

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (03): 393-410.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0061cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0061
葛俊逸1,2,3,4( ), 邓成龙5,6, 邵庆丰7, 裴树文1,2, 唐锐枰1,3, 涂华8, 高星1,2,3
), 邓成龙5,6, 邵庆丰7, 裴树文1,2, 唐锐枰1,3, 涂华8, 高星1,2,3
收稿日期:2021-03-13
修回日期:2021-04-27
出版日期:2021-06-15
发布日期:2021-06-24
作者简介:葛俊逸,中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所,副研究员,主要从事第四纪古人类年代学以及人类演化与第四纪环境变化联系研究,E-mail: 基金资助:
GE Junyi1,2,3,4( ), DENG Chenglong5,6, SHAO Qingfeng7, PEI Shuwen1,2, TANG Ruiping1,3, TU Hua8, GAO Xing1,2,3
), DENG Chenglong5,6, SHAO Qingfeng7, PEI Shuwen1,2, TANG Ruiping1,3, TU Hua8, GAO Xing1,2,3
Received:2021-03-13
Revised:2021-04-27
Online:2021-06-15
Published:2021-06-24
摘要:
我国丰富的古人类遗存为研究东亚乃至全球古人类起源、迁徙和演化提供了重要的基础材料与数据。对已发表的2000多处旧石器时代古人类遗址年代学数据的整理和统计分析发现,绝大多数遗址目前仍缺少基本的年代学数据,不足20%的遗址开展过测年,仅10%左右具有相对可靠的年代学数据,只有极少数开展了多种测年方法的交叉定年。对于80多处出土古人类化石的遗址,亦过半存在明显的年代学争议。我们对一些古人类遗址中的常见各种复杂的同沉积和沉积后改造现象进行了详细分析,探讨了我国测年平台和测年队伍建设、考古发掘以及年代学采样与测年方法学等方面存在的问题,及其对遗址年代学研究的可能影响。基于此,笔者提出改善我国古人类年代学研究现状的可能措施,希望可以抛砖引玉,引发对该研究领域更多的关注和思考。
中图分类号:
葛俊逸, 邓成龙, 邵庆丰, 裴树文, 唐锐枰, 涂华, 高星. 中国古人类遗址年代学的研究进展与问题[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(03): 393-410.
GE Junyi, DENG Chenglong, SHAO Qingfeng, PEI Shuwen, TANG Ruiping, TU Hua, GAO Xing. Progress and issues of chronological studies of human fossil sites in China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021, 40(03): 393-410.
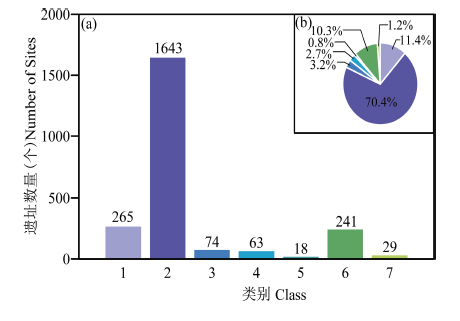
图1 2333处古人类遗址的年代不确定性分级统计结果 (a)不同不确定性级别的遗址数量/The number of sites with different levels of reliability; (b)不同不确定性级别的遗址所占比例/The proportion of sites with different levels of reliability
Fig.1 The statistical results of the age reliability classification of 2333 human fossil and Paleolithic sites
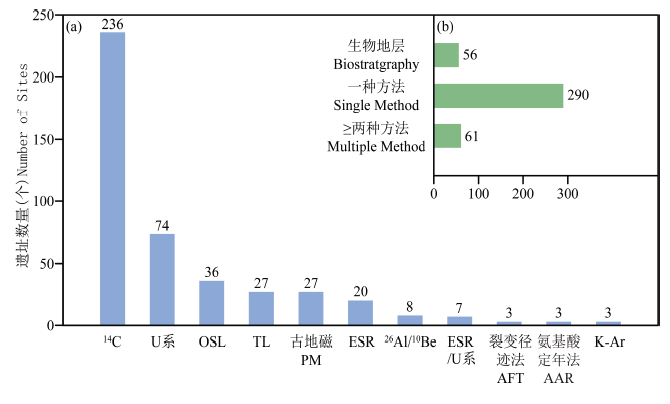
图2 已开展年代学的遗址使用的测年方法类型统计分析 (a)各种测年方法应用的遗址数量/The number of sites dated by different dating methods; (b)遗址应用的测年方法数量统计/ Statistics on the number of dating methods for these sites
Fig.2 Statistical analysis of the types of dating methods applied on all the dated human fossil and Paleolithic sites in China
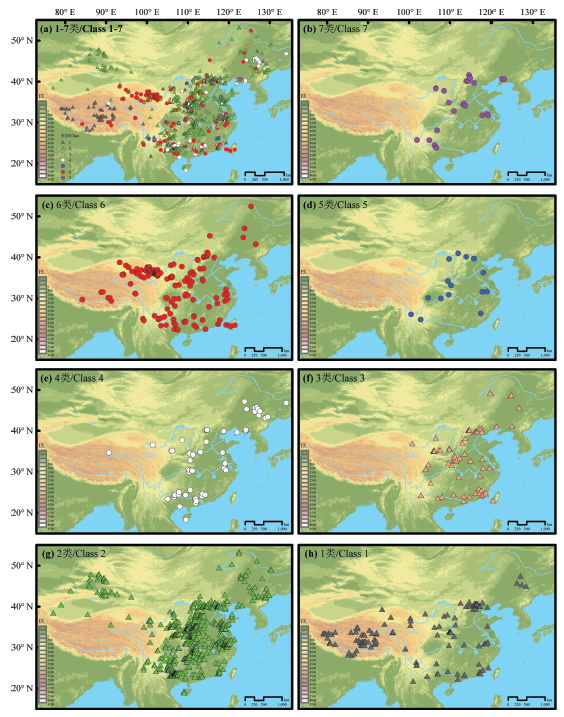
图3 我国古人类/旧石器遗址测年数据不确定性分级(1-7类)及不同分级的遗址空间分布图 (a)1-7类全部2333处遗址的空间分布/Spatial distribution of all 2333 sites; (b-h)按照不同年代确定性分级后的各类别遗址的空间分布/Spatial distribution of the sites with different reliability classification.
Fig.3 Maps showing locations of the human fossil and the Paleolithic site in China which are classified by reliability of dating data
| [1] |
Smith TM, Tafforeau P, Reid DJ, et al. Dental evidence for ontogenetic differences between modern humans and Neanderthals[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010,107(49):20923-20928
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010906107 URL |
| [2] |
Antón SC, Potts R, Aiello LC. Evolution of early Homo: An integrated biological perspective[J]. Science, 2014,345(6192):1236828
doi: 10.1126/science.1236828 URL |
| [3] |
Brunet M, Guy F, Pilbeam D, et al. A new hominid from the Upper Miocene of Chad, Central Africa[J]. Nature, 2002,418(6894):145-151
doi: 10.1038/nature00879 URL |
| [4] |
Leakey MG, Spoor F, Brown FH, et al. New hominin genus from eastern Africa shows diverse middle Pliocene lineages[J]. Nature, 2001,410(6827):433-440
pmid: 11260704 |
| [5] |
Leakey MG, Spoor F, Dean MC, et al. New fossils from Koobi Fora in northern Kenya confirm taxonomic diversity in early Homo[J]. Nature, 2012,488(7410):201-204
doi: 10.1038/nature11322 pmid: 22874966 |
| [6] |
McDougall I, Brown FH, Fleagle JG. Stratigraphic placement and age of modern humans from Kibish, Ethiopia[J]. Nature, 2005,433(7027):733-736
pmid: 15716951 |
| [7] | Wu XZ. The evolution of Humankind in China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 1990,9(4):312-321 |
| [8] |
Zhu ZY, Dennell R, Huang WQ, et al. Hominin occupation of the Chinese Loess Plateau since about 2.1 million years ago[J]. Nature, 2018,559(7715):608-612
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0299-4 URL |
| [9] |
Hou YM, Potts R, Yuan BY, et al. Mid-Pleistocene Acheulean-like stone technology of the Bose basin, South China[J]. Science, 2000,287(5458):1622-1626
doi: 10.1126/science.287.5458.1622 URL |
| [10] |
Zhu RX, Hoffman KA, Potts R, et al. Earliest presence of humans in northeast Asia[J]. Nature, 2001,413(6854):413-417
pmid: 11574886 |
| [11] |
Zhu RX, Potts R, Xie F, et al. New evidence on the earliest human presence at high northern latitudes in northeast Asia[J]. Nature, 2004,431(7008):559-562
pmid: 15457258 |
| [12] | Yang SX, Wang FG, Xie F, et al. Technological innovations at the onset of the Mid-Pleistocene Climate Transition in high-latitude East Asia[J]. National Science Review, 2020,8(1):1-11 |
| [13] | 刘武, 邢松, 吴秀杰. 中更新世晚期以来中国古人类化石形态特征的多样性[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2016,46(7):906-917 |
| [14] |
Li ZY, Wu XJ, Zhou LP, et al. Late Pleistocene archaic human crania from Xuchang, China[J]. Science, 2017,355(6328):969-972
doi: 10.1126/science.aal2482 URL |
| [15] |
Chen FH, Welker F, Shen C-C, et al. A late Middle Pleistocene Denisovan mandible from the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Nature, 2019,569(7756):409-412
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1139-x URL |
| [16] |
Hu Y, Marwick B, Zhang JF, et al. Late Middle Pleistocene Levallois stone-tool technology in southwest China[J]. Nature, 2019,565(7737):82-85
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0710-1 URL |
| [17] |
Liu W, Jin CZ, Zhang YQ, et al. Human remains from Zhirendong, South China, and modern human emergence in East Asia[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010,107(45):19201-19206
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014386107 URL |
| [18] |
Liu W, Martinón-Torres M, Cai YJ, et al. The earliest unequivocally modern humans in southern China[J]. Nature, 2015,526(7575):696-699
doi: 10.1038/nature15696 pmid: 26466566 |
| [19] | 吴新智. 现代人起源的多地区进化学说在中国的实证[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006,26(5):702-709 |
| [20] |
Gao X, Zhang XL, Yang DY, et al. Revisiting the origin of modern humans in China and its implications for global human evolution[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2010,53(12):1927-1940
doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4099-4 URL |
| [21] |
Wu XJ, Pei SW, Cai YJ, et al. Archaic human remains from Hualongdong, China, and Middle Pleistocene human continuity and variation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2019,116(20):9820-9824
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902396116 URL |
| [22] | 吴新智. 从中国晚期智人颅牙特征看中国现代人起源[J]. 人类学学报, 1998,17(4):276-282 |
| [23] | 高星. 更新世东亚人群连续演化的考古证据及相关问题论述[J]. 人类学学报, 2014,33(3):237-253 |
| [24] |
Zhang X, Ha B, Wang S, et al. The earliest human occupation of the high-altitude Tibetan Plateau 40 thousand to 30 thousand years ago[J]. Science, 2018,362(6418):1049-1051
doi: 10.1126/science.aat8824 URL |
| [25] |
Chen FH, Dong GH, Zhang DJ, et al. Agriculture facilitated permanent human occupation of the Tibetan Plateau after 3600 B.P.[J]. Science, 2015,347(6219):248-250
doi: 10.1126/science.1259172 URL |
| [26] | 武春林, 张岩, 李琴, 等. 中国古人类遗址环境数据库及遗址时空分布初步分析[J]. 科学通报, 2011,56(26):2229-2231 |
| [27] | Lu Y, Sun XF, Wen SQ. Chronological problems in Chinese human fossil sites[J]. Chinese Journal, 2020,65(20):2136-2144 |
| [28] |
Stewart JR, Stringer CB. Human evolution out of Africa: the role of refugia and climate change[J]. Science, 2012,335(6074):1317-1321
doi: 10.1126/science.1215627 URL |
| [29] |
Hublin J-J, Roebroeks W. Ebb and flow or regional extinctions? On the character of Neandertal occupation of northern environments[J]. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 2009,8(5):503-509
doi: 10.1016/j.crpv.2009.04.001 URL |
| [30] |
Grün R, Schwarcz HP, Chadam J. ESR dating of tooth enamel: coupled correction for U-uptake and U-series disequilibrium[J]. International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation. Part D. Nuclear Tracks and Radiation Measurements, 1988,14(1-2):237-241
doi: 10.1016/1359-0189(88)90071-4 URL |
| [31] |
Grün R, Eggins S, Kinsley L, et al. Laser ablation U-series analysis of fossil bones and teeth[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014,416:150-167
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.07.023 URL |
| [32] |
Grün R, Brink JS, Spooner NA, et al. Direct dating of Florisbad hominid[J]. Nature, 1996,382(6591):500-501
pmid: 8700221 |
| [33] |
Grün R, Stringer C, McDermott F, et al. U-series and ESR analyses of bones and teeth relating to the human burials from Skhul[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2005,49(3):316-334
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2005.04.006 URL |
| [34] |
Richter D, Grün R, Joannes-Boyau R, et al. The age of the hominin fossils from Jebel Irhoud, Morocco, and the origins of the Middle Stone Age[J]. Nature, 2017,546(7657):293-296
doi: 10.1038/nature22335 pmid: 28593967 |
| [35] |
Hershkovitz I, Weber GW, Quam R, et al. The earliest modern humans outside Africa[J]. Science, 2018,359(6374):456-459
doi: 10.1126/science.aap8369 URL |
| [36] | Weber GW, Hershkovitz I, Quam RM, et al. Early moderns humans in the Levant[A]. In Plavcan M, Alba DM, Elton S (Eds.). Proceedings of the 8th Annual Meeting of the European Society for the Study of Human Evolution Vol.7[C]. New York: Springer Science & Business Media, 2018,200 |
| [37] |
Boaretto E, Wu XH, Yuan JR, et al. Radiocarbon dating of charcoal and bone collagen associated with early pottery at Yuchanyan Cave, Hunan Province, China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2009,106(24):9595-9600
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900539106 URL |
| [38] |
Chen TM, Yuan SX. Uranium-series dating of bones and teeth from Chinese palaeolithic sites[J]. Archaeometry, 1988,30(1):59-76
doi: 10.1111/arch.1988.30.issue-1 URL |
| [39] |
Zhang JF, Wang XQ, Qiu WL, et al. The paleolithic site of Longwangchan in the middle Yellow River, China: chronology, paleoenvironment and implications[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2011,38(7):1537-1550
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2011.02.019 URL |
| [40] |
Zhu RX, An ZS, Potts R, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of early humans in China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2003,61(3-4):341-359
doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(02)00132-0 URL |
| [41] |
Wang HQ, Deng CL, Zhu RX, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the Donggutuo and Maliang paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2005,64(1):1-11
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2005.04.001 URL |
| [42] |
Deng CL, Wei Q, Zhu RX, et al. Magnetostratigraphic age of the Xiantai Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin and implications for early human colonization of Northeast Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006,244(1):336-348
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.02.001 URL |
| [43] |
Liu P, Deng CL, Li SH, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the Huojiadi Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010,298(3-4):399-408
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.10.027 URL |
| [44] |
Luo SD, Ku TL, Wang L, et al. 26Al, 10Be and U-Th isotopes in Blake Outer Ridge sediments: implications for past changes in boundary scavenging [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001,185(1-2):135-147
doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00372-1 URL |
| [45] | Kong P, Na CG, Fink D, et al. Erosion in northwest Tibet from in-situ-produced cosmogenic 10Be and 26Al in bedrock [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms: The Journal of the British Geomorphological Research Group, 2007,32(1):116-125 |
| [46] |
Shen GJ, Gao X, Gao B, et al. Age of Zhoukoudian Homo erectus determined with 26Al/10Be burial dating [J]. Nature, 2009,458(7235):198-200
doi: 10.1038/nature07741 URL |
| [47] |
Liu Y, Wang SJ, Xu S, et al. New evidence for the incision history of the Liuchong River, Southwest China, from cosmogenic 26Al/ 10Be burial ages in cave sediments[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013,73:274-283
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.044 URL |
| [48] | Tu H, Shen GJ, Li HX, et al. 26Al/10Be burial dating of Xujiayao-Houjiayao site in Nihewan Basin, northern China [J]. PloS One, 2015,10(2):1-11 |
| [49] |
Shen GJ, Ku T-L, Cheng H, et al. High-precision U-series dating of Locality 1 at Zhoukoudian, China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2001,41(6):679-688
doi: 10.1006/jhev.2001.0516 URL |
| [50] | 张丽, 沈冠军, 傅仁义, 等. 辽宁本溪庙后山遗址铀系测年初步结果[J]. 东南文化, 2007,197(3):54-57 |
| [51] |
Shen G, Tu H, Xiao D, et al. Age of Maba hominin site in southern China: evidence from U-series dating of Southern Branch Cave[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2014,23:56-62
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2014.06.004 URL |
| [52] |
Ao H, Liu CR, Roberts AP, et al. An updated age for the Xujiayao hominin from the Nihewan Basin, North China: Implications for Middle Pleistocene human evolution in East Asia[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2017,106:54-65
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2017.01.014 URL |
| [53] |
Shen GJ, Wang W, Wang Q, et al. U-Series dating of Liujiang hominid site in Guangxi, Southern China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2002,43(6):817-829
doi: 10.1006/jhev.2002.0601 URL |
| [54] | 李普, 钱方, 马醒华, 等. 用古地磁方法对元谋人化石年代的初步研究[J]. 中国科学, 1976,6:579-591 |
| [55] |
Zhu RX, Potts R, Pan YX, et al. Early evidence of the genus Homo in East Asia[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2008,55(6):1075-1085
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2008.08.005 URL |
| [56] |
Hyodo M, Nakaya H, Urabe A, et al. Paleomagnetic dates of hominid remains from Yuanmou, China, and other Asian sites[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2002,43(1):27-41
doi: 10.1006/jhev.2002.0555 URL |
| [57] |
Cai YJ, Qiang XK, Wang XL, et al. The age of human remains and associated fauna from Zhiren Cave in Guangxi, southern China[J]. Quaternary International, 2017,434(Part A):84-91
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.12.088 URL |
| [58] |
Ge JY, Deng CL, Wang Y, et al. Climate-influenced cave deposition and human occupation during the Pleistocene in Zhiren Cave, southwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2020,559:14-23
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2020.01.018 URL |
| [59] |
Wood RE, Douka K, Boscato P, et al. Testing the ABOx-SC method: Dating known-age charcoals associated with the Campanian Ignimbrite[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2012,9:16-26
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2012.02.003 URL |
| [60] |
Douka K, Higham T, Sinitsyn A. The influence of pretreatment chemistry on the radiocarbon dating of Campanian Ignimbrite-aged charcoal from Kostenki 14 (Russia)[J]. Quaternary Research, 2010,73(3):583-587
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2010.01.002 URL |
| [61] |
Higham T, Brock F, Peresani M, et al. Problems with radiocarbon dating the Middle to Upper Palaeolithic transition in Italy[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2009,28(13-14):1257-1267
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2008.12.018 URL |
| [62] |
Higham T. European Middle and Upper Palaeolithic radiocarbon dates are often older than they look: problems with previous dates and some remedies[J]. Antiquity, 2011,85(327):235-249
doi: 10.1017/S0003598X00067570 URL |
| [63] |
Roberts RG, Jones R, Smith MA. Beyond the radiocarbon barrier in Australian prehistory[J]. Antiquity, 1994,68(260):611-616
doi: 10.1017/S0003598X00047116 URL |
| [64] |
Bird MI, Turney CSM, Fifield LK, et al. Radiocarbon analysis of the early archaeological site of Nauwalabila I, Arnhem Land, Australia: implications for sample suitability and stratigraphic integrity[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002,21(8-9):1061-1075
doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00058-0 URL |
| [65] |
Guo YJ, Li B, Zhang JF, et al. New ages for the Upper Palaeolithic site of Xibaimaying in the Nihewan Basin, northern China: implications for small-tool and microblade industries in north-east Asia during Marine Isotope Stages 2 and 3[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2017,32(4):540-552
doi: 10.1002/jqs.v32.4 URL |
| [66] |
Wintle AG, Murray AS. A review of quartz optically stimulated luminescence characteristics and their relevance in single-aliquot regeneration dating protocols[J]. Radiation measurements, 2006,41(4):369-391
doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2005.11.001 URL |
| [67] |
Wang XL, Wintle AG, Lu YC. Thermally transferred luminescence in fine-grained quartz from Chinese loess: basic observations[J]. Radiation measurements, 2006,41(6):649-658
doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2006.01.001 URL |
| [68] |
Buylaert JP, Murray AS, Thomsen KJ, et al. Testing the potential of an elevated temperature IRSL signal from K-feldspar[J]. Radiation measurements, 2009,44(5-6):560-565
doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2009.02.007 URL |
| [69] |
Li B, Li SH. Luminescence dating of K-feldspar from sediments: a protocol without anomalous fading correction[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2011,6(5):468-479
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2011.05.001 URL |
| [70] |
Sun XF, Lu HY, Wang SJ, et al. Hominin distribution in glacial-interglacial environmental changes in the Qinling Mountains range, central China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018,198:37-55
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.08.012 URL |
| [71] |
Thiel C, Buylaert JP, Murray AS, et al. A comparison of TT-OSL and post-IR IRSL dating of coastal deposits on Cap Bon peninsula, north-eastern Tunisia[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2012,10:209-217
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2012.03.010 URL |
| [72] |
Zhao JX, Hu K, Collerson KD, et al. Thermal ionization mass spectrometry U-series dating of a hominid site near Nanjing, China[J]. Geology, 2001,29(1):27-30
doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0027:TIMSUS>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [73] | Shen GJ, Fang YS, Jin LH. Re-examination of the chronological position of Chaoxian Man[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 1994,13(3):349-356 |
| [74] | 高星. “元谋人”的年龄及相关的年代问题讨论[J]. 人类学学报, 2015,34(4):442-450 |
| [75] |
Michel V, Valladas H, Shen G, et al. The earliest modern Homo sapiens in China?[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2016,101:101-104
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2016.07.008 URL |
| [76] | 沈冠军. 洞穴地点骨化石铀系年龄可信度的讨论[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007,27(4):539-545 |
| [77] |
Schwarcz HP, Rink WJ. Dating methods for sediments of caves and rockshelters with examples from the Mediterranean region[J]. Geoarchaeology: An International Journal, 2001,16(4):355-371
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1520-6548 URL |
| [78] |
Han F, Shao QF, Bahain JJ, et al. Coupled ESR and U-series dating of Middle Pleistocene hominin site Bailongdong cave, China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2019,49:291-296
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2018.02.004 URL |
| [79] | Chen TM, Yang Q, Wu E. Electron spin resonance dating of teeth enamel samplws from jingniushan palaeoanthropological site[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 1993,12(4):337-346 |
| [80] | Huang PH, Jin SZ, Peng ZC, et al. ESR dating of tooth enamel: comparison with U-series, FT and TL dating at the Peking Man site[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 1993, 44(1-2): IN9-242 |
| [81] | 黄培华, 梁任又, 郑丽珍, 等. 和县猿人年代的研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1995,14(3):262-265 |
| [82] |
Chen TM, Yang Q, Hu YQ, et al. ESR dating of tooth enamel from Yunxian Homo erectus site, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1997,16(3-5):455-458
doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(96)00095-9 URL |
| [83] | Chen TM, Yang Q, Chen Q, et al. ESR dating of Longgupo profile, Wushan[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2000,19(1):17-20 |
| [84] | 黄培华, 吉云平. 元谋古猿遗址化石年代的测定及其有关问题的探讨[J]. 云南地质, 2000,19(1):91-96 |
| [85] |
Chen TM, Chen Q, Yang Q, et al. The problems in ESR dating of tooth enamel of Early Pleistocene and the age of Longgupo hominid, Wushan, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2001,20(5-9):1041-1045
doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(00)00057-3 URL |
| [86] | 刘春茹, 尹功明. 石英ESR测年信号衰退特征研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2013,28(1):24-30 |
| [87] |
Liu CR, Yin GM, Deng CL, et al. ESR dating of the Majuangou and Banshan Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2014,73:58-63
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2014.05.012 URL |
| [88] |
Granger DE, Gibbon RJ, Kuman K, et al. New cosmogenic burial ages for Sterkfontein Member 2 Australopithecus and Member 5 oldowan[J]. Nature, 2015,522(7554):85-88
doi: 10.1038/nature14268 pmid: 25830884 |
| [89] |
Carbonell E, De Castro JMB, Parés JM, et al. The first hominin of Europe[J]. Nature, 2008,452(7186):465-469
doi: 10.1038/nature06815 pmid: 18368116 |
| [90] |
Pappu S, Gunnell Y, Akhilesh K, et al. Early Pleistocene presence of Acheulian hominins in south India[J]. Science, 2011,331(6024):1596-1599
doi: 10.1126/science.1200183 URL |
| [91] | Guo Y, Sun CK, Luo L, et al. 26Al/10Be Burial Dating of the Middle Pleistocene Yiyuan Hominin Fossil Site, Shandong Province, Northern China[J]. Scientific reports, 2019,9(1):1-8 |
| [92] |
Luo L, Granger DE, Tu H, et al. The first radiometric age by isochron 26Al/10Be burial dating for the Early Pleistocene Yuanmou hominin site, southern China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2020,55:101022
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2019.101022 URL |
| [93] | 陈铁梅, 周力平. 周口店北京猿人遗址的年代综述兼评该遗址的铝铍埋藏年龄[J]. 人类学学报, 2009,28(3):285-291 |
| [94] |
Corbett LB, Bierman PR, Rood DH, et al. Cosmogenic 26Al/10Be surface production ratio in Greenland[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017,44(3):1350-1359
doi: 10.1002/grl.v44.3 URL |
| [95] | 张守信. 理论地层学与应用地层学:现代地层学概念[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006: 340 |
| [96] | 李锋, 陈福友, 赵海龙, 等. 试论“水平层”与旧石器时代遗址考古发掘方法[J]. 考古, 2019,1:85-95 |
| [97] | 俞伟超. 关于“考古地层学”问题[A].见:苏秉琦(主编).考古学文化论集(一)[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1987: 1-32 |
| [98] |
Curnoe D, Zhao JX, Aubert M, et al. Implications of multi-modal age distributions in Pleistocene cave deposits: A case study of Maludong palaeoathropological locality, southern China[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2019,25:388-399
doi: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2019.04.020 URL |
| [99] | 原思训, 陈铁梅, 高世君. 华南若干旧石器时代地点的铀系年代[J]. 人类学学报, 1986,5(2):179-190 |
| [100] |
Keates SG, Hodgins GW, Kuzmin YV, et al. First direct dating of a presumed Pleistocene hominid from China: AMS radiocarbon age of a femur from the Ordos Plateau[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2007,53(1):1-5
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2006.10.006 URL |
| [1] | 裴树文, 蔡演军, 董哲, 同号文, 盛锦朝, 金泽田, 吴秀杰, 刘武. 安徽东至华龙洞遗址洞穴演化与古人类活动[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(04): 593-607. |
| [2] | 杨石霞, 许竞文, 浣发祥. 古人类对赭石的利用行为在其演化中的意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(04): 649-658. |
| [3] | Francesc RIBOT Trafí, Mario GARCÍA Bartual, Alfredo José ALTAMIRANO Enciso, 王谦. 犬齿窝与人类中面部骨骼的演化[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 193-217. |
| [4] | 刘武, 惠家明, 何嘉宁, 吴秀杰. 门齿孔位置在中国古人类化石与现代人群的表现及其演化意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(05): 739-750. |
| [5] | 徐哲, 马姣, 裴树文. 哺乳动物牙釉质碳氧稳定同位素揭示早期人类演化与环境关系[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(03): 454-468. |
| [6] | 陆莹, 孙雪峰, 王社江, 鹿化煜. 早、中更新世中国古人类年代序列与区域演化特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(03): 411-426. |
| [7] | 吴秀杰, 严毅. 资阳人头骨化石的内部解剖结构[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 511-520. |
| [8] | 王谦, 张全超. 全球健康史项目亚洲模块—— 亚洲古代人群健康、疾病和生活方式的大数据[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(04): 727-732. |
| [9] | 尼古拉斯 J. 康纳德, 韩芳. 文化现代性与行为超级适应性之路 ——中科院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所系列课程纪要[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(03): 419-445. |
| [10] | 高星. 制作工具在人类演化中的地位与作用[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(03): 331-340. |
| [11] | 刘武;周蜜;邢松. 卡氏尖在中国古人类化石中出现及其演化意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(02): 159-175. |
| [12] | 张兴龙;毕忠荣;龙小平;吴红敏;王新金;蔡回阳. 贵州清水苑大洞遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(04): 512-526. |
| [13] | 贺乐天;刘武. 现代中国人颞骨乳突后部的形态变异[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(01): 74-86. |
| [14] | 张兴龙;王新金;毕忠荣;吴红敏;周仕敏;易奎香. 贵州省中部和西南部新发现的洞穴遗址调查简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(04): 503-515. |
| [15] | 陈铁梅; 周力平. 周口店北京猿人遗址的年代综述兼评该遗址的铝铍埋藏年龄[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(03): 285-291. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3