

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (01): 157-183.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0007cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0007
收稿日期:2023-10-11
出版日期:2024-02-15
发布日期:2024-02-06
作者简介:同号文,研究员,主要研究方向为第四纪哺乳动物学。E-mail: 基金资助:
TONG Haowen1,2( ), ZHANG Bei3, CHEN Xi4
), ZHANG Bei3, CHEN Xi4
Received:2023-10-11
Online:2024-02-15
Published:2024-02-06
摘要:
泥河湾盆地最初以其广泛分布的含化石河湖相地层而受关注,并以其丰富的哺乳动物化石而著称于世,而今,泥河湾盆地已成为世界著名旧石器考古重地和研究第四纪地质古生物的重要场所。狭义泥河湾动物群(或下沙沟动物群)是我国北方早更新世的标准动物群,其古地磁年龄是2.2-1.7 MaBP。随着地层古生物工作的深入开展,盆地内也发现了若干中-晚更新世化石点;丁家堡水库全新统中发现的象颊齿,之前被鉴定为亚洲象,新的测年数据表明其时代大于5万年,依据牙齿测量数据和形态特征,本研究将其归入诺氏古菱齿象。目前已在泥河湾盆地发现百余个化石地点,鉴定出236种(包括未定属种)哺乳动物,分属于8目、32科和121属,其中38个属种(包括亚种)最初是以泥河湾化石材料而建立。总而言之,泥河湾盆地哺乳动物化石以早更新世者居多,并且化石材料保存完好;有些属种在欧亚大陆古北区第四纪哺乳动物群形成过程中发挥过重要作用,例如早期猛犸象、披毛犀、野牛及真枝角鹿等,还有直隶狼、貉及各种真马。泥河湾盆地由于河流和断层切割以及沉积相变等原因,导致各个化石点及史前考古遗址地层难以直接对比,更难全窥盆地内动物群演化的整体脉络;新的生物地层对比研究表明,桑干河南岸的岑家湾台地周缘的早更新世化石点,其主化石层位与下沙沟地区经典泥河湾动物群的层位大致相当。泥河湾盆地哺乳动物化石主要产自细砂、粉砂及黏土地层;化石成堆产出或者呈条带状及凸镜状分布的特点,多数与水流搬运有关。除过1枚豪猪牙齿和少量麂类化石之外,泥河湾盆地第四纪哺乳动物群中几乎不含东洋界动物,总体反映了干冷草原为主的古环境背景。
中图分类号:
同号文, 张贝, 陈曦. 泥河湾盆地第四纪哺乳动物群概览及若干新认识[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 157-183.
TONG Haowen, ZHANG Bei, CHEN Xi. An overview and new insights into the Quaternary mammalian fauna from the Nihewan Basin in North China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(01): 157-183.
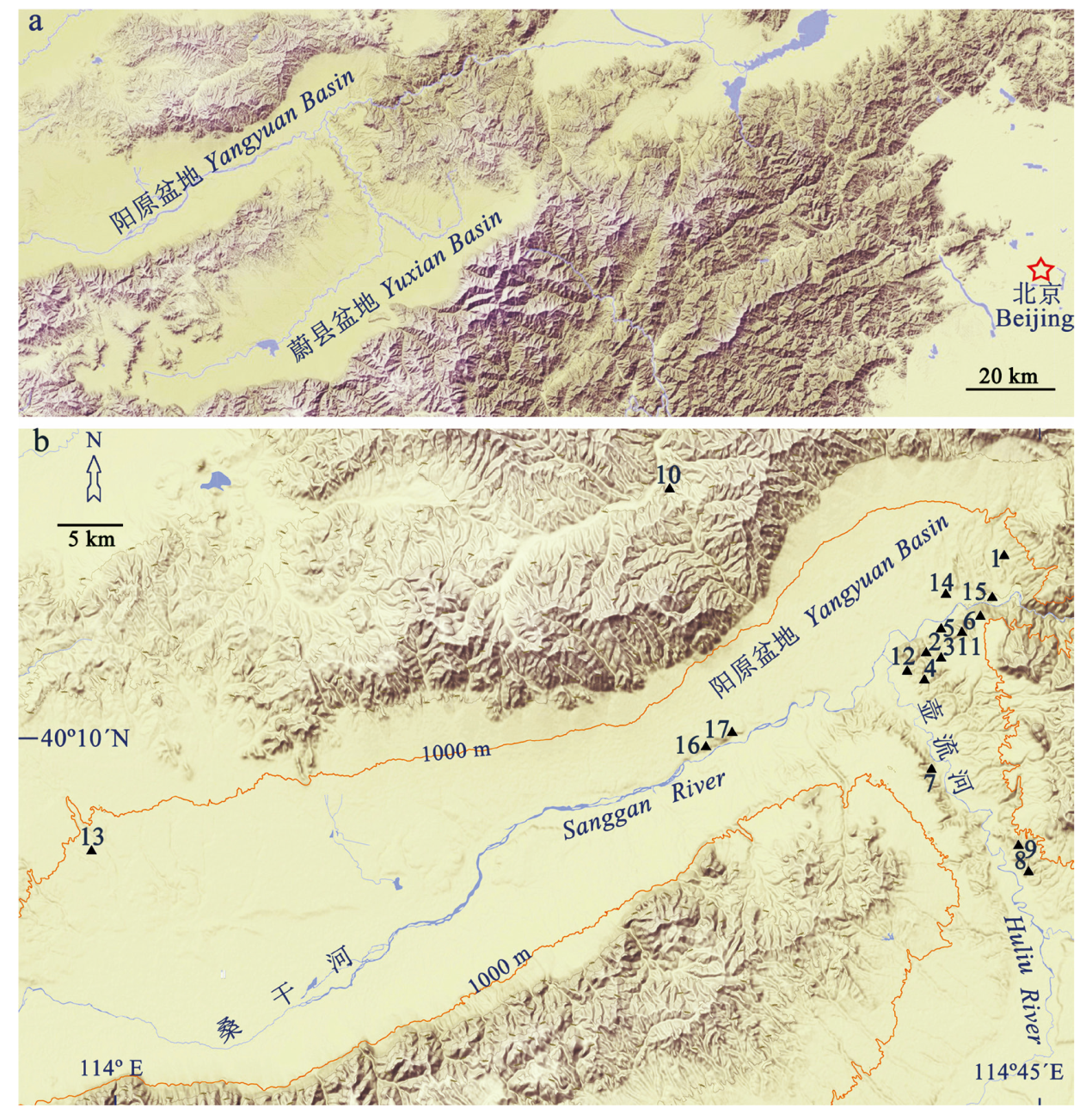
图1 阳原盆地(狭义泥河湾盆地)位置(a)及重要遗址分布图(b) 1.下沙沟Xiashagou;2.小长梁Xiaochangliang;3.山神庙咀Shanshenmiaozui;4.野牛坡Yeniupo;5.马圈沟Majuangou;6.石沟Shigou;7.红崖扬水站Yangshuizhan of Hongya;8.大南沟东陡壁Dongdoubi of Danangou;9.东窑子头Dongyaozitou;10.辛窑子Xinyaozi;11.东谷坨Donggutuo;12.小渡口Xiaodukou;13.侯家窑-许家窑Houjiayao-Xujiayao;14.上沙嘴Shangshazui;15.板井子Banjingzi;16.西白马营Xibaimaying;17.虎头梁Hutouliang—化石点Fossil sites: 1-11.早更新世Early Pleistocene;12.中更新世Middle Pleistocene;13-17.晚更新世Late Pleistocene。 图b中的橙色线条代表1000 m等高线(底图来自腾讯网 https://map.qq.com/)
Fig.1 Location map of the Yangyuan Basin (Nihewan Basin sensu stricto) (a) and its key fossil sites (b)
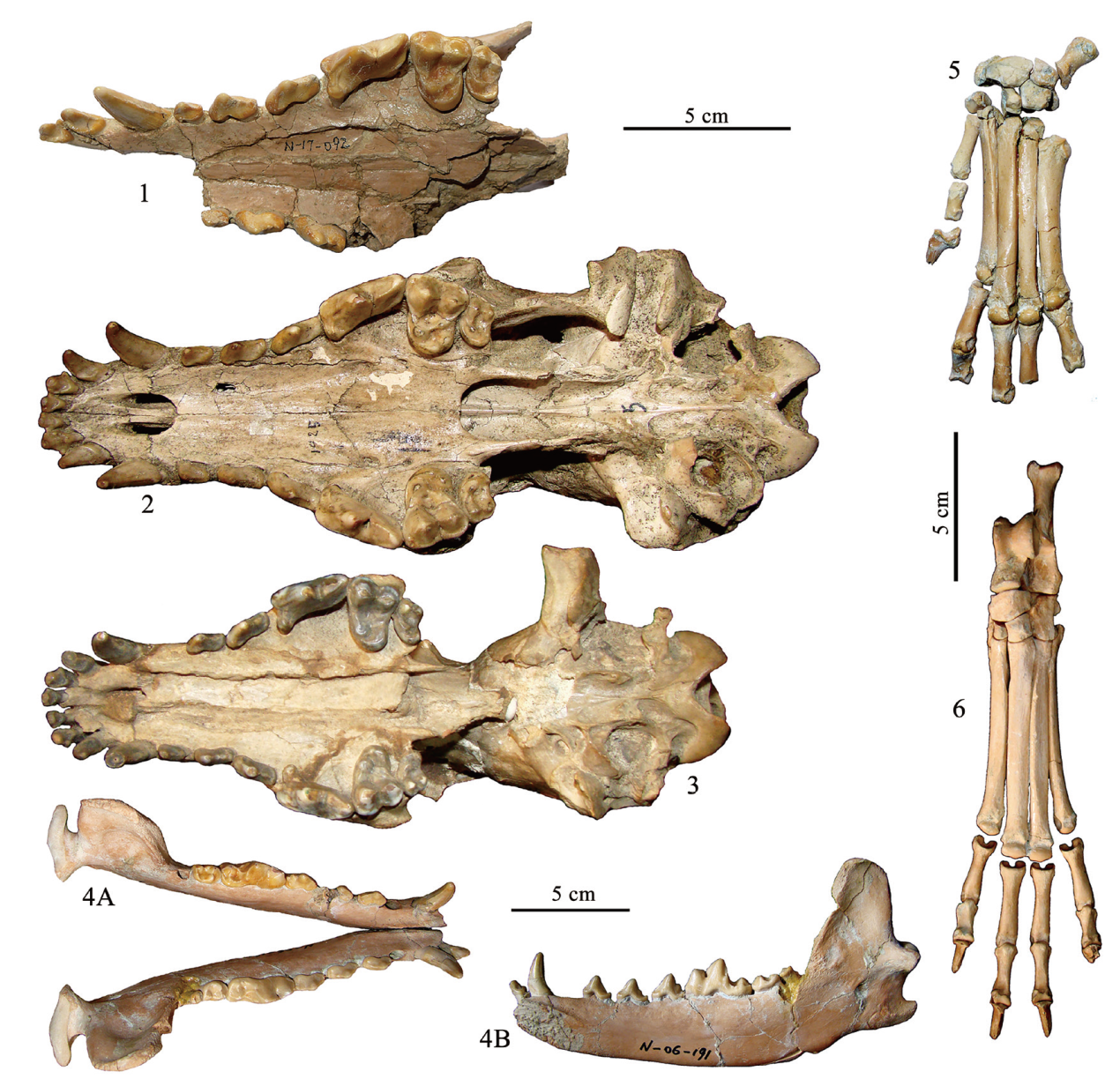
图2 泥河湾盆地的直隶狼(1-2, 4-6)及掌齿狼(3)重要化石 1.直隶狼残破头骨partial skull of C. chihliensis, IVPP V 31910; 2.直隶狼头骨skull of C. chihliensis, TNP 00162; 3, 掌齿狼头骨skull of C. palmidens, TNP 00198; 4.直隶狼下颌骨mandible of C. chihliensis, IVPP V 17755.3;5.直隶狼前脚骨manus of C. chihliensis, IVPP V 31914. (1-18);6.直隶狼后脚骨pes of C. chihliensis, V 18139.(24-48)。1-3.腭面视palatal view;4A.冠面视occlusal view;4B.舌侧视lingual view;5-6.前视anterior views。1和4-6,产自山神庙咀,中国科学院古脊椎所藏品unearthed from SSMZ (Shanshenmiaozui), housed in IVPP (Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology);2和3产自下沙沟,天津自然博物馆藏品unearthed from XSG (Xiashagou of Nihewan), housed in TNHM (Tianjin Natural History Museum)
Fig.2 Selected fossils of Canis chihliensis (1-2, 4-6) and Canis palmidens (3) from Nihewan Basin
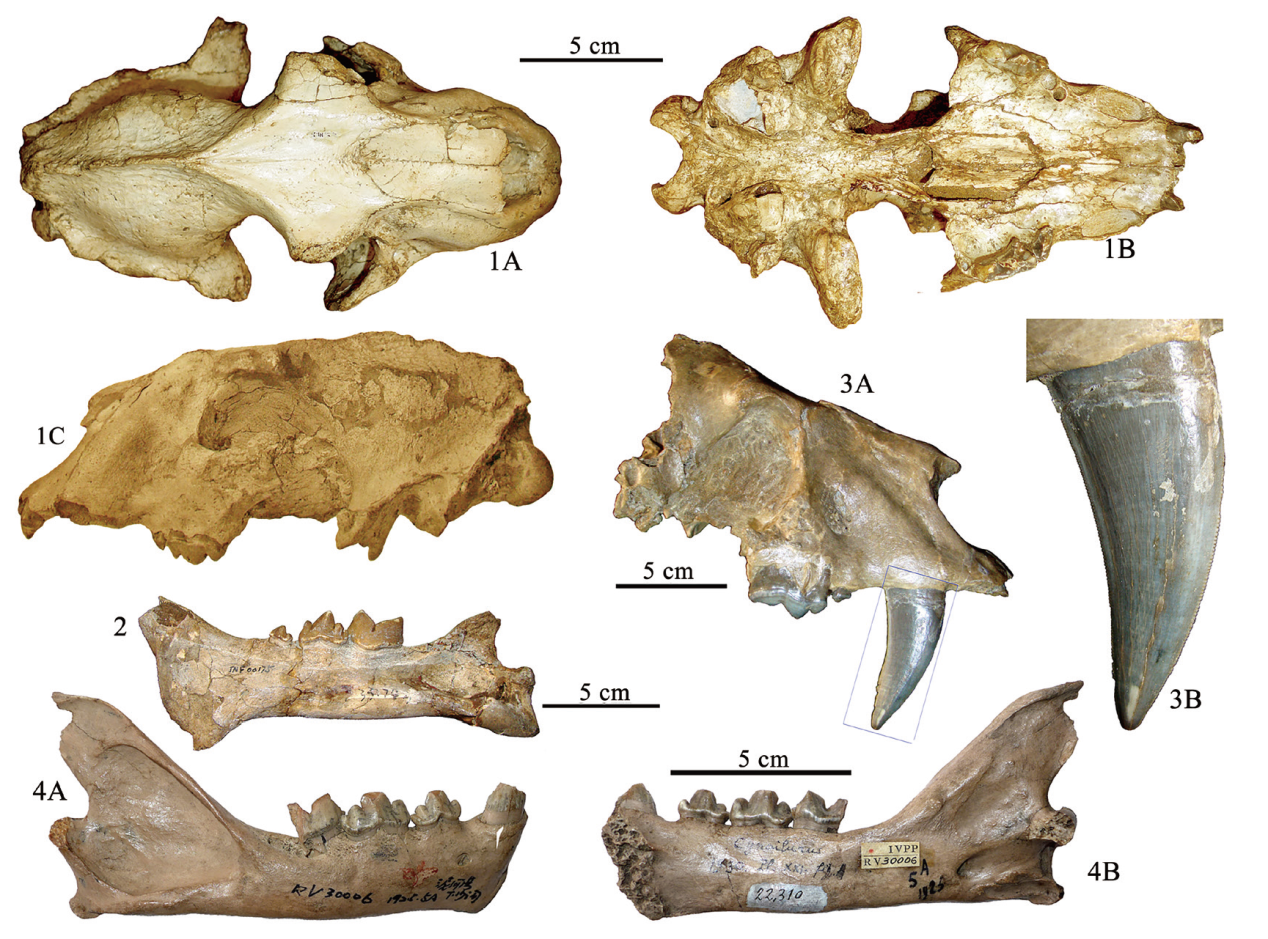
图3 泥河湾盆地的巨颏虎(1-2)、锯齿虎(3)及猎豹(4)重要化石 1.泥河湾巨颏虎头骨skull of Megantereon, NIH 153; 2.泥河湾巨颏虎下颌骨skull of Megantereon, TNP 00175; 3.锯齿虎残破头骨partial skull of Homotherium, TNP 32067; 4.猎豹下颌骨mandible of Acinonyx, IVPP RV3006。1A,顶视dorsal view;1B,腭面视palatal view;1C,3A和3B,侧面视lateral view;2和4A,颊侧视buccal views;4B,舌侧视lingual view。 1,法国国家自然历史博物馆藏品housed in MNHN (Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle);2-3,天津自然博物馆藏品housed in TNHM;4,中国科学院古脊椎所藏品housed in IVPP;全部产自下沙沟all of them were unearthed from XSG。 1C引用自Teilhard de Chardin et Piveteau[4]
Fig.3 Skull and mandible of Megantereon (1-2), partial skull of Homotherium (3), and mandible of Acinonyx (4) from Nihewan Basin
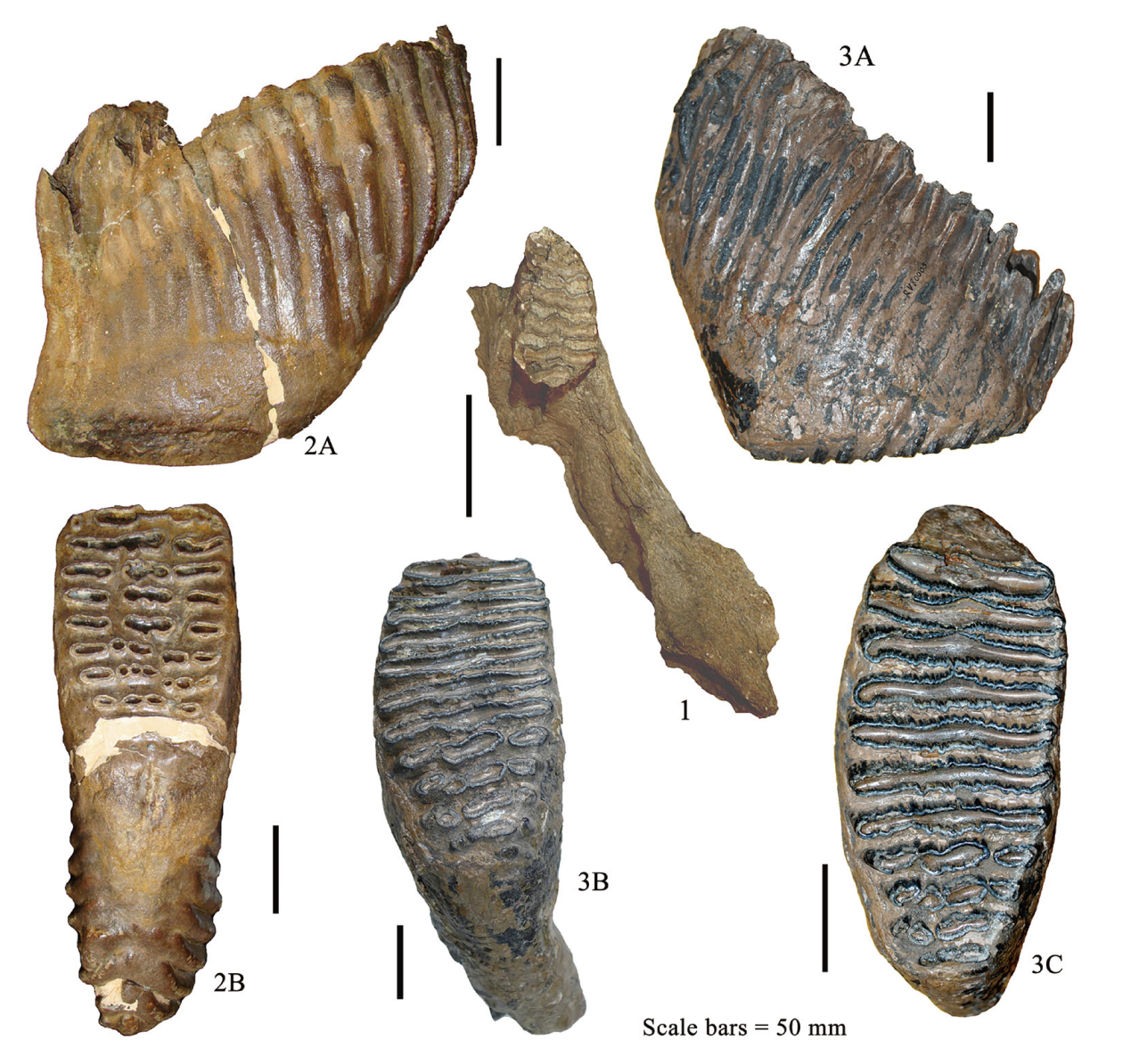

图4 泥河湾盆地发现的重要猛犸象(1-2)和诺氏古菱齿象(3)化石 1. 草原猛犸象右下颌带第三乳齿partial right mandible of M. trogontherii with dp3, NIH 158; 2A-2B. 草原猛犸象左上第三臼齿left M3 of M. trogontherii,IVPP V 13610;3A-3C. 诺氏古菱齿象右上第三臼齿right M3 of P. naumanni,IVPP RV 80005。 1, 2B, 3B-3C冠面视occlusal views,3C为嚼面放大details of the occlusal surface;2A, 3A颊侧视buccal views。 1.产自下沙沟,法国国家自然历史博物馆藏品unearthed from XSG, housed in MNHN; 2.产自马圈沟unearthed from MJG (Majuangou in Nihewan);3.产自丁家堡水库unearthed from Dingjiabu Reservoir,2-3.中国科学院古脊椎所藏品housed in IVPP
Fig.4 Selected fossils of Mummuthus trogontherii (1-2) and Palaeoloxodon naumanni (3) from Nihewan Basin
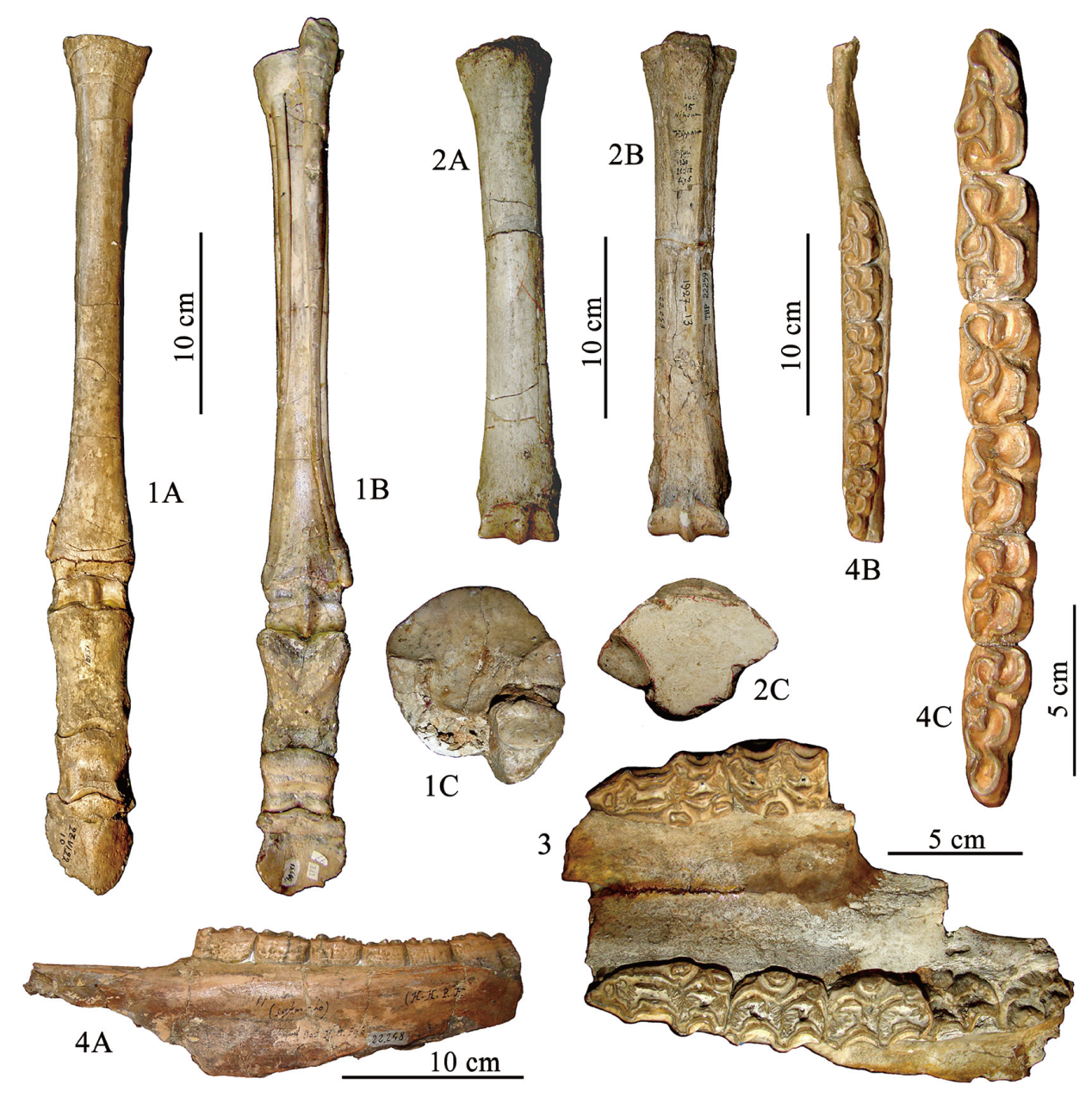

图5 泥河湾盆地的中国长鼻三趾马重要化石 1A-1C. 右后脚骨right hindlimb bone, THP15609;2A-2C.左掌骨left Mc.III,THP22259;3.上颌骨maxilla,TNP 00149;4A-4C.右下颌right mandible,THP22258。1A和2A,前视anterior views;1B和2B,后视posterior views;3,腭面视palatal view;4A,舌侧视lingual view;4B和4C,冠面视occlusal views;1C和2C, 近端关节面放大details of the proximal articular surface。 全部产自下沙沟,天津自然博物馆藏品 all of the fossils were unearthed from XSG, and housed in TNHM。 1A由博讷教授拍摄(photo 1A courtesy of Bernor R.L.)
Fig.5 Selected fossils of Hipparion (Proboscidipparion) sinense from Nihewan Basin
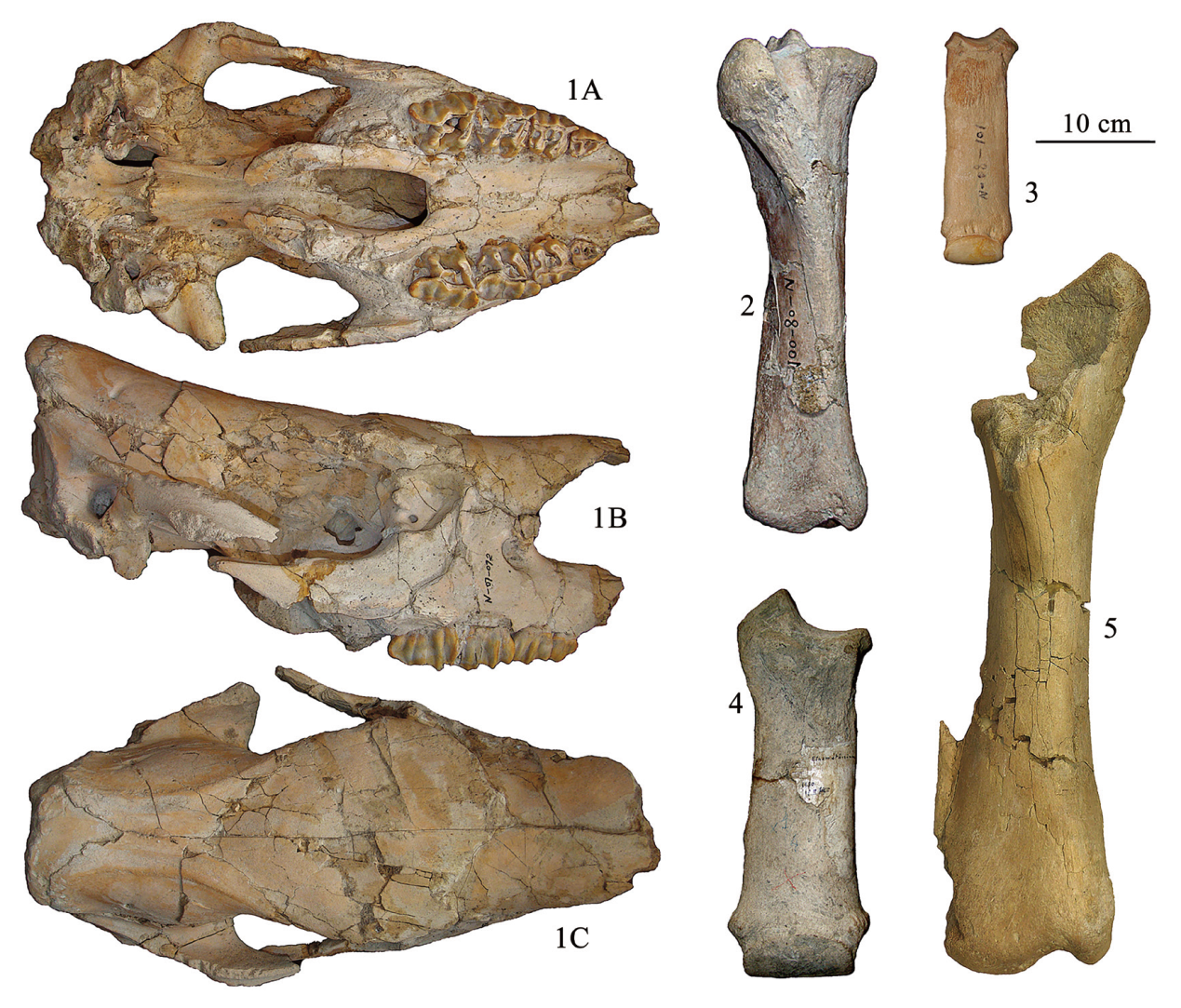
图6 泥河湾盆地的披毛犀(1-3)与板齿犀(4-5)的重要化石 1A-1C.头骨skull of C. nihowanensis,IVPP V 17616.1;2.右胫骨right tibia of C. nihowanensis,IVPP V 17616.30;3.左第三掌骨left Mc III of C. nihowanensis,IVPP V 17616.28;4.右第三掌骨right Mc III of E. peii,THP 22333;5.右胫骨right tibia of E. peii,IVPP V23590.6。1A.腭面视palatal view;1B.侧面视lateral view;1C.顶面视dorsal view;2-5.前视anterior views。1-3和5,产自山神庙咀,中国科学院古脊椎所藏品unearthed from SSMZ, and housed in IVPP;4,产自下沙沟,天津自然博物馆藏品unearthed from XSG, and housed in TNHM
Fig.6 Selected fossils of Coelodonta nihowanensis (1-3) and Elasmotherium peii (4-5) from Nihewan Basin
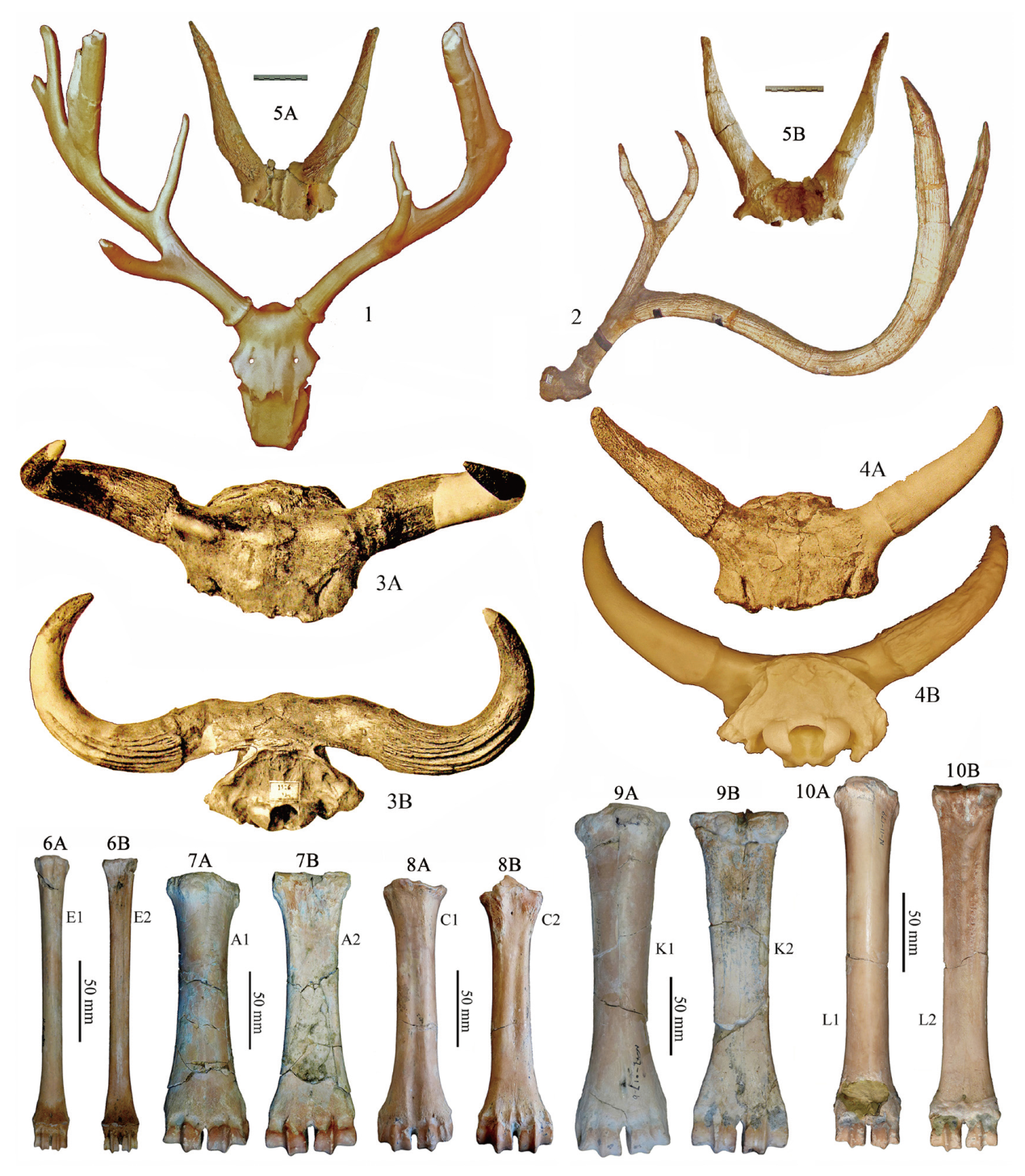

图7 泥河湾盆地鹿科及牛科重要标本 1.布氏真枝角鹿头骨带角(模型照片)skull with antlers of E. boulei (cast),THP 32184。2. 双叉麋鹿右角right antler of E. bifurcatus,TNP33731。3A-3B. 古中华野牛残破头骨带角心partial skull with horncores of B. palaeosinensis;4A-4B. 古中华野牛残破头骨带角心partial skull with horncores of B. palaeosinensis (3A-3B和4A引用自Teilhard de Chardin et Piveteau[4];4B为模型照片cast),TNP 32025。5, 7-8. 翁氏转角羚羊Spirocerus wongi;5A-5B. 残破头骨带左右角心partial skull with horncores of S. wongi;7A-7B. 左掌骨left Mc III+IV, V 28655;8A-8B.右蹠骨right Mt. III+IV, V 28656.4。6A-6B.中国羚羊 Gazella sinensis,左掌骨left Mc III+IV, V 28688。9A-9B.皮氏巨羊Megalovis piveteaui,右掌骨right Mc III+IV, V 28695。10A-10B. 山东盘羊Ovis shantungensis,左掌骨 left Mc III+IV, V 28694。 1, 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A, 9A, 10A. 前视anterior views;2.侧视lateral view;3B, 4B,5B, 6B, 7B, 8B, 9B, 10B.后视posterior views。 1-4.产自下沙沟unearthed from XSG;5-10.产自山神庙咀unearthed from SSMZ。1-2和4,天津自然博物馆藏品housed in TNHM;3,法国国家自然历史博物馆藏品housed in MNHN;5-10.中国科学院古脊椎所藏品housed in IVPP ; 6-10.引自Tong et al.[91]
Fig.7 Selected fossils of cervids and bovids from Nihewan Basin
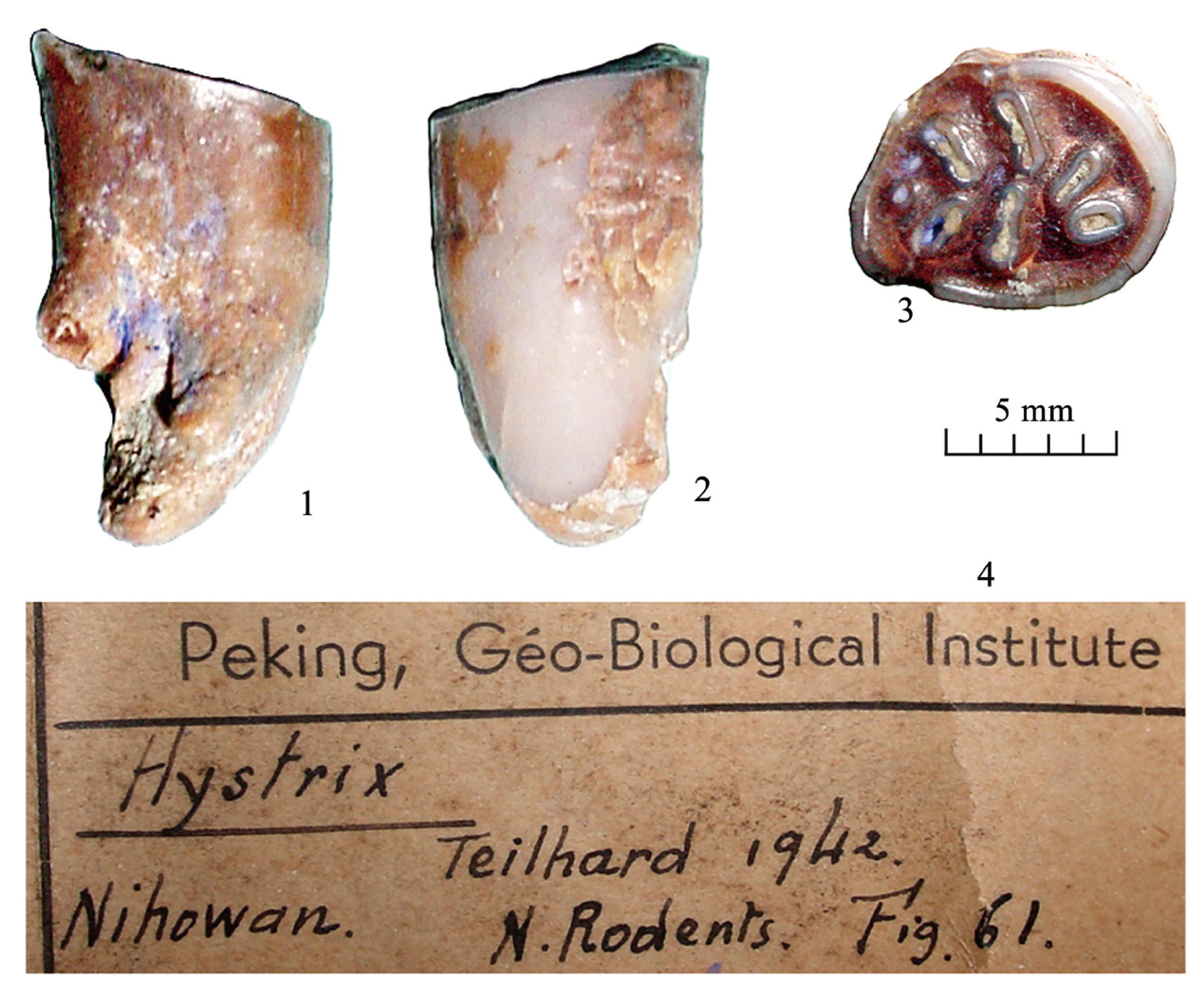
图8 泥河湾盆地发现的豪猪化石 1-3.右right P4,IVPP V 32921;1.颊侧视buccal view;2.舌侧视lingual view;3.冠面视occlusal view;4.当年的化石标签original specimen label;泥河湾盆地,具体地点不明unearthed from Nihewan but without locality information;中国科学院古脊椎所藏品housed in IVPP
Fig.8 The only fossil of Hystrix sp. from Nihewan Basin
| [1] | De Terra H. Pleistocene formations and stone age man in China[M]. Institut de Géo-Biologie, Péking, 1941, 6: 1-54 |
| [2] | Pei WC. The zoogeographical divisions of Quaternary mammalian faunas in China[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 1957, 1(1): 9-24 |
| [3] |
Barbour GB, Licent E, Teilhard de Chardin P. Geological study of the deposits of the Sangkanho Basin[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of China, 1927, 5(3-4): 263-278
doi: 10.1111/acgs.1926.5.issue-3-4 URL |
| [4] | Teilhard de Chardin P, Piveteau J. Les mammiféres fossils de Nihowan (Chine)[M]. Annales de Paléontologie, 1930, 19: 1-134 |
| [5] | Black D, Teilhard de Chardin P, Young CC, et al. Fossil Man in China: The Choukoutien cave deposits with a synopsis of our present knowledge of the Late Cenozoic in China[J]. Memoirs of the Geological Survey of China (Ser A), 1933, 11: 1-174 |
| [6] | 杨钟健. 中国人类化石及新生代地质概论[M]. 地质专报,乙种第五号, 1933,1-106 |
| [7] | Teilhard de Chardin P. Early man in China[M]. Institut de Géo-Biologie, Péking, 1941, 7: 1-99 |
| [8] | Young CC. Butler AJ (The Plio-Pleistocene boundary in China[A]. In: ed.).International Geological Congress - Report of the Eighteenth Session, Great Britain, 1948, Part IX[C]. London: Geological Society, 1950, 115-125 |
| [9] | 杨钟健. 中国上新统与更新统之分界问题[J]. 科学, 1940, 24(4): 261-280 |
| [10] | Pei WC. Geochronological table, No.1, an attempted correlation of Quaternary geology, palaeontology and prehistory in Europe and China[J]. Occasional Paper No.2, Institute of Archaeology, University of London, 1939, 1-17 |
| [11] | 汪品先. 更新统下届的半世纪之争[J]. 第四纪研究, 2000, 20(2): 178-181 |
| [12] |
Rook L, Martínez-Navarro B. Villafranchian: The long story of a Plio-Pleistocene European large mammal biochronologic unit[J]. Quaternary International, 2010, 219: 134-144
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2010.01.007 URL |
| [13] | 邱占祥. 泥河湾哺乳动物群与中国第四纪下限[J]. 第四纪研究, 2000, 20(2): 142-154 |
| [14] | 刘文晖. 泥河湾盆地红崖扬水站地点貉类化石及貉属化石分类的修订[D]. 北京: 中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所博士学位论文, 2019, 1-384 |
| [15] |
Farjand A, Zhang ZQ, Kaakinen A, et al. Rediscovery and stratigraphic calibration of the classic Nihewan Fauna, Hebei Province, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2023, 646: 1-10
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2022.12.001 URL |
| [16] | Farjand A, Zhang ZQ, Gibbard PL, et al. First results of the biostratigraphy and geochronology of the classic Nihewan Fauna, China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2023, 11: 1276816. doi: 10.3389/feart.2023.1276816 |
| [17] | 迟振卿, 卫奇. “泥河湾层”考究[J]. 文物春秋, 2013, 5: 3-10 |
| [18] | 迟振卿, 卫奇. 泥河湾动物群考究[A].见:董为,张颖奇(主编).第十四届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2014, 71-88 |
| [19] | Tedford RH, Qiu Z. A new canid genus from the Pliocene of Yushe, Shanxi Province[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 1996, 34: 27-40 |
| [20] | Koenigswald GHRv. Die Tertiaren Wirbeltiere des Steinheimer Beckens: Metaschizotherium fraasi N. G. N. sp., ein neuer Chalicotheriide aus dem Obermiocan von Steinheim am Albuch[J]. Paleontographica, 1932, Suppl, VIII: 1-24 |
| [21] | Schaub S. Ein neuer Cavicornier aus dem Oberpliocaen von Honan[J]. Bulletin of the geological institutions of the University of Uppsala, 1937, 27: 25-31 |
| [22] | Kahlke HD. Die Rhinocerotiden-Reste aus den Kiesen von Süßenborn bei Weimar[J]. Paläontologische Abhandlungen, 1969, A 3: 667-709 |
| [23] |
Eisenmann V. Nouvelles interpretations des restes d’equides (Mammalia, Perissodactyla) de Nihowan (Pleistocene inferieur de la Chine du Nord): Equus teilhardi nov. sp.[J]. Geobios, 1975, 8(2): 125-134
doi: 10.1016/S0016-6995(75)80009-X URL |
| [24] | 贾兰坡, 卫奇, 李超荣. 许家窑旧石器时代文化遗址1976年发掘报告[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1979, 17(4): 277-293 |
| [25] | 汤英俊. 河北蔚县早更新世哺乳动物化石及其在地层划分上的意义[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1980, 18(4): 314-323 |
| [26] | 郑绍华. 泥河湾地层中小哺乳动物的新发现[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1981, 19(4): 348-358 |
| [27] | 王安德. 泥河湾地区上新世哺乳动物群的发现及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 1982, 27(4): 227-229 |
| [28] | 汤英俊, 计宏祥. 河北蔚县上新世-早更新世间的一个过渡动物群[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1983, 21(3): 245-254 |
| [29] | 卫奇. 泥河湾层中的大角鹿一新种[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1983, 21(1): 87-95 |
| [30] | 邱铸鼎. 记河北蔚县泥河湾层短耳兔属一新种[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1985, 23(4): 276-286 |
| [31] | 蔡保全. 河北阳原—蔚县晚上新世兔形类化石[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1989, 27(3): 170-181 |
| [32] | 郑绍华, 蔡保全.河北蔚县东窑子头大南沟剖面中的小哺乳动物化石[A]. 见: 中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所(编著). 第十三届国际第四纪大会论文选[C]. 北京: 北京科学技术出版社, 1991, 100-131 |
| [33] | Erbajeva MA, Zheng SH. New data on Late Miocene-Pleistocene ochotonids (Ochotonidae, Lagomorpha) from North China[J]. Acta Zoologica Cracoviensia, 2005, 48A(1-2): 93-117 |
| [34] |
Dong W, Wei Q, Bai W, et al. New material of the Early Pleistocene Elaphurus (Artiodactyla, Mammalia) from North China and discussion on taxonomy of Elaphurus[J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 519: 113-121
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.05.015 |
| [35] | Zheng SH, Zhang YQ, Cui N. Five new species of Arvicolinae and Myospalacinae from the Late Pliocene-Early Pleistocene of Nihewan Basin[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2019, 57(4): 308-324 |
| [36] | Tong HW, Hu N, Wang XM. New remains of Canis chihliensis (Mammalia, Carnivora) from Shanshenmiaozui, a Lower Pleistocene Site in Yangyuan, Hebei[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2012, 50(4): 335-360 |
| [37] | Tong HW, Chen X, Zhang B, et al. Hypercarnivorous teeth and healed injuries to Canis chihliensis from Early Pleistocene Nihewan beds, China, support social hunting for ancestral wolves[J]. PeerJ, 2020, 8: e9858 |
| [38] |
Tong HW, Zhang B, Chen X, et al. New carnivoran remains from the Early Pleistocene Shanshenmiaozui site in Nihewan Basin, northern China[J]. Quaternary International, 2023, 658 (2023): 60-79
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2023.04.003 URL |
| [39] | Tedford RH, Wang X, Taylor BE. Phylogenetic systematics of the North American fossil Caninae (Carnivora: Canidae)[M]. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History, 2009, 325: 1-218 |
| [40] |
Jiangzuo QG, Liu J, Wagner J, et al. Taxonomical revision of fossil Canis in Middle Pleistocene sites of Zhoukoudian. Beijing, China and a review of fossil records of Canis mosbachensis variabilis in China[J]. Quaternary International, 2018, 482: 93-108
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.04.003 URL |
| [41] | Tedford RH, Qiu ZX. Pliocene Nyctereutes (Carnivora: Canidae) from Yushe, Shanxi, with comments on Chinese fossilracoon-dogs[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 1991, 29(3): 176-189 |
| [42] |
Farjand A, Zhang ZQ, Liu WH, et al. The evolution of Nyctereutes (Carnivora: Canidae) in the Nihewan Basin, Hebei, northern China[J]. Palaeoworld, 2021, 30(2): 373-381
doi: 10.1016/j.palwor.2020.07.002 URL |
| [43] | Liu JY, Zhang YQ, Chi ZQ, et al. A Late Pliocene Hipparion houfenense fauna from Yegou, Nihewan Basin and its biostratigraphic significance[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2022, 60(4): 278-323 |
| [44] | 邱占祥, 邓涛, 王伴月. 甘肃东乡龙担早更新世哺乳动物群[M].中国古生物志新丙种第27号. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004, 1-224 |
| [45] | Jiangzuo QG, Zhao HL, Chen X, et al. The first complete cranium of Homotherium (Machairodontinae, Felidae) from the Nihewan Basin (northern China)[J]. The Anatomical Record, 2022: 1-11 |
| [46] | 刘金毅, 房迎三, 张镇洪. 食肉目[A].见:南京博物院和江苏省考古研究所(编).南京驼子洞早更新世哺乳动物群[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007, 25-68 |
| [47] |
Spassov N. Acinonyx pardinensis (Croizet et Jobert) remains from the Middle Villafranchian locality of Varshets (Bulgaria) and the Plio-Pleistocene history of the cheetahs in Eurasia[J]. Estudios Geológicos, 2011, 67(2): 245-253
doi: 10.3989/egeol.11672 URL |
| [48] |
Geraads D. How old is the cheetah skull shape? The case of Acinonyx pardinensis (Mammalia, Felidae)[J]. Geobios, 2014, 47: 39-44
doi: 10.1016/j.geobios.2013.12.003 URL |
| [49] |
Cherin M, Iurino DA, Sardella R, et al. Acinonyx pardinensis (Carnivora, Felidae) from the Early Pleistocene of Pantalla (Italy): predatory behavior and ecological role of the giant Plio-Pleistocene cheetah[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 87: 82-97
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.01.004 URL |
| [50] | 赵文俭, 李凯清, 刘文晖, 等. 泥河湾盆地钱家沙洼象头山地点2014年发掘简报[A].见:董为(主编).第十五届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2016, 69-86 |
| [51] | Tong HW. Proboscidean fossil records in Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Quaternaire, Hors série, 2010, (3): 173-174 |
| [52] | 李凯清, 赵文俭, 岳峰, 等. 河北泥河湾盆地晚新生代的长鼻类化石[A].见:董为(主编).第十五届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2016, 87-96 |
| [53] | 卫奇. 在泥河湾层中发现纳玛象头骨化石[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1976, 4(1): 53-58 |
| [54] | 宗冠福, 卫奇. 泥河湾盆地发现短喙象化石[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1993, 31(2): 102-109 |
| [55] | 谢飞, 李琚, 刘连强. 泥河湾旧石器文化[M]. 石家庄: 花山文艺出版, 2006, 1-278 |
| [56] |
Tong HW. New remains of Mammuthus trogontherii from the Early Pleistocene Nihewan beds at Shanshenmiaozui, Hebei[J]. Quaternary International, 2012, 255: 217-230
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2011.07.035 URL |
| [57] |
Tong HW, Chen X. On newborn calf skulls of Early Pleistocene Mammuthus trogontherii from Shanshenmiaozui in Nihewan Basin, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 406: 57-69
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.02.026 URL |
| [58] | 同号文. 河北蔚县大南沟晚更新世草原猛犸象(长鼻目,哺乳动物纲)[J]. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(2): 307-318 |
| [59] |
Chen X, Tong HW. On the hindfoot bones of Mammuthus trogontherii from Shanshenmiaozui in Nihewan Basin, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 445: 50-59
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.09.001 URL |
| [60] | 陈曦, 赵海龙, 张贝, 等. 泥河湾盆地石沟遗址B区发掘报告[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(4): 895-907 |
| [61] | Lister AM, Sher AV, van Essen H, et al. The pattern and process of mammoth evolution in Eurasia[J]. Quaternary International, 2005, 126-28: 49-64 |
| [62] | Wei GB, Taruno H, Yoshinari K, et al. Pliocene and Early Pleistocene primitive mammoths of northern China: Their revised taxonomy, biostratigraphy and evolution[J]. Journal of Geosciences, Osaka City University, 2006, 49(5): 59-101 |
| [63] | 贾兰坡, 卫奇. 桑干河阳原县丁家堡水库全新统中的动物化石[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1980, 18(4): 327-333 |
| [64] | Turvey ST, Tong HW, Stuart AJ, et al. Holocene survival of Late Pleistocene megafauna in China: a critical review of the evidence[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 15: 156-166 |
| [65] | Nakashima R, Itoh M, Kaneko N, et al. A fossil elephantoid molar of Palaeoloxodon naumanni (Makiyama) collected from the latest Pleistocene deposits of the Hanamurogawa River, Tsukuba City, Ibaraki, Japan[J]. Quaternary Research, 2004, 43 (3): 225-230 |
| [66] | 魏光飚, 胡松梅, 余克服, 等. 草原猛犸象(Mammuthus trogontherii)新材料及猛犸象的起源与演化模式探讨[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2010, 40(6): 715-723 |
| [67] |
Roth VL, Shoshani J. Dental identification and age determination in Elephas maximus[J]. Journal of Zoology, 1988, 214: 567-588
doi: 10.1111/jzo.1988.214.issue-4 URL |
| [68] |
Lister AM, Dirks W, Assaf A, et al. New fossil remains of Elephas from the southern Levant: implications for the evolutionary history of the Asian elephant[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2013, 386: 119-130
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.05.013 URL |
| [69] |
Lin HF, Hu JM, Baleka S, et al. A genetic glimpse of the Chinese straight-tusked elephants[J]. Biology letters, 2023, 19: 20230078
doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2023.0078 URL |
| [70] | 邱占祥, 黄为龙, 郭志慧. 中国的三趾马化石[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987, 1-250 |
| [71] |
Sun BY, Deng T, Liu Y. Early Pleistocene Equus (Equidae, Perissodactyla) from Andersson Loc. 32 in Qixian, Shanxi, China[J]. Historical Biology, 2019, 31: 211-222
doi: 10.1080/08912963.2017.1357718 URL |
| [72] |
Dong W, Bai WP, Liu WH, et al. The first description of Equidae (Perissodactyla, Mammalia) from Xinyaozi Ravine in Shanxi, North China[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2023, 61 (3): 212-244
doi: 10.19615/j.cnki.2096-9899.220926 |
| [73] | 李永项, 张云翔, 孙博阳, 等. 泥河湾新发现的早更新世真马化石[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2015, 45(10): 1457-1468 |
| [74] | 邓涛, 薛祥煦. 中国的真马化石及其生活环境[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1999, 1-158 |
| [75] | 李凯清, 岳峰, 王旭日, 等. 泥河湾动物群化石新材料[A].见:董为,张颖奇(主编).第十七届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2021, 87-96 |
| [76] |
Tong HW, Wang XM. Juvenile skulls and other postcranial bones of Coelodonta nihowanensis from Shanshenmiaozui, Nihewan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, 2014, 34(3): 710-724
doi: 10.1080/02724634.2013.814661 URL |
| [77] |
Deng T. Comparison between woolly rhino forelimbs from Longdan, Northwestern China and Tologoi, Transbaikalian region[J]. Quaternary International, 2008, 179 (1): 196-207
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2007.09.008 URL |
| [78] | 裴树文. 泥河湾盆地虎头梁发现披毛犀化石[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 2001, 39(1): 72-75 |
| [79] | 李凯清, 岳峰. 泥河湾盆地的披毛犀化石[J]. 化石, 2022, 1: 13-16 |
| [80] | Deng T, Zheng M. Limb bones of Elasmotherium (Rhinocerotidae, Perissodactyla) from Nihewan (Hebei, China)[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2005, 43(2): 110-121 |
| [81] | Tong HW, Chen X, Zhang B. New postcranial bones of Elasmotherium peii from Shanshenmiaozui in Nihewan Basin, Northern China[J]. Quaternaire, 2018, 29 (3): 195-204 |
| [82] | 同号文, 王法岗, 郑敏, 等. 泥河湾盆地新发现的梅氏犀及裴氏板齿犀化石[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(3): 369-388 |
| [83] | Chow MC. New elasmotherine rhinoceroses from Shansi[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 1958, 2(2-3): 131-142 |
| [84] | 黄万波, 计宏祥. 三门峡地区含哺乳动物化石的几个第四纪剖面[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1984, 22(3): 230-238 |
| [85] | 同号文, 张贝, 陈曦, 等. 泥河湾盆地早更新世山神庙咀遗址动物群及其时代意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(3): 469-489 |
| [86] | 陈冠芳. 榆社盆地第三纪晚期的Gazella羚羊[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1997, 35(4): 233-249 |
| [87] |
Deng T, Wang XM, Fortelius M, et al. Out of Tibet: Pliocene woolly rhino suggests high-plateau origin of ice age megaherbivores[J]. Science, 2011, 333:1285-1288
doi: 10.1126/science.1206594 pmid: 21885780 |
| [88] |
Tong HW, Zhang B. New fossils of Eucladoceros boulei (Artiodactyla, Mammalia) from Early Pleistocene Nihewan Beds, China[J]. Palaeoworld, 2019, 28 (3): 403-424
doi: 10.1016/j.palwor.2019.05.003 URL |
| [89] | Woodburne MO, Tedford RH, Lindsay E. North China Neogene Biochronology: A Chinese standard[A]. In: WangXM, FlynnLJ,Fortelius M(eds). Fossil mammals of Asia: Neogene Biostratigraphy and chronology[C]. New York: Columbia University Press, 2013, 91-123 |
| [90] |
Jones FW. A contribution to the history and anatomy of Père David's deer (Elaphurus davidianus)[J]. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London, 1951, 121: 319-370
doi: 10.1111/jzo.1951.121.issue-2 URL |
| [91] | Tong HW, Zhang B, Chen Xi, et al. New fossils of small and medium-sized bovids from the Early Pleistocene Site of Shanshenmiaozui in Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2022, 60(2): 134-168 |
| [92] |
Heckeberg NS, Zachos FE, Kierdorf U. Antler tine homologies and cervid systematics: A review of past and present controversies with special emphasis on Elaphurus davidianus[J]. Anat Rec (Hoboken), 2023, 306(1): 5-28
doi: 10.1002/ar.v306.1 URL |
| [93] | Milne-Edwards A. Note sur l'Elaphurus davidianus: espèce nouvelle de la famille des cerfs[J]. Nouvelles Archives du Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de Paris, 1866, 2: 27-39 |
| [94] | Groves CP, Grubb P. Wemme CM (Relationships of living deer[A]. In: ed.).Biology and management of the Cervidae[C]. Washington DC: Smithsonian Institute Press, 1987, 21-59 |
| [95] | Bubenik AB. Epigenetical, morphological, physiological, and behavioral aspects of evolution of horns, pronghorns, and antlers[A]. In: Bubenik GA, Bubenik AB(Eds.). Horns, pronghorns, and antlers[C]. New York: Springer Verlag, 1990, 3-113 |
| [96] |
Meijaard E, Groves CP. Morphometrical relationships between South-east Asian deer (Cervidae, tribe Cervini): evolutionary and biogeographic implications[J]. Journal of Zoology, 2004, 263:179-196
doi: 10.1017/S0952836904005011 URL |
| [97] | 曹克清. 麋鹿研究[M]. 上海: 上海科技教育出版社, 2005,1-246 |
| [98] | 贾兰坡, 王建. 西侯度—山西更新世早期古文化遗址[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1978, 1-85 |
| [99] | Boule M, Breuil H, Licent E, et al. Le Paléolithique de la Chine[M]. Paris: Masson et Cie Editeurs, 1928, 1-138 |
| [100] | Sokolov II. On the postcranial skeleton and the outward appearance of Spirocerus kiakhtensis M. Pavlova[J]. Vertebrate Paleontology, 1959, 3(1): 23-33 |
| [101] | Teilhard de Chardin P, Trassaert M. Cavicornia of south-eastern Shansi[M]. Palaeontologia Sinica, 1938, New Ser C, 6: 1-98 |
| [102] | Sokolov JJ. Natural Classification of Bovidae[M]. Trudy Zoologicheskogo Instituta, Akademiya Nauk SSSR, 1953, 14:1-295 (in Russian) |
| [103] | McKenna MC, Bell SK. Classification of Mammals Above the Species Level[M]. New York: Columbia University Press, 1997, 1-631 |
| [104] |
Bai WP, Dong W, Zhang LM, et al. New material of the Early Pleistocene spiral horned antelope Spirocerus (Artiodactyla, Mammalia) from North China and discussion on its evolution[J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 522: 94-102
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2019.06.029 URL |
| [105] | 董为, 傅仁义, 冯兴无, 等. 辽宁朝阳龙城马山洞哺乳动物群的性质及时代探讨[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(1): 95-109 |
| [106] |
Tong HW, Chen X, Zhang B. New fossils of Bison palaeosinensis (Artiodactyla, Mammalia) from the steppe mammoth site of Early Pleistocene in Nihewan Basin, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 445: 250-268
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.07.033 URL |
| [107] | 李凯清, 岳峰, 武志军, 等. 泥河湾盆地野牛坡发现早更新世旧石器[J]. 第四纪研究, 2022, 42(2): 552-561 |
| [108] | 张镇洪. 辽宁地区远古人类及其文化的初步研究[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1981, 19(2): 184-192 |
| [109] | 傅仁义. 东北地区第四纪哺乳动物群的时代及其特征[A].见:邓涛,王原(主编).第八届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2001, 167-176 |
| [110] | 袁宝印, 夏正楷, 牛平山(主编). 泥河湾裂谷与古人类[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011, 1-257 |
| [111] | Teilhard de Chardin P. New rodents of the Pliocene and Lower Pleistocene of North China[M]. Institut de Géo-Biologie, Pékin, 1942, 9:1-101 |
| [112] | Barbour GB. Preliminary observation in the Kalgan Area[J]. Bulletin of geological Society of China, 1924, 3(2): 167-168 |
| [113] | 黄宝玉, 郭书元. 从软体动物化石讨论泥河湾地层划分、时代及岩相古地理[J]. 中国地质科学院天津地质矿产研究所所刊, 1981, No. 4: 17-31 |
| [114] | 李传夔, 吴文裕, 邱铸鼎. 中国陆相新第三系的初步划分与对比[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1984, 22(3): 163-178 |
| [115] |
Sacchi M, Horvath F. Towards a new time scale for the Upper Miocene continental series of the Pannonian basin (Central Paratethys)[J]. Stephan Mueller Special Publication Series, 2001, 3: 79-94
doi: 10.5194/smsps-3-79-2002 URL |
| [116] | 庞其清, 翟大有, 赵筑簾, 等. 泥河湾盆地晚新生代微体古生物地层及环境演化的探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(05): 817-842 |
| [117] | Liu P, Deng C, Li S, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the Xiashagou Fauna and implication for sequencing the mammalian faunas in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 315: 75-85 |
| [118] | 泥河湾新生代地层小组. 泥河湾盆地晚新生代几个地层剖面的观察[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1974, 12(2): 99-110 |
| [119] | 杜恒俭, 蔡保全, 马安成, 等. 泥河湾地区晚新生代生物地层带[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 1995, 20(1): 35-42 |
| [120] | Qiu ZX, Qiu ZD, Deng T, et al. Neogene land mammal stages/ages of China: toward the goal to establish an Asian land mammal stage/age scheme[A]. In: Wang XM, Flynn LJ, Fortelius M (eds.). Fossil Mammals of Asia-Neogene Biostratigraphy and Chronology[C]. New York: Columbia University Press, 2013, 29-90 |
| [121] | 杜恒俭, 王安德, 赵其强, 等. 泥河湾地区晚上新世一个新的地层单位—稻地组[J]. 地球科学, 1988, 13(5): 261-268 |
| [122] | 张兆群, 郑绍华, 刘建波. 泥河湾盆地上新世小哺乳动物生物地层学及相关问题讨论[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 2003, 41(4): 306-313 |
| [123] | Li HM, Wang JD.Magnetostratigraphic study of several typical geologic sections in North China[A]. In: LiuTS (ed.). Quaternary Geology and Envionment of China[C]. Bejing: China Ocean Press, 1982, 33-38 |
| [124] | 朱日祥, 邓成龙, 潘永信. 泥河湾盆地磁性地层定年与早期人类演化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(6): 922-944 |
| [125] | Cai BQ, Zheng SH, Liddicoat JC, et al. Review of the Litho-, Bio-, and Chronostratigraphy in the Nihewan Basin, Hebei, China[A]. In: ForteliusM, WangX, FlynnL (Eds.). Fossil. Mammals of Asia: Neogene Biostratigraphy and Chronology[C]. New York: Columbia University Press, 2013, 218-242 |
| [126] | Qiu ZX. Quaternary environmental changes and evolution of large mammals in North China[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2006, 44(2): 109-132 |
| [127] | 刘宪亭, 王念忠. 多刺鱼(Pungitius)在泥河湾层的发现及其意义[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1974, 12(2): 89-98 |
| [128] | 黄宝仁. 桑干河中下游流域更新世介形类初步研究[J]. 科学通报, 1980, 6: 277-278 |
| [129] | 闵隆瑞, 迟振卿. 河北阳原盆地西部第四纪地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003, 1-160 |
| [130] | 同号文, 李虹, 谢骏义, 等. 第四章:脊椎动物化石[A].见:董光荣,李保生,陈永志(主编).萨拉乌苏河晚第四纪地质与古人类综合研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017, 157-204 |
| [131] | 庞其清, 牛树银, 孙爱群, 等. 泥河湾盆地晚新生代介形类生物地层和旧石器文化遗存地层及环境演化的探讨[J]. 河北地质大学学报, 2017, 40(1): 13-40 |
| [132] | 王法岗, 李锋. “许家窑人”埋藏地层与时代探讨[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(2): 161-172 |
| [133] |
Wang XS, Yang ZY, Lcvlie R,et a1. High-resolution magnetic stratigraphy of fluvio-lacustrine succession in the Nihewan Basin, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2004, 23: 1187-1198
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2003.11.007 URL |
| [134] | 闵隆瑞, 迟振卿, 王永, 等. 河北阳原泥河湾盆地郝家台NHA钻孔岩心岩石地层划分及对比[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(4): 1068-1078 |
| [135] | 周廷儒, 李华章, 刘清泗, 等. 泥河湾盆地新生代古地理研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1991, 1-162 |
| [136] | 同号文, 胡楠, 韩非. 河北阳原泥河湾盆地山神庙咀早更新世哺乳动物群的发现[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011, 31(4): 643-653 |
| [137] | 汤英俊, 尤玉柱, 李毅. 河北阳原、 蔚县几个早更新世哺乳动物化石及旧石器地点[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1981, 19(3): 256-268 |
| [138] | 卫奇, 孟浩, 成胜泉. 泥河湾层中发现一处旧石器地点[J]. 人类学学报, 1985, 4(3): 223-232 |
| [139] | 裴树文, 马宁, 李潇丽. 泥河湾盆地东端2007年新发现的旧石器地点[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(1): 33-43 |
| [140] | 陈茅南主编. 泥河湾层的研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1988, 1-145 |
| [141] | 蔡保全, 张兆群, 郑绍华, 等. 河北泥河湾盆地典型剖面地层学研究进展[A].中国地质科学院地层古生物论文集编委会.地层古生物论文集(第二十八辑)[C]. 地质出版社, 2004, 19: 267-285 |
| [142] |
Zhang Z, Li YC, Li CZ, et al. Pollen evidence for the environmental context of the early Pleistocene Xiashagou fauna of the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 236: 106298
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106298 URL |
| [143] |
朱云, 乔仙果, 姚轶峰, 等. 华北泥河湾盆地植被、气候与早期人类生存环境研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 127-137
doi: 10.11983/CBB21117 |
| [144] | Xu Z, Pei SW, Hu YW, et al. Stable isotope analysis of mammalian enamel from the Early Pleistocene site of Madigou, Nihewan Basin: Implication for reconstructing hominin paleoenvironmental adaptations in North China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9: 789781. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.789781 |
| [145] | 同号文. 第四纪以来中国北方出现过的喜暖动物及其古环境意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2007, 37(7): 922-933 |
| [146] |
Semprebon G, Sise P, Coombs M. Potential bark and fruit browsing as revealed by stereomicrowear analysis of the peculiar clawed herbivores known as chalicotheres (Perissodactyla, Chalicotherioidea)[J]. Journal of Mammalian Evolution, 2010, 18: 33-55
doi: 10.1007/s10914-010-9149-3 URL |
| [147] |
Kahlke RD. The origin of Eurasian Mammoth Faunas (Mammuthus-Coelodonta Faunal Complex)[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 96: 32-49
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.01.012 URL |
| [148] | 蔡保全, 李强. 泥河湾早更新世早期人类遗物和环境[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2003, 5: 418-424 |
| [149] | 李强, 郑绍华, 蔡保全. 泥河湾盆地上新世生物地层序列与环境[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 2008, 46(3): 210-232 |
| [150] | 陈淳, 沈辰, 陈万勇, 等. 河北阳原小长梁遗址1998年发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 1999, 18(3): 225-239 |
| [1] | 胡海虔, 黄万波, 魏光飚, 代辉, 熊璨, 何树兴, 姜涛. 重庆武隆早更新世地层中发现巨猿化石[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 701-711. |
| [2] | 任进成, 李锋, 陈福友, 高星. 泥河湾盆地板井子遗址2015年出土石制品的剥片技术[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 712-726. |
| [3] | 张遂新, 张珂. 台湾海峡古环境变迁与南岛语族起源新探[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 797-812. |
| [4] | 成楠, 夏文婷, 杨青, 吉学平, 字兴, 范斌, 邹梓宁, 余童, 张俞, 石林, 张吾奇, 郑洪波. 云南巍山三鹤洞地点的石制品及年代与环境[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 392-404. |
| [5] | 高星, 张月书, 李锋, 陈福友, 王晓敏, 仪明洁. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址2016-2019年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 106-121. |
| [6] | 赵云啸, 仝广, 涂华, 赵海龙. 河北省泥河湾盆地石沟遗址C区发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 122-131. |
| [7] | 王法岗, 杨石霞, 葛俊逸, 岳健平, 赵克良, Andreu Ollé, 李文艳, 杨海勇, 刘连强, 关莹, 谢飞, Francesco d’Errico, Michael Petraglia, 邓成龙. 泥河湾盆地下马碑遗址2013年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 143-156. |
| [8] | 张振, 王莹, 李月丛. 泥河湾盆地旧石器时代人类活动与环境关系的研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 184-198. |
| [9] | 裴树文, 徐哲, 叶芷, 马东东, 贾真秀. 泥河湾盆地中更新世气候转型期人类的适应行为[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 19-39. |
| [10] | 刘连强, 蒲昱晓, 侯佳岐, 王法岗. 泥河湾盆地马圈沟遗址鱼咀沟1号地点2017-2018年发掘出土的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 40-54. |
| [11] | 周振宇, 王法岗, 关莹. 河北泥河湾盆地西白马营遗址1985-1986年出土的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 55-66. |
| [12] | 仝广, 李锋, 赵海龙, 闫晓蒙, 高星. 泥河湾盆地火山角砾岩原料的热处理实验[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 81-90. |
| [13] | 王晓敏, 刘连强, 陈国鹏, 李锋, 谢飞, 高星. 泥河湾盆地马圈沟遗址哺乳动物破碎长骨反映的古人类行为[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 91-105. |
| [14] | 侯佳岐, 王法岗. 泥河湾盆地山兑东旧石器地点初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(06): 742-750. |
| [15] | 仪明洁, 余官玥, 陈福友, 张晓凌. 泥河湾盆地白洗沟遗址出土的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(05): 590-603. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 793
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 549
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3