

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (01): 87-96.doi: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2019.0012cstr: 32091.14.j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2019.0012
收稿日期:2018-07-24
修回日期:2018-12-16
出版日期:2021-02-15
发布日期:2021-02-25
通讯作者:
杨谊时
作者简介:陈国科(1980-),男,甘肃静宁人,博士,甘肃省文物考古研究所研究馆员,主要从事冶金考古、丝绸之路考古。
基金资助:
CHEN Guoke1, YANG Yishi1( ), ZHANG Shanjia2, WANG Hui1
), ZHANG Shanjia2, WANG Hui1
Received:2018-07-24
Revised:2018-12-16
Online:2021-02-15
Published:2021-02-25
Contact:
YANG Yishi
摘要:
本文通过张掖西城驿遗址文化层沉积物及现代表土沉积物元素地球化学分析,结合高分辨率碳化植物种子14C 测年和最新考古发掘资料,揭示了西城驿遗址4200-3500 BP cal期间人类活动特征,佐证了不同文化阶段人类冶金活动强度变化。Rb/Sr比值、磁化率和重金属元素(Cu、Zn、Pb、As、Ni)含量变化过程显示,西城驿地区4200-4000 BP cal马厂文化时期人类活动增强,冶金活动开始出现;4000-3700 BP cal西城驿文化时期出现了冶金高峰期;四坝文化时期(3700-3500 BP cal)冶金活动强度相对减弱。
中图分类号:
陈国科, 杨谊时, 张山佳, 王辉. 张掖西城驿遗址新石器时代晚期-青铜时代人类冶金活动的元素地球化学记录[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(01): 87-96.
CHEN Guoke, YANG Yishi, ZHANG Shanjia, WANG Hui. Elemental geochemistry records of metallurgical activities during the late Neolithic and Bronze age in the Xichengyi site, Zhangye[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021, 40(01): 87-96.
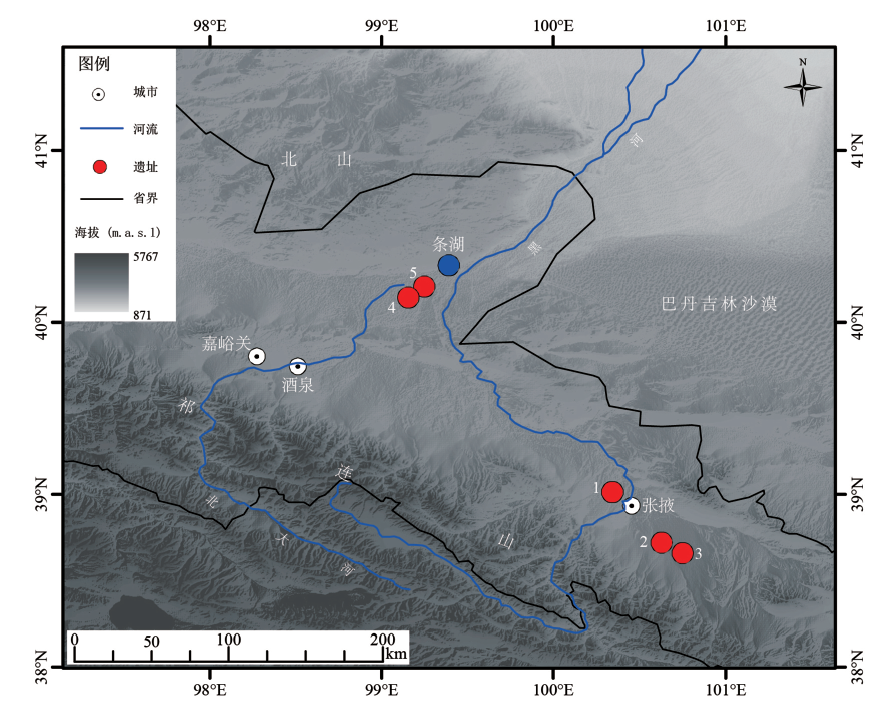
图1 研究区域史前文化遗址分布 1.西城驿遗址/Xichengyi site;2.西灰山遗址/Xihuishan site; 3.东灰山遗址/Donghuishan site;4.缸缸洼遗址/Ganggangwa site;5.火石梁遗址/Huoshiliang site
Fig.1 The distribution of prehistoric cultural sites in the study area
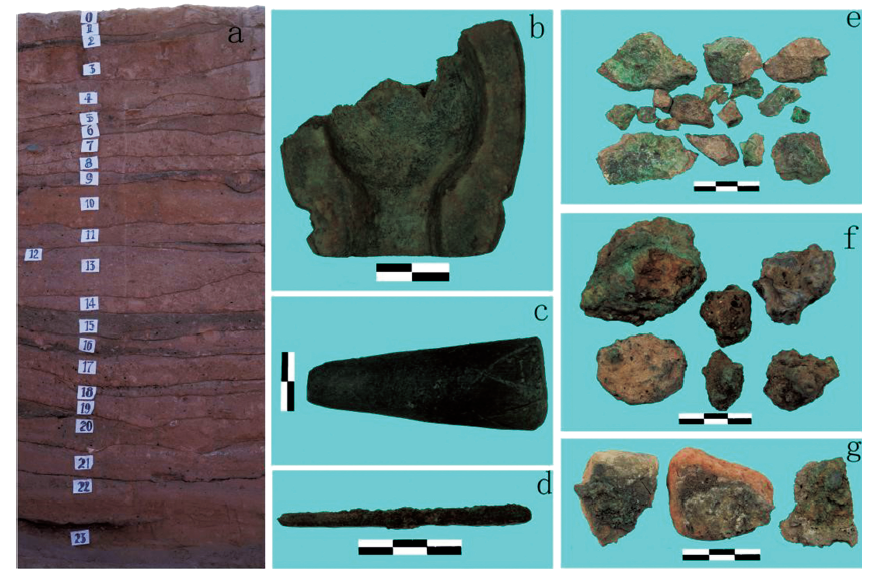

图2 西城驿遗址剖面及出土相关冶金遗物 a. 2012ZXT0702,东壁剖面/ East wall section;b. 2011ZHT0404,石范/ Stone molds;c. 2010ZXT0101⑦b,鼓风管/Blowpipe nozzles;d. 2010ZHT0302H8⑤,铜锥/Copper cone;e. 2010-2011ZH,铜矿石/Copper ores; f. 2010ZHT0301⑤c,铜渣Copper slags;g. 2010ZHH15③,炉壁Furnace wall fragments
Fig.2 Xichengyi site section and related metallurgical relics
| 实验室编号 Lab No. | 采样单位 Samping position | 测年材料 Dating material | 14C年龄 Radioncarbon age (a BP) | 树轮校正年龄 Calibrated age (BP cal) | 文化类型 Cultural type | 参考文献 Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Sigma(68.2%) | 2Sigma(95.4%) | ||||||
| ZK3458 | T0301-6e | 炭化植物 | 3412±24 | 3633-3695 | 3586-3719 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3480 | T0301-F4④ | 木炭 | 3451±24 | 3644-3818 | 3640-3826 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3477 | T0301-F4① | 炭化植物 | 3355±24 | 3571-3632 | 3511-3686 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3457 | T0301-6c | 小麦 | 3391±26 | 3594-3686 | 3575-3695 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK4997 | T0301-M4 | 人骨 | 3481±25 | 3702-3826 | 3650-3834 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK5017 | T0302-6a | 羊骨 | 3452±22 | 3645-3818 | 3640-3826 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3501 | T0301-H8① | 木炭 | 3401±24 | 3612-3690 | 3581-3699 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3487 | T0302-H8④ | 木炭 | 3480±22 | 3701-3826 | 3692-3832 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3468 | T0301-5a | 炭化植物 | 3396±25 | 3608-3689 | 3580-3695 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| LZU15133 | 地层-9 | 木炭 | 3670±25 | 3931-4079 | 3920-4086 | 西城驿文化 | 本文 |
| LZU15135 | 地层-11 | 粟 | 3610±50 | 3853-3978 | 3731-4084 | 西城驿文化 | 本文 |
| LZU15134 | 地层-20 | 粟 | 3745±25 | 4013-4150 | 3988-4223 | 马厂文化 | 本文 |
| ZK3464 | T0301-8c | 炭化植物 | 3700±24 | 3987-4085 | 3972-4145 | 马厂文化 | [31,33] |
表1 西城驿遗址剖面AMS 14C测年结果
Tab.1 Results of AMS 14C dates from Xichengyi site section
| 实验室编号 Lab No. | 采样单位 Samping position | 测年材料 Dating material | 14C年龄 Radioncarbon age (a BP) | 树轮校正年龄 Calibrated age (BP cal) | 文化类型 Cultural type | 参考文献 Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Sigma(68.2%) | 2Sigma(95.4%) | ||||||
| ZK3458 | T0301-6e | 炭化植物 | 3412±24 | 3633-3695 | 3586-3719 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3480 | T0301-F4④ | 木炭 | 3451±24 | 3644-3818 | 3640-3826 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3477 | T0301-F4① | 炭化植物 | 3355±24 | 3571-3632 | 3511-3686 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3457 | T0301-6c | 小麦 | 3391±26 | 3594-3686 | 3575-3695 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK4997 | T0301-M4 | 人骨 | 3481±25 | 3702-3826 | 3650-3834 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK5017 | T0302-6a | 羊骨 | 3452±22 | 3645-3818 | 3640-3826 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3501 | T0301-H8① | 木炭 | 3401±24 | 3612-3690 | 3581-3699 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3487 | T0302-H8④ | 木炭 | 3480±22 | 3701-3826 | 3692-3832 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| ZK3468 | T0301-5a | 炭化植物 | 3396±25 | 3608-3689 | 3580-3695 | 四坝文化 | [31,33] |
| LZU15133 | 地层-9 | 木炭 | 3670±25 | 3931-4079 | 3920-4086 | 西城驿文化 | 本文 |
| LZU15135 | 地层-11 | 粟 | 3610±50 | 3853-3978 | 3731-4084 | 西城驿文化 | 本文 |
| LZU15134 | 地层-20 | 粟 | 3745±25 | 4013-4150 | 3988-4223 | 马厂文化 | 本文 |
| ZK3464 | T0301-8c | 炭化植物 | 3700±24 | 3987-4085 | 3972-4145 | 马厂文化 | [31,33] |
| [1] |
Crutzen PJ. Geology of mankind[J]. Nature, 2002, 415(6867): 23
doi: 10.1038/415023a URL pmid: 11780095 |
| [2] | Crutzen PJ, Stoemer EF. The “Anthropocene”[R]. IGBP Newsletter, 2000, 41:17-18 |
| [3] |
Foley SF, Gronenborn D, Andreae MO, et al. The Palaeoanthropocene - The beginnings of anthropogenic environmental change[J]. Anthropocene, 2013, 3:83-88
doi: 10.1016/j.ancene.2013.11.002 URL |
| [4] | 刘东生. 科学工作假说(Working Hypojournal)是科学创新的基础[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(5): 673-677 |
| [5] |
Roberts BW, Thornton CP, Pigott VC. Development of metallurgy in Eurasia[J]. Antiquity, 2009, 83(322): 1012-1022
doi: 10.1017/S0003598X00099312 URL |
| [6] |
Jones MK, Harriet H, Kneale CJ, et al. Food globalisation in prehistory: The agrarian foundation of an interconnected continent[J]. Journal of the British Academy. 2016, 4:73-87
doi: 10.5871/jba/004.073 URL |
| [7] |
Dong GH, Yang YS, Han JY, et al. Exploring the history of cultural exchange in prehistoric Eurasia from the perspectives of crop diffusion and consumption[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2017, 60(6): 1110-1123
doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-9037-x URL |
| [8] |
Linduff KM, Mei JJ. Metallurgy in Ancient Eastern Asia: Retrospect and Prospects[J]. Journal of World Prehistory, 2009, 22(3): 265-281
doi: 10.1007/s10963-009-9023-5 URL |
| [9] | 杨建华, 邵会秋. 欧亚草原东部金属之路的形成[J]. 文物, 2017(6): 60-74 |
| [10] | 董广辉, 张山佳, 杨谊时, 等. 中国北方新石器时代农业强化及对环境的影响[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(26): 2913 |
| [11] |
Gignoux CR, Bar-Yosef O. Rapid, global demographic expansions after the origins of agriculture[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(15): 6044-6049
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914274108 URL |
| [12] | Biraben JN. The rising numbers of humankind.[J]. Population & Societies, 2003, 394:1-4 |
| [13] |
Hong S, Candelone JP, Patterson CC, et al. History of ancient copper smelting pollution during roman and medieval times recording in Greenland ice[J]. Science. 1996, 272(5259): 246
doi: 10.1126/science.272.5259.246 URL |
| [14] |
Monna F, Galop D, Carozza L, et al. Environmental impact of early Basque mining and smelting recorded in a high ash minerogenic peat deposit[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2004, 327(1-3): 197-214
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.01.010 URL |
| [15] |
Nocete F, Álex E, Nieto JM, et al. An archaeological approach to regional environmental pollution in the south-western Iberian Peninsula related to Third millennium BC mining and metallurgy[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2005, 32(10): 1566-1576
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2005.04.012 URL |
| [16] | Martínez CA, Lópezmerino L, Bindler R, et al. Early atmospheric metal pollution provides evidence for Chalcolithic/Bronze Age mining and metallurgy in Southwestern Europe[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 545-546:398-406 |
| [17] |
Zhuang Y, Kidder TR. Archaeology of the Anthropocene in the Yellow River region, China, 8000-2000 cal. BP. Holocene, 2014, 24:1602-1623
doi: 10.1177/0959683614544058 URL |
| [18] | 李小强, 纪明, 周新郢, 等. 甘肃东灰山遗址3700~3400 cal BP人类活动的元素地球化学记录[J]. 地球环境学报, 2010, 1(1): 48-51 |
| [19] | 李小强, 赵克良, 纪明, 等. 河西走廊西部全新世气候环境变化的元素地球化学记录[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(1): 110-120 |
| [20] |
Zhang S, Yang Y, Storozum MJ, et al. Copper smelting and sediment pollution in Bronze Age China: A case study in the Hexi corridor, Northwest China[J]. Catena, 2017, 156:92-101
doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.04.001 URL |
| [21] |
Yang Y, Dong G, Zhang S, et al. Copper content in anthropogenic sediments as a tracer for detecting smelting activities and its impact on environment during prehistoric period in Hexi Corridor, Northwest China[J]. Holocene, 2016, 27(2): 282-291
doi: 10.1177/0959683616658531 URL |
| [22] |
Lee CS, Qi SH, Zhang G, et al. Seven thousand years of records on the mining and utilization of metals from lake sediments in central China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(13): 4732-8
doi: 10.1021/es702990n URL pmid: 18677998 |
| [23] |
Dodson JR, Li X, Zhou X, et al. Origin and spread of wheat in China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 72(2): 108-111
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.04.021 URL |
| [24] | 董广辉, 杨谊时, 韩建业, 等. 农作物传播视角下的欧亚大陆史前东西方文化交流[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2017, 47(5): 530-543 |
| [25] | 李水城. 西北与中原早期冶铜业的区域特征及交互作用[J]. 考古学报, 2005, 3:239-278 |
| [26] | 陈国科. 西城驿——齐家冶金共同体——河西走廊地区早期冶金人群及相关问题初探[J]. 考古与文物, 2017, 5:37-44 |
| [27] | 杨谊时, 石乃玉, 史志林. 考古发现所见河西走廊史前的农业双向传播[J]. 敦煌学辑刊, 2016, 1(1): 82-91 |
| [28] | 陈国科, 王辉, 李延祥, 等. 甘肃张掖市西城驿遗址[J]. 考古, 2014, 7:3-17 |
| [29] |
Ramsey CB. Methods for Summarizing Radiocarbon Datasets[J]. Radiocarbon, 2017, 59(6): 1-25
doi: 10.1017/RDC.2016.95 URL |
| [30] | Reimer PJ, Bard E, Bayliss A, et al. IntCal13 and Marine13 Radiocarbon Age Calibration Curves 0-50,000 Years cal BP[J]. Radiocarbon, 2013, 55(4): 1869-1887 |
| [31] | 张雪莲, 张良仁, 王辉, 等. 张掖市西城驿遗址的碳十四测年及初步分析[J]. 华夏考古, 2015, 4:38-45 |
| [32] |
Dong G, Wang Z, Ren L, et al. A comparative study of radiocarbon dating charcoal and charred seeds from the same flotation samples in the Late Neolithic and Bronze Age sites in the Gansu and Qinghai Provinces, northwest China[J]. Radiocarbon, 2014, 56(1): 157-163
doi: 10.2458/56.16507 URL |
| [33] | 张雪莲, 仇士华, 钟建, 等. 放射性碳素测定年代报告(四一)[J]. 考古, 2015, 7:107-109 |
| [34] |
Gallet S, Jahn B M, Torii M. Geochemical characterization of the Luochuan loess-paleosol sequence, China, and paleoclimatic implications[J]. Chemical Geology, 1996, 133(1-4): 67-88
doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00070-8 URL |
| [35] | 陈骏, 汪永进, 陈旸, 等. 中国黄土地层Rb和Sr地球化学特征及其古季风气候意义[J]. 地质学报, 2001, 75(2): 259-266 |
| [36] |
Li X, Sun N, Dodson J, et al. The impact of early smelting on the environment of Huoshiliang in Hexi Corridor, NW China, as recorded by fossil charcoal and chemical elements[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology. 2011, 305(1-4): 329-336
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2011.03.015 URL |
| [37] |
Zhou X, Li X, Dodson J, et al. Rapid agricultural transformation in the prehistoric Hexi corridor, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 426(28): 33-41
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.04.021 URL |
| [38] | Heller F, Liu TS. Palaeoclimatic and sedimentary history from magnetic susceptibility of loess in China[J]. Geophys.res.lett, 1986, 13(11): 1169-1172 |
| [39] |
An Z, Kukla GJ, Porter SC, et al. Magnetic susceptibility evidence of monsoon variation on the Loess Plateau of central China during the last 130,000 years[J]. Quaternary Research, 1991, 36(1): 29-36
doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(91)90015-W URL |
| [40] | Fang XM, Ono Y, Fukusawa H, et al. Asian summer monsoon instability during the past 60,000 years: magnetic susceptibility and pedogenic evidence from the western Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 168(3-4): 219-232 |
| [41] |
史威, 朱诚, 徐伟峰, 等. 重庆中坝遗址剖面磁化率异常与人类活动的关系[J]. 地理学报, 2007, 62(3): 257-267
doi: 10.11821/xb200703003 URL |
| [42] |
李续彬, 强小科, 符超峰, 等. 甘肃西山坪遗址岩石磁学性质及其研究意义探讨[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(2): 500-511
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.02.017 URL |
| [43] | 何翔宇, 吴克宁, 查理思, 等. 古人类活动对土壤理化性质的影响——以河南仰韶村文化遗址为例[J]. 土壤, 2017, 49(5): 1038-1048 |
| [44] | 吴克宁, 王文静, 查理思, 等. 文化遗址区古土壤特性及古环境研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 2014, 6:1169-1182 |
| [45] | 国家文物局. 中国文物地图集:甘肃省分册[M]. 北京: 测绘出版社, 2011 |
| [46] |
Liu X, Lightfoot E, O’Connell TC, et al. From necessity to choice: dietary revolutions in west China in the second millennium BC[J]. World Archaeology. 2014, 46(5): 661-680
doi: 10.1080/00438243.2014.953706 URL |
| [47] | 陈国科, 李延祥, 潜伟, 等. 张掖西城驿遗址出土铜器的初步研究[J]. 考古与文物, 2015, 2:105-118 |
| [48] | 李延祥, 陈国科, 潜伟, 等. 张掖西城驿遗址冶铸遗物研究[J]. 考古与文物, 2015, 2:119-128 |
| [49] | 甘肃省文物考古研究所, 北京大学考古文博学院. 河西走廊史前考古调查报告[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2011 |
| [50] |
Dodson J, Li X, Ji M, et al. Early bronze in two Holocene archaeological sites in Gansu, NW China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2009, 72(3): 309-314
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.07.004 URL |
| [51] | 李延祥, 陈国科, 潜伟, 等. 敦煌西土沟遗址冶金遗物研究[J]. 敦煌研究, 2018, 2:131-140 |
| [1] | 黄嫣, 胡耀武. 陶器脂肪酸揭示古人类食谱的研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 865-880. |
| [2] | 陶大卫, 张国文, 周亚威, 陈朝云, 韩国河. 生物考古所见两周时期官庄聚落的人群与社会[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(02): 320-327. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 253
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 591
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3