

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (02): 308-318.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0025cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0025
收稿日期:2020-04-19
修回日期:2020-12-22
出版日期:2022-04-15
发布日期:2022-04-13
通讯作者:
郭怡
作者简介:施崇阳(1997-),男,浙江杭州人,硕士研究生,主要从事科技考古学研究。E-mail: 基金资助:Received:2020-04-19
Revised:2020-12-22
Online:2022-04-15
Published:2022-04-13
Contact:
GUO Yi
摘要:
对渔业食用资源的利用是人类生业经济的重要方面,然而至今尚无专文介绍如何定量分析渔业食物资源在先民食物结构中所占的比例。本文采用利用同位素传递信号重建食谱(FRUITS)模型,以田螺山遗址与梁王城遗址已发表的先民和动植物稳定同位素数据为例,对先民食物结构中的多种食物资源比重进行分析。结果显示,梁王城遗址渔业资源在食谱中占5%~22%;田螺山遗址淡水渔业资源在食谱中占5%~20%,而海洋渔业资源在10%以下。
中图分类号:
施崇阳, 郭怡. 通过食谱分析探讨田螺山与梁王城遗址先民对渔业资源的利用[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 308-318.
SHI Chongyang, GUO Yi. Discussion on the utilization of fishery resources by the ancestors of Tianluoshan and liangwangcheng sites based on the diet analysis[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022, 41(02): 308-318.
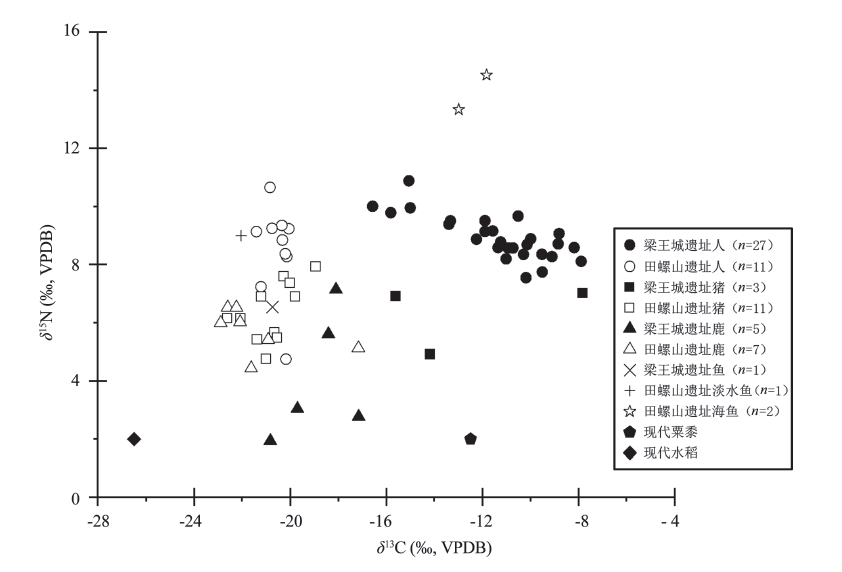
图1 田螺山与梁王城遗址先民、动物碳氮稳定同位素散点图
Fig.1 Scatter diagram of carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes of ancestors and animals in Tianluoshan site and liangwangcheng site
| 样品 | δ13C‰ | δ15N |
|---|---|---|
| DWK87 | -10.293 | 8.355 |
| DWK89 | -12.250 | 8.876 |
| DWK91 | -11.248 | 8.780 |
| DWK93 | -8.814 | 9.072 |
| DWK95 | -16.572 | 10.007 |
| DWK97 | -8.852 | 8.720 |
| DWK99 | -15.010 | 9.955 |
| DWK101 | -11.898 | 9.143 |
| DWK103 | -13.335 | 9.509 |
| DWK105 | -15.064 | 10.888 |
| DWK107 | -10.519 | 9.673 |
| DWK109 | -10.939 | 8.579 |
| DWK111 | -11.018 | 8.202 |
| DWK231 | -7.896 | 8.114 |
| DWK115 | -8.182 | 8.591 |
| DWK117 | -11.897 | 9.517 |
| DWK119 | -9.530 | 8.361 |
| DWK121 | -10.729 | 8.576 |
| DWK123 | -15.819 | 9.792 |
| DWK125 | -9.993 | 8.888 |
| DWK127 | -13.402 | 9.394 |
| DWK129 | -10.191 | 7.555 |
| DWK131 | -9.513 | 7.747 |
| DWK133 | -10.146 | 8.691 |
| DWK135 | -9.108 | 8.278 |
| DWK137 | -11.353 | 8.593 |
| DWK139 | -11.576 | 9.161 |
| TLS No.1 | -20.84 | 10.66 |
| TLS No.2 | -21.41 | 9.14 |
| TLS No.3 | -20.34 | 9.35 |
| TLS No.4 | -20.06 | 9.24 |
| TLS No.5 | -21.22 | 7.24 |
| TLS No.6 | -20.35 | 9.35 |
| TLS No.7 | -20.76 | 9.25 |
| TLS No.8 | -20.15 | 8.28 |
| TLS No.9 | -20.18 | 4.75 |
| TLS No.10 | -20.21 | 8.38 |
| TLS No.11 | -20.33 | 8.85 |
表1 田螺山遗址与梁王城遗址稳定同位素数据[17,18]
Tab.1 Data of stable isotopes from the Tianluoshan site and Liangwangcheng site
| 样品 | δ13C‰ | δ15N |
|---|---|---|
| DWK87 | -10.293 | 8.355 |
| DWK89 | -12.250 | 8.876 |
| DWK91 | -11.248 | 8.780 |
| DWK93 | -8.814 | 9.072 |
| DWK95 | -16.572 | 10.007 |
| DWK97 | -8.852 | 8.720 |
| DWK99 | -15.010 | 9.955 |
| DWK101 | -11.898 | 9.143 |
| DWK103 | -13.335 | 9.509 |
| DWK105 | -15.064 | 10.888 |
| DWK107 | -10.519 | 9.673 |
| DWK109 | -10.939 | 8.579 |
| DWK111 | -11.018 | 8.202 |
| DWK231 | -7.896 | 8.114 |
| DWK115 | -8.182 | 8.591 |
| DWK117 | -11.897 | 9.517 |
| DWK119 | -9.530 | 8.361 |
| DWK121 | -10.729 | 8.576 |
| DWK123 | -15.819 | 9.792 |
| DWK125 | -9.993 | 8.888 |
| DWK127 | -13.402 | 9.394 |
| DWK129 | -10.191 | 7.555 |
| DWK131 | -9.513 | 7.747 |
| DWK133 | -10.146 | 8.691 |
| DWK135 | -9.108 | 8.278 |
| DWK137 | -11.353 | 8.593 |
| DWK139 | -11.576 | 9.161 |
| TLS No.1 | -20.84 | 10.66 |
| TLS No.2 | -21.41 | 9.14 |
| TLS No.3 | -20.34 | 9.35 |
| TLS No.4 | -20.06 | 9.24 |
| TLS No.5 | -21.22 | 7.24 |
| TLS No.6 | -20.35 | 9.35 |
| TLS No.7 | -20.76 | 9.25 |
| TLS No.8 | -20.15 | 8.28 |
| TLS No.9 | -20.18 | 4.75 |
| TLS No.10 | -20.21 | 8.38 |
| TLS No.11 | -20.33 | 8.85 |
| 种类 | δ13C | δ15N | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻 | -26.5‰ | 2‰ | [ |
| 鹿类 | -21.37‰ | 5.73‰ | [ |
| 猪 | -20.42‰ | 6.45‰ | [ |
| 淡水鱼 | -22.05‰ | 9‰ | [ |
| 海鱼 | -12.41‰ | 13.94‰ | [ |
表2 田螺山遗址食谱模型
Tab.2 Food model of the Tianluoshan site
| 种类 | δ13C | δ15N | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻 | -26.5‰ | 2‰ | [ |
| 鹿类 | -21.37‰ | 5.73‰ | [ |
| 猪 | -20.42‰ | 6.45‰ | [ |
| 淡水鱼 | -22.05‰ | 9‰ | [ |
| 海鱼 | -12.41‰ | 13.94‰ | [ |
| 食物种类 | δ13C | δ15N | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粟黍 | -12.5‰ | 2‰ | [ |
| 鹿类 | -19.26‰ | 4.44‰ | [ |
| 猪 | -14.9‰ | 5.92‰ | [ |
| 淡水鱼 | -20.74‰ | 6.54‰ | [ |
表3 梁王城遗址食谱模型
Tab.3 Food model of the Liangwangcheng site
| 食物种类 | δ13C | δ15N | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粟黍 | -12.5‰ | 2‰ | [ |
| 鹿类 | -19.26‰ | 4.44‰ | [ |
| 猪 | -14.9‰ | 5.92‰ | [ |
| 淡水鱼 | -20.74‰ | 6.54‰ | [ |
| [1] | Crawford MA, Bloom M, Broadhurst CL, et al. Evidence for the unique function of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) during the evolution of the modern hominid brain[J]. Lipids, 1999, 34 Suppl(S1):S39-47 |
| [2] |
Wing S. Wing E. Prehistoric fisheries in the Caribbean[J]. Coral Reefs, 2001, 20(1):1-8
doi: 10.1007/s003380100142 URL |
| [3] | 吴诗池. 从考古资料看我国史前的渔业生产[J]. 农业考古, 1987, (1):234-248 |
| [4] |
Nakajima T, Nakajima M, Mizuno T, et al. On the Pharyngeal Tooth Remains of Crucian and Common Carp from the Neolithic Tianluoshan Site, Zhejiang Province, China, with Remarks on the Relationship Between Freshwater Fishing and Rice Cultivation in the Neolithic Age[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2012, 22(3):294-304
doi: 10.1002/oa.1206 URL |
| [5] | 刘宪亭. 禄丰古猿化石地点的鱼化石[J]. 人类学学报, 1985,(2):109-112 |
| [6] | Broadhurst C L, Wang Y, Crawford MA, et al. Brain-specific lipids from marine, lacustrine, or terrestrial food resources: potential impact on early African Homo sapiens[J]. Comparative Biochemistry & Physiology Part B Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 2002, 131(4):653-673 |
| [7] | 王芬, 樊榕, 康海涛, 等. 即墨北阡遗址人骨稳定同位素分析:沿海先民的食物结构[J]. 科学通报, 2012,(12):1037-1044 |
| [8] | 袁靖. 长江三角洲地区新石器时代动物考古学研究的思考——兼论田螺山遗址动物考古学研究的相关问题[A].见:北京大学中国考古学研究中心,浙江省文物考古研究所.田螺山遗址自然遗存综合研究[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2011, 270-278 |
| [9] | 赵荦. 中国沿海先秦贝丘遗址研究[D]. 上海:复旦大学, 2014 |
| [10] | Richards MP, Schulting R J, Hedges R E M. Archaeology: sharp shift in diet at onset of Neolithic[J]. Nature, 2003, 425(6956):366-366. |
| [11] | Limburg KE, Walther Y, Hong B, et al. Prehistoric versus modern Baltic Sea cod fisheries: selectivity across the millennia[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society Biological Sciences, 2008, 275(1652):2659-2665 |
| [12] |
Richards MP, Pettitt PB, Stiner M C, et al. Stable isotope evidence for increasing dietary breadth in the European mid-Upper Paleolithic[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2001, 98(11):6528-6532
pmid: 11371652 |
| [13] | Hu Y, Shang H, Tong H, et al. Stable isotope dietary analysis of the Tianyuan 1 early modern human[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(27):10971-10974. |
| [14] | 王芬, 宋艳波, 李宝硕, 等. 北阡遗址人和动物骨的C, N稳定同位素分析[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2013(12):2029-2036 |
| [15] | 胡耀武, 李法军, 王昌燧, 等. 广东湛江鲤鱼墩遗址人骨的C、N稳定同位素分析:华南新石器时代先民生活方式初探[J]. 人类学学报, 2010(3):264-269 |
| [16] | Porcasi JF, Andrews SL. Evidence for a Prehistoric Fishery on the Southern California Coast[J]. Journal of California & Great Basin Anthropology, 2015, 23(1):51-66 |
| [17] | Dong Y. Eating identity: food, gender, and social organization in late Neolithic northern China[D]. Urbana, Illinois: University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Phd thesis. 2013 |
| [18] | 董艳芳. 以田螺山遗址先民(动物)的食物结构分析为例[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2016 |
| [19] | 胡耀武, 李法军, 王昌燧, 等. 广东湛江鲤鱼墩遗址人骨的C、N稳定同位素分析:华南新石器时代先民生活方式初探[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(03):264-269 |
| [20] |
Benstead JP, March JG, Fry B, et al. Testing isosource: Stable isotope analysis of a tropical fishery with diverse organic matter sources[J]. Ecology, 2006, 87(2):326-333
doi: 10.1890/05-0721 URL |
| [21] |
Phillips DL, Gregg JW. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too many sources[J]. Oecologia, 2003, 136(2):261-269
pmid: 12759813 |
| [22] | Phillips D. Mixing models in analyses of diet using multiple stable isotopes: a critique[J]. Oecologia, 2001, 172(2):180-184 |
| [23] |
Moore JW, Semmens BX. Incorporating Uncertainty and Prior Information Into Stable Isotope Mixing Models[J]. Ecology Letters, 2008, 11(5):470-480
doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01163.x URL |
| [24] |
Fernandes R, Grootes P, Nadeau, Marie-Josée, et al. Quantitative diet reconstruction of a Neolithic population using a Bayesian mixing model (FRUITS): The case study of Ostorf (Germany)[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2015, 158(2):325-340
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.22788 pmid: 26175210 |
| [25] |
Hu Y. Thirty-Four Years of Stable Isotopic Analyses of Ancient Skeletons in China: an Overview, Progress and Prospects[J]. Archaeometry, 2018, 60(1):144-156
doi: 10.1111/arcm.v60.1 URL |
| [26] |
Ambrose SH, Krigbaum J. Bone chemistry and bioarchaeology[J]. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, 2003, 22(3):193-199.
doi: 10.1016/S0278-4165(03)00033-3 URL |
| [27] | Limburg KE, Walther Y, Hong B, et al. Prehistoric versus modern Baltic Sea cod fisheries: selectivity across the millennia[J]. Proceedings Biological Sciences, 2008, 275(1652):2659-2665 |
| [28] |
Phillips DL, Inger R, Bearhop S, et al. Best practices for use of stable isotope mixing models in food-web studies[J]. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 2014, 92(10):823-835
doi: 10.1139/cjz-2014-0127 URL |
| [29] |
Armas YCD, Roksandic M, Dejana Nikitović, et al. Isotopic reconstruction of the weaning process in the archaeological population of Canímar Abajo, Cuba: A Bayesian probability mixing model approach[J]. Plos One, 2017, 12(5):e0176065
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176065 URL |
| [30] |
Aguraiuja L, Constantinescu M, Lamb A, et al. Bronze Age subsistence strategies in the southeastern Carpathian Bend area, Romania: Results from stable isotope analyses[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2018, 17:510-519
doi: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2017.12.013 URL |
| [31] |
Pate FD. Stable carbon isotope assessment of hunter—Gatherermobility in prehistoric South Australia[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1995, 22(1):81-87
doi: 10.1016/S0305-4403(95)80164-2 URL |
| [32] | Ricardo F, Marie-Josée N, Pieter M. G. Macronutrient-based model for dietary carbon routing in bone collagen and bioapatite[J]. 2012. 4(4):291-301 |
| [33] | 南京博物馆. 梁王城遗址发掘报告(史前卷)(上下)[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2013 |
| [34] | 张颖, 袁靖, 黄蕴平, 等. 田螺山遗址2004年出土哺乳动物遗存的初步分析[A].见:北京大学中国考古学研究中心,浙江省文物考古研究所.田螺山遗址自然遗存综合研究[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2011, 172-205 |
| [35] | 孙国平, 黄渭金, 郑云飞, 等. 浙江余姚田螺山新石器时代遗址2004年发掘简报[J]. 文物, 2007(11):4-24 |
| [36] | Guo Y, Wu R, Sun G, et al. Neolithic cultivation of water chestnuts (Trapa L.) at Tianluoshan (7000-6300 cal BP), Zhejiang Province, China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, e16206 |
| [37] |
Li C, Zheng Y, Yu S, et al. Understanding the ecological background of rice agriculture on the Ningshao Plain during the Neolithic Age: pollen evidence from a buried paddy field at the Tianluoshan cultural site[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 35:131-138
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.01.007 URL |
| [38] | 秦岭, 傅稻镰, 张海. 早期农业聚落的野生食物资源域研究——以长江下游和中原地区为例[J]. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(2):245-261 |
| [39] | 郑云飞, 孙国平, 陈旭高. 7000年前考古遗址出土稻谷的小穗轴特征[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(009):1037-1041 |
| [40] | 南京博物院, 徐州博物馆, 邳州博物馆. 江苏邳州梁王城遗址大汶口文化遗存发掘简报[J]. 东南文化, 2013(4):21-41 |
| [41] | 郑淑蕙. 稳定同位素地球化学分析[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1986 |
| [42] |
Kohn MJ. You Are What You Eat[J]. Science, 1999, 283(5400):335-336
pmid: 9925492 |
| [43] | 王淑云, 莫多闻, 孙国平, 等. 浙江余姚田螺山遗址古人类活动的环境背景分析——植硅体、硅藻等化石证据[J]. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(2):326-334 |
| [44] |
Deniro MJ. Influence of diet on the distribution of nitrogen isotopes in animals[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 1981, 45:341-351
doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90244-1 URL |
| [45] |
Nakajima T, Nakajima M, Mizuno T, et al. On the Pharyngeal Tooth Remains of Crucian and Common Carp from the Neolithic Tianluoshan Site, Zhejiang Province, China, with Remarks on the Relationship Between Freshwater Fishing and Rice Cultivation in the Neolithic Age[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2012, 22(3):294-304
doi: 10.1002/oa.1206 URL |
| [46] | 南川雅男, 松井章, 中村慎一, 等. 由田螺山遗址出土的人类与动物骨骼胶质炭氮同位素组成推测河姆渡文化的食物资源与家畜利用[A]. 见:北京大学中国考古学研究中心,浙江省文物考古研究所.田螺山遗址自然遗存综合研究[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2011, 262-269 |
| [47] | 潘艳, 袁靖. 新石器时代至先秦时期长江下游的生业形态研究(上)[J]. 南方文物, 2018(04):117-131 |
| [48] | 赵琳, 马春梅, 林留根, 等. 苏北梁王城遗址地层记录的环境演变与人类活动[J]. 地层学杂志, 2014, 38(1):33-41 |
| [1] | 黄嫣, 胡耀武. 陶器脂肪酸揭示古人类食谱的研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 865-880. |
| [2] | 刘柯雨, 孙周勇, 孙战伟, 邵晶, 陈靓, 凌雪. 黄陵寨头河与史家河墓地人骨的碳氮稳定同位素[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(03): 419-428. |
| [3] | 吴晓桐, 张兴香. 关于锶同位素考古研究的几个问题[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(03): 535-550. |
| [4] | 胡耀武. 稳定同位素生物考古学的概念、简史、原理和目标[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(03): 526-534. |
| [5] | 张兴香, 李雍, 吴晓桐, 宋艳波, 栾丰实, 薛新明, 金正耀. 黄河流域出土龙山时期扬子鳄骨板的多种同位素分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(01): 75-86. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 444
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 569
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3