

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (06): 1063-1071.doi: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0075cstr: 32091.14.j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0075
收稿日期:2019-08-24
出版日期:2021-12-15
发布日期:2020-11-25
通讯作者:
李素婷
作者简介:刘焕,主要从事植物考古相关研究。E-mail: 基金资助:
LIU Huan1( ), SONG Guoding2, LI Suting3(
), SONG Guoding2, LI Suting3( )
)
Received:2019-08-24
Online:2021-12-15
Published:2020-11-25
Contact:
LI Suting
摘要:
先商文化一直是学术界探索的重点,商代文明的诸多特征在先商文化时期已萌芽或得到加强。然而,对这一时期的经济与生业模式,相关研究尚有欠缺。本文对河南安阳鄣邓遗址先商文化时期的大植物遗存进行了分析,结果表明,粟是该时期先民最重要的作物,黍其次;小麦、大豆已被利用,但只是处于辅助地位。这些是先商文化时期农业的最直接证据,与文献记载及考古研究得出的先商农业发展状况基本一致。发轫于河北中部地区的商族最初的生计方式为渔猎畜牧,在南下的过程中逐渐学习并采纳了中原地区的生计方式,这对商族的发展壮大起到了积极的推动作用。
中图分类号:
刘焕, 宋国定, 李素婷. 河南鄣邓遗址浮选碳化植物遗存分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(06): 1063-1071.
LIU Huan, SONG Guoding, LI Suting. Analysis of carbonized macroremains from the Zhangdeng site, Henan[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021, 40(06): 1063-1071.
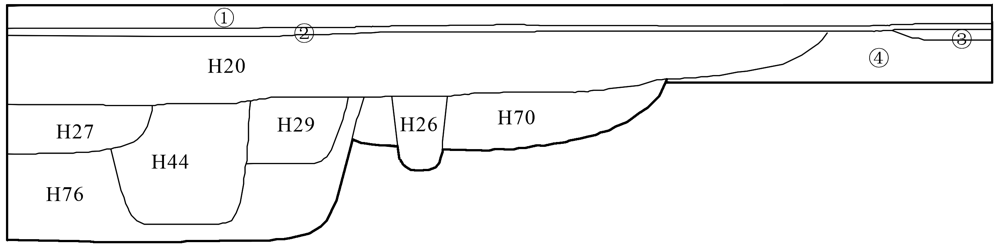
图2 鄣邓遗址T0405南壁剖面示意图 第1层:淡灰色土/ Light grey soil;第2层:淡黄色土/ Light brown soil;第3层:黄褐色土/ Filemot soil;第4层:红褐色黏土/ Mahogany clay
Fig.2 Line drawing of the south wall of the unit T0405, Zhangdeng site
| 实验室编号/ Lab No. | 14C年代/ Age (T1/2=5568) | 树轮校正后年代/ Dendrocalibrated Age | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1δ(68.2%) | 2δ(95.4%) | ||
| BA101319 | 3380±30 BP | 1740BC (13.6%) - 1710BC; 1700BC (54.6%) - 1630BC | 1750BC (95.4%) -1600BC |
表1 鄣邓遗址H7碳化粟粒AMS测年报告
Tab.1 AMS 14C dating of the carbonized foxtail millet grains from pit H7 of Zhangdeng site
| 实验室编号/ Lab No. | 14C年代/ Age (T1/2=5568) | 树轮校正后年代/ Dendrocalibrated Age | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1δ(68.2%) | 2δ(95.4%) | ||
| BA101319 | 3380±30 BP | 1740BC (13.6%) - 1710BC; 1700BC (54.6%) - 1630BC | 1750BC (95.4%) -1600BC |
| 类别/Taxa | 出土单位/ Pit Number (n) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H7 | H18 | H35 | H86 | H64 | H32 | H96 | H41 | H42 | 总数/ Total | |
| 粟/ Setaria italica | 1313 | 331 | 501 | 51 | 65 | 37 | 15 | 14 | 15 | 2342 |
| 黍/ Panicum miliaceum | 101 | 13 | 36 | _ | 1 | _ | 3 | _ | _ | 154 |
| 小麦/ Triticum aestivum | 5f | 3 f | 1 f | _ | _ | 1 f | _ | _ | _ | 10 |
| 大豆/ Glycine max | _ | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 野大豆/ Glycine soja | _ | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 马齿苋/ Portulaca oleracea | _ | _ | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| 牛筋草/ Eleusine indica | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 | 1 |
| 藜属/ Chenopodium sp. | 19 | 6 | 13 | 27 | 2 | 6 | 26 | 4 | 9 | 112 |
| 苋属/ Amaranthus sp. | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 酸浆属/ Physalis sp. | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 黍亚科/ Panicoideae | 595 | 190 | 337 | 8 | 15 | 17 | 4 | 23 | 4 | 1193 |
| 禾本科/ Poaceae | 399 | 148 | 192 | 1 | 30 | 13 | 4 | 8 | 5 | 800 |
| 豆科/ Fabaceae | 2 | 5 | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 | _ | 9 |
| 菊科/ Asterasece | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 唇形科/ Labiatae | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 大戟科/ Euphorbiaceae | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 石竹科/ Caryophyllaceae | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 锦葵科/ Malvaceae | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 未知/ Unknown | 354 | 224 | 153 | 27 | 61 | 53 | 10 | 24 | 46 | 952 |
表2 鄣邓遗址浮选碳化植物遗存统计
Tab.2 Absolute numbers of carbonized macroremains of Zhangdeng site
| 类别/Taxa | 出土单位/ Pit Number (n) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H7 | H18 | H35 | H86 | H64 | H32 | H96 | H41 | H42 | 总数/ Total | |
| 粟/ Setaria italica | 1313 | 331 | 501 | 51 | 65 | 37 | 15 | 14 | 15 | 2342 |
| 黍/ Panicum miliaceum | 101 | 13 | 36 | _ | 1 | _ | 3 | _ | _ | 154 |
| 小麦/ Triticum aestivum | 5f | 3 f | 1 f | _ | _ | 1 f | _ | _ | _ | 10 |
| 大豆/ Glycine max | _ | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 野大豆/ Glycine soja | _ | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 马齿苋/ Portulaca oleracea | _ | _ | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| 牛筋草/ Eleusine indica | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 | 1 |
| 藜属/ Chenopodium sp. | 19 | 6 | 13 | 27 | 2 | 6 | 26 | 4 | 9 | 112 |
| 苋属/ Amaranthus sp. | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 酸浆属/ Physalis sp. | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 黍亚科/ Panicoideae | 595 | 190 | 337 | 8 | 15 | 17 | 4 | 23 | 4 | 1193 |
| 禾本科/ Poaceae | 399 | 148 | 192 | 1 | 30 | 13 | 4 | 8 | 5 | 800 |
| 豆科/ Fabaceae | 2 | 5 | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 | _ | 9 |
| 菊科/ Asterasece | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 唇形科/ Labiatae | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 大戟科/ Euphorbiaceae | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 石竹科/ Caryophyllaceae | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 锦葵科/ Malvaceae | 1 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | 1 |
| 未知/ Unknown | 354 | 224 | 153 | 27 | 61 | 53 | 10 | 24 | 46 | 952 |
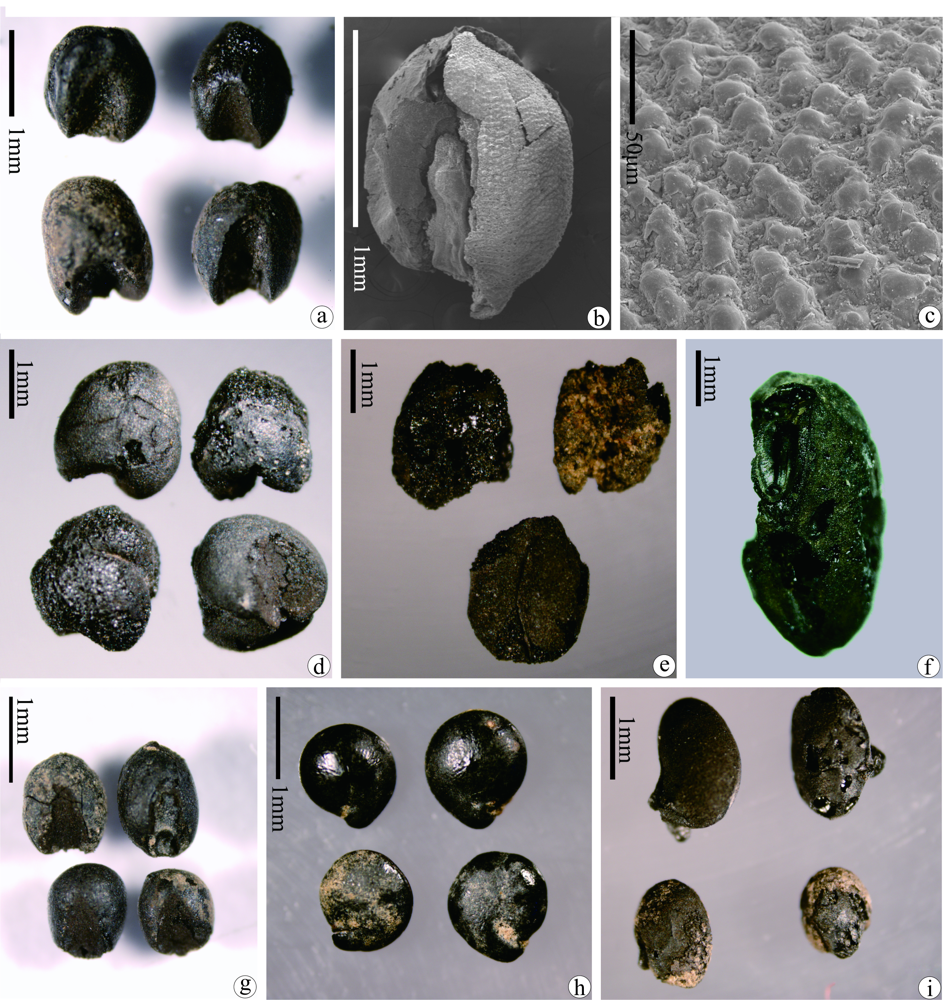

图3 鄣邓遗址浮选碳化植物遗存 a.粟的颖果/ Caryopses of foxtail millet (Setaria italica);b.粟的带稃颖果/ SEM micrograph of a foxtail millet grain with husks;c.粟稃片上的小突起/ SEM micrograph of the papillae on the husk surface of foxtail millet;d.黍的颖果/ Caryopses of common millet (Panicum milliaceum);e.破碎的小麦/ Fragments of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) caryopses;f.大豆种子/ Seed of soybean (Glycine max);g.黍亚科颖果/ Caryopses belonging to Panicoideae;h.藜属种子/ Seeds belonging to Chenopodium sp;i.豆科种子/ Seeds belonging to Fabaceae
Fig.3 Images of macroremains from Zhangdeng site
| 样品/ Sample | 长度/ Length (mm) | 宽度/ Width(mm) | 样本量/ Number of sample (n) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值/Average | 范围/Range | 平均值/Average | 范围/Range | ||
| 粟/foxtail millet | 1.23±0.15 | 0.73-1.86 | 1.15±0.15 | 0.73-1.6 | 50 |
| 黍/common millet | 1.8±0.16 | 1.59-2.25 | 1.65±0.18 | 1.26-1.9 | 15 |
| 大豆/soybean | 5.07 | 3.31 | 1 | ||
| 黍亚科/Panicoideae | 1.08±0.21 | 0.66-1.48 | 0.88±0.15 | 0.63-1.17 | 30 |
| 藜属/Chenopodium sp. | 1.28±0.1 | 1.12-1.37 | 1.16±0.06 | 1.1-1.24 | 6 |
| 豆科/Fabaceae | 1.32±0.22 | 1.07-1.63 | 0.88±0.07 | 0.78-0.99 | 7 |
表3 碳化植物遗存主要种类的测量
Tab.3 Statistical results of macrobotanical samples
| 样品/ Sample | 长度/ Length (mm) | 宽度/ Width(mm) | 样本量/ Number of sample (n) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值/Average | 范围/Range | 平均值/Average | 范围/Range | ||
| 粟/foxtail millet | 1.23±0.15 | 0.73-1.86 | 1.15±0.15 | 0.73-1.6 | 50 |
| 黍/common millet | 1.8±0.16 | 1.59-2.25 | 1.65±0.18 | 1.26-1.9 | 15 |
| 大豆/soybean | 5.07 | 3.31 | 1 | ||
| 黍亚科/Panicoideae | 1.08±0.21 | 0.66-1.48 | 0.88±0.15 | 0.63-1.17 | 30 |
| 藜属/Chenopodium sp. | 1.28±0.1 | 1.12-1.37 | 1.16±0.06 | 1.1-1.24 | 6 |
| 豆科/Fabaceae | 1.32±0.22 | 1.07-1.63 | 0.88±0.07 | 0.78-0.99 | 7 |
| [1] | Pearsall DM (Eds.). Encyclopedia of Archaeology[M]. San Diego: Academic Press, 2006 |
| [2] | 中国社会科学院考古研究所. 新中国的考古发现和研究[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1984 |
| [3] | 中国社会科学院考古研究所. 中国考古学—夏商卷[M]. 北京: 中国社会科学出版社, 2003 |
| [4] | 李伯谦. 先商文化探索[A].见:《庆祝苏秉琦考古五十五年论文集》编辑组.庆祝苏秉琦考古五十五年论文集[C]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1989, 280-293 |
| [5] | 邹衡. 试论夏文化[A].见: 邹衡.夏商周考古学论文集[C]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1980 |
| [6] | 拒马河考古队. 河北易县涞水古遗址试掘报告[J]. 考古学报, 1988, 4:421-454 |
| [7] | 魏兴涛. 试论下七垣文化鹿台岗类型[J]. 考古, 1999, 5:65-74 |
| [8] | 沈勇. 保北地区夏时代两种青铜文化之探讨[J]. 华夏考古, 1991, 3:79-88 |
| [9] | 朱彦民. 从考古发现看商族发展过程中的经济转型[J]. 殷都学刊, 2006, 2:9-16 |
| [10] | 王震中. 商族起源与先商社会变迁[M]. 北京: 中国社会科学出版社, 2010 |
| [11] | 河北省文物研究所, 沧州地区文化管理所. 河北省任邱市哑叭庄遗址发掘报告[J]. 文物春秋, 1992, S1: 178-219+303-304 |
| [12] | 河北省文物管理处. 磁县下七垣遗址发掘报告[J]. 考古学报, 1979, 2:185-214 |
| [13] | 河南省文物考古研究所. 安阳鄣邓[M]. 郑州: 大象出版社, 2012 |
| [14] | 侯彦峰, 李素婷, 马萧林, 等. 安阳鄣邓遗址动物资源的获取与利用[J]. 中原文物, 2009, 5:38-47 |
| [15] |
Hou L, Hu Y, Zhao X, et al. Human subsistence strategy at Liuzhuang site, Henan, China during the proto-Shang culture (2000-1600 BC) by stable isotopic analysis[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2013, 40(5):2344-2351
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2013.01.005 URL |
| [16] | 侯亮亮, 李素婷, 胡耀武, 等. 先商文化时期家畜饲养方式初探[J]. 华夏考古, 2013, 2:130-139 |
| [17] | 侯亮亮, 徐海峰. 河北赞皇南马遗址先商文化时期动物骨骼的稳定同位素分析[J]. 边疆考古研究, 2015, 1:385-397 |
| [18] | 侯亮亮. 先商文化时期先民生业经济研究[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学, 2013 |
| [19] | 李素婷. 豫北地区漳河型先商文化的特征、来源及相关问题[J]. 郑州大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2009, 2:136-141 |
| [20] | 张立东. 先商文化的探索历程[A].见: 三代文明研究编委会.三代文明研究(一)[C]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999 |
| [21] | Pearsall DM. Paleoethnobotany-A handbook of Procedures (2nd edition)[M]. San Diego: Academic Press, 2000 |
| [22] | 赵志军. 植物考古学的田野工作方法——浮选法[J]. 考古, 2004, 3:80-87 |
| [23] | 中国科学院植物研究所. 杂草种子图说[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1980 |
| [24] | 关广清, 张玉茹, 孙国友, 等. 杂草种子图鉴[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000 |
| [25] | Jacomet S. Identification of Cereal Remains from Archaeological Sites (2nd edition)[M/OL]. Translator: Greig[J]. Basel: IPAS Basel University, 2006 |
| [26] |
Reimer PJ, Baillie MGL, Bard E, et al. IntCal04 - terrestrial radiocarbon age calibration, 0-26 cal kyr BP[J]. Radiocarbon, 2004, 46(3):1029-1058
doi: 10.1017/S0033822200032999 URL |
| [27] | Ramsey CB. OxCal Program v3.10. 2005[CP/OL]. URL: http://www.rlaha.ox.ac.uk/orau/oxcal.html |
| [28] | 洛阳市文物工作队. 洛阳皂角树—1992-1993年洛阳皂角树二里头文化聚落遗址发掘报告[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002 |
| [29] | 杨晓燕, 刘长江, 张健平, 等. 汉阳陵外藏坑农作物遗存分析及西汉早期农业[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 13:1917-1921 |
| [30] | 刘焕, 胡松梅, 张鹏程, 等. 陕西两处仰韶时期遗址浮选结果分析及其对比[J]. 考古与文物, 2013, 4:106-112 |
| [31] |
Hubbard RNLB. Development of agriculture in Europe and the Near East: Evidence from quantitative studies[J]. Economic Botany, 1980, 34(1):51-67
doi: 10.1007/BF02859554 URL |
| [32] | Popper VS. Selecting quantitative measurements in paleoethnobotany[A]. Hastorf CA, Popper VS. Current Paleoethnobotany: Analytical Methods and Cultural Interpretations of Archaeological Plant Remains[C]. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1988: 53-71 |
| [33] | Thompson GB. The Excavation of Khok Phanom Di: A Prehistoric Site in Central Thailand, Volume IV: Subsistence and Environment: The Botanical Evidence (The Biological Remains, Part Ⅱ)[M]. London: Society of Antiquaries of London, 1996 |
| [34] | 赵志军. 两城镇与教场铺龙山时代农业生产特点的对比分析[A].见:山东大学东方考古研究中心.东方考古(第1辑)[C]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 210-216 |
| [35] | 王传明, 赵新平, 靳桂云. 河南鹤壁市刘庄遗址浮选结果分析[J]. 华夏考古, 2010, 3:90-99 |
| [36] | 赵志军, 方燕明. 登封王城岗遗址浮选结果及分析[J]. 华夏考古, 2007, 2: 78-89+I0015-I0016 |
| [37] | 赵志军, 何弩. 陶寺城址2002年度浮选结果及分析[J]. 考古, 2006, 5: 77-86+i0008 |
| [38] | 赵敏, 王富强, 张博 山东烟台照格庄岳石文化遗址植物考古初步结果[N]. 中国文物报, 2008-03-28(07) |
| [39] | 孙永刚. 夏家店下层文化经济形态研究[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古大学, 2010 |
| [40] | 陈雪香, 郭俊峰. 山东章丘马安遗址2008年浮选植物遗存分析[A].见:山东大学东方考古研究中心.东方考古(第5辑)[C]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 368-371 |
| [41] | 赵志军, 徐良高. 周原遗址(王家嘴地点)尝试性浮选的结果及初步分析[J]. 文物, 2004, 10:89-96 |
| [42] |
Lee G, Crawford GE, Liu L, et al. Plants and people from the early Neolithic to Shang periods in North China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2007, 104:1087-1092
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609763104 URL |
| [43] | 赵志军. 关于夏商周文明形成时期农业经济特点的一些思考[J]. 华夏考古, 2005, 1: 75-81+101 |
| [1] | 陶大卫, 邹慧琳. 古代牙结石残留物的研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 344-354. |
| [2] | 顾纯光, 罗武宏, 张东, 杨玉璋. 安徽禹会村遗址双墩文化时期农业发展的植硅体证据[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(01): 110-121. |
| [3] | 李小强. 农业的起源、传播与影响[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(06): 1097-1108. |
| [4] | 夏秀敏, 王力之, 陶大卫, 杜伟, 靳松安, 张建, 吴妍. 从文坎沟东地点的植物遗存分析南阳盆地先秦时期的农业活动[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(05): 899-912. |
| [5] | 杨凡, 顾万发, 段绮梦, 郑晓蕖, 贾茵, 靳桂云. 河南郑州汪沟遗址出土的植硅体[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(03): 429-438. |
| [6] | 魏偏偏, 张全超. 内蒙古和林格尔土城子农业人群与林西井沟子游牧人群股骨中部的生物力学对比[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 238-247. |
| [7] | 原海兵, 顾万发, 魏青利, 吴倩, 丁兰坡, 曹豆豆. 郑州青台遗址新石器时代中晚期人群龋齿的统计与分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 226-237. |
| [8] | 程至杰, 齐鸣, 曾令园, 张居中, 杨玉璋, 李全立. 河南项城贾庄和后高老家遗址炭化植物遗存揭示的仰韶时期的原始农业[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(01): 85-95. |
| [9] | 陶大卫, 刘雪玲, 肖艺琦, 陈朝云. 河南鹿台遗址炭化植物遗存揭示的新石器时代晚期的人类生计活动[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(01): 73-84. |
| [10] | 陈冠翰, 周新郢, 沈慧, Khasannov Mutalibjon, 马建, 任萌, Annaev Tukhtash, 王建新, 李小强. 中亚河中地区青铜时代以来绿洲农业的演化与文明的交流[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(06): 1108-1120. |
| [11] | 赵美莹, 党志豪, 蒋洪恩. 新疆米兰遗址吐蕃时期的植物遗存[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(06): 1055-1062. |
| [12] | 刘晓迪, 魏东, 王婷婷, 张昕煜, 胡耀武. 内蒙古东南部战国时期的农业经济及人群融合[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(05): 764-775. |
| [13] | 包易格, 李小强, 刘汉斌, 赵克良, John Dodson, 沈慧, 张贵林, 王建, 周新郢. 中国黄土高原北部地区新石器-青铜时代农业结构演变及其对区域生态环境的适应[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(03): 461-472. |
| [14] | 罗武宏, 禤华丽, 姚凌, 杨玉璋, 易文文, 阚绪杭, 张居中, 张爱冰. 安徽定远侯家寨遗址二期植物性食物资源利用的淀粉粒证据[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(02): 292-305. |
| [15] | 杨玉璋;袁增箭;张家强;程至杰;禤华丽;方方;张居中;顾万发. 郑州东赵遗址炭化植物遗存记录的夏商时期农业特征及其发展过程[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(01): 119-130. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3