

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (04): 712-730.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0032cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0032
收稿日期:2022-04-15
修回日期:2022-05-22
出版日期:2022-08-12
发布日期:2022-08-10
作者简介:张家富,教授,主要从事释光年代学及其在考古和地貌第四纪上的应用研究。Email: 基金资助:Received:2022-04-15
Revised:2022-05-22
Online:2022-08-12
Published:2022-08-10
摘要:
释光测年技术已成为旧石器和古人类遗址,尤其是现代人类遗址,建立年代框架的重要工具之一。这一技术提供了现代人类出现在非洲、亚洲和澳大利亚的最早年代证据。本文简要介绍了释光测年的基本原理,对释光测年的可靠性和上限及所受的影响因素进行了综述。光释光测年的精密度(相对标准误差σ)一般为5%-10%,在理想条件下σ<5%,但是σ>10%的情况也不少见。与大量其他测年方法所获结果的一致性表明,光释光测年技术是可靠的。光释光测年的上限与样品的释光性质及环境剂量率有关,释光可靠年龄最大可达1百万年。对大多数遗址50万年的测年上限是可行的,这个年代范围涵盖了所有的现代人遗址。不同样品或颗粒间的释光性质差异很大,因而它们有不同的测年上限。同一样品中钾长石比石英有更高的测年上限,同一矿物中不同的释光信号对应的测年上限也不同。
中图分类号:
张家富. 旧石器和古人类遗址释光测年技术的可靠性和测年上限[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(04): 712-730.
ZHANG Jiafu. Reliability and upper age limit of luminescence dating for the Paleolithic and paleoanthropological sites[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022, 41(04): 712-730.
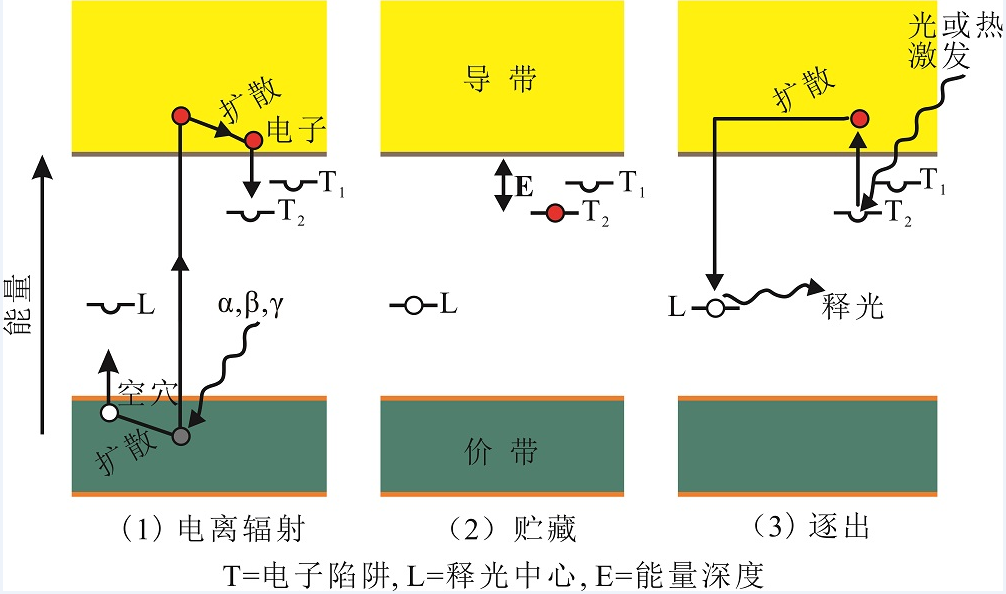
图1 说明释光过程的能带模型示意图(修改自文献[1,2]) 1) 晶体受到放射性辐照使原子发生电离产生电子-空穴对,将电子从价带推入导带并在价带留下空穴,电子和空穴分别被T和L晶体缺陷(陷阱)捕获Ionizing radiation (α, β, γ) produces electron-hole pairs, pushing electrons into the conduction band, leaving holes in the valence band, and resulting in the trapping of electrons and holes at T and L defects (traps), respectively;2) 在电子陷阱中的电子(T)和在复合释光中心(L)的空穴的储存寿命从数秒到数百万年不等,它取决于陷阱在导带下面的能量深度(E),陷阱越深,电子越稳定,停留的时间越长Electrons in electron traps (T) and holes in the recombination center have lifetimes ranging from seconds to millions of years. The lifetime is dependent on the energy depth (E) of the traps below the conduction band. The more stable the electron and the longer it stays trapped;3) 当样品受到加热或合适波长的光照时,电子从电子陷阱中被驱逐出来,其中一些通过导带到达释光中心(L)与捕获的空穴重新复合并发出释光 By heating and shining light, electrons are released from the electron traps, some of them reach the luminescence center (L) through the conduction band, recombine with holes at luminescence centers and emit light (TL or OSL)
Fig.1 Simple energy-band-model for luminescence processes (after reference [1,2])
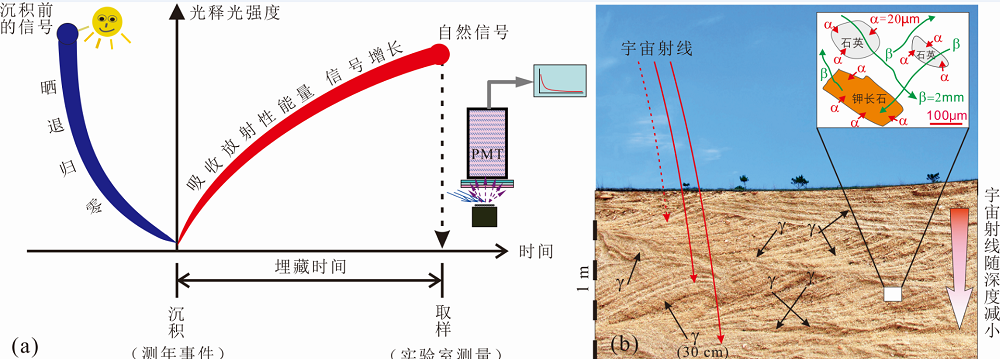
图2 沉积物释光测年基本原理示意图 图中PMT表示光电倍增管;(a)沉积物颗粒在搬运过程中原来的释光信号因光照晒退回零,在埋藏后接受周围中的放射性(α、β和γ射线)辐照(b)产生新的释光信号直到取样测量。
Fig.2 The basic principle of luminescence dating of sediments PMT refers to photomultiplier; (a) Sediment grains are exposed to sunlight during transportation, their luminescence signals are bleached and zeroed. The grains are irradiated by α-particles, beta and gamma rays during the burial period (b), and the signals have been accumulated until sampling for OSL measurement.
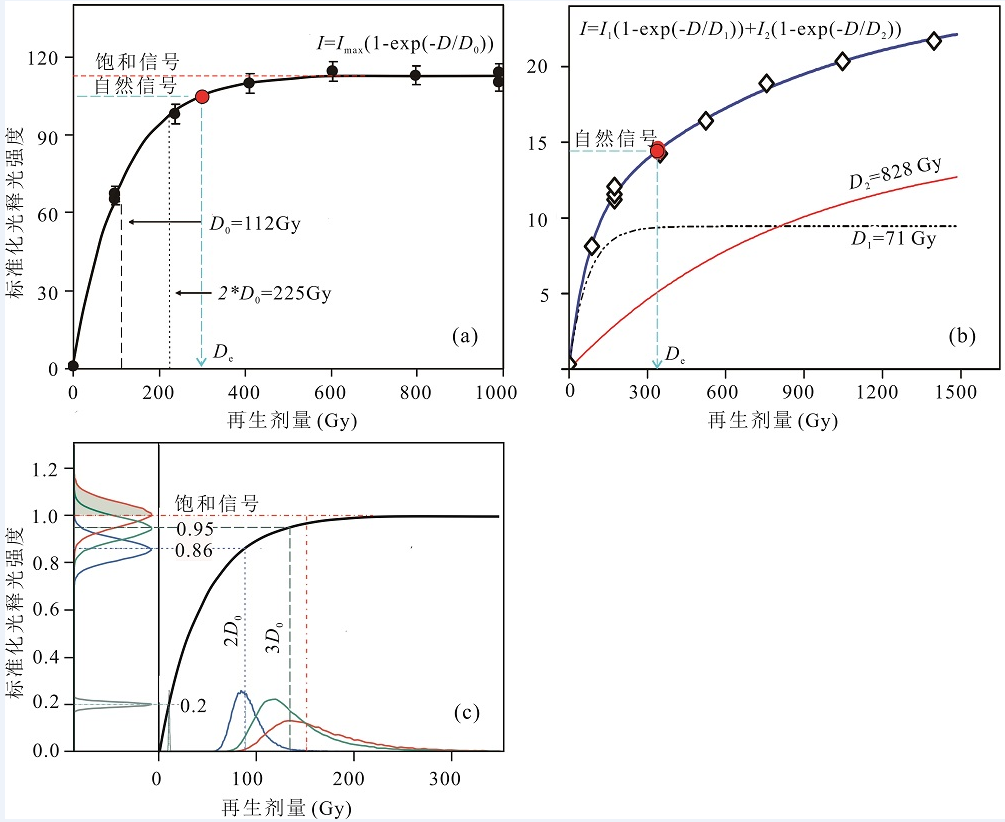
图3 用单片再生法建立的石英光释光信号生长曲线(剂量-反应曲线) a)当辐照(再生)剂量(D)达到600 Gy 左右时,光释光信号(I)达到完全饱和,样品的特征饱和剂量(D0)为112 Gy,将样品的自然光释光信号投影到曲线上可求出样品的等效剂量(De),该样品(HS11-1)来自西班牙Huéscar-1动物化石遗址中的河流沉积物[31,32]。b)该生长曲线为双饱和指数方程拟合,样品在1500 Gy剂量后还在随再生剂量增加而增加,两个函数的特征饱和指数分别是71 Gy和828 Gy,该样品为来自贵州盘县大洞旧石器洞穴遗址的堆积物[33]。c)生长曲线斜率对计算等效剂量误差的影响(修改自文献[26]),当光释光信号是饱和信号强度的20%、86%、96% 和100%(y轴)时对对应的等效剂量分布(x轴),图中假设光释光信号的相对准偏差为5%,且是正态分布,当光释光信号为饱和信号强度95%和100%时,它们分别有15%和50%的信号(图中灰色部分)不能投影到曲线上,从而引起等效剂量的低估[34,35]。
Fig.3 Growth (dose-response) curves for quartz obtained using the single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol (a) The curve is fitted using a single saturation exponential function. The OSL signal (I) is saturated when the regenerative dose (D) reaches 600 Gy, and the characteristic saturation dose (D0) of the curve is 112 Gy. The natural signal is projected onto the fitted growth curve to estimate the De value by interpolation. This sample (HS11-1) is fluvial sediment from the Huéscar-1 site in Spain[31,32]. (b) Growth curve was fitted using double saturating exponential function. The OSL signal increases with increasing dose when the dose was larger than 1500 Gy, the two characteristic saturation doses are 71 Gy and 828 Gy, respectively. This sample from the Panxian Dadong cave in Guizhou province[33]. (c) The effect of the slope of a growth curve on De error (see details in reference [26]). When the natural luminescence signals are close to the maximum level of the curve, the corresponding De obtained may be underestimated [34,35]
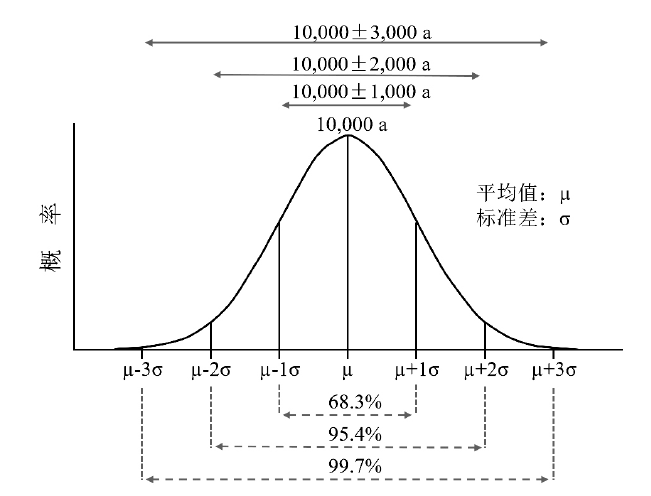
图4 正态或高斯分布和标准差 图中的年代是一个例子; µ 和 σ 分别表示平均值和标准差
Fig.4 The normal or Gaussian distribution and standard deviation the age in the figure is an example; µ and σ refer to mean and standard deviation, respectively
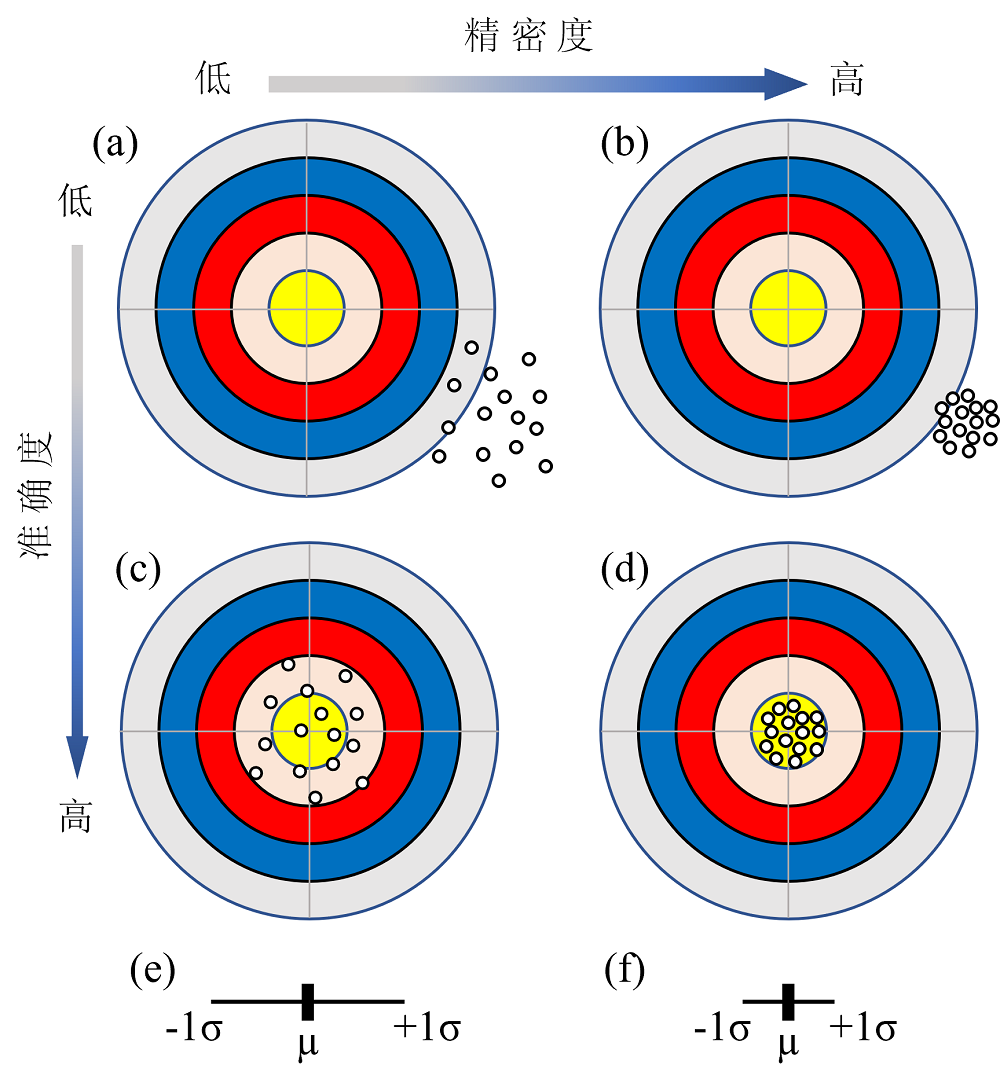
图5 用来说明精密度和准确度区别的靶标 µ 和 σ 分别表示平均值和标准差
Fig.5 Targets used to illustrate the difference between precision and accuracy µ and σ refer to mean and standard error, respectively
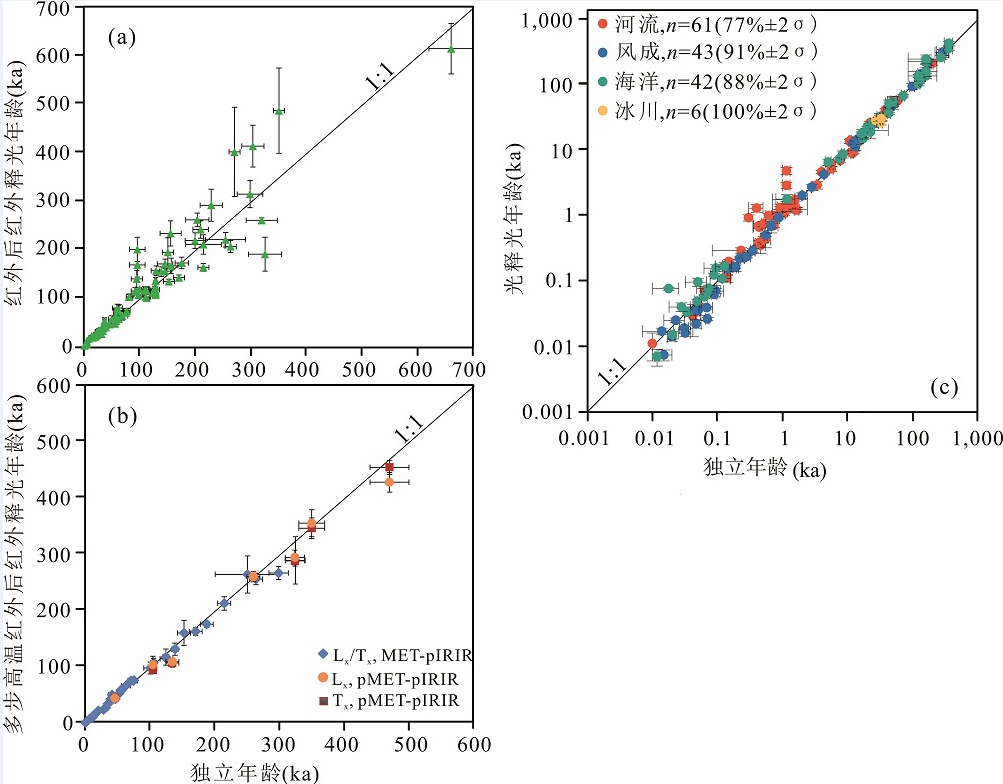
图 6 钾长石和石英的光释光年龄与其对应的独立年龄(其他测年方法得到的年龄)的比较 图中的斜线为1:1线或比值,每个数据点的误差棒为 1σ误差。(a)来自世界各地116个样品的钾长石两步法红外后红外释光年龄和(b)来自欧亚45个样品的钾长石多步高温红外后红外(MET-pIRIR 或pMET-pIRIR)释光年龄,其中Lx、Tx和 Lx/Tx,分别表示再生(或自然)剂量和试验剂量产生的释光信号和灵敏度校正后的释光信号(修改自文献[4]);(c)来自世界各地152个释光信号晒退回零较好样品的石英光释光年龄,图中n表示样品数,以及在1:1线±2σ误差范围内的样品百分比(修改自文献[26])。
Fig.6 Comparison of potassium feldspar and quartz OSL ages with their corresponding independent ages obtained by other dating methods The lines in the figures are 1:1 lines or ratios, and the error bars for each data point refer to 1σ error. (a) The two-step pIRIR ages of potassium feldspar for 116 samples around the world, and (b) Multi-elevated-temperature (METor pMET) pIRIR ages of potassium feldspar from 45 samples from Europe and Asia, where Lx, Tx and Lx/Tx respectively represent regeneration-dose (or natural) OSL, test-dose OSL and sensitivity-corrected OSL signals (modified from reference [4]); (c) The quartz OSL ages of the 152 samples from all over the world. The samples are fluvial, eolian, ocean, and glacial sediments, which were well bleached prior to deposition. n = the number of samples, followed by the percentage of samples within ±2σ error of the 1:1 line (modified from reference [26])
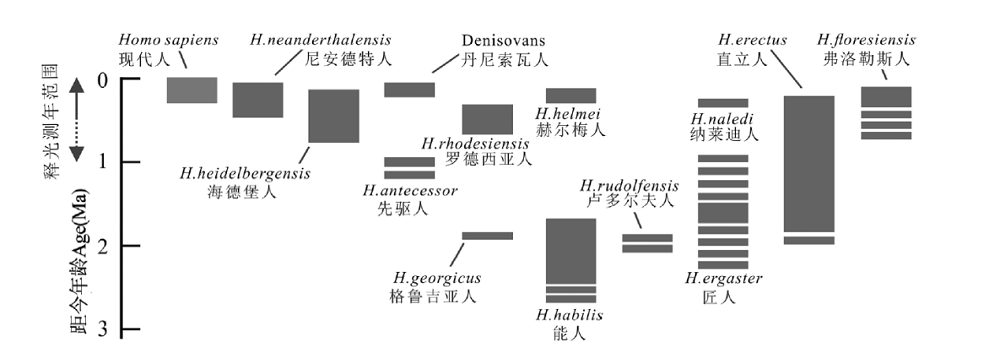
图7 已经公认的部分古人类分类群时间范围和释光测年范围 释光测年范围:双箭头表示获得可靠释光年龄的大致区间,虚线是理想环境下的范围(修改自文献[25])
Fig.7 The time range of hominin taxa currently recognized and the age range and luminescence dating Luminescence dating range: The double arrows indicate the approximate interval where reliable luminescence ages can be obtained (modified from reference [25])
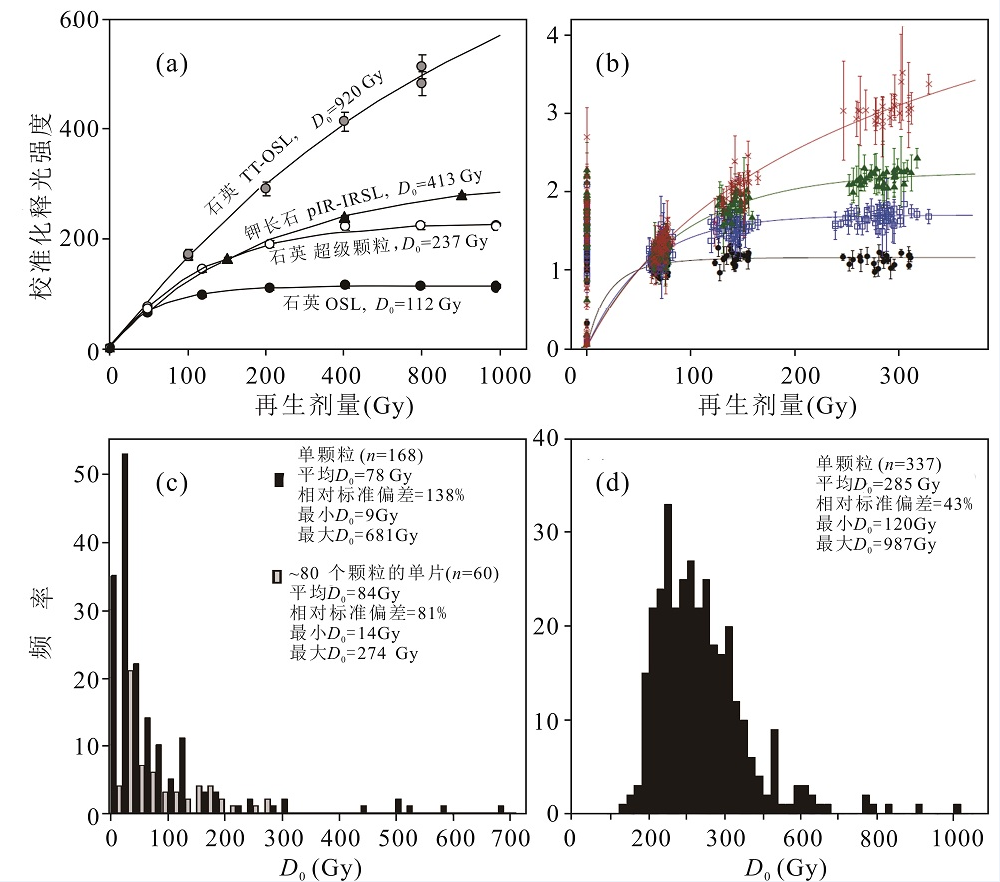
图8 石英和钾长石光释光信号生长曲线和其特征饱和剂量(D0)分布 (a)同一样品中不同矿物和释光信号的生长曲线:石英TT-OSL信号、钾长石红外后红外释光信号(pIRIR),石英超级颗粒的OSL和一般石英的OSL信号,该样品(HS11-1)来自西班牙Huéscar-1遗址中的河流堆积物[31,32] Growth curves for different luminescence signals from quartz and potassium feldspar, the sample (HS11-1)is from the Huéscar-1 site in Spain[31,32]。(b)来自贵州观音洞遗址堆积物中样品GYD-OSL8的粗粒石英生长曲线,根据曲线的形状可将该样品中的石英颗粒分为4类,其中有近40%的颗粒的自然光释光信号已经饱和[19]Growth curve for a fine quartz aliquot from sample GYD-OSL8 from the Guanyindong cave in Guizhou province[19], based on the shapes of the curves, four groups are divided。(c) 西伯利亚3个石英样品和 (d)西班牙Cuesta de la Bajada旧石器遗址3个石英样品的D0值分布的直方图[31,32] (c) and (d) D0 distribution of the quartz grains from three samples from Siberia and three quartz samples from the Cuesta de la Bajada site, respectively[31,32]
Fig.8 Dose response curves for different luminescence signals from quartz and potassium feldspar and distribution of characteristic dose (D0)
| [1] | Aitken MJ. Thermoluminescence Dating[M]. London: Academic Press, 1985 |
| [2] | Aitken MJ. An Introduction to Optical Dating: The Dating of Quaternary Sediments by the Use of Photon-Stimulated Luminescence[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998 |
| [3] |
Zhang JF, Dennell R. The last of Asia conquered by Homo sapiens[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6418): 992-993
doi: 10.1126/science.aav6863 URL |
| [4] |
Roberts RG, Jacobs Z, Li B, et al. Optical dating in archaeology: thirty years in retrospect and grand challenges for the future[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015, 56: 41-60
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2015.02.028 URL |
| [5] |
Athanassas CD, Wagner GA. Geochronology beyond radiocarbon: optically stimulated luminescence dating of palaeoenvironments and archaeological sites[J]. Elements, 2016, 12(1): 27-32
doi: 10.2113/gselements.12.1.27 URL |
| [6] |
Daniels F, Boyd CA, Saunders DF. Thermoluminescence as a research tool[J]. Science, 1953, 117(3040): 343-349
pmid: 17756578 |
| [7] |
Zimmerman DW, Huxtable J. Thermoluminescent dating of Upper Palaeolithic fired clay from Dolni Vestonice[J]. Archaeometry, 1971, 13(1): 53-57
doi: 10.1111/j.1475-4754.1971.tb00029.x URL |
| [8] |
Roberts RG. Luminescence dating in archaeology: from origins to optical[J]. Radiation Measurements, 1997, 27(5-6): 819-892
doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(97)00221-7 URL |
| [9] |
Göksu HY, Fremlin JH, Irwin HT, et al. Age determination of burned flint by a thermoluminescent method[J]. Science, 1974, 183(4125): 651-654
pmid: 17778839 |
| [10] | Adams G, Mortlock A J. Thermoluminescent dating of baked sand from fire hearths at Lake Mungo, New South Wales[J]. Archaeology and Physical Anthropology in Oceania, 1974, 9(3): 236-237 |
| [11] |
Huntley DJ, Godfrey-Smith DI, Thewalt MLW. Optical dating of sediments[J]. Nature, 1985, 313(5998): 105-107
doi: 10.1038/313105a0 URL |
| [12] | Balter M. Dating duo illuminates modern humans' journey[J]. Science, 2011, 332(6030): 658-661 |
| [13] |
Roberts RG, Lian OB. Illuminating the past[J]. Nature, 2015, 520(7548): 438-439
doi: 10.1038/520438a URL |
| [14] |
Armitage SJ, Jasim SA, Marks AE, et al. The southern route “out of Africa”: evidence for an early expansion of modern humans into Arabia[J]. Science, 2011, 331(6016): 453-456
doi: 10.1126/science.1199113 pmid: 21273486 |
| [15] |
Henshilwood CS, d’Errico F, Van Niekerk KL, et al. A 100,000-year-old ochre-processing workshop at Blombos Cave, South Africa[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6053): 219-222
doi: 10.1126/science.1211535 URL |
| [16] |
Slimak L, Svendsen JI, Mangerud J, et al. Late Mousterian persistence near the Arctic circle[J]. Science, 2011, 332(6031): 841-845
doi: 10.1126/science.1203866 URL |
| [17] |
Waters MR, Forman SL, Jennings TA, et al. The Buttermilk Creek complex and the origins of Clovis at the Debra L. Friedkin site, Texas[J]. Science, 2011, 331(6024): 1599-1603
doi: 10.1126/science.1201855 URL |
| [18] |
Jacobs Z, Li B, Shunkov MV, et al. Timing of archaic hominin occupation of Denisova Cave in southern Siberia[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7741): 594-599
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0843-2 URL |
| [19] |
Hu Y, Marwick B, Zhang J F, et al. Late Middle Pleistocene Levallois stone-tool technology in southwest China[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7737): 82-85
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0710-1 URL |
| [20] |
Douka K, Slon V, Jacobs Z, et al. Age estimates for hominin fossils and the onset of the Upper Palaeolithic at Denisova Cave[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7741): 640-644
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0870-z URL |
| [21] |
Feathers JK. Luminescence dating and modern human origins[J]. Evolutionary Anthropology, 1996, 5(1): 25-36
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6505(1996)5:1<25::AID-EVAN7>3.0.CO;2-V URL |
| [22] |
Jacobs Z, Roberts RG. Advances in optically stimulated luminescence dating of individual grains of quartz from archeological deposits[J]. Evolutionary Anthropology, 2007, 16(6): 210-223
doi: 10.1002/evan.20150 URL |
| [23] |
Richter D. Advantages and limitations of thermoluminescence dating of heated flint from Paleolithic sites[J]. Geoarchaeology: An International Journal, 2007, 22(6): 671-683
doi: 10.1002/gea.20180 URL |
| [24] |
Cochrane GWG, Doelman T, Wadley L. Another dating revolution for prehistoric archaeology?[J]. Journal of Archaeological Method and Theory, 2013, 20(1): 42-60
doi: 10.1007/s10816-011-9125-0 URL |
| [25] | Roberts RG, Jacobs Z. Timelines for human evolution and dispersals[J]. Elements: An International Magazine of Mineralogy, Geochemistry, and Petrology, 2018, 14(1): 27-32 |
| [26] |
Murray A, Arnold LJ, Buylaert JP, et al. Optically stimulated luminescence dating using quartz[J]. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 2021, 1(1): 1-31
doi: 10.1038/s43586-020-00001-2 URL |
| [27] |
Zhang J, Li SH. Review of the post-IR IRSL dating protocols of K-Feldspar[J]. Methods and Protocols, 2020, 3(1): 7
doi: 10.3390/mps3010007 URL |
| [28] | Duller G. Luminescence Dating: Guidelines on using luminescence dating in archaeology[M]. Swindon: English Heritage, 2008 |
| [29] |
Nelson MS, Gray HJ, Johnson JA, et al. User guide for luminescence sampling in archaeological and geological contexts[J]. Advances in Archaeological Practice, 2015, 3(2): 166-177
doi: 10.7183/2326-3768.3.2.166 URL |
| [30] |
Murray AS, Wintle AG. Luminescence dating of quartz using an improved single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2000, 32(1): 57-73
doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(99)00253-X URL |
| [31] |
Demuro M, Arnold LJ, Parés JM, et al. Extended-range luminescence chronologies suggest potentially complex bone accumulation histories at the Early-to-Middle Pleistocene palaeontological site of Huéscar-1 (Guadix-Baza basin, Spain)[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 389: 191-212
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.08.035 URL |
| [32] |
Arnold LJ, Demuro M, Parés JM, et al. Evaluating the suitability of extended-range luminescence dating techniques over early and Middle Pleistocene timescales: published datasets and case studies from Atapuerca, Spain[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 389: 167-190
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.08.010 URL |
| [33] |
Zhang JF, Huang WW, Hu Y, et al. Optical dating of flowstone and silty carbonate-rich sediments from Panxian Dadong Cave, Guizhou, southwestern China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015, 30: 479-486
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.01.011 URL |
| [34] |
Li B, Jacobs Z, Roberts RG, et al. Variability in quartz OSL signals caused by measurement uncertainties: Problems and solutions[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2017, 41: 11-25
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2017.05.006 URL |
| [35] |
Li B, Jacobs Z, Roberts RG. Validation of the LnTn method for De determination in optical dating of K-feldspar and quartz[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2020, 58: 101066
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2020.101066 URL |
| [36] |
Rodnight H, Duller GAT, Wintle AG, et al. Assessing the reproducibility and accuracy of optical dating of fluvial deposits[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2006, 1(2): 109-120
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.05.017 URL |
| [37] |
Galbraith RF, Roberts RG. Statistical aspects of equivalent dose and error calculation and display in OSL dating: an overview and some recommendations[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2012, 11: 1-27
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2012.04.020 URL |
| [38] | Huntley DJ, Lian OB, Lemmen DS, et al. Determining when a sediment was last exposed to sunlight by optical dating[J]. Holocene climate and environmental change in the Pallister Triangle: a geoscientific context for evaluating the impacts of climate change on the Southern Canada Prairies. Geological Survey of Canada Bulletin, 1999, 543: 211-222 |
| [39] | Murray AS, Olley JM. Precision and accuracy in the optically stimulated luminescence dating of sedimentary quartz: a status review[J]. Geochronometria, 2002, 21(1): 1-16 |
| [40] |
Martini M, Sibilia E. Radiation in archaeometry: archaeological dating[J]. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2001, 61(3-6): 241-246
doi: 10.1016/S0969-806X(01)00247-X URL |
| [41] |
Rhodes EJ. Optically stimulated luminescence dating of sediments over the past 200,000 years[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2011, 39: 461-488
doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-040610-133425 URL |
| [42] |
Duller GAT, Tooth S, Barham L, et al. New investigations at Kalambo Falls, Zambia: Luminescence chronology, site formation, and archaeological significance[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2015, 85: 111-125
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2015.05.003 pmid: 26073072 |
| [43] |
Jacobs Z, Roberts RG, Galbraith R F, et al. Ages for the Middle Stone Age of southern Africa: implications for human behavior and dispersal[J]. Science, 2008, 322(5902): 733-735
doi: 10.1126/science.1162219 URL |
| [44] |
Guérin G, Murray AS, Jain M, et al. How confident are we in the chronology of the transition between Howieson’s Poort and Still Bay[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2013, 64(4): 314-317
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.01.006 URL |
| [45] |
Jacobs Z, Roberts RG. Single-grain OSL chronologies for the Still Bay and Howieson's Poort industries and the transition between them: Further analyses and statistical modelling[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2017, 107: 1-13
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2017.02.004 URL |
| [46] |
Watanuki T, Murray AS, Tsukamoto S. Quartz and polymineral luminescence dating of Japanese loess over the last 0.6 Ma: Comparison with an independent chronology[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 240(3-4): 774-789
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.09.027 URL |
| [47] |
Madsen AT, Murray AS, Andersen TJ, et al. Optically stimulated luminescence dating of young estuarine sediments: a comparison with 210Pb and 137Cs dating[J]. Marine Geology, 2005, 214(1-3): 251-268
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.10.034 URL |
| [48] |
Murray AS, Wintle AG. The single aliquot regenerative dose protocol: potential for improvements in reliability[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2003, 37(4-5): 377-381
doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(03)00053-2 URL |
| [49] |
Wintle AG, Murray AS. A review of quartz optically stimulated luminescence characteristics and their relevance in single-aliquot regeneration dating protocols[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2006, 41(4): 369-391
doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2005.11.001 URL |
| [50] |
Falguères C. The first human settlements out Africa into Europe: A chronological perspective[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 247: 106551
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106551 URL |
| [51] |
Lian OB, Roberts RG. Dating the Quaternary: progress in luminescence dating of sediments[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(19-20): 2449-2468
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2005.11.013 URL |
| [52] | Smedley RK. Telling the time with dust, sand and rocks[J]. Elements: An International Magazine of Mineralogy, Geochemistry, and Petrology, 2018, 14(1): 9-14 |
| [53] |
Parés JM, Pérez-González A. Paleomagnetic age for hominid fossils at Atapuerca archaeological site, Spain[J]. Science, 1995, 269(5225): 830-832
pmid: 7638599 |
| [54] |
Berger GW, Pérez-González A, Carbonell E, et al. Luminescence chronology of cave sediments at the Atapuerca paleoanthropological site, Spain[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2008, 55(2): 300-311
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2008.02.012 pmid: 18423801 |
| [55] |
Parés JM, Arnold L, Duval M, et al. Reassessing the age of Atapuerca-TD6 (Spain): new paleomagnetic results[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2013, 40(12): 4586-4595
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2013.06.013 URL |
| [56] |
Pickering R, Jacobs Z, Herries AIR, et al. Paleoanthropologically significant South African sea caves dated to 1.1-1.0 million years using a combination of U-Pb, TT-OSL and palaeomagnetism[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 65: 39-52
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.12.016 URL |
| [57] | 覃金堂, 周力平. 沙漠边缘厚层黄土上部光释光测年的初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(4): 546-552 |
| [58] |
Zhou LP, Shackleton NJ. Photon-stimulated luminescence of quartz from loess and effects of sensitivity change on palaeodose determination[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2001, 20(5-9): 853-857
doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(00)00024-X URL |
| [59] |
Buylaert JP, Vandenberghe D, Murray AS, et al. Luminescence dating of old (>70 ka) Chinese loess: a comparison of single-aliquot OSL and IRSL techniques[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2007, 2(1-4): 9-14
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.05.028 URL |
| [60] |
Buylaert JP, Murray AS, Vandenberghe D, et al. Optical dating of Chinese loess using sand-sized quartz: Establishing a time frame for Late Pleistocene climate changes in the western part of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2008, 3(1-2): 99-113
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2007.05.003 URL |
| [61] |
Chapot MS, Roberts HM, Duller GAT, et al. A comparison of natural-and laboratory-generated dose response curves for quartz optically stimulated luminescence signals from Chinese Loess[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2012, 47(11-12): 1045-1052
doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2012.09.001 URL |
| [62] |
Lai Z, Fan A. Examining quartz OSL age underestimation for loess samples from Luochuan in the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Geochronometria, 2014, 41(1): 57-64
doi: 10.2478/s13386-013-0138-1 URL |
| [63] |
Timar-Gabor A, Buylaert JP, Guralnik B, et al. On the importance of grain size in luminescence dating using quartz[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2017, 106: 464-471
doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2017.01.009 URL |
| [64] |
Rui X, Li B, Guo YJ, et al. Variability in the thermal stability of OSL signal of single-grain quartz from the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2019, 49: 25-30
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2018.04.011 |
| [65] |
Singarayer JS, Bailey RM. Further investigations of the quartz optically stimulated luminescence components using linear modulation[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2003, 37(4-5): 451-458
doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(03)00062-3 URL |
| [66] |
Li SH, Chen G. Studies of thermal stability of trapped charges associated with OSL from quartz[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2001, 34(4): 493
doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/34/4/309 URL |
| [67] |
Tsukamoto S, Murray AS, Huot S, et al. Luminescence property of volcanic quartz and the use of red isothermal TL for dating tephras[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2007, 42(2): 190-197
doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2006.07.008 URL |
| [68] |
Lowick SE, Preusser F. Investigating age underestimation in the high dose region of optically stimulated luminescence using fine grain quartz[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2011, 6(1): 33-41
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2010.08.001 URL |
| [69] |
Smith BW, Rhodes EJ, Stokes S, et al. The optical dating of sediments using quartz[J]. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 1990, 34(1-4): 75-78
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a080851 URL |
| [70] |
Wintle AG, Murray AS. Towards the development of a preheat procedure for OSL dating of quartz[J]. Radiation Measurements, 1998, 29(1): 81-94
doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(97)00228-X URL |
| [71] |
Murray AS, Wintle AG. Isothermal decay of optically stimulated luminescence in quartz[J]. Radiation Measurements, 1999, 30(1): 119-125
doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(98)00097-3 URL |
| [72] |
Spooner NA, Questiaux DG. Kinetics of red, blue and UV thermoluminescence and optically-stimulated luminescence from quartz[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2000, 32(5-6): 659-666
doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(00)00067-6 URL |
| [73] |
Huntley DJ, Short MA, Dunphy K. Deep traps in quartz and their use for optical dating[J]. Canadian Journal of Physics, 1996, 74(3-4): 81-91
doi: 10.1139/p96-013 URL |
| [74] |
Lowick SE, Valla PG. Characterizing the luminescence behavior of ‘infinitely old’ quartz samples from Switzerland[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2018, 43: 1-11
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2017.09.004 URL |
| [75] |
Lowick SE, Buechi MW, Gaar D, et al. Luminescence dating of Middle Pleistocene proglacial deposits from northern Switzerland: methodological aspects and stratigraphical conclusions[J]. Boreas, 2015, 44(3): 459-482
doi: 10.1111/bor.12114 URL |
| [76] |
Buechi MW, Lowick SE, Anselmetti FS. Luminescence dating of glaciolacustrine silt in overdeepened basin fills beyond the last interglacial[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2017, 37: 55-67
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2016.09.009 URL |
| [77] |
Klasen N, Fiebig M, Preusser F. Applying luminescence methodology to key sites of Alpine glaciations in Southern Germany[J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 420: 249-258
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.11.023 URL |
| [78] |
Yoshida H, Roberts RG, Olley JM, et al. Extending the age range of optical dating using single ‘supergrains’ of quartz[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2000, 32(5-6): 439-446
doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(99)00287-5 URL |
| [79] |
Zhang JF, Qiu WL, Hu G, et al. Determining the age of terrace formation using luminescence dating-A case of the Yellow River terraces in the Baode area, China[J]. Methods and Protocols, 2020, 3(1): 17
doi: 10.3390/mps3010017 URL |
| [80] |
Duller GAT. Improving the accuracy and precision of equivalent doses determined using the optically stimulated luminescence signal from single grains of quartz[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2012, 47(9): 770-777
doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2012.01.006 URL |
| [81] |
Thomsen KJ, Murray AS, Buylaert JP, et al. Testing single-grain quartz OSL methods using sediment samples with independent age control from the Bordes-Fitte rock shelter (Roches d'Abilly site, Central France)[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2016, 31: 77-9
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.11.002 URL |
| [82] |
Li B, Jacobs Z, Roberts RG. Investigation of the applicability of standardised growth curves for OSL dating of quartz from Haua Fteah cave, Libya[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2016, 35: 1-15
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2016.05.001 URL |
| [83] |
Guo J, Li B, Zhang F, et al. New ages for the Upper Palaeolithic site of Xibaimaying in the Nihewan Basin, northern China: implications for small-tool and microblade industries in north-east Asia during Marine Isotope Stages 2 and 3[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2017, 32(4): 540-552
doi: 10.1002/jqs.2949 URL |
| [84] |
Jacobs Z, Li B, Shunkov MV, et al. Timing of archaic hominin occupation of Denisova Cave in southern Siberia[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7741): 594-599
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0843-2 URL |
| [85] |
Li B, Jacobs Z, Roberts RG, et al. Review and assessment of the potential of post-IR IRSL dating methods to circumvent the problem of anomalous fading in feldspar luminescence[J]. Geochronometria, 2014, 41(3): 178-201
doi: 10.2478/s13386-013-0160-3 URL |
| [86] |
Lai ZP. Chronology and the upper dating limit for loess samples from Luochuan section in the Chinese Loess Plateau using quartz OSL SAR protocol[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 37(2): 176-185
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.08.003 URL |
| [87] |
Lu YC, Wang XL, Wintle AG. A new OSL chronology for dust accumulation in the last 130,000 yr for the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Research, 2007, 67(1): 152-160
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2006.08.003 URL |
| [88] |
Li B, Li SH. Luminescence dating of Chinese loess beyond 130 ka using the non-fading signal from K-feldspar[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2012, 10: 24-31
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2011.12.005 URL |
| [89] |
Wang XL, Lu YC, Wintle AG. Recuperated OSL dating of fine-grained quartz in Chinese loess[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2006, 1(2): 89-100
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.05.020 URL |
| [90] |
Wang X, Peng J, Adamiec G. Extending the age limit of quartz OSL dating of Chinese loess using a new multiple-aliquot regenerative-dose (MAR) protocol with carefully selected preheat conditions[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2021, 62: 101144
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2020.101144 URL |
| [91] |
Zhang JF, Li YY, Han YS, et al. Luminescence dating of weathered sediments from the Paleolithic site of Fengshuzui in northern Hunan province, China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2019, 49: 211-217
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2018.07.003 URL |
| [92] |
Rhodes EJ, Singarayer JS, Raynal JP, et al. New age estimates for the Palaeolithic assemblages and Pleistocene succession of Casablanca, Morocco[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(19-20): 2569-2585
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2005.09.010 URL |
| [1] | 長友恒人; 下冈順直; 波冈久惠; 佐川正敏; 卫奇. 泥河湾盆地几处旧石器时代文化遗址光释光测年[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(03): 276-284. |
| [2] | 彭菲;刘德成;王春雪. 光释光技术的新应用[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(04): 386-386. |
| [3] | 张晓凌;于汇历;高星. 黑龙江十八站遗址的新材料与年代[J]. 人类学学报, 2006, 25(02): 115-128. |
| [4] | 韩志勇,沈冠军,张家富. 光释光单片技术及其在澳大利亚旧石器遗址上的应用[J]. 人类学学报, 2004, 23(03): 248-253. |
| [5] | 裴树文,高星,冯兴无,陈福友,卫奇,朱松林,李国洪,吴天清. 井水湾旧石器遗址初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2003, 22(04): 261-278. |
| [6] | 房迎三,李徐生,杨达源. 江西新余旧石器地点的埋藏环境与时代[J]. 人类学学报, 2003, 22(02): 139-144. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 654
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 975
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3