

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (06): 979-992.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0095
李浩1( ), 肖培源1,2, 彭培洺1,2, 王雨晴1,2, 陈清懿1,2, Ikram QAYUM1, 贾真秀1, 阮齐军1,3, 陈发虎1
), 肖培源1,2, 彭培洺1,2, 王雨晴1,2, 陈清懿1,2, Ikram QAYUM1, 贾真秀1, 阮齐军1,3, 陈发虎1
收稿日期:2024-05-27
修回日期:2024-08-28
出版日期:2024-12-15
发布日期:2024-11-28
作者简介:李浩,研究员,主要从事旧石器时代考古研究。E-mail: lihao@itpcas.ac.cn
基金资助:
LI Hao1( ), XIAO Peiyuan1,2, PENG Peiming1,2, WANG Yuqing1,2, CHEN Qingyi1,2, Ikram QAYUM1, JIA Zhenxiu1, RUAN Qijun1,3, CHEN Fahu1
), XIAO Peiyuan1,2, PENG Peiming1,2, WANG Yuqing1,2, CHEN Qingyi1,2, Ikram QAYUM1, JIA Zhenxiu1, RUAN Qijun1,3, CHEN Fahu1
Received:2024-05-27
Revised:2024-08-28
Online:2024-12-15
Published:2024-11-28
摘要:
西南丝绸之路是连接中国西南地区和青藏高原、东南亚大陆、南亚及中亚南部等区域的重要纽带,为理解旧石器时代古人类的迁徙扩散与文化交流提供了独特的跨区域视角。本文首先根据历史文献、现代交通网络和遥感影像等资料,重建了历史时期西南丝绸之路的复杂路网格局。在此基础上,系统总结梳理了旧石器时代中期和晚期早段西南丝绸之路上的考古发现和研究成果,探讨了不同地区古人类石器技术和文化面貌的演变过程以及潜在的人群扩散交流历史。整体来看,在旧石器时代中期和晚期早段,中国西南地区和青藏高原与亚洲东南部其他区域在石器技术和文化面貌上均存在阶段性的变化和革新;亚洲东南部不同区域之间相互连通,古老型人类和早期现代人都曾以历史时期的西南丝绸之路为主线进行迁徙和扩散。今后,在西南丝绸之路概念引导下,进一步开展跨区域比较研究,有助于深入理解和认识中国西南地区和青藏高原早期人类的演化历史。
中图分类号:
李浩, 肖培源, 彭培洺, 王雨晴, 陈清懿, Ikram QAYUM, 贾真秀, 阮齐军, 陈发虎. 西南丝绸之路上的旧石器文化与人群交流[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(06): 979-992.
LI Hao, XIAO Peiyuan, PENG Peiming, WANG Yuqing, CHEN Qingyi, Ikram QAYUM, JIA Zhenxiu, RUAN Qijun, CHEN Fahu. Paleolithic culture and human interactions on the Southwest Silk Road[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(06): 979-992.
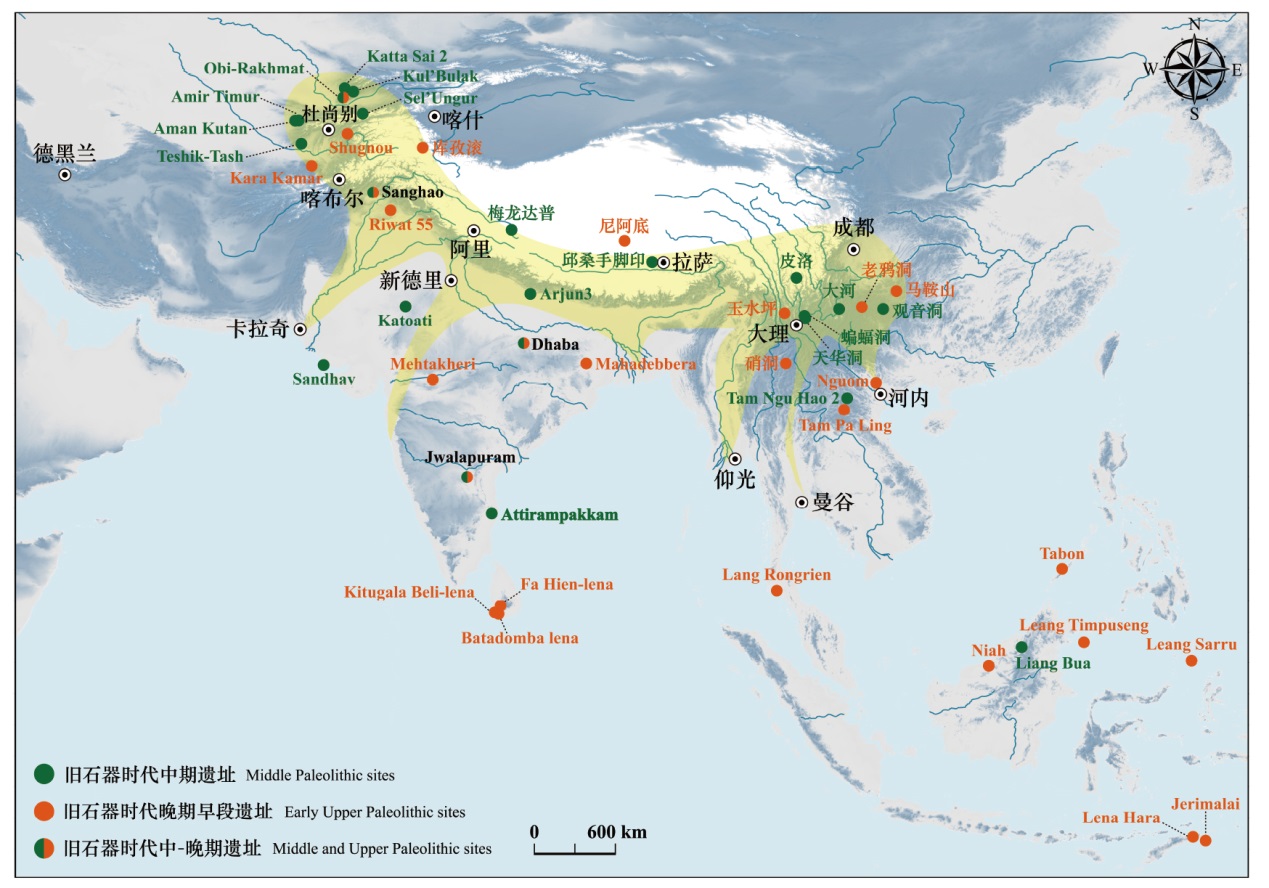
图2 西南丝绸之路沿线及周边区域旧石器时代中期、旧石器时代晚期早段和旧石器时代中-晚期遗址分布
Fig.2 Distribution of the Middle Paleolithic, the Early Upper Paleolithic and the Middle-Upper Paleolithic sites along the Southwest Silk Route and adjacent regions
| [1] | Jacobs Z, Li B, Shunkov MV, et al. Timing of archaic hominin occupation of Denisova Cave in southern Siberia[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7741): 594-599 |
| [2] | Kolobova KA, Roberts RG, Chabai VP, et al. Archaeological evidence for two separate dispersals of Neanderthals into southern Siberia[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2020, 117(6): 2879-2885 |
| [3] |
Li F, Kuhn SL, Chen F, et al. The easternmost middle paleolithic (Mousterian) from Jinsitai cave, north China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2018, 114: 76-84
doi: S0047-2484(17)30303-2 pmid: 29447762 |
| [4] | 张弘. 从西南丝绸之路的线路节点研析其功能及需求[J]. 学术探索, 2015, 7: 117-121 |
| [5] | 方铁. 南方丝绸之路的拓建与管理[J]. 社会科学战线, 2024, 2: 131-139 |
| [6] | 冯小莉, 周永卫. 汉代陆海丝绸之路对接的西南路径[J]. 石河子大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2023, 37(2): 101-106 |
| [7] | 方铁. 简论西南丝绸之路[J]. 长安大学学报(社会科学版), 2015, 17(3): 114-120 |
| [8] | 管雪竹. 简述西南地区丝绸之路的文化影响及其传承与保护[J]. 丝绸之路, 2015, 6: 40-41 |
| [9] | 蓝勇. 四川古代交通路线史[M]. 重庆: 西南师范大学出版社, 1989 |
| [10] | 蓝勇. 南方丝绸之路[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 1989 |
| [11] | 陆韧. 云南对外交通史记[M]. 昆明: 云南民族出版社, 1997 |
| [12] | 邓廷良. 西南丝绸之路考察礼记[M]. 成都: 成都出版社, 1990, 3-17 |
| [13] | 伍加伧, 江玉祥, 等. 古代西南丝绸之路研究[M]. 成都: 四川大学出版社, 1990 |
| [14] | 袁绍文. 西南民族与南方丝绸之路[M]. 北京: 民族出版社, 2016 |
| [15] | 先燕云. 西南丝绸之路[M]. 广州: 广东旅游出版社, 2007 |
| [16] | 申再望. 巴蜀文化系列画集:西南丝绸之路[G]. 成都: 四川人民出版社, 1992 |
| [17] | 赵廷光. 中国西南丝绸之路[G]. 昆明: 云南民族出版社, 1992 |
| [18] | 王立教, 戴蓉. 南方丝绸之路开凿对西南边疆文化塑造探析[J]. 贵州社会科学, 2020, 5: 102-108 |
| [19] | 屈小玲. 中国西南与境外古道:南方丝绸之路及其研究述略[J]. 西北民族研究, 2011, 1: 172-179 |
| [20] | 黄剑华. 中华文明与西南丝绸之路[J]. 月读, 2022, 5: 4-13 |
| [21] | 周智生. 中国云南与印度古代交流史述略(上)[J]. 南亚研究, 2002, 1 |
| [22] |
霍仁龙, 任柳. 基于GIS的南方丝绸之路国内段交通路线网络重建研究[J]. 地理研究, 2022, 41(4): 1122-1135
doi: 10.11821/dlyj020210210 |
| [23] | 张萍. 丝绸之路交通地理定位与道路网络复原研究[J]. 首都师范大学学报(社会科学版), 2018, 2: 33-40 |
| [24] | 【东晋】常璩. 华阳国志:卷三·蜀志[M]. 校注:刘琳. 成都: 巴蜀书社, 1984, 324 |
| [25] | 【宋】欧阳修, 宋祁(著). 新唐书:卷四十三下·地理志[M] .北京: 中华书局, 1975, 1253-1254 |
| [26] | 【汉】司马迁. 史记:卷一二三·大宛列传[M]. 北京: 中华书局, 1959, 3166 |
| [27] | Clark MK, House MA, Royden LH, et al. Late Cenozoic uplift of southeastern Tibet[J]. Geology, 2005, 33(6): 525-528 |
| [28] | Kirby E, Whipple KX. Quantifying differential rock-uplift rates via stream profile analysis[J]. Geology, 2001, 29(5): 415-418 |
| [29] | Pan GT, Wang LQ, Li RS, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53: 3-14 |
| [30] | Blisniuk PM, Hacker BR, Glodny J, et al. Normal faulting in central Tibet since at least 13.5 Myr ago[J]. Nature, 2001, 412(6847): 628-632 |
| [31] | Zhang WL, Zhang DW, Fang XM, et al. New paleomagnetic constraints on rift basin evolution in the northern Himalaya mountains[J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 77: 98-110 |
| [32] | 【元】索南坚赞. 西藏王统记[M]. 译者:刘立千. 拉萨: 西藏人民出版社, 2000, 57 |
| [33] | 霍巍. 论青藏高原古代各族人民共同开创了“高原丝绸之路”[J]. 中央民族大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2021, 48(2): 5-15 |
| [34] | Akhilesh K, Pappu S, Rajapara HM, et al. Early Middle Palaeolithic culture in India around 385-172 ka reframes Out of Africa models[J]. Nature, 2018, 554(7690): 97-101 |
| [35] | Hu Y, Marwick B, Zhang JF, et al. Late Middle Pleistocene Levallois stone-tool technology in southwest China[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7737): 82-85 |
| [36] | Li F, Li Y, Gao X, et al. A refutation of reported Levallois technology from Guanyindong Cave in south China[J]. National Science Review, 2019, 6(6): 1094-1096 |
| [37] | 郑喆轩, 冯玥, 谭培阳, 等. 四川稻城县皮洛旧石器时代遗址[J]. 考古, 2022, 7: 3-14+2 |
| [38] | 陈发虎, 夏欢, 贾真秀, 等. 手脚印遗迹可能指示夏河丹尼索瓦人距今20万年前生活在青藏高原腹地[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2022, 52(5): 966-969 |
| [39] | 阮齐军, 刘建辉, 叶荣波, 等. 云南鹤庆蝙蝠洞旧石器遗址2019年度发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(4): 503-513 |
| [40] | 肖培源, 阮齐军, 高玉, 等. 2022年云南宾川盆地旧石器遗址调查报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(3): 448-457 |
| [41] | 阮齐军, 刘建辉, 胡越, 等. 云南鹤庆天华洞旧石器遗址石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(2): 166-181 |
| [42] | Hu Y, Ruan Q, Liu J, et al. Luminescence chronology and lithic technology of Tianhuadong Cave, an early Upper Pleistocene Paleolithic site in southwest China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2020, 94: 121-136 |
| [43] | 吉学平. 云南富源大河旧石器遗址入选2006年度全国十大考古新发现[J]. 人类学学报, 2007, 3: 221 |
| [44] | 2023·全国十大考古新发现特刊·入围项目[N]. 中国文物报,2024-03-29(008) |
| [45] |
Clarkson C, Harris C, Li B, et al. Human occupation of northern India spans the Toba super-eruption -74,000 years ago[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 961
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14668-4 pmid: 32098950 |
| [46] | Blinkhorn J, Achyuthan H, Ditchfifield P, et al. Palaeoenvironmental dynamics and Palaeolithic occupation at Katoati, Thar Desert, India[J]. Quaternary Research, 2017, 87: 298-313 |
| [47] | Blinkhorn J, Ajithprasad P, Mukherjee A, et al. The first directly dated evidence for Palaeolithic occupation on the Indian coast at Sandhav, Kachchh[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 224: 105975 |
| [48] | Haslam M, Clarkson C, Petraglia M, et al. The 74 ka Toba super-eruption and southern Indian hominins: archaeology, lithic technology and environments at Jwalapuram Locality 3[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2010, 37(12): 3370-3384 |
| [49] | Haslam M, Clarkson C, Roberts RG, et al. A southern Indian Middle Palaeolithic occupation surface sealed by the 74 ka Toba eruption: further evidence from Jwalapuram Locality 22[J]. Quaternary International, 2012, 258: 148-164 |
| [50] | Nishiaki Y, Aripdjanov O. A new look at the Middle Paleolithic lithic industry of the Teshik-Tash Cave, Uzbekistan, West Central Asia[J]. Quaternary International, 2021(596): 22-37 |
| [51] | Krivoshapkin A, Viola B, Chargynov T, et al. Middle Paleolithic variability in Central Asia: lithic assemblage of Sel’Ungur cave[J]. Quaternary International, 2020, 535: 88-103 |
| [52] | Krivoshapkin AI, Anoikin AA, Brantingham PJ. The lithic industry of Obi-Rakhmat grotto, Uzbekistan[J]. Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association, 2006, 26: 5-19 |
| [53] | Nishiaki Y, Aripdjanov O, Suleymanov R, et al. An archaeological reconnaissance survey of caves and rockshelters in the Kashkadarya Valley, South Uzbekistan, 2014[J]. Bulletin of the Ancient Orient Museum, 2016, 36: 1-11 |
| [54] |
Trinkaus E, Ranov VA, Lauklin S. Middle Paleolithic human deciduous incisor from Khudji, Tajikistan[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2000, 38(4): 575-584
pmid: 10715197 |
| [55] | Davis R, Ranov V. Recent work on the paleolithic of Central Asia[J]. Evolutionary Anthropology, 1999, 8(5): 186-193 |
| [56] |
Demeter F, Zanolli C, Westaway KE, et al. A Middle Pleistocene Denisovan molar from the Annamite chain of northern Laos[J]. Nature communications, 2022, 13(1): 2557
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29923-z pmid: 35581187 |
| [57] |
Moore MW, Sutikna T, Jatmiko, et al. Continuities in stone flaking technology at Liang Bua, Flores, Indonesia[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2009, 57(5): 503-526
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2008.10.006 pmid: 19361835 |
| [58] | Clarkson C, Jones S, Harris C. Continuity and change in the lithic industries of the Jurreru Valley, India, before and after the Toba eruption[J]. Quaternary International, 2012 (258): 165-179 |
| [59] | Mellars P, Gori KC, Carr M, et al. Genetic and archaeological perspectives on the initial modern human colonization of southern Asia[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(26): 10699-10704 |
| [60] | Ji X, Kuman K, Clarke RJ, et al. The oldest Hoabinhian technocomplex in Asia (43.5 ka) at Xiaodong rockshelter, Yunnan Province, southwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 400: 166-174 |
| [61] | 云南省文物考古研究所. 兰坪玉水坪[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2020 |
| [62] | 黄泗亭, 龙凤骧, 安家瑗. 马鞍山南洞旧石器文化遗址试掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 1992, 11(1): 1-10 |
| [63] | Zhang S, d'Errico F, Backwell LR, et al. Ma'anshan cave and the origin of bone tool technology in China[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2016, 65: 57-69 |
| [64] | 关莹, 蔡回阳, 王晓敏, 等. 贵州毕节老鸦洞遗址2013年发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(4): 461-477 |
| [65] |
Zhang XL, Ha BB, Wang SJ, et al. The earliest human occupation of the high-altitude Tibetan Plateau 40 thousand to 30 thousand years ago[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6418): 1049-1051
doi: 10.1126/science.aat8824 pmid: 30498126 |
| [66] | 冯玥, 李文成, 艾涛, 等. 新疆塔什库尔干县库孜滚遗址发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2022, 9: 3-13 |
| [67] | Anisyutkin NK, Timofeyev VI. The Paleolithic flake industry in Vietnam[J]. Archaeology, Ethnology & Anthropology of Eurasia, 2006, 3(27): 16-24 |
| [68] | Mudar K, Anderson D. New evidence for Southeast Asian Pleistocene foraging economies: Faunal remains from the early levels of Lang Rongrien rockshelter, Krabi, Thailand[J]. Asian Perspectives, 2007, 46(2): 298-334 |
| [69] | Demeter F, Shackelford LL, Bacon A, et al. Anatomically modern human in Southeast Asia (Laos) by 46 ka[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(36): 14375-14380 |
| [70] | Curnoe D, Datan I, Taçon PSC, et al. Deep skull from Niah Cave and the Pleistocene peopling of Southeast Asia[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2016, 4: 75 |
| [71] | Détroit F, Dizon E, Falguères C, et al. Upper Pleistocene Homo sapiens from the Tabon cave (Palawan, The Philippines): description and dating of new discoveries[J]. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 2004, 3(8): 705-712 |
| [72] |
Storm P, Wood R, Stringer C, et al. U-series and radiocarbon analyses of human and faunal remains from Wajak, Indonesia[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2013, 64: 356-365
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2012.11.002 pmid: 23465338 |
| [73] | Tanudirjo DA. Long-continuous or short-occasional occupation? The human use of Leang Sarru rockshelter in the Talaud Islands, northeastern Indonesia[J]. Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association Bulletin, 2005, 25(3): 15-19 |
| [74] |
Shipton C, O’Connor S, Jankowski N, et al. A new 44,000-year sequence from Asitau Kuru (Jerimalai), Timor-Leste, indicates long-term continuity in human behaviour[J]. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 2019, 11(10): 5717-5741
doi: 10.1007/s12520-019-00840-5 |
| [75] | Langley MC, O’Connor S. An enduring shell artefact tradition from Timor-Leste: Oliva bead oroduction from the Pleistocene to late Holocene at Jerimalai, Lene Hara, and Matja Kuru 1 and 2[J]. PLOS ONE, 2016, 11(8): e0161071 |
| [76] | Aubert M, Brumm A, Ramli M, et al. Pleistocene cave art from Sulawesi, Indonesia[J]. Nature, 2014 (514): 223-227 |
| [77] | Basak B, Srivastava P. Earliest dates of microlithic industries (42-25 ka) from West Bengal, Eastern India: New light on modern human occupation in the Indian subcontinent[J]. Asian Perspectives, 2017, 56(2): 237-259 |
| [78] |
Clarkson C, Harris C, Li B, et al. Human occupation of northern India spans the Toba super-eruption -74,000 years ago[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 961
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14668-4 pmid: 32098950 |
| [79] | Khansili G. A study of early microblade technology from Mehtakheri, Mafhya Pradesh[D]. Deccan College Post-Graduate and Research Institute, 2021 |
| [80] | Clarkson C, Petraglia MD, Korisettar R, et al. The oldest and longest enduring microlithic sequence in India: 35, 000 years of modern human occupation and change at the Jwalapuram Locality 9 rockshelter[J]. Antiquity, 2009, 83: 326-348 |
| [81] | Dennell RW, Rendell HM, Halim M, et al. A 45,000-Year-Old Open-air Paleolithic Site at Riwat, Northern Pakistan[J]. Journal of Field Archaeology, 1992, 19(1): 17-33 |
| [82] | Wedage O, Picin A, Blinkhorn J, et al. Microliths in the South Asian rainforest -45-4 ka: New insights from Fa-Hien Lena Cave, Sri Lanka[J]. PLOS ONE, 2019, 14(10): e0222606 |
| [83] | Wedage O, Roberts P, Faulkner P, et al. Late Pleistocene to early-Holocene rainforest foraging in Sri Lanka: Multidisciplinary analysis at Kitulgala Beli-lena[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 231: 106200 |
| [84] |
Perera N, Kourampas N, Simpson IA, et al. People of the ancient rainforest: Late Pleistocene foragers at the Batadomba-lena rockshelter, Sri Lanka[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2011, 61(3): 254-269
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2011.04.001 pmid: 21777951 |
| [85] | Davis R. Kara kamar in northern Afghanistan: Aurignacian, aurignacoid or just plain Upper Paleolithic?[A]. In: Derevianko AP, Nokhrina TI (Eds). Arkheologiya I Paleoekologiya Evrazii[C]. Novosibirsk: Rossijskaya Akademiya Nauk, Sibirskoe Otdenie, Institut Arkheologii i Etnografii, 2004, 211-217 |
| [86] | Ranov VA, Kolobova KA, Krivoshapkin AI. The Upper Paleolithic assemblages of Shugnou, Tajikistan[J]. Archaeology, Ethnology and Anthropology of Eurasia, 2012, 40(2): 2-24 |
| [87] | Vandenberghe DAG, Flas D, De Dapper M, et al. Revisiting the Palaeolithic site of Kulbulak (Uzbekistan): First results from luminescence dating[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 324: 180-189 |
| [88] | Kot M, Pavlenok G, Krajcarz MT, et al. Is there Initial Upper Palaeolithic in Western Tian Shan? Example of an open-air site Katta Sai 2 (Uzbekistan)[J]. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, 2022, 65: 101391 |
| [89] | Biagi P, Starnini E. Neanderthals and modern humans in the Indus valley? The middle and late (Upper) palaeolithic settlement of Sindh, a forgotten region of the Indian subcontinent[A]. In: Nishiaki Y, Akazawa T(Eds). The Middle and Upper Paleolithic Archeology of the Levant and Beyond[C]. Singapore: Springer, 2018, 175-197 |
| [90] | Derevianko AP. The Middle to Upper Paleolithic Transition and Formation of Homo sapiens sapiens in Eastern, Central and Northern Asia[M]. Novosibirsk: Institute of Archaeology and Ethnography Press, 2009 |
| [91] | Glantz MM. The history of hominin occupation of Central Asia in review[A]. In: Norton C, Braun D(Eds). Asian Paleoanthropology: From Africa to China and Beyond[C]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2011, 101-112 |
| [92] | Clarkson C, Hiscock P, Mackay A, et al. Small, sharp, and standardized: Global convergence in backed-microlith technology[A]. In: O’Brien M, Buchanan B, Eren M(Eds). Convergent Evolution in Stone-Tool Technology[C]. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 2018,175-200 |
| [93] | Gao X. Paleolithic cultures in China: Uniqueness and divergence[J]. Current Anthropology, 2013, 54(S8): 358-370 |
| [1] | 孙琦雅慧, 邢松. 广西通天岩洞穴遗址柳江人的多生齿[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(06): 1027-1037. |
| [2] | 张亚盟, 吴秀杰. 中国晚更新世早期现代人内耳迷路的形态变异[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(06): 1038-1047. |
| [3] | 肖培源, 阮齐军, 高玉, 贾真秀, 张明, 杨李靖, 刘建辉, 李三灵, 李浩. 2022年云南宾川盆地旧石器遗址调查报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 448-457. |
| [4] | Hiroyuki SATO, Kazuki MORISAKI. 日本旧石器晚期石器技术起源的新考古学与人类学证据[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 470-487. |
| [5] | 王法岗, 杨石霞, 葛俊逸, 岳健平, 赵克良, Andreu Ollé, 李文艳, 杨海勇, 刘连强, 关莹, 谢飞, Francesco d’Errico, Michael Petraglia, 邓成龙. 泥河湾盆地下马碑遗址2013年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 143-156. |
| [6] | 李浩. 探究早期现代人的南方扩散路线[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(04): 630-648. |
| [7] | 慕占雄, 陈国科, 杜水生, 王辉. 甘肃环县楼房子遗址2018年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(01): 121-134. |
| [8] | 袁文明, 夏宏茹, 兰会才, 王益人. 山西襄汾洞门遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(06): 1072-1085. |
| [9] | 阮齐军, 刘建辉, 胡越, 李波, 杨长城, 罗兴荣. 云南鹤庆天华洞旧石器遗址石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(02): 166-181. |
| [10] | 武仙竹;王照魁. 重庆丰都瓦啄嘴遗址的小哺乳动物[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(03): 452-466. |
| [11] | 张明;付巧妹. 史前古人类之间的基因交流及对当今现代人的影响[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(02): 206-218. |
| [12] | 刘扬;侯亚梅;杨泽蒙. 鄂尔多斯乌兰木伦遗址石制品拼合研究及其对遗址成因的指示意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(01): 41-54. |
| [13] | 杜抱朴;周易;孙金慧;张立召;夏宏茹;王益人;赵凌霞. 山西襄汾石沟砂场发现人类枕骨化石[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(04): 437-447. |
| [14] | 刘武. 早期现代人在中国的出现与演化[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(03): 233-246. |
| [15] | 李占扬; 张双权; 张乐; 高星. 河南灵井许昌人遗址普通马(Equus caballus)化石居群的死亡年龄曲线[J]. 人类学学报, 2011, 30(01): 45-54. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3