

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (04): 521-531.doi: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0019cstr: 32091.14.j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0019
收稿日期:2020-03-27
修回日期:2020-04-30
出版日期:2020-11-15
发布日期:2020-11-23
作者简介:邢松,中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所研究员,Email:基金资助:
XING Song1,2( ), ZHOU Mi3, PAN Lei1,2
), ZHOU Mi3, PAN Lei1,2
Received:2020-03-27
Revised:2020-04-30
Online:2020-11-15
Published:2020-11-23
摘要:
东亚中更新世古人类在头骨、下颌骨、牙齿等解剖部位表现出不同程度的形态多样性,中期成员代表为直立人,而晚期成员的演化地位具有较大争议。为进一步了解东亚中更新世古人类内部的形态变异特点和为东亚中更新世晚期古人类分类提供依据,本文使用微分同胚的表面匹配(Diffeomorphic Surface Matching, DSM)和形态测量图(Morphometric map)对下颌第二臼齿(M2)釉质-齿质连接面的形状和齿冠侧面釉质厚度分布模式进行了量化分析。结果显示:1)东亚中更新世古人类与晚期人属成员(尼安德特人和现代人)存在较明显的形态差别;2)该时段晚期的东亚古人类相对中期直立人在侧面釉质厚度分布规律上具有独特性,并在釉质-齿质连接面的三维形状上与晚期人属成员更加接近。本文在以往对东亚中更新世古人类牙齿内外结构单个性状研究的基础上,使用三维形态测量方法进一步量化了M2釉质-齿质连接面三维形状和侧面釉质厚度分布模式两项重要特征的变异特点,这对未来该时段同类型牙齿的形态鉴定以及解决东亚中更新世晚期古人类的分类地位具有一定意义。
中图分类号:
邢松, 周蜜, 潘雷. 东亚中更新世古人类下颌第二臼齿釉质-齿质连接面三维形状和釉质厚度分布[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 521-531.
XING Song, ZHOU Mi, PAN Lei. Enamel-dentine junction shape and enamel thickness distribution of East Asian Middle Pleistocene hominin lower second molars[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2020, 39(04): 521-531.
| 分类 | 标本 | 磨耗级别 |
|---|---|---|
| 东亚中更新世中期直立人(n=2) | 周口店PA70 | 2 |
| 淅川PA533 | 2 | |
| 东亚中更新世晚期古人类(n=1) | 华龙洞 HLD1 | 2 |
| 尼安德特人 (n=5) | Krapina D1, D6, D10, D86, D107 | 1-2 |
| 全新世现代人(湖北、河南)(n=16) | MTS101; PJL17; QJY23; WJP16, 47, 50; YQM22; YYM19, 27, 43, 50, 71, 102, 199, 206, 248 | 2 |
| 全新世现代人(法国、德国)(n=5) | EMBR628; SP2613, 3027,5678, 6046 | 1-2 |
表1 本文使用的东亚中更新世古人类下颌第二臼齿(M2)及对比标本
Tab.1 The M2 of East Asian Middle Pleistocene hominins and comparative specimens
| 分类 | 标本 | 磨耗级别 |
|---|---|---|
| 东亚中更新世中期直立人(n=2) | 周口店PA70 | 2 |
| 淅川PA533 | 2 | |
| 东亚中更新世晚期古人类(n=1) | 华龙洞 HLD1 | 2 |
| 尼安德特人 (n=5) | Krapina D1, D6, D10, D86, D107 | 1-2 |
| 全新世现代人(湖北、河南)(n=16) | MTS101; PJL17; QJY23; WJP16, 47, 50; YQM22; YYM19, 27, 43, 50, 71, 102, 199, 206, 248 | 2 |
| 全新世现代人(法国、德国)(n=5) | EMBR628; SP2613, 3027,5678, 6046 | 1-2 |
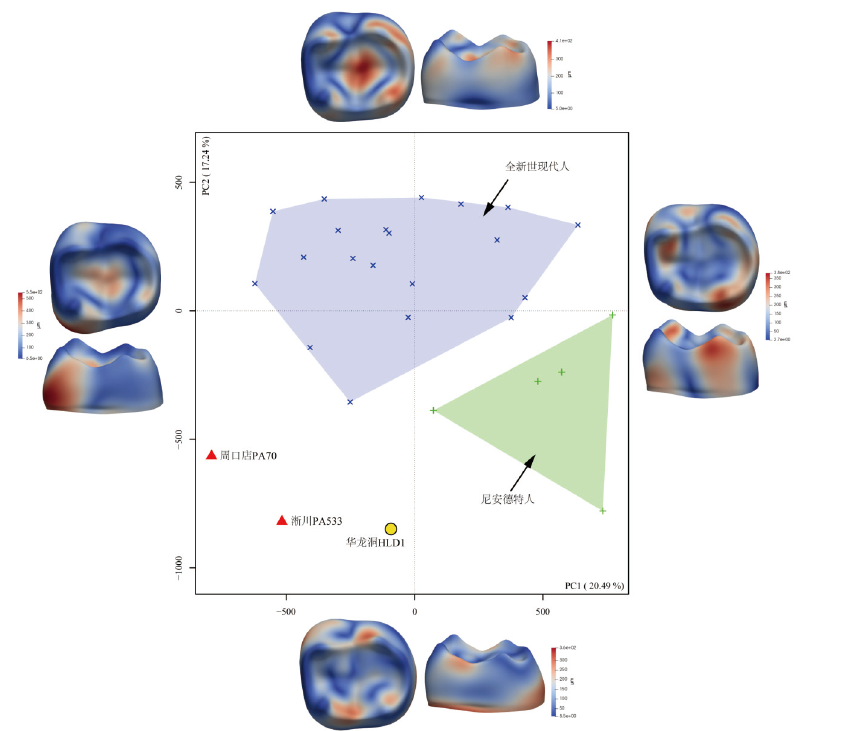
图1 基于微分同胚表面匹配的下颌第二臼齿(M2)釉质-齿质连接面三维形状的主成分分析 位于PC1和PC2轴四个极值位置上的牙齿EDJ形状分别从咬合面和远中舌侧角度展示;EDJ上蓝色到红色代表每个极值位置上的形状相对平均形状变化的绝对值由小到大(单位为μm)
Fig.1 The principal component analysis (PCA) of M2 enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) shape variation based on Diffeomorphic Surface Matching (DSM) The figures at four sides of the graphic represent the EDJ shape (occlusal and distolingual view) at the positive and negative poles of PC1 and PC2. The color gradient from blueness to redness means that the deformation degree between shape at each extreme and mean shape is increasing (in micron)
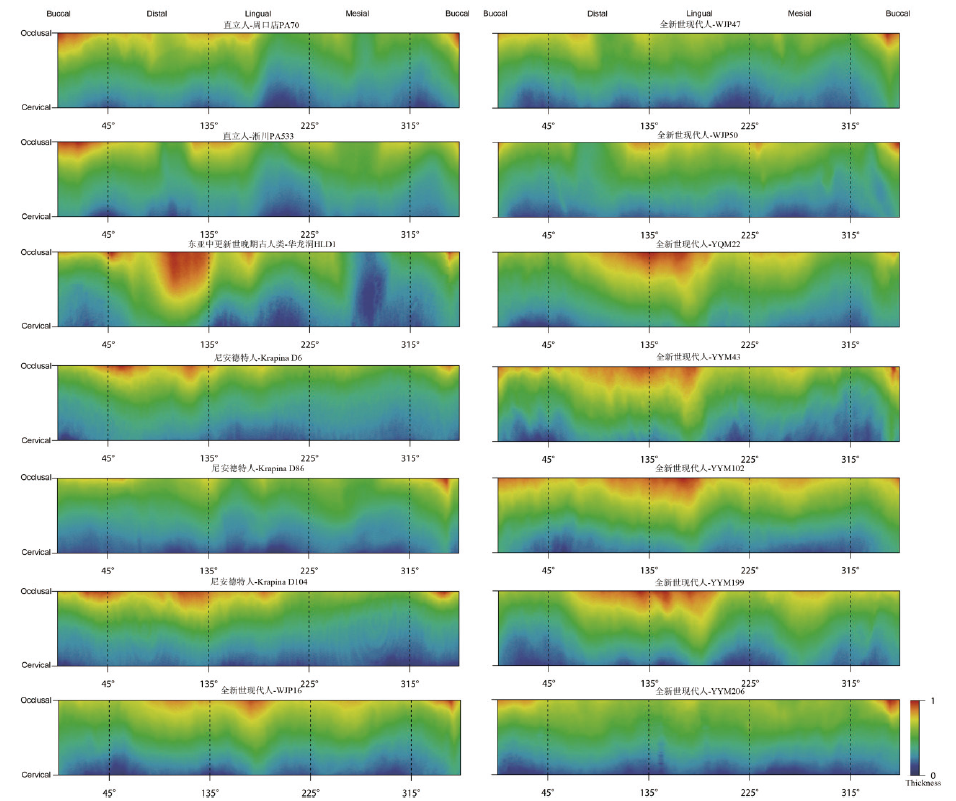
图2 下颌第二臼齿(M2)侧面釉质厚度的形态测量图 每张图上方为咬合面方向,下方为齿颈线方向,从左到右依次为颊侧远中部、远中侧、舌侧、近中侧、颊侧近中部/
Fig.2 The morphometric map of M2 lateral enamel thickness Each map was displayed with the occlusal side being at the top and cervical side at the bottom. From left to right on each map: distal section of the buccal side, distal, lingual, mesial, mesial section of the buccal side
| [1] | Wu X, Poirier FE. Human evolution in China: a metric description of the fossils and a review of the sites[M]. Oxford University Press, USA, 1995 |
| [2] | 刘武, 吴秀杰, 邢松, 等. 中国古人类化石[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014 |
| [3] | 刘武, 吴秀杰, 邢松. 更新世中期中国古人类演化区域连续性与多样性的化石证据[J]. 人类学学报, 2019,38:473-490 |
| [4] |
Li ZY, Wu XJ, Zhou LP, et al. Late Pleistocene archaic human crania from Xuchang, China[J]. Science, 2017,355:969-972
doi: 10.1126/science.aal2482 URL pmid: 28254945 |
| [5] |
Buck LT, Stringer CB. Homo heidelbergensis[J]. Current Biology, 2014,24:R214-R215
URL pmid: 24650901 |
| [6] | Stringer CB, Barnes I. Deciphering the Denisovans[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 2015,112:15542-15543 |
| [7] |
Wu XJ, Maddux SD, Pan LEI, et al. Nasal floor variation among eastern Eurasian Pleistocene Homo[J]. Anthropological Science, 2012,120:217-226
doi: 10.1537/ase.120709 URL |
| [8] | Gokhman D, Mishol N, de Manuel M, et al. Reconstructing Denisovan anatomy using DNA methylation maps[J]. Cell, 2019, 179: 180-192.e110 |
| [9] |
Liu W, Zhang Y, Wu X. Middle Pleistocene human cranium from Tangshan (Nanjing), Southeast China: A new reconstruction and comparisons with Homo erectus from Eurasia and Africa[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2005,127:253-262
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.20066 URL pmid: 15584056 |
| [10] |
Cui Y, Wu X. A geometric morphometric study of a Middle Pleistocene cranium from Hexian, China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2015,88:54-69
URL pmid: 26553818 |
| [11] |
Liu W, Martinón-Torres M, Kaifu Y, et al. A mandible from the Middle Pleistocene Hexian site and its significance in relation to the variability of Asian Homo erectus[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2017,162:715-731
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.23162 URL pmid: 28109118 |
| [12] |
Liu W, Schepartz LA, Xing S, et al. Late Middle Pleistocene hominin teeth from Panxian Dadong, South China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2013,64:337-355
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2012.10.012 URL pmid: 23465337 |
| [13] |
Xing S, Martinón-Torres M, Bermúdez de Castro JM, et al. Hominin teeth from the early Late Pleistocene site of Xujiayao, Northern China[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2015,156:224-240
URL pmid: 25329008 |
| [14] |
Xing S, Martinón-Torres M, de Castro JMB, et al. Middle Pleistocene hominin teeth from Longtan Cave, Hexian, China[J]. PLOS ONE, 2014,9:e114265
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114265 URL pmid: 25551383 |
| [15] |
Xing S, Sun C, Martinón-Torres M, et al. Hominin teeth from the Middle Pleistocene site of Yiyuan, Eastern China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2016,95:33-54
URL pmid: 27260173 |
| [16] |
Xing S, Martinón-Torres M, Bermúdez de Castro JM. The fossil teeth of the Peking Man[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018,8:1-11
URL pmid: 29311619 |
| [17] |
Xing S, Martinón-Torres M, Bermúdez de Castro JM. Late Middle Pleistocene hominin teeth from Tongzi, southern China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2019,130:96-108
URL pmid: 31010547 |
| [18] |
Xing S, Martinón-Torres M, Bermúdez de Castro JM. et al. Middle Pleistocene Hominin Teeth from Longtan Cave, Hexian, China[J]. PLOS ONE, 2015,9:e114265
URL pmid: 25551383 |
| [19] | Butler P. The ontogeny of molar pattern[J]. Biological Reviews, 1956,31:30-69 |
| [20] |
Skinner MM, Gunz P, Wood BA, et al. Enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) morphology distinguishes the lower molars of Australopithecus africanus and Paranthropus robustus[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2008,55:979-988
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2008.08.013 URL pmid: 18824253 |
| [21] |
Skinner MM, Wood B, Hublin JJ. Protostylid expression at the enamel-dentine junction and enamel surface of mandibular molars of Paranthropus robustus and Australopithecus africanus[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2009,56:76-85
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2008.08.021 URL |
| [22] | 刘武, 周蜜, 邢松. 卡氏尖在中国古人类化石中出现及其演化意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2018,37:159-175 |
| [23] |
Pan L, Dumoncel J, de Beer F, et al. Further morphological evidence on South African earliest Homo lower postcanine dentition: enamel thickness and enamel dentine junction[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2016,96:82-96
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2016.05.003 URL pmid: 27343773 |
| [24] |
Zanolli C, Kullmer O, Kelley J, et al. Evidence for increased hominid diversity in the Early-Middle Pleistocene of Java, Indonesia[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2019,3:755-764
doi: 10.1038/s41559-019-0860-z URL pmid: 30962558 |
| [25] |
Zanolli C, Martinón-Torres M, Bernardini F, et al. The Middle Pleistocene (MIS 12) human dental remains from Fontana Ranuccio (Latium) and Visogliano (Friuli-Venezia Giulia), Italy. A comparative high resolution endostructural assessment[J]. PLOS ONE, 2018,13:e0189773
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189773 URL pmid: 30281595 |
| [26] |
Olejniczak A, Smith TM, Skinner MM, et al. Three-dimensional molar enamel distribution and thickness in Australopithecus and Paranthropus[J]. Biology Letters, 2008,4:406-410
doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2008.0223 URL pmid: 18522924 |
| [27] |
Smith TM, Olejniczak AJ, Zermeno JP, et al. Variation in enamel thickness within the genus Homo[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2012,62:395-411
URL pmid: 22361504 |
| [28] |
Braga J, Zimmer V, Dumoncel J, et al. Efficacy of diffeomorphic surface matching and 3D geometric morphometrics for taxonomic discrimination of Early Pleistocene hominin mandibular molars[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2019,130:21-35
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2019.01.009 URL pmid: 31010541 |
| [29] |
Durrleman S, Pennec X, Trouvé A, et al. Comparison of the endocranial ontogenies between chimpanzees and bonobos via temporal regression and spatiotemporal registration[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2012,62:74-88
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2011.10.004 URL pmid: 22137587 |
| [30] |
Beaudet A, Dumoncel J, de Beer F, et al. Morphoarchitectural variation in South African fossil cercopithecoid endocasts[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2016,101:65-78
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2016.09.003 URL pmid: 27886811 |
| [31] |
Beaudet A, Dumoncel J, Thackeray F, et al. Upper third molar internal structural organization and semicircular canal morphology in Plio-Pleistocene South African cercopithecoids[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2016,95:104-120
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2016.04.004 URL pmid: 27260177 |
| [32] |
Urciuoli A, Zanolli C, Beaudet A, et al. The evolution of the vestibular apparatus in apes and humans[J]. eLife, 2020,9:e51261
URL pmid: 32122463 |
| [33] |
Zanolli C, Pan L, Dumoncel J, et al. Inner tooth morphology of Homo erectus from Zhoukoudian. New evidence from an old collection housed at Uppsala University, Sweden[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2018,116:1-13
URL pmid: 29477178 |
| [34] |
Morimoto N, De León MSP, Zollikofer CPE. Exploring femoral diaphyseal shape variation in wild and captive chimpanzees by means of morphometric mapping: A test of Wolff's law[J]. The Anatomical Record, 2011,294:589-609
URL pmid: 21328564 |
| [35] |
Puymerail L, Ruff CB, Bondioli L, et al. Structural analysis of the Kresna 11 Homo erectus femoral shaft (Sangiran, Java)[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2012,63:741-749
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2012.08.003 URL pmid: 23036460 |
| [36] | Puymerail L, Volpato V, Debénath A, et al. A Neanderthal partial femoral diaphysis from the “grotte de la Tour”, La Chaise-de-Vouthon (Charente, France): Outer morphology and endostructural organization[J]. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 2012,11:581-593 |
| [37] | Wei P, Wallace IJ, Jashashvili T, et al. Structural analysis of the femoral diaphyses of an early modern human from Tianyuan Cave, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2017,434:48-56 |
| [38] | Jashashvili T, Dowdeswell MR, Lebrun R, et al. Cortical structure of hallucal metatarsals and locomotor adaptations in hominoids[J]. PLOS ONE, 2015,10:e0117905 |
| [39] |
Zanolli C, Bondioli L, Coppa A, et al. The late Early Pleistocene human dental remains from Uadi Aalad and Mulhuli-Amo (Buia), Eritrean Danakil: macromorphology and microstructure[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2014,74:96-113
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2014.04.005 URL pmid: 24852385 |
| [40] |
Molnar S. Human tooth wear, tooth function and cultural variability[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1971,34:175-189
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330340204 URL pmid: 5572602 |
| [41] | NESPOS database. Neanderthal Studies Professional Online Service[DB/OL], 2019, https://www.nespos.org/display/openspace/Home |
| [42] | Dumoncel J, Durrleman S, Braga J, et al. Landmark-free 3D method for comparison of fossil hominins and hominids based on endocranium and EDJ shapes[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2014, 153: suppl.56, 110 |
| [43] |
Durrleman S, Pennec X, Trouvé A, et al. Comparison of the endocranial ontogenies between chimpanzees and bonobos via temporal regression and spatiotemporal registration[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2012,62:74-88
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2011.10.004 URL pmid: 22137587 |
| [44] |
Durrleman S, Prastawa M, Charon N, et al. Morphometry of anatomical shape complexes with dense deformations and sparse parameters[J]. NeuroImage, 2014,101:35-49
URL pmid: 24973601 |
| [45] | Durrleman S, Prastawa M, Korenberg JR, et al. Topology preserving atlas construction from shape data without correspondence using sparse parameters[A]. In: Ayache, N, Delingette, H, Golland, P, Mori, K (Eds.), Proceedings of Medical image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention[C]. Springer, Nice, France, 2012: 223-230 |
| [46] |
Durrleman S, Prastawa M, Charon N, et al. Morphometry of anatomical shape complexes with dense deformations and sparse parameters[J]. NeuroImage, 2014,101:35-49
URL pmid: 24973601 |
| [47] | Bône A, Louis M, Martin B, et al. Deformetrica 4: An open-source software for statistical shape analysiss[A]//International Workshop on Shape in Medical Imaging[C]. Springer, Cham, 2018: 3-13 |
| [48] | R Development Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing[EB/OL],. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, 2012 |
| [49] | Dray S, Dufour AB. The ade4 package: Implementing the duality diagram for ecologists[J]. Journal of statistical software, 2007,22:1-20 |
| [50] |
Schlager S, Profico A, Di Vincenzo F, et al. Retrodeformation of fossil specimens based on 3D bilateral semi-landmarks: Implementation in the R package “Morpho”[J]. PLOS ONE, 2018,13:e0194073
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194073 URL pmid: 29554122 |
| [51] | Dumoncel J. add_colormap_shooting.py[CP/OL],, 2020, https://gitlab.com/jeandumoncel/tools-for-deformetrica/-/blob/master/src/postprocessing/add_colormap_shooting.py |
| [52] |
Wu X-J, Pei S-W, Cai Y-J, et al. Archaic human remains from Hualongdong, China, and Middle Pleistocene human continuity and variation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 2019,116:9820-9824
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902396116 URL |
| [53] |
Chen F, Welker F, Shen C-C, et al. A late Middle Pleistocene Denisovan mandible from the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Nature, 2019,569:409-412
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1139-x URL pmid: 31043746 |
| [54] |
Pan L, Dumoncel J, Mazurier A, et al. Structural analysis of premolar roots in Middle Pleistocene hominins from China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2019,136:102669
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2019.102669 URL pmid: 31614276 |
| [55] | Wu XJ, Trinkaus E. The Xujiayao 14 Mandibular Ramus and Pleistocene Homo Mandibular Variation[J]. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 2014,13:333-341 |
| [56] | Wu XJ, Crevecoeur I, Liu W, et al. Temporal labyrinths of eastern Eurasian Pleistocene humans[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 2014,111:10509-10513 |
| [1] | 祝海歌, 乔辉, 杨晨, 管海娟, 张航, 文少卿, 夏斌, 谭婧泽. 中国汉族、回族、蒙古族、苗族和维吾尔族的牙齿形态[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(04): 613-628. |
| [2] | 陈峰, 曾雨欣, 付昶, 张海龙, 王博, 肖小勇, 李海军. 新疆且末扎滚鲁克墓地二期居民的牙齿磨耗[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 273-286. |
| [3] | 陈晓颖, 游海杰, 宋美玲, 郭明晓, 肖雨妮, 曾雯. 广西敢造遗址史前居民口腔的健康状况[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(01): 98-109. |
| [4] | 雷帅, 郭怡. 生物考古学视野下人类的牙齿与饮食[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(03): 501-513. |
| [5] | 杨诗雨, 张群, 王龙, 张全超. 新疆吐鲁番胜金店墓地人骨的牙齿微磨耗[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 218-225. |
| [6] | 熊建雪, 陈国科, 殷杏, 蒙海亮, 杨谊时, 陶驿辰, 谭婧泽, 李辉, 文少卿. 黑水国遗址汉代人群的上颌窦炎症[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(05): 776-786. |
| [7] | 李海军, 陈慧敏, 刘力铭, 刘琳如. 儿童牙齿磨耗研究概述[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(04): 695-705. |
| [8] | 华李成, Peter S UNGAR. 牙齿微痕研究在古食性重建中应用的简述[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(02): 292-306. |
| [9] | 周亚威, 张晓冉, 顾万发. 郑州汪沟遗址仰韶文化居民的牙齿磨耗及口腔健康状况[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(01): 49-62. |
| [10] | 潘雷, 廖卫, 王伟, 刘建辉, 吉学平, 杨晓梅, 郝以鑫. 禄丰古猿蝴蝶种下第四前臼齿釉质-齿质交界面的三维几何形态[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 555-563. |
| [11] | 潘雷. 人类牙齿齿冠和齿根分离两种技术方法对牙釉质厚度测量的影响[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(03): 398-406. |
| [12] | 孙承凯, 孙小玲, 周蜜, 刘立群, 邢松. 山东新泰乌珠台人类牙齿的形态学特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(03): 446-459. |
| [13] | 张雅军, 仝涛, 李林辉, 赤列次仁. 西藏故如甲木墓地人群牙齿磨耗和食物结构的关系[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(01): 107-118. |
| [14] | 刘武;周蜜;邢松. 卡氏尖在中国古人类化石中出现及其演化意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(02): 159-175. |
| [15] | 赵凌霞;李璇;顾雪军;杜抱朴;史家珍;高星. 河南栾川发现直立人化石及其演化意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(02): 192-205. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 611
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 852
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3