

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (04): 749-763.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0026cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0026
收稿日期:2022-03-24
修回日期:2022-05-30
出版日期:2022-08-12
发布日期:2022-08-10
通讯作者:
董广辉
作者简介:芦永秀,硕士研究生,主要从事动物考古方向研究。E-mail: 基金资助:Received:2022-03-24
Revised:2022-05-30
Online:2022-08-12
Published:2022-08-10
Contact:
DONG Guanghui
摘要:
中国西北地区史前人类活动与生存环境变化的关系是学术界关注的热点科学问题。本文通过总结分析西北地区新石器至青铜时代遗址14C测年、动植物遗存以及人骨碳同位素数据,梳理了不同降水量区域人与环境相互作用的时空特征和变化过程,以及可能的影响因素。研究结果表明,10000-6000 BP,人类活动强度较弱且多分布在降水量大于400 mm的区域,人类活动与气候的关系尚不清楚;6000-4000 BP,粟黍农业的强化促进了人类活动空间向西扩散,显著的气候事件导致人类活动强度下降,人类活动对自然环境的影响开始显现;4000-2200 BP,史前跨大陆文化交流带来的农牧业元素促使不同降水量区域生存资料多样化,人类适应和影响环境的能力进一步加强,但该时期人类活动强度存在时空差异性,对环境的影响仅在区域尺度上呈现。
中图分类号:
芦永秀, 董广辉. 西北不同降水区域新石器至青铜时代人类活动与环境变化的关系[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(04): 749-763.
LU Yongxiu, DONG Guanghui. Relationship between the human activity and environment changes during the Neolithic and Bronze Age in different precipitation areas of Northwestern China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022, 41(04): 749-763.
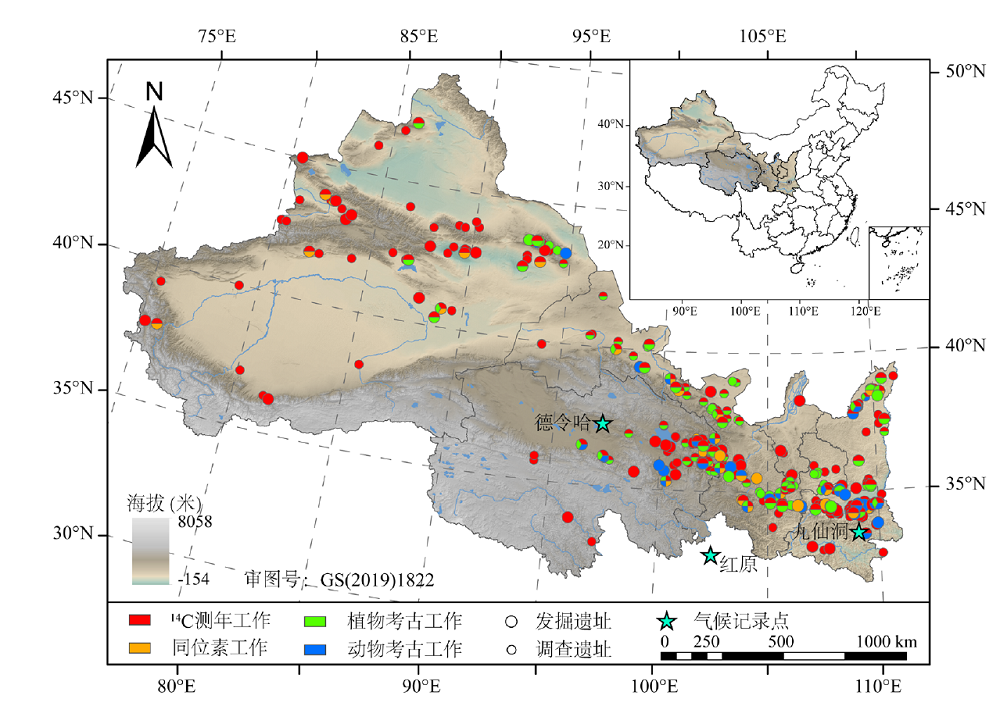
图1 西北地区新石器-青铜时代开展测年和生业模式研究的遗址点分布
Fig.1 Distribution of sites with radiocarbon dates and subsistence strategy research in northwestern China during the Neolithic and Bronze periods
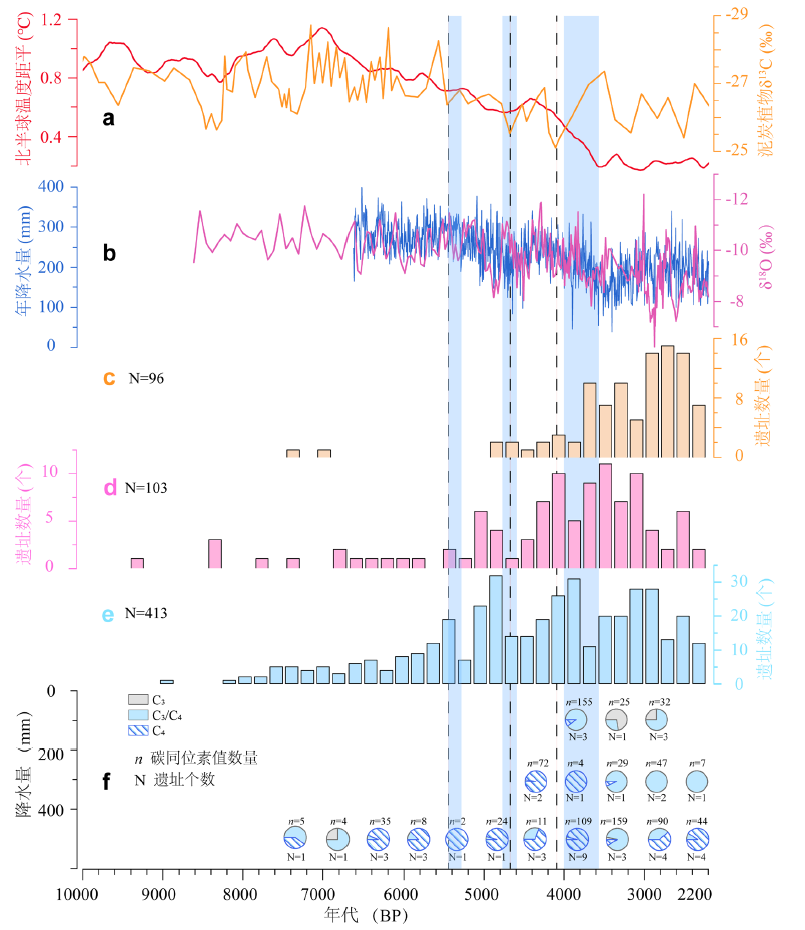
图3 西北地区10000-2200 BP人类活动强度与气候变化 a.北半球中高纬度(30°-90°N)温度集成记录[43]和青藏高原红原泥炭沼泽植物δ13C记录[44]The temperature record in middle and high latitudes (30°-90°N) of Northern Hemisphere [43] and the δ13C record of plants from Hongyuan peat bog from the Tibet Plateau[44];b.德令哈树轮δ18O定量降水曲线[45]和九仙洞石笋δ18O记录[46]Reconstructed precipitation based on δ18O of tree ring in DLH[45] and the δ18O record of stalagmites from the Jiuxian Cave[46];c、d、e.西北地区降水量200-0 mm、400-200 mm和大于400 mm区域测年遗址数量The number of the dated sites with precipitation of 200-0 mm、400-200 mm and more than 400 mm in Northwestern China;f.西北地区人骨碳稳定碳同位素值The results of the stable carbon isotopic value from human bones in Northwestern China
Fig.3 The intensity of human activity and climate change in northwestern China from 10000-2200 BP
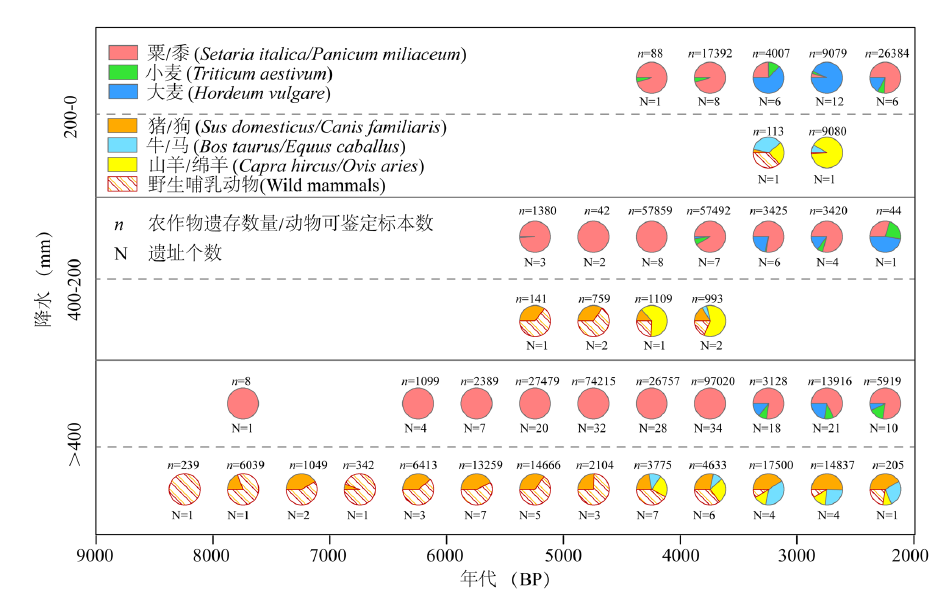
图4 西北地区不同降水量区域新石器-青铜时代遗址出土的作物数量与动物可鉴定标本数
Fig.4 The number of the different crop remains and the identified specimen of animal remains unearthed from sites in different precipitation areas in northwestern China
| [1] | Magill CR, Ashley GM, Freeman KH. Ecosystem variability and early human habitats in eastern Africa[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(4): 1167-1174 |
| [2] | Robinson JR, Rowan J, Campisano CJ, et al. Late Pliocene environmental change during the transition from Australopithecus to Homo[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2017, 1(6): 1-7 |
| [3] | 王幼平. 华北旧石器晚期环境变化与人类迁徙扩散[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(3): 341-351 |
| [4] |
Dong GH, Li R, Lu MX, et al. Evolution of human-environmental interactions in China from the Late Paleolithic to the Bronze Age[J]. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 2020, 44(2): 233-250
doi: 10.1177/0309133319876802 URL |
| [5] |
Stiner MC, Munro ND, Surovell TA, et al. Paleolithic population growth pulses evidenced by small animal exploitation[J]. Science, 1999, 283(5399): 190-194
pmid: 9880245 |
| [6] | 严文明. 农业发生与文明起源[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000, 50-89 |
| [7] | Zeder MA. Domestication and early agriculture in the Mediterranean Basin: Origins, diffusion, and impact[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(33): 11597-11604 |
| [8] |
Diamond J, Bellwood P. Farmers and their languages: the first expansions[J]. Science, 2003, 300(5619): 597-603
pmid: 12714734 |
| [9] | Gignoux CR, Henn BM, Mountain JL. Rapid, global demographic expansions after the origins of agriculture[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(15): 6044-6049 |
| [10] |
Zhou XY, Yu JJ, Spengler RN, et al. 5,200-year-old cereal grains from the eastern Altai Mountains redate the trans-Eurasian crop exchange[J]. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(2): 78-87
doi: 10.1038/s41477-019-0581-y URL |
| [11] |
Dong GH, Yang YS, Han JY, et al. Exploring the history of cultural exchange in prehistoric Eurasia from the perspectives of crop diffusion and consumption[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2017, 60(6): 1110-1123
doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-9037-x URL |
| [12] |
Manning K, Downey SS, Colledge S, et al. The origins and spread of stock-keeping: the role of cultural and environmental influences on early Neolithic animal exploitation in Europe[J]. Antiquity, 2013, 87(338): 1046-1059
doi: 10.1017/S0003598X00049851 URL |
| [13] |
董广辉, 仇梦晗, 李若, 等. 探讨过去人地关系演变机制的“支点”概念模型[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(1): 15-29
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202101002 |
| [14] | Frankopan P. The Silk Roads: A New History of the World[M]. London: Bloomsbury Publishing. 2015, 12-161 |
| [15] |
Liu XY, Jones PJ, Matuzeviciute GM, et al. From ecological opportunism to multi-cropping: Mapping food globalisation in prehistory[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 206: 21-28
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.12.017 URL |
| [16] |
Zhu ZY, Dennell R, Huang WW, et al. Hominin occupation of the Chinese Loess Plateau since about 2.1 million years ago[J]. Nature, 2018, 559(7715): 608-612
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0299-4 URL |
| [17] | 侯光良, 许长军, 樊启顺. 史前人类向青藏高原东北缘的三次扩张与环境演变[J]. 地理学报, 2010, 1: 65-72 |
| [18] |
Zhang DJ, Dong GH, Wang H, et al. History and possible mechanisms of prehistoric human migration to the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(9): 1765-1778
doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5482-x URL |
| [19] |
Chen FH, Dong GH, Zhang DJ, et al. Agriculture facilitated permanent human occupation of the Tibetan Plateau after 3600BP[J]. Science, 2015, 347(6219): 248-250
doi: 10.1126/science.1259172 pmid: 25593179 |
| [20] |
Dong GH, Yang YS, Liu XY, et al. Prehistoric trans-continental cultural exchange in the Hexi Corridor, northwest China[J]. The Holocene, 2018, 28(4): 621-628
doi: 10.1177/0959683617735585 URL |
| [21] | 董广辉, 芦永秀, 刘培伦, 等. 6000-2000 a B. P. 丝绸之路国内段人类活动的时空格局与影响因素研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2022, 42(1): 1-16 |
| [22] | 张山佳, 董广辉. 青藏高原东北部青铜时代中晚期人类对不同海拔环境的适应策略探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(4): 696-708 |
| [23] |
Zhang SJ, Yang YS, Storozum MJ, et al. Copper smelting and sediment pollution in Bronze Age China: A case study in the Hexi corridor, Northwest China[J]. Catena, 2017, 156: 92-101
doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.04.001 URL |
| [24] |
Ma MM, Dong GH, Jia X, et al. Dietary shift after 3600 cal yr BP and its influencing factors in northwestern China: Evidence from stable isotopes[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 145: 57-70
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.05.041 URL |
| [25] | 张弛. 旧大陆西部作物及家畜传入初期中国北方生业经济结构的区域特征[J]. 华夏考古, 2017, 3: 89-97 |
| [26] |
Wang W, Liu Y, Duan FT, et al. A comprehensive investigation of Bronze Age human dietary strategies from different altitudinal environments in the Inner Asian Mountain Corridor[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2020, 121: 105201
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2020.105201 URL |
| [27] | 王凤娇, 杨延征, 上官周平. 西北五省(区)耕地质量等别差异性比较[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2015, 33(2): 230-236 |
| [28] |
张华, 徐存刚, 王浩. 2001-2018年西北地区植被变化对气象干旱的响应[J]. 地理科学, 2020, 40(6): 1029-1038
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.06.019 |
| [29] | 王澄海, 张晟宁, 李课臣, 等. 1961-2018年西北地区降水的变化特征[J]. 大气科学, 2021, 45(4): 713-724 |
| [30] | 陈笑笑, 孙必云, 华维. 西北地区年平均地表温度时空特征分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(23): 182-185 |
| [31] |
Wang C, Lu HY, Zhang JP, et al. Prehistoric demographic fluctuations in China inferred from radiocarbon data and their linkage with climate change over the past 50,000 years[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 98: 45-59
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.05.015 URL |
| [32] |
Yang L, Ma MM, Chen TT, et al. How did trans-Eurasian exchanges affect spatial-temporal variation in agricultural patterns during the late prehistoric period in the Yellow River valley (China)[J]. The Holocene, 2020, 31(2): 247-257
doi: 10.1177/0959683620941140 URL |
| [33] |
Li R, Lv FY, Yang L, et al. Spatial-temporal variation of cropping patterns in relation to climate change in Neolithic China[J]. Atmosphere, 2020, 11(7): 677
doi: 10.3390/atmos11070677 URL |
| [34] |
Du LY, Ma MM, Lu YW, et al. How did human activity and climate change influence animal exploitation during 7500-2000 BP in the Yellow River Valley, China[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2020, 8: 161
doi: 10.3389/fevo.2020.00161 URL |
| [35] |
Cao HH, Dong GH. Social development and living environment changes in the Northeast Tibetan Plateau and contiguous regions during the late prehistoric period[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2020, 1(1): 59-67
doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2020.09.001 URL |
| [36] | 董广辉, 杜琳垚, 杨柳, 等. 欧亚大陆草原之路-绿洲之路史前农牧业扩散交流与生业模式时空变化[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2022, 52: 1-24 |
| [37] |
Dong GH, Lu YX, Zhang SJ, et al. Spatiotemporal variation in human settlements and their interaction with living environments in Neolithic and Bronze Age China[J]. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 2022, doi: 10.1177/03091333221087992
doi: 10.1177/03091333221087992 URL |
| [38] | 傅文彬, 邸楠, 邵晶, 等. 陕北靖边庙梁遗址浮选结果与分析[J]. 第四纪研究, 2022, 42(1): 119-128 |
| [39] | 胡松梅, 杨曈, 杨苗苗, 等. 陕北靖边庙梁遗址动物遗存研究兼论中国牧业的形成[J]. 第四纪研究, 2022, 42(1): 17-31 |
| [40] | 杨瑞琛, 邸楠, 贾鑫, 等. 从石峁遗址出土植物遗存看夏时代早期榆林地区先民的生存策略选择[J]. 第四纪研究, 2022, 42(1): 101-118 |
| [41] | 唐丽雅, 郑越, 朱津, 等. 郑州地区周代农作物资源利用研究:以荥阳官庄为例[J]. 第四纪研究, 2022, 42(1): 129-143 |
| [42] | 刘洁. 近60年来中国北方半干旱区界线与范围时空变化特征研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2019, 9-12 |
| [43] |
Marcott SA, Shakun JD, Clark PU, et al. A reconstruction of regional and global temperature for the past 11,300 years[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6124): 1198-1201
doi: 10.1126/science.1228026 pmid: 23471405 |
| [44] |
Hong YT, Hong B, Lin QH, et al. Correlation between Indian Ocean summer monsoon and North Atlantic climate during the Holocene[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 211(3-4): 371-380
doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00207-3 URL |
| [45] | Yang B, Qin C, Brauning A, et al. Long-term decrease in Asian monsoon rainfall and abrupt climate change events over the past 6,700 years[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(30): e2102007118 |
| [46] |
Cai YJ, Tan LC, Cheng H, et al. The variation of summer monsoon precipitation in central China since the last deglaciation[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 291(1-4): 21-31
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2009.12.039 URL |
| [47] |
Dong GH, Wang L, Cui YF, et al. The spatiotemporal pattern of the Majiayao cultural evolution and its relation to climate change and variety of subsistence strategy during late Neolithic period in Gansu and Qinghai Provinces, northwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2013, 316: 155-161
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2013.07.038 URL |
| [48] |
Hosner D, Wagner M, Tarasov PE, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution patterns of archaeological sites in China during the Neolithic and Bronze Age: An overview[J]. The Holocene, 2016, 26(10): 1576-1593
doi: 10.1177/0959683616641743 URL |
| [49] |
Wang L, Cui YF. The spatiotemporal pattern of cultural evolution response to agricultural development and climate change from Yangshao culture to Bronze Age in the Yellow River basin and surrounding regions, north China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9: 657179
doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.657179 URL |
| [50] | Barton L, Brantingham PJ, Ji DX. Late Pleistocene climate change and Paleolithic cultural evolution in Northern China: Implications from the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Developments in Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 9(7): 105-128 |
| [51] |
Hou GL, Dong WM, Cai LH, et al. The history and driving force for prehistoric human expansion upward to the hinterland of the Tibetan Plateau Post-Last glacial maximum[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(13): 7065
doi: 10.3390/su13137065 URL |
| [52] | 李水城. 东风西渐-中国西北史前文化之进程[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2009, 34-246 |
| [53] | 谢端琚. 甘青地区史前考古[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2002, 137-239 |
| [54] |
Brantingham PJ, Gao X. Peopling of the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. World Archaeology, 2006, 38(3): 387-414
doi: 10.1080/00438240600813301 URL |
| [55] | 中国社会科学院考古研究所. 中国考古学中碳十四年代数据集(1965- 1991)[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1991, 294-304 |
| [56] | 张雪莲, 仇士华, 蔡莲珍, 等. 放射性碳素测定年代报告(三一)[J]. 考古, 2005, 7: 57-61 |
| [57] |
Dong GH, Wang ZL, Ren LL, et al. A comparative study of 14C dating on charcoal and charred seeds from late neolithic and bronze age sites in Gansu and Qinghai provinces, NW China[J]. Radiocarbon, 2014, 56(1): 157-163
doi: 10.2458/56.16507 URL |
| [58] |
Kuper R, Kropelin S. Climate-controlled Holocene occupation in the Sahara: Motor of Africa’s evolution[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5788): 803-807
doi: 10.1126/science.1130989 URL |
| [59] |
Timmermann A, Friedrich T. Late Pleistocene climate drivers of early human migration[J]. Nature, 2016, 538(7623): 92-95
doi: 10.1038/nature19365 URL |
| [60] | 董广辉, 刘峰文, 陈发虎. 不同空间尺度影响古代社会演化的环境和技术因素探讨[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2017, 47(12): 1383-1394 |
| [61] | 张东菊, 董广辉, 王辉, 等. 史前人类向青藏高原扩散的历史过程和可能驱动机制[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2016, 46(8): 1007-1023 |
| [62] |
Chen FH, Yu ZC, Yang ML, et al. Holocene moisture evolution in arid central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with Asian monsoon history[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2008, 27(3-4): 351-364
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.10.017 URL |
| [63] |
Rhode D, Brantingham PJ, Perreault C, et al. Mind the gaps: testing for hiatuses in regional radiocarbon date sequences[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2014, 52: 567-577
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2014.02.022 URL |
| [64] |
Zhao Y, Yu ZC. Vegetation response to Holocene climate change in East Asian monsoon-margin region[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2012, 113(1-2): 1-10
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.03.001 URL |
| [65] | 董广辉, 张山佳, 杨谊时, 等. 中国北方新石器时代农业强化及对环境的影响[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(26): 2913-2925 |
| [66] | Barton L, Newsome SD, Chen FH, et al. Agricultural origins and the isotopic identity of domestication in northern China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(14): 5523-5528 |
| [67] | 吴文祥, 刘东生. 5500 aBP气候事件在三大文明古国古文明和古文化演化中的作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2002, 1: 155-162 |
| [68] | Jia X, Dong GH, Li H, et al. The development of Agriculture and its impact on cultural expansion during the late Neolithic in the Western Loess Plateau, China[J]. The Holocene, 2013, 23(1): 83-90 |
| [69] | Chen NB, Ren LL, Du LY, et al. Ancient genomes reveal tropical bovid species in the Tibetan Plateau contributed to the prevalence of hunting game until the late Neolithic[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(45): 28150-28159 |
| [70] |
Huang XZ, Peng W, Rudaya N, et al. Holocene vegetation and climate dynamics in the Altai Mountains and surrounding Areas[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(13): 6628-6636
doi: 10.1029/2018GL078028 URL |
| [71] |
Huang XZ, Xiang LX, Lei GL, et al. Sedimentary Pediastrum record of middle-late Holocene temperature change and its impacts on early human culture in the desert-oasis area of northwestern China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2021, 265: 107054
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2021.107054 URL |
| [72] |
Fiorentino G, Caldara M, De Santis V, et al. Climate changes and human-environment interactions in the Apulia region of southeastern Italy during the Neolithic period[J]. Holocene, 2013, 23(9): 1297-1316
doi: 10.1177/0959683613486942 URL |
| [73] | 陈胜前. 中国狩猎采集者的模拟研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2006, 25(1): 42-55 |
| [74] |
Wang L, Yang YS, Jia X. Hydrogeomorphic settings of late Paleolithic and early-mid Neolithic sites in relation to subsistence variation in Gansu and Qinghai Provinces, northwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 426: 18-25
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.03.017 URL |
| [75] |
Liu XY, Hunt HV, Jones MK. River valleys and foothills: changing archaeological perceptions of North China’s earliest farms[J]. Antiquity, 2009, 83(319): 82-95
doi: 10.1017/S0003598X00098100 URL |
| [76] |
Ren LL, Dong GH, Liu FW, et al. Foraging and farming: archaeobotanical and zooarchaeological evidence for Neolithic exchange on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Antiquity, 2020, 94 (375): 637-652
doi: 10.15184/aqy.2020.35 URL |
| [77] |
Zhou XY, Li XQ, Dodson J, et al. Rapid agricultural transformation in the prehistoric Hexi corridor, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 426: 33-41
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.04.021 URL |
| [78] | 甘肃省文物考古研究所. 秦安大地湾:新石器时代遗址发掘报告[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2006, 861-916 |
| [79] | 邵会秋. 新疆史前时期文化格局的演进及其与周邻文化的关系[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018, 24-429 |
| [80] | 安成邦, 张曼, 王伟, 等. 新疆地理环境特征以及农牧格局的形成[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2020, 50(2): 295-304 |
| [81] |
Chen H, Wang XY, Lu HY, et al. Anthropogenic impacts on Holocene fluvial dynamics in the Chinese Loess Plateau, an evaluation based on landscape evolution modeling[J]. Geomorphology, 2021, 392(2): 107935
doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.107935 URL |
| [82] |
Li FR, Gaillard MJ, Cao XY, et al. Towards quantification of Holocene anthropogenic land-cover change in temperate China: A review in the light of pollen-based REVEALS reconstructions of regional plant cover[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 203(8): 103119
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103119 URL |
| [83] |
Wang X, Fuller BT, Zhang PC, et al. Millet manuring as a driving force for the Late Neolithic agricultural expansion of north China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 5552
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23315-4 pmid: 29615636 |
| [84] | Huang XZ, Liu SS, Dong GH, et al. Early human impacts on vegetation on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during the middle to late Holocene[J]. Progress in Physical Geography, 2017, 41(3): 286-301 |
| [85] |
Huang XZ, Zhang J, Storozum M, et al. Long-term herbivore population dynamics in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its implications for early human impacts[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 2020, 275(3): 104171
doi: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2020.104171 URL |
| [86] |
Wei HC, Hou GL, Fan QS, et al. Using coprophilous fungi to reconstruct the history of pastoralism in the Qinghai Lake Basin, Northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 2019, 44(1): 70-93
doi: 10.1177/0309133319869596 URL |
| [87] |
Zhou XY, Li XQ, Dodson J, et al. Land degradation during the Bronze Age in Hexi Corridor (Gansu, China)[J]. Quaternary International, 2012, 254: 42-48
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2011.06.046 URL |
| [88] |
Yang YS, Dong GH, Zhang SJ, et al. Copper content in anthropogenic sediments as a tracer for detecting smelting activities and its impact on environment during prehistoric period in Hexi Corridor, Northwest China[J]. The Holocene, 2017, 27(2): 282-291
doi: 10.1177/0959683616658531 URL |
| [89] |
Miao YF, Zhang DJ, Cai XM, et al. Holocene fire on the northeast Tibetan Plateau in relation to climate change and human activity[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 443: 124-131
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.05.029 URL |
| [90] |
Zhang H, Zhang Y, Kong ZC, et al. Late Holocene climate change and anthropogenic activities in north Xinjiang: Evidence from a peatland archive, the Caotanhu wetland[J]. The Holocene, 2014, 25(2): 323-332
doi: 10.1177/0959683614558646 URL |
| [91] |
Shen H, Li XQ, Spengler R, et al. Forest cover and composition on the Loess Plateau during the Middle to Late-Holocene: Integrating wood charcoal analyses[J]. The Holocene, 2020, 31(1): 38-49
doi: 10.1177/0959683620961486 URL |
| [1] | 吕厚远. 周期性气候变化与人类适应[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(04): 731-748. |
| [2] | 张乐, 张双权, 高星. 地理信息系统在动物考古学研究中的应用: 以贵州马鞍山遗址出土的动物遗存为例[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(03): 407-418. |
| [3] | 李占扬; 张双权; 张乐; 高星. 河南灵井许昌人遗址普通马(Equus caballus)化石居群的死亡年龄曲线[J]. 人类学学报, 2011, 30(01): 45-54. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 625
|
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3