18::AID-OA303>3.0.CO;2-R URL |
| [5] | Vladimír S, Margit B, Daniel S, et al. Human Manipulative Behavior in the Central European Late Eneolithic and Early Bronze Age: Humeral Bilateral Asymmetry[J]. American Journal of Physical Antheropology, 2007, 133(1): 669-681 |
| [6] |
Kujanova M, Bigoni L, VelemIínska J, et al. Limb Bones Asymmetry and Stress in Medieval and Recent Populations of Central Europe[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2008, 18(5): 476-491
doi: 10.1002/oa.958 URL |
| [7] | Fields SJ, Spiers M, Hershkovitz I, et al. Reliability of reliability coefficients in the estimation of asymmetry[J]. American Journal of Physical Antheropology, 1995, 96(1): 83-87 |
| [8] | Sládek V, Berner M, Sosna D, et al. Human Manipulative Behavior in the Central European Late Eneolithic and Early Bronze Age: Humeral Bilateral Asymmetry[J]. American Journal of Physical Antheropology, 2007, 133: 669-681 |
| [9] | Kaya GZ, Adam DS, Christopher BR. Bilateral asymmetry and developmental plasticity of the humerus in modern humans[J]. American Journal of Physical Antheropology, 2021, 418-433 |
| [10] | Shaw CN, Stock JT. Habitual Throwing and Swimming Correspond With Upper Limb Diaphyseal Strength and Shape in Modern Human Athletes[J]. American Journal of Physical Antheropology, 2009, 140: 160-172 |
| [11] | 邓阳, 李宝华, 侯海峰, 等. 肱骨短小症致病相关基因及其变异的筛选与验证[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2016, 31(9): 961-965 |
| [12] | 谢志勇, 谭为, 李旭. 儿童骨骺损伤的治疗及研究进展[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2016, 31(11): 873-875 |
| [13] | 王建, 杨志明. 生长板损伤修复的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2001, 5: 291-294 |
| [14] | Choi IH, Kim CJ, Cho TJ, et al. Focal fibrocartilaginous dysplasia of long bones: report of eight additional cases and literature review[J]. J Pediatr Orthop, 2000, 20(4): 421-427 |
| [15] |
Chong JK, In HC, Tae JC, et al. The histological spectrum of subperiosteal fibrocartilaginous pseudotumor of long bone (focal fibrocartilaginous dysplasia)[J]. Pathology International, 1999, 49: 1000-1006
pmid: 10594847 |
| [16] | Bell SN, Campbell PE, Cole WG, et al. Tibia vara caused by focal fibrocartilaginous dysplasia: three case reports[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1985, 67(5): 780-784 |
| [17] | 焦凤萍, 刘一志, 李宝华, 等. 肱骨短小症患者骨生长因子检测及意义[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2014, 30(9): 1184-1186 |
| [18] |
Lieverse A, Metcalf M, Bazaliiskii V, et al. Pronounced Bilateral Asymmetry of the Complete Upper Extremity: A Case From the Early Neolithic Baikal, Siberia[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2008, 18: 219-239
doi: 10.1002/oa.935 URL |
| [19] |
Kacki S, Duneufjardin P, Blanchard P, et al. Humerus Varus in a Subadult Skeleton from the Medieval Graveyard of LaMadeleine (Orléans, France)[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2013, 23(1): 119-126
doi: 10.1002/oa.1249 URL |
| [20] | 惠夕平, 闫广宇, 王书成, 等. 河南荥阳官庄遗址周边考古调查简报[J]. 中国国家博物馆馆刊, 2017, 11: 22-31 |
| [21] | 邵象清. 人体测量手册[M]. 上海: 上海辞书出版社, 1985, 34-56 |
| [22] | 朱泓. 体质人类学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004, 92-106 |
| [23] | Zhou YW, Lu YP, He JN, et al. Bioarchaeological insights into disability: Skeletal dysplasia from the Iron Age northern China[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2021 |
| [24] |
David W, Roberto M, Margherita M. A Case of Chondrodystrophic Dwarfism in the Italian Late Upper Paleolithic[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1988, 75(4): 549-565
pmid: 3291617 |
| [25] | 李崇, 富建华. 早产儿代谢性骨病诊治的研究进展[J]. 中国小儿急救医学, 2021, 28(1): 50-54 |
| [26] | 吕俊杰, 钟彩琴, 马长德, 等. 代谢性骨病患者BMD与TRAP、D-Pyr/Cr、NTX/Cr、HOP/Cr的检测及相关性研究[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2016, 22(10): 902-905 |
| [27] | 张锦. 内分泌系统与疾病[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2008, 144-243 |
| [28] | 李新民, 蒋雯, 程克斌, 等. 儿童局灶性纤维软骨发育不良的影像特征[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2017, 6(8): 582-586 |
| [29] |
Jouve JL, Kohler R, Mubarak SJ, et al. Focal fibrocartilaginous dysplasia (“fibrous periosteal inclusion”): an additional series of eleven cases and literature review[J]. J Pediatr Orthop, 2007, 27(1): 75-84
doi: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e31802b7139 URL |
| [30] | 赵定麟, 陈德玉, 赵杰. 现代骨科学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014, 50-58 |
| [31] | 中国疾病预防控制中心地方病控制中心网. 大骨节病[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2019, 34(2): 211. |
| [32] | 李群伟, 次央, 侯海峰, 等. 肱骨短小症流行病学调查报告[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2012, 13(10): 721-723 |
| [33] | 李群伟, 龚弘强, 侯海峰, 等. 肱骨短小症患者临床体征与骨骼X线改变特征分析[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2015, 30 (1): 4-6 |
| [34] | 刘明嫦, 马敬. 中国软骨发育不全特征分析及产前诊断方法探讨[J]. 云南医药, 2019, 40(2): 97-100 |
| [35] | 郑敏. 软骨发育不全 X 线诊断分析[J]. 中国伤残医学, 2014, 22(8): 194-195 |
| [36] |
Stirland AJ. Asymmetry and activity-related change in the male humerus[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 1993, 3(2): 105-113
doi: 10.1002/oa.1390030207 URL |
| [37] |
Schaeffer A. Spiral movement in man[J]. Journal of Morphology, 1928, 45(1): 293-399
doi: 10.1002/jmor.1050450110 URL |
| [38] |
Eshed V, Gopher A, Galili E, et al. Musculoskeletal stress markers in Natufian Hunte-Gatherers and Neolothic Farmers in the Levant: The upper limb[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2004, 123(4): 303-315
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.10312 URL |
| [39] |
Flachsmann R, Broom ND, Hardy AE, et al. Why is the adolescent joint particularly susceptible to osteochondral shear fracture?[J]. Clin Orthop Rel Res, 2000, 381: 212-21
doi: 10.1097/00003086-200012000-00025 URL |
| [40] | Micheli LJ. Pediatric and adolescent sports injury: recent trends[J]. In: Pandolf KB(Eds.). Exercise and sport science reviews[C]. New York: Macmillan, 1986, 359 |
| [41] |
Salter RB, Harris WR. Injuries involving the epiphyseal plate[J]. J Bone Joint Surg, 1963, 45: 587-622
doi: 10.2106/00004623-196345030-00019 URL |
| [42] | 王香港, 万谦, 刘贺, 等. 组织工程软骨在生长板损伤修复治疗中的作用及特点[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(28): 4539-4545 |
| [43] | Beaty JH, Kasser JR. Rockwood and Wilkins' Fractures in Children[J]. J Bone Joint Surg, 2015, 88(10): 2313 |
| [44] | 洪意侠, 利春叶. 儿童骨骺损伤的诊断和治疗进展[J]. 罕少疾病杂志, 2021, 28(1): 107-110 |
| [1] | 高国帅, 王安琦, 王龙, 张全超. 新疆加依墓地人体脊椎溶解的古病理学[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 744-756. |
| [2] | 刘驷统, 顾万发, 吴倩, 周亚威. 河南双槐树遗址人群肱骨肌腱的起止点形变[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 757-766. |
| [3] | 赵东月, 李昊潞. 人类颅骨筛状眶与多孔性骨肥厚研究回顾[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(04): 564-574. |
| [4] | 王邦彦, 王久存, 文少卿. 古代强直性脊柱炎的诊断标准及国内研究回顾[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(03): 422-434. |
| [5] | 饶慧芸. 古蛋白质分析在东亚古人类演化中的应用前景[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(06): 1083-1096. |
| [6] | 刘燕, 李玉玲. 遗传和环境因素对儿童青少年身体高度及其比例的影响[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(05): 875-882. |
| [7] | 孙蕾. 河南淇县宋庄东周墓葬一例殉人骨骼上发现疑似类风湿关节炎[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 248-260. |
| [8] | 周亚威, 高国帅. 性病梅毒的古病理学研究回顾[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(01): 157-168. |
| [9] | 魏偏偏, 赵昱浩, 何嘉宁. 辽宁建平古人类肱骨形态结构分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(06): 943-954. |
| [10] | 德力格尔, 乌云格日勒. 内蒙古汉族、蒙古族与日本学生身高和体质量的最大发育年龄段差异[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(05): 847-856. |
| [11] | 周立刚, 韩朝会, 孙蕾, 呼国强. 河南淇县宋庄东周墓地人骨稳定同位素分析——东周贵族与殉人食谱初探[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(01): 63-74. |
| [12] | 赵昱浩, 周蜜, 魏偏偏, 邢松. 肱骨骨干骨密质厚度的二维可视化及其定量分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 632-647. |
| [13] | 何嘉宁, 李楠. 北京军都山古代居民的颅骨创伤[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 576-585. |
| [14] | 王谦, 张全超. 全球健康史项目亚洲模块—— 亚洲古代人群健康、疾病和生活方式的大数据[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 727-732. |
| [15] | 孙蕾, 高振龙, 周立刚, 韩朝会. 淇县宋庄东周墓殉人颅骨的形态学[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(03): 420-434. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 384
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 652
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3