

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (04): 706-716.doi: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0062
收稿日期:2020-07-30
修回日期:2020-09-27
出版日期:2020-11-15
发布日期:2020-11-23
通讯作者:
王传超
作者简介:赵静(1987-),西安交通大学博士,主要从事生物考古和古人类DNA研究,E-mail:基金资助:
ZHAO Jing1,2( ), WANG Chuanchao1(
), WANG Chuanchao1( )
)
Received:2020-07-30
Revised:2020-09-27
Online:2020-11-15
Published:2020-11-23
Contact:
WANG Chuanchao
摘要:
从古代原始材料中提取古DNA的方法多种多样,但是古DNA的研究受限于降解严重,内源性古DNA含量低,微生物和现生人群DNA污染严重等因素的影响。能否从古代人类遗骸中成功获取可靠且足量的内源性古DNA,一直是古DNA研究领域面临的实际困难和挑战。控制污染最直接且简便的策略就是在古DNA提取阶段的有效排除,本文整理了古DNA提取常用的去除污染的方法,对比分析了每种方法表现出来的优缺点。介绍了通常使用的骨粉裂解时间,并研究了在常温环境下,不同的裂解时间对古DNA回收效率的影响,提出了常温裂解过程中最佳孵育时间。同时对常用的古DNA纯化方法及其原理和在实际应用中的表现进行了概述与讨论。本文对古DNA提取技术的概述和实践经验,为古DNA相关领域的研究提供借鉴与参考。
中图分类号:
赵静, 王传超. 古DNA提取技术对比及概述[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 706-716.
ZHAO Jing, WANG Chuanchao. Comparison and summary of ancient DNA extraction technology[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2020, 39(04): 706-716.
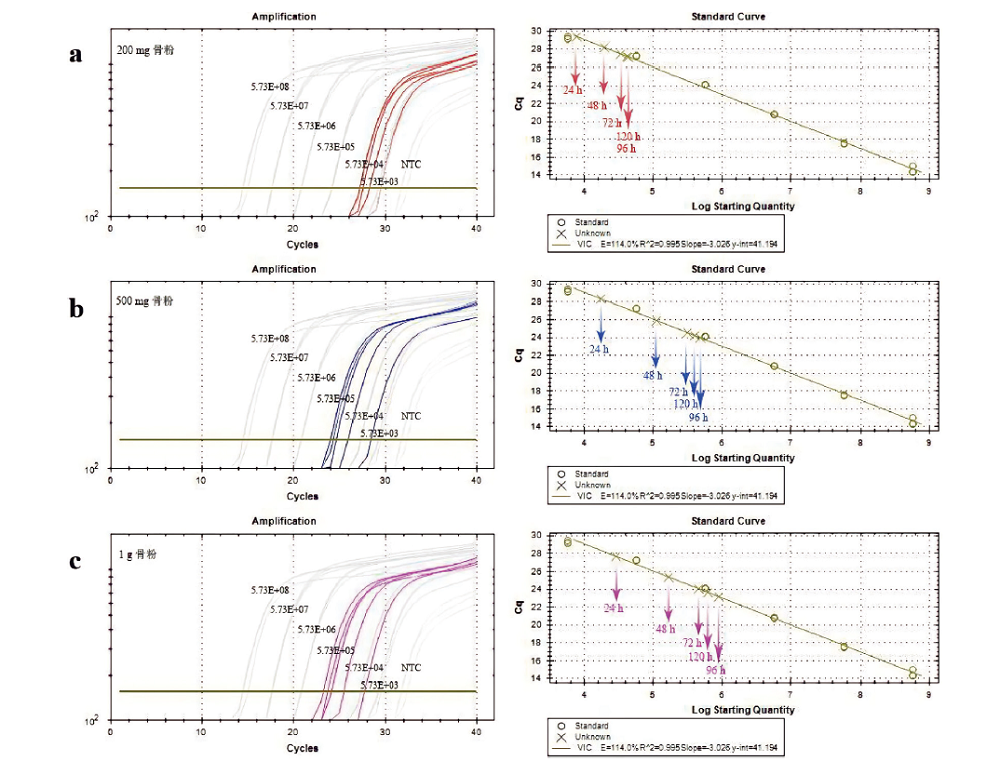
图1 常温条件下不同的孵育时间对DNA提取效率的影响 注:左侧为扩增曲线,X轴对应PCR扩增循环数,Y轴对应荧光强度值;右侧为标准曲线,X轴为模板的起始拷贝数的对数,Y轴为每个反应荧光信号到达设定阈值时所经历的循环数。a 200mg骨粉在5个不同裂解时间下的扩增曲线和标准曲线;b 500mg骨粉在5个不同裂解时间下的扩增曲线和标准曲线;c 1g骨粉在5个不同裂解时间下的扩增曲线和标准曲线。
Fig.1 The effect of different incubation time on DNA extraction efficiency at room temperature
| [1] |
Campos PF, Willerslev E, Sher A, et al. Ancient DNA analyses exclude humans as the driving force behind late Pleistocene musk ox (Ovibos moschatus) population dynamics[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010,107(12):5675-5680
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907189107 URL pmid: 20212118 |
| [2] |
Leonard JA, Wayne RK, Cooper A. Population genetics of ice age brown bears[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2000,97(4):1651-1654
doi: 10.1073/pnas.040453097 URL pmid: 10677513 |
| [3] |
Pinsky ML, Newsome SD, Dickerson BR, et al. Dispersal provided resilience to range collapse in a marine mammal: insights from the past to inform conservation biology[J]. Mol Ecol, 2010,19(12):2418-2429
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04671.x URL pmid: 20497323 |
| [4] | Shapiro B, Drummond AJ, Rambaut A, et al. Rise and fall of the Beringian steppe bison[J]. Science, 2004,306(5701):1561-1565 |
| [5] |
Stiller M, Baryshnikov G, Bocherens H, et al. Withering away--25,000 years of genetic decline preceded cave bear extinction[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2010,27(5):975-978
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq083 URL pmid: 20335279 |
| [6] |
Ning C, Li TJ, Wang K, et al. Ancient genomes from northern China suggest links between subsistence changes and human migration[J]. Nature communications, 2020,11(1):2700
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16557-2 URL pmid: 32483115 |
| [7] | Wang K, Goldstein S, Bleasdale M, et al. Ancient genomes reveal complex patterns of population movement, interaction, and replacement in sub-Saharan Africa[J]. Science Advance, 2020, 6 eaaz0183 |
| [8] |
Narasimhan VM, Patterson N, Moorjani P, et al. The Genomic Formation of South and Central Asia[J]. bioRxiv, 2018
doi: 10.1101/2020.11.06.371971 URL pmid: 33173866 |
| [9] |
Green RE, Krause J, Briggs AW, et al. A draft sequence of the Neandertal genome[J]. Science, 2010,328(5979):710-722
doi: 10.1126/science.1188021 URL pmid: 20448178 |
| [10] | Shapiro B, Sibthorpe D, Rambaut A, et al. Flight of the Dodo[J]. Science, 2002,2951683 |
| [11] | Krause J, Unger T, Nocon A, et al. Mitochondrial genomes reveal an explosive radiation of extinct and extant bears near the Miocene-Pliocene boundary[J]. BMC Evol Biol, 2008,8220 |
| [12] | Orlando L, Metcalf J, Alberdi M, et al. Revising the recent evolutionary history of equids using ancient DNA[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009, 10621754-21759 |
| [13] | Barquera R, Krause J. An ancient view on host-pathogen interaction across time and space[J]. Current opinion in immunology, 2020, 6565-69. |
| [14] | 吴苡婷. 古DNA检测技术在抗击新冠中的特殊作用[N]. 上海科技报, 2020. |
| [15] | Collins MJ, Nielsen-Marsh CM, Hiller J, et al. The survival of organic matter in bone: a review[J]. Archaeometry, 2002,44(3):383-394 |
| [16] |
Hofreiter M, Paijmans JL, Goodchild H, et al. The future of ancient DNA: Technical advances and conceptual shifts[J]. Bioessays, 2015,37(3):284-293
doi: 10.1002/bies.201400160 URL pmid: 25413709 |
| [17] |
Campos PF, Craig OE, Turner-Walker G, et al. DNA in ancient bone - where is it located and how should we extract it?[J]. Ann Anat, 2012,194(1):7-16
doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2011.07.003 URL pmid: 21855309 |
| [18] | Korlevic P, Gerber T, Gansauge MT, et al. Reducing microbial and human contamination in DNA extractions from ancient bones and teeth[J]. BioTechniques, 2015,59(2):87-93 |
| [19] | Lindahl T. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA[J]. Nature, 1993, 362709-715 |
| [20] |
Brundin M, Figdor D, Sundqvist G, et al. DNA binding to hydroxyapatite: a potential mechanism for preservation of microbial DNA[J]. J Endod, 2013,39(2):211-216
URL pmid: 23321233 |
| [21] |
Svintradze DV, Mrevlishvili GM, Metreveli N, et al. Collagen-DNA Complex[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2008, 921-28
URL pmid: 11710050 |
| [22] |
Reich D, Green RE, Kircher M, et al. Genetic history of an archaic hominin group from Denisova Cave in Siberia[J]. Nature, 2010,468(7327):1053-1060
doi: 10.1038/nature09710 URL pmid: 21179161 |
| [23] |
Prufer K, Racimo F, Patterson N, et al. The complete genome sequence of a Neanderthal from the Altai Mountains[J]. Nature, 2014,505(7481):43-49
doi: 10.1038/nature12886 URL pmid: 24352235 |
| [24] | Gamba C, Jones ER, Teasdale MD, et al. Genome flux and stasis in a five-millennium transect of European prehistory[J]. Nature, communications, 2014,55257 |
| [25] | Burbano HA, Hodges E, Green RE, et al. Targeted Investigation of the Neandertal Genome by Array-Based Sequence[J]. Science, 2010, 328723-725 |
| [26] | Avila-Arcos MC, Cappellini E, Romero-Navarro JA, et al. Application and comparison of large-scale solution-based DNA capture-enrichment methods on ancient DNA[J]. Sci Rep, 2011,174 |
| [27] |
Fu QM, Meyer M, Gao X, et al. DNA analysis of an early modern human from Tianyuan Cave, China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013,110(6):2223-2227
URL pmid: 23341637 |
| [28] |
Carpenter ML, Buenrostro JD, Valdiosera C, et al. Pulling out the 1%: whole-genome capture for the targeted enrichment of ancient DNA sequencing libraries[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2013,93(5):852-864
URL pmid: 24568772 |
| [29] |
Castellano S, Parra G, Sanchez-Quinto FA, et al. Patterns of coding variation in the complete exomes of three Neandertals[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014,111(18):6666-6671
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1405138111 URL pmid: 24753607 |
| [30] | Meynert AM, Ansari M, FitzPatrick DR, et al. Variant detection sensitivity and biases in whole genome and exome sequencing[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2014,15247 |
| [31] | Briggs AW, Stenzel U, Johnson PLF, et al. Patterns of damage in genomic DNA sequences from a Neandertal[J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, 2007, 10414616-14621 |
| [32] |
Gansauge MT, Meyer M. Selective enrichment of damaged DNA molecules for ancient genome sequencing[J]. Genome Res, 2014,24(9):1543-1549
doi: 10.1101/gr.174201.114 URL pmid: 25081630 |
| [33] | Geigl E. On the circumstances surrounding the preservation and analysis of very old DNA[J]. Archaeometry, 2002, 44337-342 |
| [34] | Höss M, Dilling A, Currant A, et al. Molecular phylogeny of the extinct ground sloth mylodon darwinii[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1996, 93181-185 |
| [35] | Hansen AJ, Mitchell DL, Wiuf C, et al. Crosslinks rather than strand breaks determine access to ancient DNA sequences from frozen sediments[J]. Genetics, 2006, 1731175-1179 |
| [36] | Hofreiter M, Jaenicke V, Serre D, et al. DNA sequences from multiple amplifications reveal artifacts induced by cytosine deamination in ancient dna[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2001, 294793-4799 |
| [37] | Rohland N, Hofreiter M. Comparison and optimization of ancient DNA extraction[J]. BioTechniques, 2007, 42343-352 |
| [38] | Tebbe CC, Vahjen W. Interference of humic acids and DNA extracted directly from soil in detection and transformation of recombinant DNA from bacteria and a yeast[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1993, 592657-2665 |
| [39] | Tuross N. The biochemistry of ancient DNA in bone[J]. Experientia, 1994, 50530-535 |
| [40] | Li R, Liriano L. A bone sample cleaning method using trypsin for the isolation of DNA[J]. Leg Med (Tokyo), 2011,13(6):304-308 |
| [41] | Kemp BM, Smith DG. Use of bleach to eliminate contaminating DNA from the surface of bones and teeth[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2005,154(1):53-61 |
| [42] |
Barta JL, Monroe C, Kemp BM. Further evaluation of the efficacy of contamination removal from bone surfaces[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2013,231(1-3):340-348
doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2013.06.004 URL pmid: 23890658 |
| [43] |
Salamon M, Tuross N, Arensburg B, et al. Relatively well preserved DNA is present in the crystal aggregates of fossil bones[J]. PNAS, 2005,102(39):13783-13788
URL pmid: 16162675 |
| [44] |
Malmstrom H, Svensson EM, Gilbert MT, et al. More on contamination: the use of asymmetric molecular behavior to identify authentic ancient human DNA[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2007,24(4):998-1004
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm015 URL pmid: 17255122 |
| [45] | Dabney J, Knapp M, Glocke I, et al. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence of a Middle Pleistocene cave bear reconstructed from ultrashort DNA fragments[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013,110(39):15758-15763 |
| [46] |
Hajdinjak M, Fu QM, Hubner A, et al. Reconstructing the genetic history of late Neanderthals[J]. Nature, 2018
URL pmid: 33208969 |
| [47] | Ginolhac A, Vilstrup J, Stenderup J, et al. Improving the performance of true single molecule sequencing for ancient DNA[J]. BMC Genomics, 2012,13177 |
| [48] | Peter B. Damgaard AM, Hannes Schroeder, Ludovic Orlando,, Eske Willerslev MEA. Improving access to endogenous DNA in ancient bones and teeth[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015,511184 |
| [49] | Sikora M, Pitulko VV, Sousa VC, et al. The population history of northeastern Siberia since the Pleistocene[J]. Nature, 2019,570(7760):182-188 |
| [50] | Bernardi G. Chromatography of Nucleic Acids on Hydroxyapatite[J]. Nature, 1965, 206779-783 |
| [51] | Grunenwald A, Keyser C, Sautereau AM, et al. Adsorption of DNA on biomimetic apatites: Toward the understanding of the role of bone and tooth mineral on the preservation of ancient DNA[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 292867-875 |
| [52] | Persson P. A method to recover DNA from ancient bones[J]. Ancient DNA Newsl, 1992, 125-27 |
| [53] | Götherström A, Lidén K. A modified DNA extraction method for bone and teeth[J]. Laborativ Arkeologi, 1996, 953-56 |
| [54] | Bajorath J, Saenger W, Pal GP. Autolysis and inhibition of proteinase K, a subtilisin-related serine proteinase isolated from the fungus Tritirachium album Limber[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology, 1988,954:176-182 |
| [55] | 刘杨柳, 武小芳, 胡树样, 等. 蛋白酶K的性质及其在核酸提取中的应用[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2017,38(10):196-199 |
| [56] | Hofreiter M, Rabeder G, Jaenicke-Despres V, et al. Evidence for reproductive isolation between cave bear populations[J]. Curr Biol, 2004,14(1):40-43 |
| [57] |
Rohland N, Hofreiter M. Ancient DNA extraction from bones and teeth[J]. Nature protocols, 2007,2(7):1756-1762
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.247 URL pmid: 17641642 |
| [58] |
Yang DY, Eng B, Waye JS, et al. Improved DNA extraction from Ancient Bones Using Silica-Based Spin Columns[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1998,105(4):539-543
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8644(199804)105:4<539::AID-AJPA10>3.0.CO;2-1 URL pmid: 9584894 |
| [59] |
Juras A, Makarowicz P, Chylenski M, et al. Mitochondrial genomes from Bronze Age Poland reveal genetic continuity from the Late Neolithic and additional genetic affinities with the steppe populations[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol, 2020,172(2):176-188
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.24057 URL pmid: 32297323 |
| [60] |
Rohland N, Siedel H, Hofreiter M. A rapid column-based ancient DNA extraction method for increased sample throughput[J]. Molecular ecology resources, 2010,10(4):677-683
doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02824.x URL pmid: 21565072 |
| [61] | Sullivan NO, Posth C, Coia V, et al. Ancient genome-wide analyses infer kinship structure[J]. Science Advance, 2018, 4 eaao1262 |
| [62] |
Gaudio D, Fernandes DM, Schmidt R, et al. Genome-Wide DNA from Degraded Petrous Bones and the Assessment of Sex and Probable Geographic Origins of Forensic Cases[J]. Sci Rep, 2019,9(1):8226
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44638-w URL pmid: 31160682 |
| [63] | 杨百全, 王利君, 遇长青, 等. 磁珠法回收纯化 DNA样本[J]. 中国法医学杂志, 2006,21:10-11 |
| [64] |
Zhao J, Liu FE, Lin S, et al. Investigation on maternal lineage of a Neolithic group from northern Shaanxi based on ancient DNA[J]. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal, 2017,28(5):732-739
URL pmid: 27246811 |
| [65] |
Kalmár T, Bachrati CZ, Marcsik A, et al. A simple and efficient method for PCR amplifiable DNA extraction from ancient bones[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2000,28(12):E67
doi: 10.1093/nar/28.12.e67 URL pmid: 10871390 |
| [66] |
Orlando L, Ginolhac A, Raghavan M, et al. True single-molecule DNA sequencing of a pleistocene horse bone[J]. Genome Res, 2011,21(10):1705-1719
doi: 10.1101/gr.122747.111 URL |
| [67] | Rohland N, Siedel H, Hofreiter M. Nondestructive DNA extraction method for mitochondrial DNA analyses of museum specimens[J]. BioTechniques, 2004, 36814-821 |
| [68] |
Hervella M, Iniguez MG, Izagirre N, et al. Nondestructive methods for recovery of biological material from human teeth for DNA extraction[J]. J Forensic Sci, 2015,60(1):136-141
doi: 10.1111/1556-4029.12568 URL pmid: 25047360 |
| [69] | Gomes C, Palomo-Díez S, Roig J, et al. Nondestructive extraction DNA method from bones or teeth, true or false?[J]. Forensic Science International: Genetics Supplement Series, 2015, 5e279-e282 |
| [1] | 张明, 平婉菁, 付巧妹. 古基因组揭示史前欧亚大陆现代人复杂遗传历史[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(03): 412-421. |
| [2] | 丁曼雨, 何伟, 王恬怡, 夏格旺堆, 张明, 曹鹏, 刘峰, 戴情燕, 付巧妹. 中国西藏拉托唐古墓地古代居民线粒体全基因组研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(01): 1-11. |
| [3] | 王恬怡, 赵东月, 张明, 乔诗雨, 杨帆, 万杨, 杨若薇, 曹鹏, 刘峰, 付巧妹. 古DNA捕获新技术与中国南方早期人群遗传研究新格局[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 680-694. |
| [4] | 李春香, 张帆, 马鹏程, 王立新, 崔银秋. 线粒体全基因组揭示嫩江流域史前人群遗传结构的动态变化[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 695-705. |
| [5] | 张雅军, 张旭, 赵欣, 仝涛, 李林辉. 从头骨形态学和古DNA探究公元3~4世纪西藏阿里地区人群的来源[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(03): 435-449. |
| [6] | 张明;付巧妹. 史前古人类之间的基因交流及对当今现代人的影响[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(02): 206-218. |
| [7] | 文少卿;王传超;敖雪;韦兰海;佟欣竹;王凌翔;王占峰;韩昇;李辉. 古DNA证据支持曹操的父系遗传类型属于单倍群O2[J]. 人类学学报, 2016, 35(04): 617-625. |
| [8] | 张芃胤; 徐智; 许渤松; 韩康信; 周慧; 金力; 谭婧泽. 青海大通上孙家寨古代居民mtDNA遗传分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(02): 204-218. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3