

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (04): 632-647.doi: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0021cstr: 32091.14.j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0021
赵昱浩1,2,3( ), 周蜜4, 魏偏偏5, 邢松1,2,*(
), 周蜜4, 魏偏偏5, 邢松1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-02-25
修回日期:2020-04-09
出版日期:2020-11-15
发布日期:2020-11-23
通讯作者:
邢松
作者简介:赵昱浩(1996-),男,中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所硕士研究生。Email:基金资助:
ΖΗΑΟ Yuhao1,2,3( ), ΖHOU Mi4, WEI Pianpian5, XING Song1,2,*(
), ΖHOU Mi4, WEI Pianpian5, XING Song1,2,*( )
)
Received:2020-02-25
Revised:2020-04-09
Online:2020-11-15
Published:2020-11-23
Contact:
XING Song
摘要:
形态示量图是一种展示三维形态测量信息的二维可视化手段,能有效地反应骨密质厚度的分布特点。虽然现代人、更新世古老型人类和大猿的骨密质厚度分布存在差别,但全新世现代人内部是否有变异存在尚未被充分研究。本文选择全新世华中、华北地区的6个农业人群的34例右侧肱骨标本(23例男性、11例女性),使用形态示量图对其骨干骨密质厚度的分布特征进行了全面分析。在方法上,本文比较了通过厚度最大值和生物力学长度对骨密质厚度进行标准化后分析结果的差别,并验证了主成分分析在形态示量图上的适用性。结果显示,在全新世华中、华北地区的农业人群中,男、女的厚度分布模式存在一定差异,而不同人群男性的差别并不明显。本文虽通过全新世华中、华北地区的农业人群揭示出全新世现代人在肱骨骨干骨密质厚度分布上存在一定程度的变异,但仍需在未来工作中依托本文方法,选择人群种类更丰富、标本量更大、个体变量控制更严格的材料,进一步验证或扩展本文所得结论。
中图分类号:
赵昱浩, 周蜜, 魏偏偏, 邢松. 肱骨骨干骨密质厚度的二维可视化及其定量分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 632-647.
ΖΗΑΟ Yuhao, ΖHOU Mi, WEI Pianpian, XING Song. 2D visualization and quantitative analysis of the humeral diaphysis cortical thickness[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2020, 39(04): 632-647.
| 地点 Site | 时代 Chronological age | 男Male | 女 Female |
|---|---|---|---|
| 河南省淅川县马岭Maling, Xichuan, Henan | 后冈一期Hougang I | 4 | 2 |
| 湖北省江陵县高台Gaotai, Jiangling, Hubei | 汉代Han Dynasty | 5 | 3 |
| 湖北省武汉市新洲区邾城工业园Zhucheng industrial park, Wuhan, Hubei | 汉代Han Dynasty | 1 | 1 |
| 湖北省房县计家湾Jijiawan, Fang, Hubei | 秦代Qin Dynasty | 1 | 1 |
| 湖北省襄阳市吴家坡Wujiapo, Xiangyang, hubei | 唐代Tang Dynasty | 2 | 0 |
| 河南省新乡市君子村Junzicun, Xinxiang, Henan | 清代Qing Dynasty | 10 | 4 |
表1 本文所用肱骨标本的基本信息*
Tab.1 The basic information of humeri used in the present study*
| 地点 Site | 时代 Chronological age | 男Male | 女 Female |
|---|---|---|---|
| 河南省淅川县马岭Maling, Xichuan, Henan | 后冈一期Hougang I | 4 | 2 |
| 湖北省江陵县高台Gaotai, Jiangling, Hubei | 汉代Han Dynasty | 5 | 3 |
| 湖北省武汉市新洲区邾城工业园Zhucheng industrial park, Wuhan, Hubei | 汉代Han Dynasty | 1 | 1 |
| 湖北省房县计家湾Jijiawan, Fang, Hubei | 秦代Qin Dynasty | 1 | 1 |
| 湖北省襄阳市吴家坡Wujiapo, Xiangyang, hubei | 唐代Tang Dynasty | 2 | 0 |
| 河南省新乡市君子村Junzicun, Xinxiang, Henan | 清代Qing Dynasty | 10 | 4 |
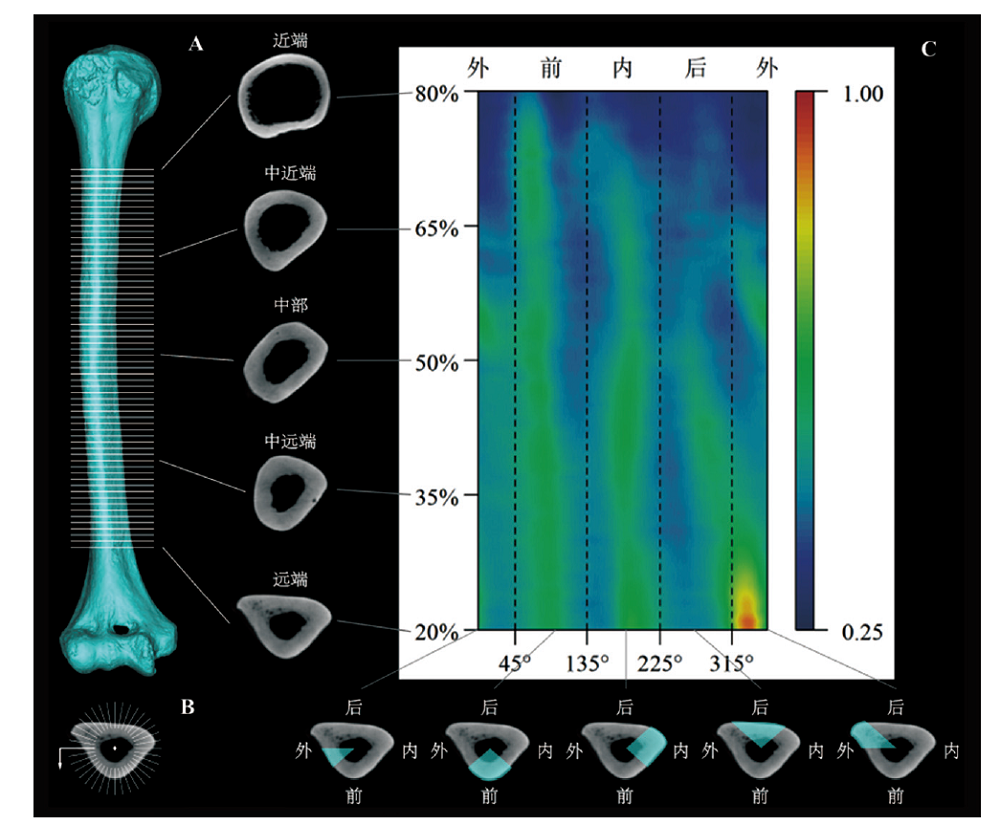
图1 形态示量图原理示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of morphometric maps (MM) Y axis of MM (from top to bottom): proximal, mid-proximal, midshaft, mid-distal, distal; X axis of MM (from left to right): lateral, anterior, medial, posterior, lateral.
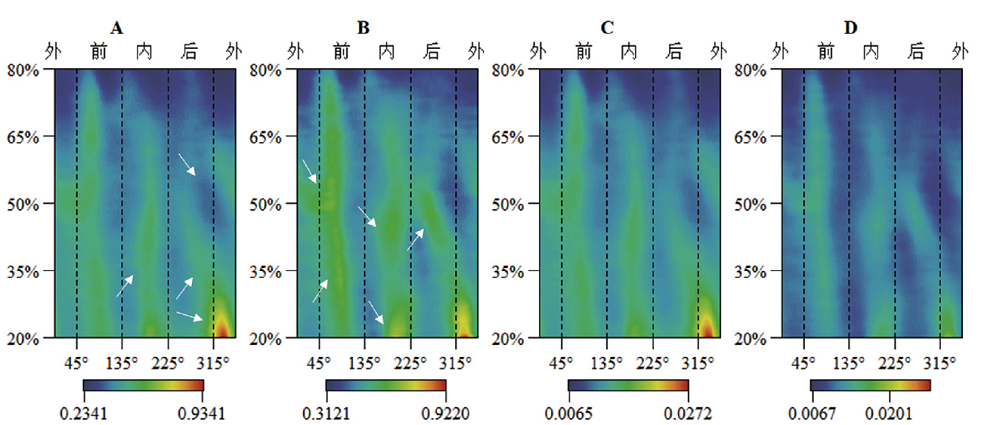
图2 男、女的平均形态示量图 A、B:通过厚度最大值标准化;C、D:通过生物力学长度标准化;A、C:男性;B、D:女性;白色箭头指示反映男、女厚度分布差异的位置
Fig.2 Mean morphometric maps of male and female A, B: Standardized by maximum thickness; C, D: Standardized by biomechanical length; A, C: males; B, D: females; The white arrows indicate the positions that reflect the difference in thickness distribution between male and female
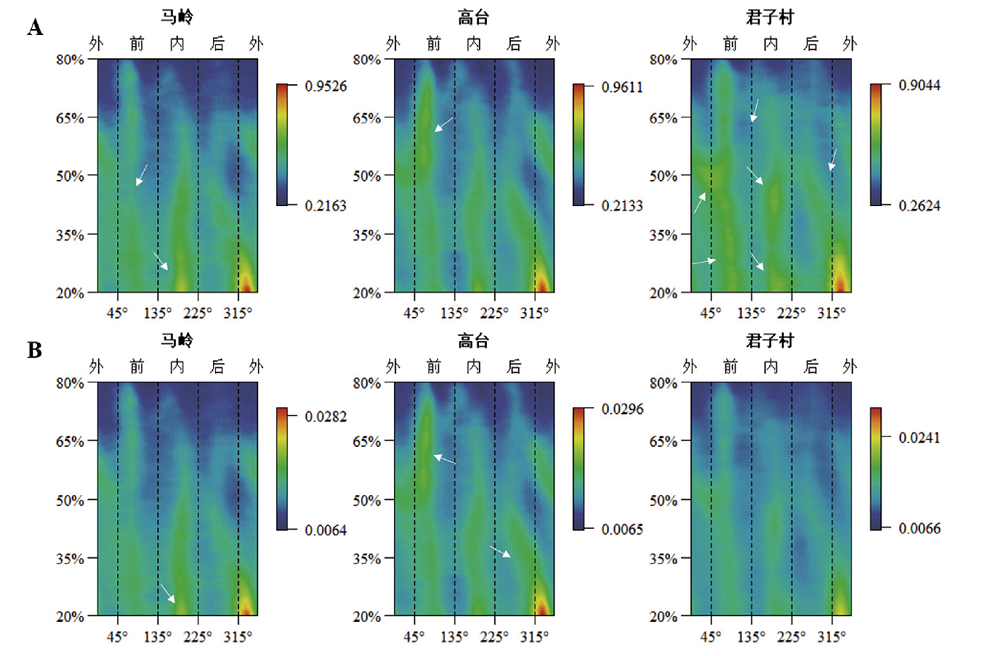
图3 人群的平均形态示量图 A:通过厚度最大值标准化;B:通过生物力学长度标准化;白色箭头指示反应人群厚度分布差异的位置
Fig.3 Mean morphometric maps of different populations A: Standardized by maximum thickness; B: Standardized by biomechanical length; The white arrows indicate the positions that reflect the differences in thickness distribution between different populations. From left to right: Maling, Gaotai, Junzicun.
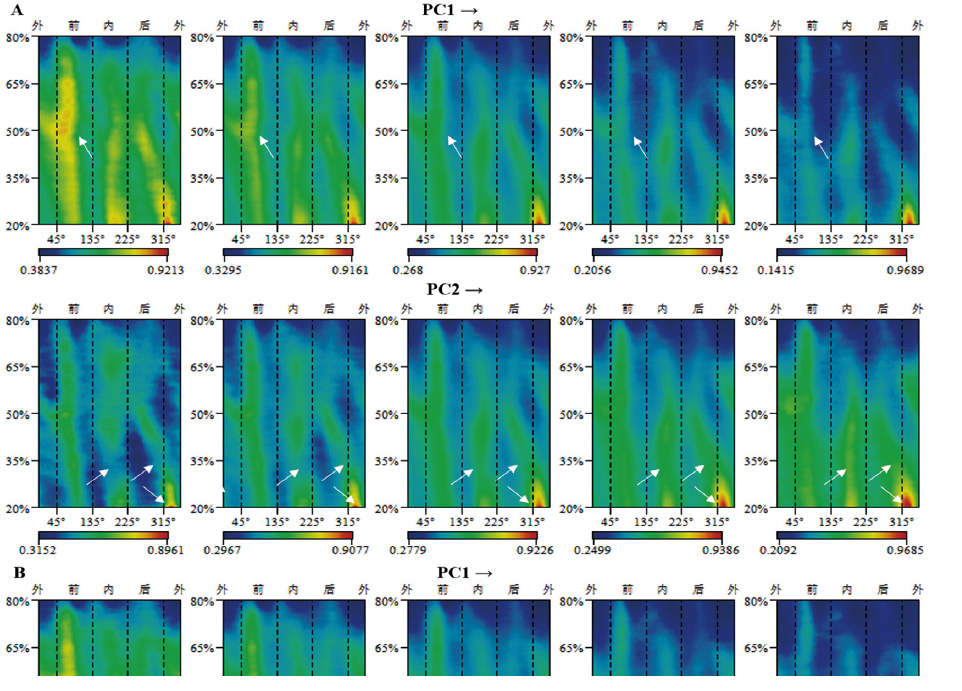
图4 通过厚度最大值标准化后的主成分分析结果 A:全部标本的主成分分析结果,主要展示性别差异;B:全部男性标本的主成分分析结果,用于展示人群差异
Fig.4 The results of PCA after standardized by maximum thickness A: The PCA results of all specimens for demonstrating gender differences primarily. B: The PCA results of all male specimens for demonstrating population differences

图5 通过厚度最大值标准化后的主成分分析结果所对应的形态示量图变化模式 A:全部标本的主成分分析结果对应的形态示量图变化模式,主要展示性别差异;B:全部男性标本的主成分分析结果对应的形态示量图变化模式,用于展示人群差异;→:分析结果中PC值由小变大的方向。白色箭头指示反应性别或人群厚度分布差异的位置
Fig.5 The changing pattern of morphometric maps corresponding to the PCA results after standardized by maximum thickness A: The changing pattern of morphometric maps corresponding to the PCA results of all specimens for demonstrating gender differences primarily; B: The changing pattern of morphometric maps corresponding to the PCA results of all male specimens for demonstrating population differences; →:the direction which the PC value changes from small to large in the PCA results. The white arrows indicate the positions that reflect the differences in thickness distribution between different genders or populations
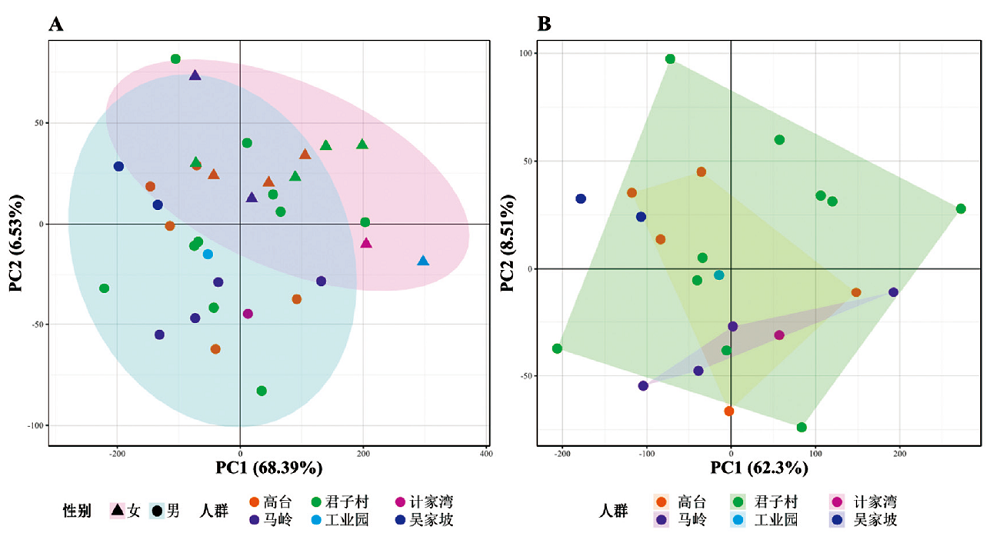
图6 通过生物力学长度标准化后的主成分分析结果 A:全部标本的主成分分析结果,主要展示性别差异;B:全部男性标本的主成分分析结果,用于展示人群差异
Fig.6 The results of PCA after standardized by biomechanical length A: The PCA results of all specimens for demonstrating gender differences primarily. B: The PCA results of all male specimens for demonstrating population differences
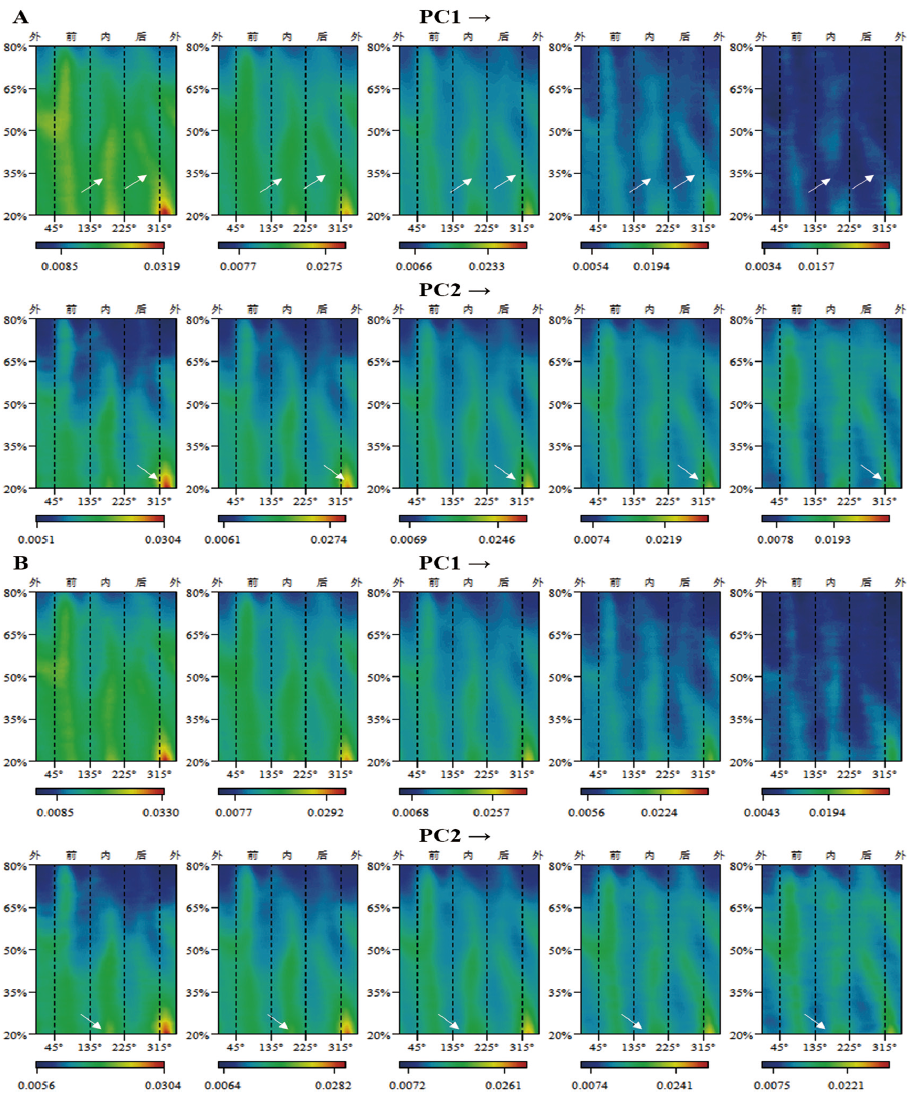
图7 通过生物力学长度标准化后的主成分分析结果所对应的形态示量图变化模式 A:全部标本的主成分分析结果对应的形态示量图变化模式,主要展示性别差异;B:全部男性标本的主成分分析结果对应的形态示量图变化模式,用于展示人群差异;→:分析结果中PC值由小变大的方向。白色箭头指示反应性别或人群厚度分布差异的位置
Fig.7 The changing pattern of morphometric maps corresponding to the PCA results after standardized by biomechanical length A: The changing pattern of morphometric maps corresponding to the PCA results of all specimens for demonstrating gender differences primarily; B: The changing pattern of morphometric maps corresponding to the PCA results of all male specimens for demonstrating population differences; →:the direction which the PC value changes from small to large in the PCA results. The white arrows indicate the positions that reflect the differences in thickness distribution between different genders or populations
| [1] |
Morimoto N, Zollikofer CPE, Ponce de León MS. Shared human-chimpanzee pattern of perinatal femoral shaft morphology and its implications for the evolution of hominin locomotor adaptations[J]. PLOS ONE, 2012,7(7):e41980
URL pmid: 22848680 |
| [2] | Carlson KJ, Marchi D. Reconstructing mobility[M]. New York: Springer, 2014 |
| [3] |
Carlson KJ, Sumner DR, Morbeck ME, et al. Role of nonbehavioral factors in adjusting long bone diaphyseal structure in free-ranging Pan troglodytes[J]. Int J Primatol, 2008,29(6):1401-1420
doi: 10.1007/s10764-008-9297-y URL pmid: 19816545 |
| [4] | 吴汝康, 贾兰坡. 周口店新发现的中国猿人化石[J]. 古生物学报, 1954, 2(3): 267-288+348-354 |
| [5] | 张旭, 李婧, 朱泓. 内蒙古和林格尔县大堡山墓地古代居民的肢骨研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2015,34(2):216-224 |
| [6] | 陈德珍, 吴新智. 河南长葛石固早期新石器时代人骨的研究(续)[J]. 人类学学报, 1985,4(4):314-323 |
| [7] | Trinkaus E, Ruff CB. Femoral and tibial diaphyseal cross-sectional geometry in Pleistocene Homo[J]. PaleoAnthropology, 2012: 13-62 |
| [8] |
Ruff CB, Hayes WC. Cross-sectional geometry of Pecos Pueblo femora and tibiae—A biomechanical investigation: I. Method and general patterns of variation[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol, 1983,60(3):359-381
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330600308 URL pmid: 6846510 |
| [9] |
Ruff CB, Hayes WC. Cross-sectional geometry of Pecos Pueblo femora and tibiae—A biomechanical investigation: II. Sex, age, and side differences[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol, 1983,60(3):383-400
URL pmid: 6846511 |
| [10] |
Sparacello VS, Villotte S, Shackelford LL, et al. Patterns of humeral asymmetry among Late Pleistocene humans[J]. C R Palevol, 2017,16(5):680-689
doi: 10.1016/j.crpv.2016.09.001 URL |
| [11] | Ruff CB. Biomechanical analyses of archaeological human skeletons[M]. Katzenberg M A, Grauer A L. Biological anthropology of the human skeleton. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2019, 189-224 |
| [12] |
Amtmann E, Schmitt HP. Über die Verteilung der Corticalisdichte im menschlichen Femurschaft und ihre Bedeutung für die Bestimmung der Knochenfestigkeit[J]. Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte, 1968,127(1):25-41
doi: 10.1007/BF00523600 URL |
| [13] | Amtmann E. Mechanical stress, functional adaptation and the variation structure of the human femur diaphysis[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1971 |
| [14] | Zollikofer CPE, Ponce de León MS. Computer-assisted morphometry of hominoid fossils: the role of morphometric maps[M]. Phylogeny of the Neogene hominoid primates of Eurasia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001, 50-59 |
| [15] |
Bondioli L, Bayle P, Dean C, et al. Technical note: Morphometric maps of long bone shafts and dental roots for imaging topographic thickness variation[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol, 2010,142(2):328-334
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.21271 URL pmid: 20229503 |
| [16] |
Puymerail L, Ruff CB, Bondioli L, et al. Structural analysis of the Kresna 11 Homo erectus femoral shaft (Sangiran, Java)[J]. J Hum Evol, 2012,63(5):741-749
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2012.08.003 URL |
| [17] | Puymerail L, Volpato V, Debénath A, et al. A Neanderthal partial femoral diaphysis from the “grotte de la Tour”, La Chaise-de-Vouthon (Charente, France): Outer morphology and endostructural organization[J]. C R Palevol, 2012,11(8):581-593 |
| [18] |
Zanolli C, Bondioli L, Coppa A, et al. The late Early Pleistocene human dental remains from Uadi Aalad and Mulhuli-Amo (Buia), Eritrean Danakil: Macromorphology and microstructure[J]. J Hum Evol, 2014,74:96-113
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2014.04.005 URL pmid: 24852385 |
| [19] |
Jashashvili T, Dowdeswell MR, Lebrun R, et al. Cortical Structure of Hallucal Metatarsals and Locomotor Adaptations in Hominoids[J]. PLOS ONE, 2015,10(1):e0117905
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117905 URL |
| [20] |
Morimoto N, Ponce de León MS, Zollikofer CPE. Exploring femoral diaphyseal shape variation in wild and captive chimpanzees by means of morphometric mapping: a test of Wolff’s law[J]. The Anatomical Record, 2011,294(4):589-609
doi: 10.1002/ar.21346 URL pmid: 21328564 |
| [21] | Puymerail L. The functionally-related signatures characterizing the endostructural organisation of the femoral shaft in modern humans and chimpanzee[J]. C R Palevol, 2013,12(4):223-231 |
| [22] | Wei PP, Wallace IJ, Jashashvili T, et al. Structural analysis of the femoral diaphyses of an early modern human from Tianyuan Cave, China[J]. Quat Int, 2017,434:48-56 |
| [23] |
Ruff C. Growth tracking of femoral and humeral strength from infancy through late adolescence[J]. Acta Paediatr, 2005,94(8):1030-1037
doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2005.tb02041.x URL pmid: 16188845 |
| [24] |
Sumner DR, Andriacchi TP. Adaptation to differential loading: Comparison of growth-related changes in cross-sectional properties of the human femur and humerus[J]. Bone, 1996,19(2):121-126
URL pmid: 8853855 |
| [25] |
Morimoto N, Nakatsukasa M, Ponce de León MS, et al. Femoral ontogeny in humans and great apes and its implications for their last common ancestor[J]. Sci Rep, 2018,8(1):1930
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20410-4 URL pmid: 29386644 |
| [26] |
Dupej J, Lacoste Jeanson A, Pelikán J, et al. Semiautomatic extraction of cortical thickness and diaphyseal curvature from CT scans[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol, 2017,164(4):868-876
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.23315 URL pmid: 28913906 |
| [27] | 邵象清. 人体测量手册[M]. 上海: 上海辞书出版社, 1985 |
| [28] | 吴汝康, 吴新智, 张振标. 人体测量方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984 |
| [29] |
Ruff CB. Long bone articular and diaphyseal structure in old world monkeys and apes. I: Locomotor effects[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol, 2002,119(4):305-342
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.10117 URL pmid: 12448016 |
| [30] | R Development Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing[M]. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria. 2019 |
| [31] | Bishop CM. Pattern recognition and machine learning[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2006 |
| [32] | 何晓群. 多元统计分析[M]. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2019 |
| [33] | 费宇, 郭民之, 陈贻娟. 多元统计分析——基于R[M]. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2014 |
| [34] | Klovan JE. R-and Q-Mode Factor Analysis[M]. McCammon R B. Concepts in Geostatistics. Berlin: Springer Berlin, 1975, 21-69 |
| [35] |
Março PH, Scarminio IS. Q-mode curve resolution of UV-vis spectra for structural transformation studies of anthocyanins in acidic solutions[J]. Anal Chim Acta, 2007,583(1):138-146
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2006.09.057 URL pmid: 17386538 |
| [36] | Paatero P, Tapper U. Analysis of different modes of factor analysis as least squares fit problems[J]. Chemometrics Intell Lab Syst, 1993,18(2):183-194 |
| [37] | Steyn M, İşcan MY. Osteometric variation in the humerus: sexual dimorphism in South Africans[J]. Forensic SciInt, 1999,106(2):77-85 |
| [38] |
Sládek V, Ruff CB, Berner M, et al. The impact of subsistence changes on humeral bilateral asymmetry in Terminal Pleistocene and Holocene Europe[J]. J Hum Evol, 2016,92:37-49
URL pmid: 26989015 |
| [39] | Lovejoy CO, McCollum MA, Reno PL, et al. Developmental biology and human evolution[J]. Annu Rev Anthropol, 2003,32(1):85-109 |
| [40] | Chiu CH, Hamrick MW. Evolution and development of the primate limb skeleton[J]. Evol Anthropol, 2002,11(3):94-107 |
| [41] | Pearson OM, Lieberman DE. The aging of Wolff’s “law”: Ontogeny and responses to mechanical loading in cortical bone[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol, 2004,125(S39):63-99 |
| [42] |
Ruff C, Holt B, Trinkaus E. Who’s afraid of the big bad wolff? “Wolff is law” and bone functional adaptation[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol, 2006,129(4):484-498
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.20371 URL pmid: 16425178 |
| [43] | Hsieh YF, Robling AG, Ambrosius WT, et al. Mechanical Loading of Diaphyseal Bone In Vivo: The Strain Threshold for an Osteogenic Response Varies with Location[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2001,16(12):2291-2297 |
| [44] |
Burr DB, Robling AG, Turner C H. Effects of biomechanical stress on bones in animals[J]. Bone, 2002,30(5):781-786
URL pmid: 11996920 |
| [45] |
Niinimäki S, Söderling S, Junno JA, et al. Cortical bone thickness can adapt locally to muscular loading while changing with age[J]. Homo, 2013,64(6):474-490
doi: 10.1016/j.jchb.2013.07.004 URL pmid: 24028817 |
| [1] | 刘驷统, 顾万发, 吴倩, 周亚威. 河南双槐树遗址人群肱骨肌腱的起止点形变[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 757-766. |
| [2] | 赵永生, 孙田璐, 杨张翘楚, 王子孟, 刘文涛, 曾雯. 山东古代居民骨化甲状软骨的观测[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(02): 214-224. |
| [3] | 周亚威, 王惠, 丁思聪, 陈博. 东周一例人体肱骨发育不对称的病理分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(01): 87-97. |
| [4] | 张全超, 孙语泽, 侯亮亮, 吉平, 朱永刚. 哈民忙哈遗址人和动物骨骼的C、N稳定同位素分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 261-273. |
| [5] | 魏偏偏, 赵昱浩, 何嘉宁. 辽宁建平古人类肱骨形态结构分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(06): 943-954. |
| [6] | 孙泽阳, 郑连斌, 宇克莉, 张兴华. 孟高棉语族未识别民族的体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(05): 811-823. |
| [7] | 张兴华, 宇克莉, 郑连斌. 中国14个特殊旁系族群的头面部特征比较[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(02): 226-238. |
| [8] | 魏偏偏. 云南丽江古人类股骨的形态结构[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 616-631. |
| [9] | 张亚盟;魏偏偏;吴秀杰. 现代人头骨断面轮廓的性别鉴定——基于几何形态测量的研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2016, 35(02): 172-180. |
| [10] | 郑连斌;陆舜华;罗东梅;许渤松. 怒族的体质调查[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(02): 156-164. |
| [11] | 吴秀杰;张全超;李海军. 聚类分析和主成分分析方法在人类学研究中价值的判定[J]. 人类学学报, 2007, 26(04): 361-371. |
| [12] | 郑连斌;陆舜华;于会新;刘海萍. 佤族的体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2007, 26(03): 249-258. |
| [13] | 薛付忠,王洁贞,郭亦寿,胡平. 人类群体遗传结构的协方差阵主成分分析方法[J]. 人类学学报, 2005, 24(03): 221-231. |
| [14] | 郑连斌,陆舜华,郑琪,栗淑媛. 中国人群肤纹的主成分分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2002, 21(03): 231-238. |
| [15] | 郑连斌,郑明霞,陆舜华,栗淑媛,郑琪,李咏兰. 亚洲21个人群体部特征的比较研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2000, 19(01): 49-56. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 434
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 602
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3