

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (01): 61-74.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0054cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0054
张月书1,2,3( ), 李锋4(
), 李锋4( ), 陈福友1,3, 仪明洁5, 高星1,2,3
), 陈福友1,3, 仪明洁5, 高星1,2,3
收稿日期:2021-05-14
修回日期:2021-08-13
出版日期:2023-02-15
发布日期:2023-02-20
通讯作者:
李锋,研究员,主要从事旧石器时代考古学研究。E-mail: 作者简介:张月书, 博士研究生,主要从事旧石器时代考古学研究。E-mail: 基金资助:
ZHANG Yueshu1,2,3( ), LI Feng4(
), LI Feng4( ), CHEN Fuyou1,3, YI Mingjie5, GAO Xing1,2,3
), CHEN Fuyou1,3, YI Mingjie5, GAO Xing1,2,3
Received:2021-05-14
Revised:2021-08-13
Online:2023-02-15
Published:2023-02-20
摘要:
东谷坨遗址是泥河湾盆地内重要的旧石器时代早期遗址,其文化层以河湖相堆积为主,大量的文化遗物在埋藏过程中会受到流水等自然作用的影响,明确遗址的形成过程、了解遗物在埋藏过程中被改造的程度是我们开展其他各项研究的基础。2016-2020年,中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所和河北省文物考古研究院对东谷坨遗址T1区域开展了新的发掘,通过此次发掘,我们将原6A文化层划分为2个亚层。其中6A2为粗砂砾石堆积,显示水动力较强的沉积环境,但该层出土的多数石制品表面新鲜,并未显示出受高能水流的改造或被长距离搬运的特征。鉴于此,我们以探讨搬运改造石制品所形成破损特点为目的设计并实施了模拟搬运试验,开展了遗址内沉积物、石制品特征等多指标分析探讨遗址的形成过程。结果表明,6A2层的多数石制品并非由高能水流搬运而来,而是粗砂砾石堆积在遗址形成后,古人类活动于其上所遗留,此层石制品显示了原地埋藏的特点。
中图分类号:
张月书, 李锋, 陈福友, 仪明洁, 高星. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址6A2层的形成过程[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(01): 61-74.
ZHANG Yueshu, LI Feng, CHEN Fuyou, YI Mingjie, GAO Xing. Formation processes of Layer 6A2 of the Donggutuo site in the Nihewan Basin[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2023, 42(01): 61-74.
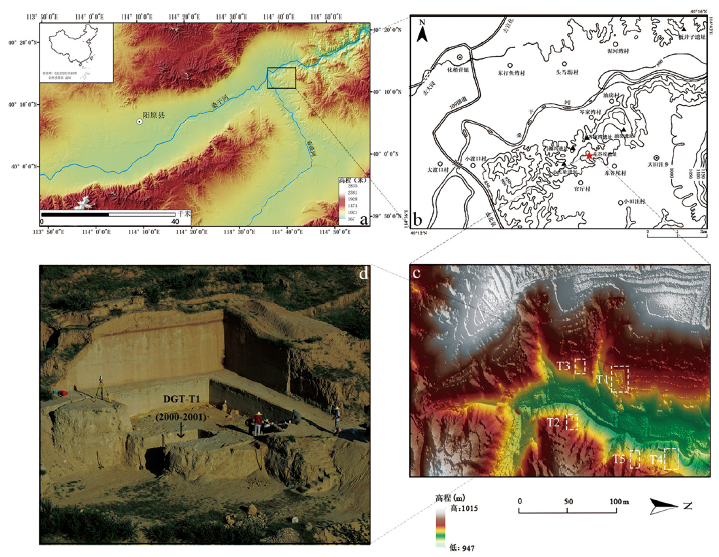
图1 东谷坨遗址的地理位置及其探方分布 a.泥河湾盆地 Nihewan basin in North China;b.泥河湾盆地东缘遗址相对位置(修改自参考文献[15])Relevant sites in the eastern part of Nihewan basin. It is modified from reference [15];c.东谷坨遗址各探方位置图 Plan distribution of the five trenches;d.东谷坨遗址T1发掘区 Location of the Trench 1
Fig.1 Geographical location and trenches distribution of the Donggutuo site
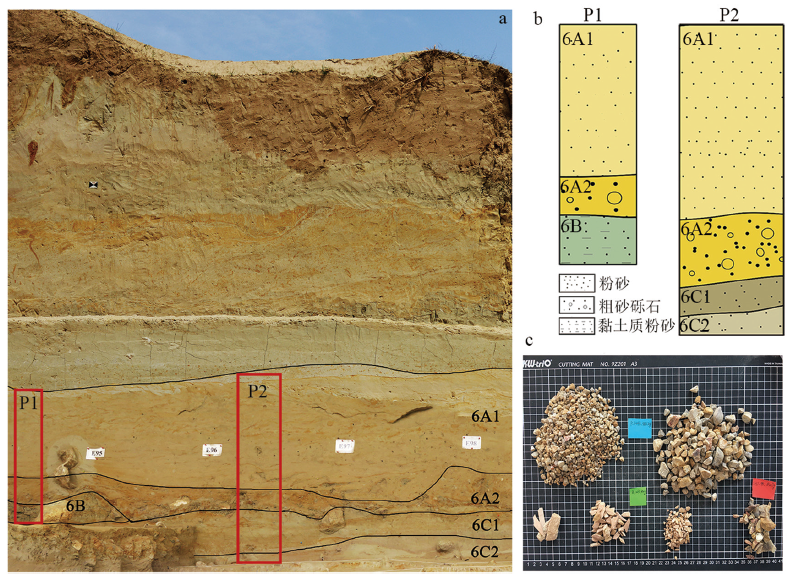

图2 东谷坨遗址2016-2020年T1发掘区剖面图 a.遗址北剖面图The northern profile;b.地层序列The stratigraphic sequence;c.6A2层单个探方出土考古材料及砾石The archaeological remains and pebbles of one square from layer 6A2
Fig.2 Stratigraphic profile of the Trench 1 excavated in 2016-2020 at the Donggutuo site
| 石制品类型Category | 数量Number (n) | 百分比Percentage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 剥片类Flaked Pieces | 117 | 22% | ||
| 石器Retouched pieces | 30 | 5.6% | ||
| 石核Cores | 87 | 16.4% | ||
| 打击类Pounded pieces | 石锤Hammer stone | 1 | 0.2% | |
| 废片类Detached pieces or Debitage | 414 | 77.8% | ||
| 碎块Shatters | 139 | 26.1% | ||
| 断块Chunks | 111 | 20.9% | ||
| 完整石片Complete Flakes | 124 | 23.3% | ||
| 残片Flake Fragements | 40 | 7.5% | ||
| 总计Total | 532 | 100% | ||
表1 2016年东谷坨遗址6A2层出土的石制品
Tab.1 Lithics uncovered from layer 6A2 of the Donggutuo site in 2016
| 石制品类型Category | 数量Number (n) | 百分比Percentage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 剥片类Flaked Pieces | 117 | 22% | ||
| 石器Retouched pieces | 30 | 5.6% | ||
| 石核Cores | 87 | 16.4% | ||
| 打击类Pounded pieces | 石锤Hammer stone | 1 | 0.2% | |
| 废片类Detached pieces or Debitage | 414 | 77.8% | ||
| 碎块Shatters | 139 | 26.1% | ||
| 断块Chunks | 111 | 20.9% | ||
| 完整石片Complete Flakes | 124 | 23.3% | ||
| 残片Flake Fragements | 40 | 7.5% | ||
| 总计Total | 532 | 100% | ||

图3 模拟搬运实验 a.打制实验标本 Knapping experimental specimens;b.实验标本称重 Weighting experimental samples;c.实验标本 The experimental samples;d.转动实验装置 Rolling the experimental device
Fig.3 The transportation-simulation experiment
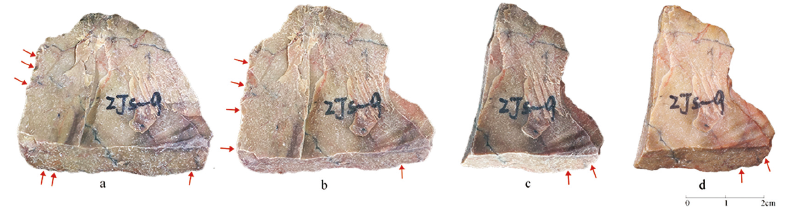
图4 实验标本ZJS-9在不同实验阶段表面的变化(原料来自周家山) a. 5 分钟5 mins;b. 10 分钟10 mins;c. 15 分钟15 mins;d. 20 分钟 20 mins
Fig.4 The changes on the surface of an experimental sample at different stages(raw material was collected at the Zhoujiashan hill)

图5 实验标本与遗址出土标本 a. 实验改造标本 Experimental modified sample;b. 东谷坨遗址6A2层出土石器 Retouched piece from Layer 6A2 of the Donggutuo site;c. 疑似石制品 Geofacts;d.实验修理石器 Experimental retouched piece
Fig.5 The experimental samples and unearthed lithics
| 检验项目 t-test Category | t | p |
|---|---|---|
| 实验改造标本Exp. modified samples (20 mins.) vs. 遗址出土石器 Retouched pieces from Donggutuo site | -13.135 | 4.03742E-98 |
| 实验改造标本Exp. modified samples (20 mins.) vs. 疑似石制品 Geofacts | -13.297 | 1.9497E-117 |
| 实验改造标本Exp. modified samples (20 mins.) vs.实验修理标本Exp. retouched pieces | -8.828 | 1.6091E-62 |
| 疑似石制品Geofacts vs. 遗址出土石器Retouched pieces from Donggutuo site | 0.604 | 0.571729284 |
| 疑似石制品Geofacts vs. 实验修理标本 Exp. retouched pieces | 1.834 | 0.06721793 |
| 遗址出土石器Retouched pieces from Donggutuo site vs.实验修理标本Exp. retouched pieces | 1.357 | 0.175044886 |
表2 实验标本和考古标本片疤长度t检验结果
Tab.2 Results of t test on scar sizes of the experimental samples and stone artifacts
| 检验项目 t-test Category | t | p |
|---|---|---|
| 实验改造标本Exp. modified samples (20 mins.) vs. 遗址出土石器 Retouched pieces from Donggutuo site | -13.135 | 4.03742E-98 |
| 实验改造标本Exp. modified samples (20 mins.) vs. 疑似石制品 Geofacts | -13.297 | 1.9497E-117 |
| 实验改造标本Exp. modified samples (20 mins.) vs.实验修理标本Exp. retouched pieces | -8.828 | 1.6091E-62 |
| 疑似石制品Geofacts vs. 遗址出土石器Retouched pieces from Donggutuo site | 0.604 | 0.571729284 |
| 疑似石制品Geofacts vs. 实验修理标本 Exp. retouched pieces | 1.834 | 0.06721793 |
| 遗址出土石器Retouched pieces from Donggutuo site vs.实验修理标本Exp. retouched pieces | 1.357 | 0.175044886 |
| 标本类型Type | 最小值Min | 最大值Max | 平均数AVG | 中位数Med | 方差Var | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验改造标本Exp. modified samples(Ex.m) | 5 mins (Ex.5) | 4 | 65 | 27 | 26 | 194.7 |
| 10 mins (Ex.10) | 17 | 66 | 42 | 40 | 165.8 | |
| 15 mins (Ex.15) | 23 | 80 | 48 | 47.5 | 168.5 | |
| 20 mins (Ex.20) | 27 | 102 | 56 | 55.5 | 295.8 | |
| 实验修理标本Exp. retouched pieces(Ex.r) | 3 | 10 | 6 | 5 | 3.9 | |
| 出土石器Retouched pieces from the Donggutuo site (DGT) | 3 | 9 | 5 | 5 | 2.4 | |
| 疑似石制品Geofacts(Geo) | 1 | 20 | 5 | 5 | 12.7 | |
表3 实验标本和考古标本的片疤数量
Tab.3 Number of scar of the experimental and the archaeological samples (n)
| 标本类型Type | 最小值Min | 最大值Max | 平均数AVG | 中位数Med | 方差Var | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验改造标本Exp. modified samples(Ex.m) | 5 mins (Ex.5) | 4 | 65 | 27 | 26 | 194.7 |
| 10 mins (Ex.10) | 17 | 66 | 42 | 40 | 165.8 | |
| 15 mins (Ex.15) | 23 | 80 | 48 | 47.5 | 168.5 | |
| 20 mins (Ex.20) | 27 | 102 | 56 | 55.5 | 295.8 | |
| 实验修理标本Exp. retouched pieces(Ex.r) | 3 | 10 | 6 | 5 | 3.9 | |
| 出土石器Retouched pieces from the Donggutuo site (DGT) | 3 | 9 | 5 | 5 | 2.4 | |
| 疑似石制品Geofacts(Geo) | 1 | 20 | 5 | 5 | 12.7 | |
| 来源Data source→ 数量Number(n)↘ 长度Size(cm)↓ | 东谷坨Donggutuo | 文献Refference [ | 文献Refference [ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5-1 | 101 | 6101 | 1635 |
| 1-2 | 507 | 2394 | 2422 |
| 2-3 | 173 | 662 | 947 |
| 3-4 | 76 | 331 | 410 |
| 4-5 | 30 | 210 | 221 |
| 5-6 | 13 | 165 | 129 |
| 6-7 | 2 | 101 | 75 |
| 7-8 | 1 | 60 | 41 |
| 8-9 | 0 | 34 | 29 |
| 9-10 | 0 | 7 | 6 |
| 10-11 | 0 | 4 | 5 |
| 11-12 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| 12-13 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 13-14 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 14-15 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 15-16 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 16-17 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 17-18 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 18-19 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 19-20 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
表4 实验数据和东谷坨遗址废片长度分布数据
Tab.4 Data of debitage size distribution of experiments and the Donggutuo site
| 来源Data source→ 数量Number(n)↘ 长度Size(cm)↓ | 东谷坨Donggutuo | 文献Refference [ | 文献Refference [ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5-1 | 101 | 6101 | 1635 |
| 1-2 | 507 | 2394 | 2422 |
| 2-3 | 173 | 662 | 947 |
| 3-4 | 76 | 331 | 410 |
| 4-5 | 30 | 210 | 221 |
| 5-6 | 13 | 165 | 129 |
| 6-7 | 2 | 101 | 75 |
| 7-8 | 1 | 60 | 41 |
| 8-9 | 0 | 34 | 29 |
| 9-10 | 0 | 7 | 6 |
| 10-11 | 0 | 4 | 5 |
| 11-12 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| 12-13 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 13-14 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 14-15 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 15-16 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 16-17 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 17-18 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 18-19 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 19-20 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
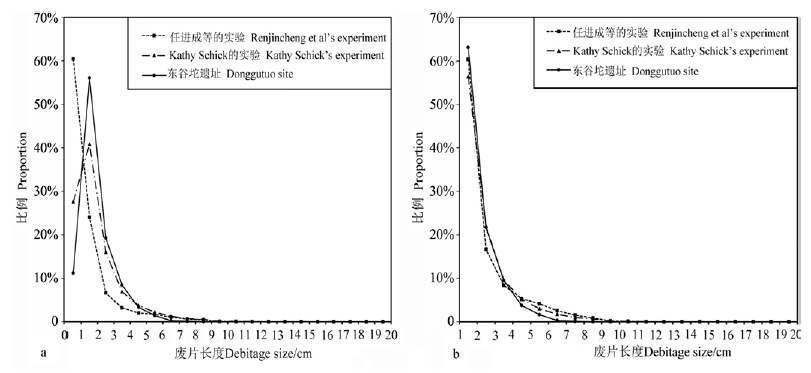
图11 东谷坨遗址、任进成等实验[34,35]与Kathy Schick实验[33]废片尺寸分布对比 a.所有废片 All of the debitages;b. L≥1 cm的废片 debitages L≥1 cm
Fig.11 Comparison of debitage size distributions among the Donggutuo site and the Renjincheng et al’s[34,35] and Schick’s experiments[33]
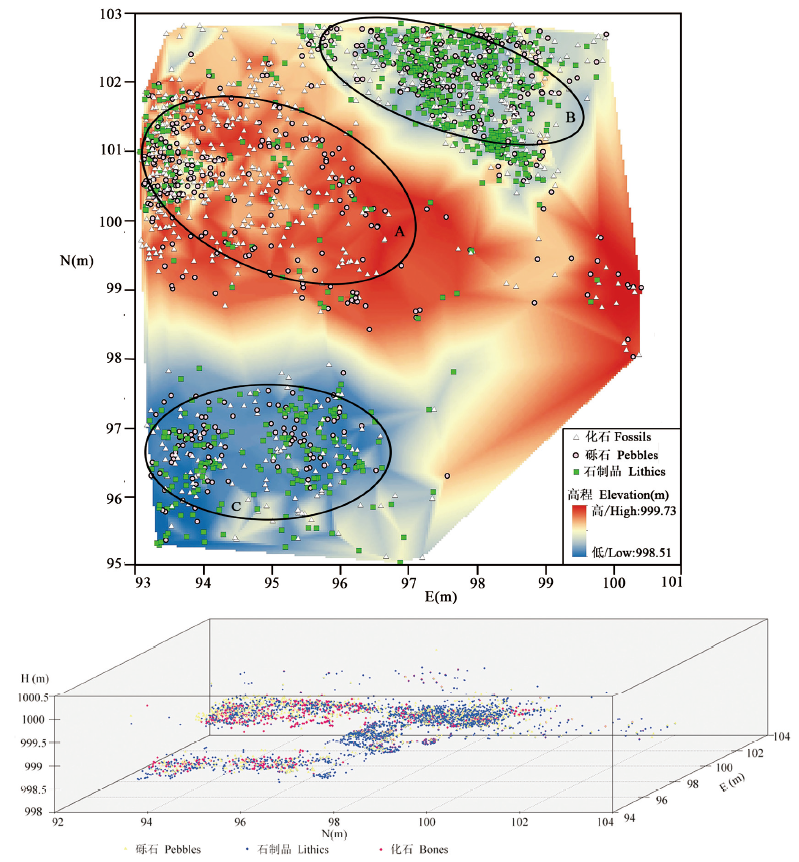
图13 东谷坨遗址6A2层遗物空间分布 a. 6A2层遗物平面分布及微地形 Spatial distribution of the archaeological remians and the microtopography of layer 6A2;b.遗物空间分布三维散点图 3D scatter plot for the archaeological remians of layer 6A2
Fig.13 The spatial distribution of the archaeological remians in layer 6A2 of the Donggutuo site
| [1] | Isaac GL. Towards the interpretation of occupation debris: some experiments and observations[J]. Kroeber Anthropological Society Papers, 1967, 37(3): 31-57 |
| [2] |
Petraglia MD, Potts R. Water flow and the formation of Early Pleistocene artifacts sites in Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania[J]. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, 1994, 13: 228-254
doi: 10.1006/jaar.1994.1014 URL |
| [3] |
de la Torre I, Wehr K. Site formation processes of the early Acheulean assemblage at EF-HR (Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania)[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2018, 120: 298-328
doi: S0047-2484(17)30304-4 pmid: 28802723 |
| [4] | Schiffer MB. Formation process of the archaeological record[M]. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, 1987 |
| [5] | Karkanas Panagiotis, Goldberg Paul. Reconstructing archaeological sites: understanding the geoarchaeological matrix[M]. Wiley Blackwell, 2018 |
| [6] | 裴树文. 旧石器时代旷野遗址形成过程研究综述[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(1): 1-18 |
| [7] |
Barbour G B, Lincent E, Chardin P T D. Geological Study of the Deposits of the Sangkanho Basin[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of China, 1926, 5(3-4): 263-278
doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.1926.mp53-4005.x URL |
| [8] |
Deng CL, Hao QZ, Guo ZT, et al. Quaternary integrative stratigraphy and timescale of China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(1): 324-348
doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9195-4 |
| [9] |
Deng CL, Zhu RX, Zhang R, et al. Timing of the Nihewan formation and faunas[J]. Quaternary Research, 2008, 69(1): 77-90
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2007.10.006 URL |
| [10] | 卫奇, 孟浩, 成胜泉. 泥河湾层中发现一处旧石器地点[J]. 人类学学报, 1985, 4(3): 223-232 |
| [11] | 侯亚梅, 卫奇, 冯兴无, 等. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址再发掘[J]. 第四纪研究, 1999(2): 139-147 |
| [12] | 裴树文, 李潇丽, 刘德成, 等. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址古人类生存环境探讨[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54(19): 2895-2901 |
| [13] | 贾真秀. 泥河湾盆地早更新世古人类遗址成因与石器技术比较研究——以东谷坨、麻地沟和飞梁遗址为例[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2018 |
| [14] | Keates SG. Early and middle Plesitence Hominid behavior in Northern China[M]. England: British Archaeological Reports Limited, 2000 |
| [15] | 谢飞, 李珺, 刘连强. 泥河湾旧石器文化[M]. 石家庄: 花山文艺出版社, 2006 |
| [16] | 卫奇. 东谷坨旧石器初步观察[J]. 人类学学报, 1985(4): 289-300 |
| [17] | 卫奇. 东谷坨遗址石制品再研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(3): 254-269 |
| [18] | 侯亚梅. “东谷坨石核”类型的命名与初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2003, 22(4): 279-291 |
| [19] | 裴树文, 侯亚梅. 东谷坨遗址石制品原料利用浅析[J]. 人类学学报, 2001, 20(4): 271-281 |
| [20] | 邢增锐. 东谷坨遗址 2016 年出土石制品研究[D]. 北京: 中国人民大学, 2018 |
| [21] | 张月书, 李锋, 王晓敏, 等. 旧石器时代遗址发掘与记录方法讨论[J]. 人类学学报, 40(2): 181-193 |
| [22] |
Yang SX, Petraglia M, Hou YM, et al. The lithic assemblages of Donggutuo, Nihewan basin: Knapping skills of early pleistocene hominins in North China[J]. PloS One, 2017, 12 (9): e0185101
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185101 URL |
| [23] |
Schick K, Toth N, Qi W, et al. Archaeological perspectives in the Nihewan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 1991, 21(1): 13-26
doi: 10.1016/0047-2484(91)90033-R URL |
| [24] |
Jia ZX, Pei SW, Benito‐Calvo A, et al. Site formation processes at Donggutuo: a major Early Pleistocene site in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2019, 34(8): 1-12
doi: 10.1002/jqs.3070 URL |
| [25] | 李潇丽, 裴树文, 马宁, 等. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址剖面易溶盐沉积及其环境意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2010, 12(3): 307-314 |
| [26] | 王红强. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨剖面磁性特征及环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007(6): 1081-1091 |
| [27] | 李华梅, 王俊达. 中国北方几个典型地质剖面的磁性地层学研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 1982, 6(2): 29-33 |
| [28] |
Ao H, Deng CL, Dekkers M J, et al. Astronomical dating of the Xiantai, Donggutuo and Maliang Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin (North China) and implications for early human evolution in East Asia[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010, 297(1): 129-137
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.07.022 URL |
| [29] | Wang HQ, Deng Cl, Zhu RX, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the Donggutuo and Maliang Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2005, 64(1): nwaa053 |
| [30] |
Liu CR, Yin GM, Fang F, et al. ESR dating of the Donggutuo Palaeolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, northern China[J]. Geochronometria, 2013, 40(4): 348-354
doi: 10.2478/s13386-013-0127-4 URL |
| [31] |
Duval M. et al. Comments on “ESR dating of the Majuangou and Banshan Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin, North China” by Liu et al. (2014)[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2016, 90: 198-202
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2015.04.010 URL |
| [32] | 李锋, 陈福友, 赵海龙, 等. 试论“水平层”与旧石器时代遗址考古发掘方法[J]. 考古, 2019, 1: 85-95 |
| [33] | Schick K D. Stone Age sites in the making: experiments in the formation and transformation of archaeological occurrences[M]. Oxford: British Archaeological Reports Ltd, 1986 |
| [34] | 任进成, 李锋, 陈福友, 等. 石制品废片尺寸分布的实验研究:以泥河湾盆地大田洼区域燧石原料为例[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(3): 379-391 |
| [35] | 任进成. 泥河湾板井子遗址旧石器时代遗址形成过程与石器技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019 |
| [36] |
Grosman L, Sharon G, Goldman-Neuman T, et al. Studying post depositional damage on Acheulian bifaces using 3-D scanning[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2011, 60(4): 398-406
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2010.02.004 pmid: 20304464 |
| [37] | Shea J J. Artifact abrasion, fluvial processes, and “living floors” from the Early Paleolithic site of ’Ubeidiya (Jordan Valley, Israel)[J]. 1999, 14(2): 191-207 |
| [38] | 唐锐枰, 葛俊逸, 庞海娇, 等. 泥河湾黑土沟剖面磁组构特征及古湖水文环境变化[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(11): 1027-1045 |
| [39] | Yang SX, Wang FG, Xie F, et al. Technological innovations at the onset of the Mid-Pleistocene Climate Transition in high-latitude East Asia[J]. National Science Review, 2021, 8(1): 1-11 |
| [1] | 胡海虔, 黄万波, 魏光飚, 代辉, 熊璨, 何树兴, 姜涛. 重庆武隆早更新世地层中发现巨猿化石[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 701-711. |
| [2] | 任进成, 李锋, 陈福友, 高星. 泥河湾盆地板井子遗址2015年出土石制品的剥片技术[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 712-726. |
| [3] | 陈育芝, 武仙竹. 长江三峡及周边地区早期人类的生存环境与生存行为[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 287-297. |
| [4] | 高星, 张月书, 李锋, 陈福友, 王晓敏, 仪明洁. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址2016-2019年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 106-121. |
| [5] | 赵云啸, 仝广, 涂华, 赵海龙. 河北省泥河湾盆地石沟遗址C区发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 122-131. |
| [6] | 王法岗, 杨石霞, 葛俊逸, 岳健平, 赵克良, Andreu Ollé, 李文艳, 杨海勇, 刘连强, 关莹, 谢飞, Francesco d’Errico, Michael Petraglia, 邓成龙. 泥河湾盆地下马碑遗址2013年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 143-156. |
| [7] | 张振, 王莹, 李月丛. 泥河湾盆地旧石器时代人类活动与环境关系的研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 184-198. |
| [8] | 裴树文, 徐哲, 叶芷, 马东东, 贾真秀. 泥河湾盆地中更新世气候转型期人类的适应行为[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 19-39. |
| [9] | 刘连强, 蒲昱晓, 侯佳岐, 王法岗. 泥河湾盆地马圈沟遗址鱼咀沟1号地点2017-2018年发掘出土的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 40-54. |
| [10] | 周振宇, 王法岗, 关莹. 河北泥河湾盆地西白马营遗址1985-1986年出土的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 55-66. |
| [11] | 仝广, 李锋, 赵海龙, 闫晓蒙, 高星. 泥河湾盆地火山角砾岩原料的热处理实验[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 81-90. |
| [12] | 王晓敏, 刘连强, 陈国鹏, 李锋, 谢飞, 高星. 泥河湾盆地马圈沟遗址哺乳动物破碎长骨反映的古人类行为[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 91-105. |
| [13] | 杜雨薇, 张乐, 叶芷, 裴树文. 蔚县盆地吉家庄旧石器遗址动物骨骼的埋藏学分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(03): 359-372. |
| [14] | 范文田, 杨晓冬. 泥河湾盆地南山根地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(02): 260-271. |
| [15] | 王元, 王一飒, 王奕迪, 秦超, 秦大公, 金昌柱. 广西扶绥岩亮洞与巨猿伴生的鼠亚科及其动物群的层序对比[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(06): 1041-1054. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 276
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 500
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3