

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (04): 613-628.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0050cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0050
祝海歌1( ), 乔辉1, 杨晨1, 管海娟1, 张航2, 文少卿1, 夏斌2, 谭婧泽1(
), 乔辉1, 杨晨1, 管海娟1, 张航2, 文少卿1, 夏斌2, 谭婧泽1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-04
修回日期:2024-05-07
出版日期:2024-08-15
发布日期:2024-08-13
通讯作者:
谭婧泽,副教授,主要从事体质人类学研究。E-mail: jztan@fudan.edu.cn作者简介:祝海歌,硕士研究生,主要从事体质人类学研究。E-mail: 20210700109@fudan.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHU Haige1( ), QIAO Hui1, YANG Chen1, GUAN Haijuan1, ZHANG Hang2, WEN Shaoqing1, XIA Bin2, TAN Jingze1(
), QIAO Hui1, YANG Chen1, GUAN Haijuan1, ZHANG Hang2, WEN Shaoqing1, XIA Bin2, TAN Jingze1( )
)
Received:2023-12-04
Revised:2024-05-07
Online:2024-08-15
Published:2024-08-13
摘要:
研究表明牙齿形态特征具有高度遗传性,在不同群体中存在明显差异。本研究针对中国汉族、回族、蒙古族、苗族和维吾尔族5个人群的牙齿形态特征,进行侧别、性别、年龄等检验,并对这5个人群与其他中国人群及日本、东北亚、东南亚、欧洲、非洲等地区人群进行多元统计分析。研究结果显示,5个人群的多数牙齿特征未见侧别和性别差异,多数牙齿特征与年龄无显著相关性。汉族、维吾尔族的铲形门齿和双铲形门齿出现率较高及Y型沟纹出现率偏低与东北亚人群相似;苗族的铲形门齿和双铲形门齿出现率也偏高;蒙古族、回族的铲形门齿和双铲形门齿出现率较低与东南亚人群相似;维吾尔族的四尖型出现率较高与欧洲人群相似。多元统计分析结果证实蒙古人种牙齿复合体及巽他型齿、中国型齿是客观存在的。
中图分类号:
祝海歌, 乔辉, 杨晨, 管海娟, 张航, 文少卿, 夏斌, 谭婧泽. 中国汉族、回族、蒙古族、苗族和维吾尔族的牙齿形态[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(04): 613-628.
ZHU Haige, QIAO Hui, YANG Chen, GUAN Haijuan, ZHANG Hang, WEN Shaoqing, XIA Bin, TAN Jingze. Teeth morphology of Han, Hui, Mongolia, Miao and Uyghur peoples in China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(04): 613-628.
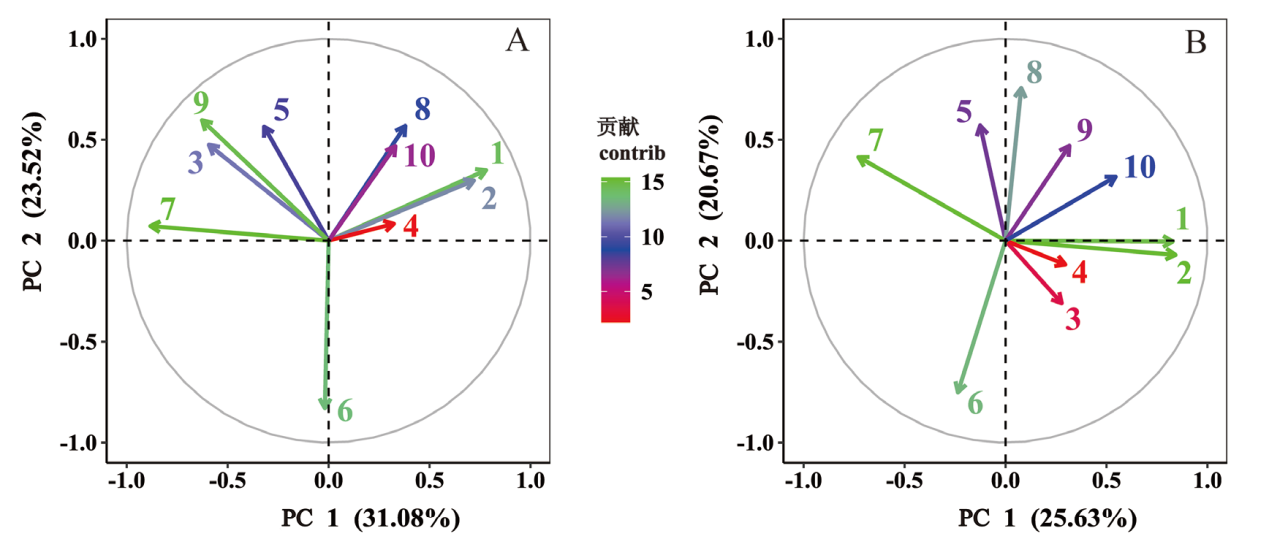
图1 牙齿形态特征变量相关图 A.世界人群World Populations ;B.东亚人群East Asia Populations;1.铲形门齿Shoveling (SUI1); 2.双铲形门齿Double Shoveling (DSUI1); 3.近中嵴Mesial Ridge (MRUC); 4.卡氏尖Carabelli’s Trait (CCUM1); 5.第5尖Cusp 5 (C5UM1); 6.四尖型Cusp 4 (C4LM2); 7.Y型沟纹Y-Groove (GPYLM2); 8.第6尖Cusp 6 (C6LM1); 9.第7尖Cusp 7 (C7LM1); 10.转向皱纹Deflecting Wrinkle (DWLM1)
Fig.1 Variables Correlation of Dental Morphological Traits
| 人群Populations | 编号No. | 铲形门齿Shoveling (I1) | 双铲形门齿Double Shoveling(I1) | 近中嵴Mesial Ridge (C) | 卡氏尖Carabelli’s Trait (M1) | 第5尖 Cusp 5 (M1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比R | |||
| 5个中国人群Five Chinese populations | 泰州汉族 Taizhou Han | 1 | 381 | 80% | 381 | 29% | 358 | 6% | 381 | 21% | 381 | 11% |
| 宁夏回族 Ningxia Hui | 2 | 421 | 22% | 435 | 7% | 435 | 11% | 435 | 37% | 435 | 31% | |
| 内蒙古蒙古族 Neimenggu Mongolia | 3 | 390 | 23% | 434 | 6% | 434 | 8% | 434 | 27% | 434 | 30% | |
| 贵州苗族 Guizhou Miao | 4 | 256 | 45% | 278 | 14% | 278 | 7% | 277 | 39% | 274 | 49% | |
| 新疆维吾尔族 Xinjiang Uyghur | 5 | 227 | 39% | 227 | 22% | 227 | 10% | 227 | 67% | 227 | 7% | |
| 中国其他人群Other Chinese populations | 苗族Miao[ | 6 | 92 | 61% | 94 | 17% | 94 | 13% | 96 | 10% | 83 | 17% |
| 普米族Pumi[ | 7 | 76 | 63% | 84 | 11% | 80 | 8% | 85 | 22% | 75 | 24% | |
| 纳西族Naxi[ | 8 | 92 | 64% | 97 | 13% | 90 | 11% | 89 | 6% | 87 | 13% | |
| 哈尼族Hani[ | 9 | 80 | 55% | 86 | 15% | 76 | 8% | 90 | 16% | 86 | 17% | |
| 傣族Dai[ | 10 | 89 | 34% | 93 | 45% | 90 | 0% | 93 | 16% | 93 | 29% | |
| 达斡尔族Dafur[ | 11 | 172 | 51% | 172 | 32% | 166 | 11% | 163 | 36% | 159 | 17% | |
| 回族Hui[ | 12 | 162 | 58% | 155 | 47% | 167 | 10% | 157 | 46% | 166 | 24% | |
| 朝鲜族Chaoxian[ | 13 | 167 | 69% | 165 | 50% | 166 | 11% | 157 | 50% | 153 | 27% | |
| 满族Man[ | 14 | 208 | 62% | 200 | 43% | 211 | 8% | 212 | 34% | 212 | 26% | |
| 辽宁汉族Liaoning Han[ | 15 | 145 | 57% | 143 | 23% | 147 | 5% | 135 | 16% | 130 | 20% | |
| 布侬族Bunun[ | 16 | 95 | 77% | 90 | 42% | 86 | 7% | 94 | 47% | 90 | 36% | |
| 阿美人Ami[ | 17 | 146 | 71% | 141 | 33% | 135 | 6% | 146 | 42% | 138 | 26% | |
| 雅美人Yami[ | 18 | 192 | 70% | 191 | 23% | 155 | 10% | 197 | 37% | 192 | 41% | |
| 中国蒙古族China Mongolia 1[ | 19 | 542 | 72% | 545 | 29% | 615 | 3% | 774 | 16% | 633 | 24% | |
| 中国蒙古族China Mongolia 2[ | 20 | 200 | 84% | 213 | 30% | 255 | 2% | 374 | 30% | 295 | 28% | |
| 香港Hong Kong[ | 21 | 307 | 64% | 299 | 28% | 305 | 3% | 301 | 38% | 276 | 22% | |
| 华南South China[ | 22 | 35 | 74% | 33 | 24% | 55 | 4% | 99 | 25% | 62 | 16% | |
| 史前台湾Prehistric Taiwan[ | 23 | 22 | 59% | 21 | 0% | 10 | 0% | 15 | 33% | 9 | 22% | |
| 日本人群 Japanese populations | 现代日本Recent Japan 1[ | 24 | 276 | 66% | 267 | 20% | 365 | 3% | 458 | 15% | 390 | 20% |
| 现代日本Recent Japan 2[ | 25 | 276 | 66% | 267 | 19% | 365 | 3% | 458 | 31% | 390 | 20% | |
| 绳文Jomon 1[ | 26 | 117 | 26% | 138 | 1% | 136 | 2% | 181 | 2% | 146 | 32% | |
| 绳文Jomon 2[ | 27 | 117 | 26% | 138 | 1% | 136 | 2% | 181 | 8% | 146 | 32% | |
| 东北亚人群Northeast Asia populations | 贝加尔湖Lake Baikal[ | 28 | 13 | 92% | 10 | 50% | 16 | 6% | 10 | 30% | 3 | 67% |
| 阿穆尔Amur[ | 29 | 16 | 69% | 18 | 44% | 27 | 11% | 60 | 27% | 42 | 21% | |
| 东南亚人群 Southeast Asia populations | 巴厘岛Bali[ | 30 | 172 | 25% | 169 | 12% | 173 | 2% | 169 | 59% | 168 | 29% |
| 菲律宾Philippines[ | 31 | 54 | 43% | 29 | 17% | 76 | 3% | 146 | 37% | 132 | 27% | |
| 泰国Thailand[ | 32 | 127 | 37% | 111 | 9% | 143 | 8% | 179 | 40% | 143 | 29% | |
| 缅甸Burma[ | 33 | 15 | 13% | 13 | 0% | 33 | 6% | 93 | 30% | 72 | 33% | |
| 尼泊尔Nepal[ | 34 | 10 | 20% | 11 | 9% | 17 | 0% | 50 | 26% | 50 | 32% | |
| 史前东南亚Early Southeast Asia 1[ | 35 | 184 | 31% | 182 | 16% | 235 | 6% | 262 | 19% | 328 | 32% | |
| 史前东南亚Early Mainland SE Asia 2[ | 36 | 99 | 32% | 100 | 10% | 120 | 3% | 140 | 37% | 132 | 37% | |
| 东南亚人群 Southeast Asia populations | 现代东南亚Recent Southeast Asia 1[ | 37 | 261 | 35% | 199 | 12% | 366 | 6% | 701 | 21% | 581 | 31% |
| 现代东南亚Recent SE Asia 2[ | 38 | 13 | 46% | 14 | 29% | 39 | 3% | 93 | 42% | 74 | 14% | |
| 现代印尼-马来西亚Recent Indomalaysia[ | 39 | 49 | 24% | 36 | 11% | 82 | 6% | 207 | 46% | 177 | 36% | |
| 史前马来群岛Early Malay Archipelago[ | 40 | 71 | 30% | 67 | 28% | 103 | 10% | 100 | 23% | 90 | 24% | |
| 东马来群岛East Malay Archipelago[ | 41 | 12 | 8% | 3 | 0% | 16 | 6% | 28 | 50% | 22 | 45% | |
| 欧洲人群 European populations | 西欧Western Europe[ | 42 | 186 | 3% | 184 | 4% | 230 | 4% | 249 | 27% | 238 | 12% |
| 北欧Northern Europe[ | 43 | 46 | 2% | 100 | 5% | 125 | 0% | 138 | 18% | 140 | 26% | |
| 非洲人群 African populations | 北非North Africa[ | 44 | 194 | 8% | 175 | 9% | 261 | 6% | 200 | 20% | 357 | 19% |
| 西非West Africa[ | 45 | 41 | 7% | 39 | 3% | 55 | 29% | 61 | 21% | 48 | 63% | |
| 南非South Africa[ | 46 | 220 | 9% | 282 | 2% | 398 | 13% | 246 | 11% | 439 | 22% | |
| 科伊桑Khoisan[ | 47 | 155 | 13% | 79 | 0% | 77 | 35% | 155 | 17% | 66 | 35% | |
表1 10项牙齿形态特征在世界人群中的频率分布(1)
Tab.1 Frequencies of 10 dental morphological characteristics in the World Populations (1)
| 人群Populations | 编号No. | 铲形门齿Shoveling (I1) | 双铲形门齿Double Shoveling(I1) | 近中嵴Mesial Ridge (C) | 卡氏尖Carabelli’s Trait (M1) | 第5尖 Cusp 5 (M1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比R | |||
| 5个中国人群Five Chinese populations | 泰州汉族 Taizhou Han | 1 | 381 | 80% | 381 | 29% | 358 | 6% | 381 | 21% | 381 | 11% |
| 宁夏回族 Ningxia Hui | 2 | 421 | 22% | 435 | 7% | 435 | 11% | 435 | 37% | 435 | 31% | |
| 内蒙古蒙古族 Neimenggu Mongolia | 3 | 390 | 23% | 434 | 6% | 434 | 8% | 434 | 27% | 434 | 30% | |
| 贵州苗族 Guizhou Miao | 4 | 256 | 45% | 278 | 14% | 278 | 7% | 277 | 39% | 274 | 49% | |
| 新疆维吾尔族 Xinjiang Uyghur | 5 | 227 | 39% | 227 | 22% | 227 | 10% | 227 | 67% | 227 | 7% | |
| 中国其他人群Other Chinese populations | 苗族Miao[ | 6 | 92 | 61% | 94 | 17% | 94 | 13% | 96 | 10% | 83 | 17% |
| 普米族Pumi[ | 7 | 76 | 63% | 84 | 11% | 80 | 8% | 85 | 22% | 75 | 24% | |
| 纳西族Naxi[ | 8 | 92 | 64% | 97 | 13% | 90 | 11% | 89 | 6% | 87 | 13% | |
| 哈尼族Hani[ | 9 | 80 | 55% | 86 | 15% | 76 | 8% | 90 | 16% | 86 | 17% | |
| 傣族Dai[ | 10 | 89 | 34% | 93 | 45% | 90 | 0% | 93 | 16% | 93 | 29% | |
| 达斡尔族Dafur[ | 11 | 172 | 51% | 172 | 32% | 166 | 11% | 163 | 36% | 159 | 17% | |
| 回族Hui[ | 12 | 162 | 58% | 155 | 47% | 167 | 10% | 157 | 46% | 166 | 24% | |
| 朝鲜族Chaoxian[ | 13 | 167 | 69% | 165 | 50% | 166 | 11% | 157 | 50% | 153 | 27% | |
| 满族Man[ | 14 | 208 | 62% | 200 | 43% | 211 | 8% | 212 | 34% | 212 | 26% | |
| 辽宁汉族Liaoning Han[ | 15 | 145 | 57% | 143 | 23% | 147 | 5% | 135 | 16% | 130 | 20% | |
| 布侬族Bunun[ | 16 | 95 | 77% | 90 | 42% | 86 | 7% | 94 | 47% | 90 | 36% | |
| 阿美人Ami[ | 17 | 146 | 71% | 141 | 33% | 135 | 6% | 146 | 42% | 138 | 26% | |
| 雅美人Yami[ | 18 | 192 | 70% | 191 | 23% | 155 | 10% | 197 | 37% | 192 | 41% | |
| 中国蒙古族China Mongolia 1[ | 19 | 542 | 72% | 545 | 29% | 615 | 3% | 774 | 16% | 633 | 24% | |
| 中国蒙古族China Mongolia 2[ | 20 | 200 | 84% | 213 | 30% | 255 | 2% | 374 | 30% | 295 | 28% | |
| 香港Hong Kong[ | 21 | 307 | 64% | 299 | 28% | 305 | 3% | 301 | 38% | 276 | 22% | |
| 华南South China[ | 22 | 35 | 74% | 33 | 24% | 55 | 4% | 99 | 25% | 62 | 16% | |
| 史前台湾Prehistric Taiwan[ | 23 | 22 | 59% | 21 | 0% | 10 | 0% | 15 | 33% | 9 | 22% | |
| 日本人群 Japanese populations | 现代日本Recent Japan 1[ | 24 | 276 | 66% | 267 | 20% | 365 | 3% | 458 | 15% | 390 | 20% |
| 现代日本Recent Japan 2[ | 25 | 276 | 66% | 267 | 19% | 365 | 3% | 458 | 31% | 390 | 20% | |
| 绳文Jomon 1[ | 26 | 117 | 26% | 138 | 1% | 136 | 2% | 181 | 2% | 146 | 32% | |
| 绳文Jomon 2[ | 27 | 117 | 26% | 138 | 1% | 136 | 2% | 181 | 8% | 146 | 32% | |
| 东北亚人群Northeast Asia populations | 贝加尔湖Lake Baikal[ | 28 | 13 | 92% | 10 | 50% | 16 | 6% | 10 | 30% | 3 | 67% |
| 阿穆尔Amur[ | 29 | 16 | 69% | 18 | 44% | 27 | 11% | 60 | 27% | 42 | 21% | |
| 东南亚人群 Southeast Asia populations | 巴厘岛Bali[ | 30 | 172 | 25% | 169 | 12% | 173 | 2% | 169 | 59% | 168 | 29% |
| 菲律宾Philippines[ | 31 | 54 | 43% | 29 | 17% | 76 | 3% | 146 | 37% | 132 | 27% | |
| 泰国Thailand[ | 32 | 127 | 37% | 111 | 9% | 143 | 8% | 179 | 40% | 143 | 29% | |
| 缅甸Burma[ | 33 | 15 | 13% | 13 | 0% | 33 | 6% | 93 | 30% | 72 | 33% | |
| 尼泊尔Nepal[ | 34 | 10 | 20% | 11 | 9% | 17 | 0% | 50 | 26% | 50 | 32% | |
| 史前东南亚Early Southeast Asia 1[ | 35 | 184 | 31% | 182 | 16% | 235 | 6% | 262 | 19% | 328 | 32% | |
| 史前东南亚Early Mainland SE Asia 2[ | 36 | 99 | 32% | 100 | 10% | 120 | 3% | 140 | 37% | 132 | 37% | |
| 东南亚人群 Southeast Asia populations | 现代东南亚Recent Southeast Asia 1[ | 37 | 261 | 35% | 199 | 12% | 366 | 6% | 701 | 21% | 581 | 31% |
| 现代东南亚Recent SE Asia 2[ | 38 | 13 | 46% | 14 | 29% | 39 | 3% | 93 | 42% | 74 | 14% | |
| 现代印尼-马来西亚Recent Indomalaysia[ | 39 | 49 | 24% | 36 | 11% | 82 | 6% | 207 | 46% | 177 | 36% | |
| 史前马来群岛Early Malay Archipelago[ | 40 | 71 | 30% | 67 | 28% | 103 | 10% | 100 | 23% | 90 | 24% | |
| 东马来群岛East Malay Archipelago[ | 41 | 12 | 8% | 3 | 0% | 16 | 6% | 28 | 50% | 22 | 45% | |
| 欧洲人群 European populations | 西欧Western Europe[ | 42 | 186 | 3% | 184 | 4% | 230 | 4% | 249 | 27% | 238 | 12% |
| 北欧Northern Europe[ | 43 | 46 | 2% | 100 | 5% | 125 | 0% | 138 | 18% | 140 | 26% | |
| 非洲人群 African populations | 北非North Africa[ | 44 | 194 | 8% | 175 | 9% | 261 | 6% | 200 | 20% | 357 | 19% |
| 西非West Africa[ | 45 | 41 | 7% | 39 | 3% | 55 | 29% | 61 | 21% | 48 | 63% | |
| 南非South Africa[ | 46 | 220 | 9% | 282 | 2% | 398 | 13% | 246 | 11% | 439 | 22% | |
| 科伊桑Khoisan[ | 47 | 155 | 13% | 79 | 0% | 77 | 35% | 155 | 17% | 66 | 35% | |
| 人群Populations | 编号No. | 四尖型Cusp 4 (m2) | Y型沟纹Y-Groove (m2) | 第6尖Cusp 6(m1) | 第7尖Cusp 7(m1) | 转向皱纹Deflecting Wrinkle (m1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比 R | 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比 R | |||
| 5个中国人群 Five Chinese populations | 泰州汉族 Taizhou Han | 1 | 366 | 36% | 373 | 5% | 357 | 19% | 381 | 4% | 381 | 15% |
| 宁夏回族 Ningxia Hui | 2 | 430 | 24% | 435 | 32% | 424 | 18% | 425 | 10% | 435 | 8% | |
| 内蒙古蒙古族 Neimenggu Mongolia | 3 | 433 | 23% | 434 | 17% | 408 | 21% | 416 | 13% | 434 | 5% | |
| 贵州苗族 Guizhou Miao | 4 | 271 | 14% | 274 | 15% | 253 | 33% | 267 | 9% | 274 | 22% | |
| 新疆维吾尔族 Xinjiang Uyghur | 5 | 227 | 70% | 227 | 7% | 221 | 8% | 226 | 8% | 225 | 15% | |
| 中国其他人群 other Chinese populations | 苗族 Miao[ | 6 | 68 | 18% | 77 | 10% | 68 | 35% | 89 | 6% | 80 | 0% |
| 普米族Pumi[ | 7 | 72 | 50% | 71 | 4% | 57 | 21% | 77 | 1% | 64 | 2% | |
| 纳西族Naxi[ | 8 | 76 | 34% | 80 | 5% | 64 | 23% | 81 | 1% | 68 | 1% | |
| 哈尼族Hani[ | 9 | 79 | 53% | 79 | 4% | 76 | 8% | 88 | 3% | 67 | 1% | |
| 傣族Dai[ | 10 | 90 | 49% | 90 | 4% | 86 | 30% | 90 | 4% | 82 | 1% | |
| 达斡尔族Dafur[ | 11 | 155 | 33% | 160 | 4% | 150 | 54% | 157 | 10% | 158 | 22% | |
| 回族Hui[ | 12 | 147 | 30% | 153 | 5% | 159 | 34% | 160 | 8% | 159 | 33% | |
| 朝鲜族Chaoxian[ | 13 | 160 | 34% | 161 | 3% | 153 | 40% | 156 | 6% | 152 | 7% | |
| 满族Man[ | 14 | 207 | 36% | 209 | 3% | 209 | 34% | 208 | 6% | 209 | 28% | |
| 辽宁汉族Liaoning Han[ | 15 | 112 | 28% | 115 | 1% | 115 | 41% | 115 | 5% | 107 | 31% | |
| 中国其他人群 Other Chinese populations | 布侬族Bunun[ | 16 | 85 | 27% | 84 | 6% | 76 | 47% | 79 | 9% | 70 | 31% |
| 阿美人Ami[ | 17 | 144 | 40% | 146 | 5% | 137 | 34% | 142 | 12% | 122 | 31% | |
| 雅美人Yami[ | 18 | 141 | 22% | 144 | 8% | 190 | 46% | 188 | 5% | 188 | 26% | |
| 中国蒙古族China Mongolia 1[ | 19 | 639 | 21% | 646 | 8% | 538 | 36% | 721 | 8% | 343 | 16% | |
| 中国蒙古族China Mongolia 2[ | 20 | 258 | 17% | 338 | 7% | 211 | 37% | 341 | 9% | 89 | 29% | |
| 香港Hong Kong[ | 21 | 296 | 24% | 228 | 7% | 267 | 34% | 295 | 9% | 215 | 10% | |
| 华南South China[ | 22 | 77 | 19% | 80 | 13% | 60 | 40% | 85 | 11% | 39 | 18% | |
| 史前台湾Prehistric Taiwan[ | 23 | 21 | 19% | 19 | 11% | 15 | 47% | 33 | 6% | 9 | 44% | |
| 日本人群 Japanese populations | 现代日本Recent Japan 1[ | 24 | 345 | 14% | 352 | 13% | 314 | 43% | 382 | 6% | 262 | 15% |
| 现代日本Recent Japan 2[ | 25 | 345 | 14% | 352 | 13% | 314 | 43% | 382 | 7% | 262 | 15% | |
| 绳文Jomon 1[ | 26 | 244 | 29% | 290 | 32% | 214 | 47% | 285 | 3% | 162 | 5% | |
| 绳文Jomon 2[ | 27 | 244 | 29% | 290 | 32% | 214 | 47% | 285 | 5% | 162 | 5% | |
| 东北亚人群Northeast Asia populations | 贝加尔湖Lake Baikal[ | 28 | 18 | 22% | 21 | 5% | 9 | 33% | 21 | 19% | 2 | 0% |
| 阿穆尔Amur[ | 29 | 52 | 12% | 56 | 13% | 44 | 50% | 55 | 7% | 38 | 39% | |
| 东南亚人群Southeast Asia populations | 巴厘岛Bali[ | 30 | 155 | 41% | 51 | 0% | 157 | 20% | 162 | 8% | 146 | 13% |
| 菲律宾Philippines[ | 31 | 122 | 28% | 123 | 13% | 98 | 39% | 129 | 6% | 74 | 19% | |
| 泰国Thailand[ | 32 | 163 | 26% | 176 | 19% | 120 | 28% | 178 | 6% | 80 | 19% | |
| 缅甸Burma[ | 33 | 28 | 21% | 33 | 6% | 21 | 52% | 35 | 9% | 14 | 0% | |
| 尼泊尔Nepal[ | 34 | 28 | 54% | 30 | 23% | 21 | 43% | 34 | 6% | 14 | 7% | |
| 史前东南亚Early Southeast Asia 1[ | 35 | 314 | 32% | 348 | 18% | 248 | 40% | 370 | 8% | 150 | 22% | |
| 史前东南亚Early Mainland SE Asia 2[ | 36 | 163 | 39% | 187 | 17% | 136 | 37% | 217 | 10% | 76 | 32% | |
| 现代东南亚Recent Southeast Asia 1[ | 37 | 555 | 30% | 587 | 18% | 418 | 33% | 588 | 7% | 290 | 16% | |
| 现代东南亚Recent SE Asia 2[ | 38 | 79 | 32% | 83 | 16% | 61 | 28% | 84 | 7% | 36 | 19% | |
| 现代印尼-马来西亚[ | 39 | 134 | 30% | 142 | 18% | 97 | 36% | 137 | 13% | 66 | 11% | |
| 史前马来群岛Early Malay Archipelago[ | 40 | 130 | 25% | 139 | 19% | 99 | 45% | 131 | 5% | 66 | 11% | |
| 东马来群岛East Malay Archipelago[ | 41 | 24 | 46% | 25 | 20% | 18 | 39% | 25 | 4% | 17 | 0% | |
| 欧洲人群 European populations | 西欧Western Europe[ | 42 | 284 | 71% | 257 | 27% | 217 | 8% | 291 | 5% | 154 | 5% |
| 北欧Northern Europe[ | 43 | 225 | 84% | 319 | 21% | 130 | 17% | 179 | 5% | 75 | 16% | |
| 非洲人群 African populations | 北非North Africa[ | 44 | 381 | 66% | 402 | 31% | 352 | 8% | 414 | 9% | 267 | 8% |
| 西非West Africa[ | 45 | 75 | 12% | 67 | 33% | 47 | 45% | 71 | 44% | 30 | 17% | |
| 南非South Africa[ | 46 | 370 | 30% | 392 | 46% | 362 | 19% | 385 | 27% | 298 | 18% | |
| 科伊桑Khoisan[ | 47 | 88 | 7% | 89 | 72% | 85 | 5% | 87 | 26% | 60 | 17% | |
表2 10项牙齿形态特征在世界人群中的频率分布(2)
Tab.2 Frequencies of 10 dental morphological characteristics in the World Populations (2)
| 人群Populations | 编号No. | 四尖型Cusp 4 (m2) | Y型沟纹Y-Groove (m2) | 第6尖Cusp 6(m1) | 第7尖Cusp 7(m1) | 转向皱纹Deflecting Wrinkle (m1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比 R | 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比R | 样本n | 占比 R | |||
| 5个中国人群 Five Chinese populations | 泰州汉族 Taizhou Han | 1 | 366 | 36% | 373 | 5% | 357 | 19% | 381 | 4% | 381 | 15% |
| 宁夏回族 Ningxia Hui | 2 | 430 | 24% | 435 | 32% | 424 | 18% | 425 | 10% | 435 | 8% | |
| 内蒙古蒙古族 Neimenggu Mongolia | 3 | 433 | 23% | 434 | 17% | 408 | 21% | 416 | 13% | 434 | 5% | |
| 贵州苗族 Guizhou Miao | 4 | 271 | 14% | 274 | 15% | 253 | 33% | 267 | 9% | 274 | 22% | |
| 新疆维吾尔族 Xinjiang Uyghur | 5 | 227 | 70% | 227 | 7% | 221 | 8% | 226 | 8% | 225 | 15% | |
| 中国其他人群 other Chinese populations | 苗族 Miao[ | 6 | 68 | 18% | 77 | 10% | 68 | 35% | 89 | 6% | 80 | 0% |
| 普米族Pumi[ | 7 | 72 | 50% | 71 | 4% | 57 | 21% | 77 | 1% | 64 | 2% | |
| 纳西族Naxi[ | 8 | 76 | 34% | 80 | 5% | 64 | 23% | 81 | 1% | 68 | 1% | |
| 哈尼族Hani[ | 9 | 79 | 53% | 79 | 4% | 76 | 8% | 88 | 3% | 67 | 1% | |
| 傣族Dai[ | 10 | 90 | 49% | 90 | 4% | 86 | 30% | 90 | 4% | 82 | 1% | |
| 达斡尔族Dafur[ | 11 | 155 | 33% | 160 | 4% | 150 | 54% | 157 | 10% | 158 | 22% | |
| 回族Hui[ | 12 | 147 | 30% | 153 | 5% | 159 | 34% | 160 | 8% | 159 | 33% | |
| 朝鲜族Chaoxian[ | 13 | 160 | 34% | 161 | 3% | 153 | 40% | 156 | 6% | 152 | 7% | |
| 满族Man[ | 14 | 207 | 36% | 209 | 3% | 209 | 34% | 208 | 6% | 209 | 28% | |
| 辽宁汉族Liaoning Han[ | 15 | 112 | 28% | 115 | 1% | 115 | 41% | 115 | 5% | 107 | 31% | |
| 中国其他人群 Other Chinese populations | 布侬族Bunun[ | 16 | 85 | 27% | 84 | 6% | 76 | 47% | 79 | 9% | 70 | 31% |
| 阿美人Ami[ | 17 | 144 | 40% | 146 | 5% | 137 | 34% | 142 | 12% | 122 | 31% | |
| 雅美人Yami[ | 18 | 141 | 22% | 144 | 8% | 190 | 46% | 188 | 5% | 188 | 26% | |
| 中国蒙古族China Mongolia 1[ | 19 | 639 | 21% | 646 | 8% | 538 | 36% | 721 | 8% | 343 | 16% | |
| 中国蒙古族China Mongolia 2[ | 20 | 258 | 17% | 338 | 7% | 211 | 37% | 341 | 9% | 89 | 29% | |
| 香港Hong Kong[ | 21 | 296 | 24% | 228 | 7% | 267 | 34% | 295 | 9% | 215 | 10% | |
| 华南South China[ | 22 | 77 | 19% | 80 | 13% | 60 | 40% | 85 | 11% | 39 | 18% | |
| 史前台湾Prehistric Taiwan[ | 23 | 21 | 19% | 19 | 11% | 15 | 47% | 33 | 6% | 9 | 44% | |
| 日本人群 Japanese populations | 现代日本Recent Japan 1[ | 24 | 345 | 14% | 352 | 13% | 314 | 43% | 382 | 6% | 262 | 15% |
| 现代日本Recent Japan 2[ | 25 | 345 | 14% | 352 | 13% | 314 | 43% | 382 | 7% | 262 | 15% | |
| 绳文Jomon 1[ | 26 | 244 | 29% | 290 | 32% | 214 | 47% | 285 | 3% | 162 | 5% | |
| 绳文Jomon 2[ | 27 | 244 | 29% | 290 | 32% | 214 | 47% | 285 | 5% | 162 | 5% | |
| 东北亚人群Northeast Asia populations | 贝加尔湖Lake Baikal[ | 28 | 18 | 22% | 21 | 5% | 9 | 33% | 21 | 19% | 2 | 0% |
| 阿穆尔Amur[ | 29 | 52 | 12% | 56 | 13% | 44 | 50% | 55 | 7% | 38 | 39% | |
| 东南亚人群Southeast Asia populations | 巴厘岛Bali[ | 30 | 155 | 41% | 51 | 0% | 157 | 20% | 162 | 8% | 146 | 13% |
| 菲律宾Philippines[ | 31 | 122 | 28% | 123 | 13% | 98 | 39% | 129 | 6% | 74 | 19% | |
| 泰国Thailand[ | 32 | 163 | 26% | 176 | 19% | 120 | 28% | 178 | 6% | 80 | 19% | |
| 缅甸Burma[ | 33 | 28 | 21% | 33 | 6% | 21 | 52% | 35 | 9% | 14 | 0% | |
| 尼泊尔Nepal[ | 34 | 28 | 54% | 30 | 23% | 21 | 43% | 34 | 6% | 14 | 7% | |
| 史前东南亚Early Southeast Asia 1[ | 35 | 314 | 32% | 348 | 18% | 248 | 40% | 370 | 8% | 150 | 22% | |
| 史前东南亚Early Mainland SE Asia 2[ | 36 | 163 | 39% | 187 | 17% | 136 | 37% | 217 | 10% | 76 | 32% | |
| 现代东南亚Recent Southeast Asia 1[ | 37 | 555 | 30% | 587 | 18% | 418 | 33% | 588 | 7% | 290 | 16% | |
| 现代东南亚Recent SE Asia 2[ | 38 | 79 | 32% | 83 | 16% | 61 | 28% | 84 | 7% | 36 | 19% | |
| 现代印尼-马来西亚[ | 39 | 134 | 30% | 142 | 18% | 97 | 36% | 137 | 13% | 66 | 11% | |
| 史前马来群岛Early Malay Archipelago[ | 40 | 130 | 25% | 139 | 19% | 99 | 45% | 131 | 5% | 66 | 11% | |
| 东马来群岛East Malay Archipelago[ | 41 | 24 | 46% | 25 | 20% | 18 | 39% | 25 | 4% | 17 | 0% | |
| 欧洲人群 European populations | 西欧Western Europe[ | 42 | 284 | 71% | 257 | 27% | 217 | 8% | 291 | 5% | 154 | 5% |
| 北欧Northern Europe[ | 43 | 225 | 84% | 319 | 21% | 130 | 17% | 179 | 5% | 75 | 16% | |
| 非洲人群 African populations | 北非North Africa[ | 44 | 381 | 66% | 402 | 31% | 352 | 8% | 414 | 9% | 267 | 8% |
| 西非West Africa[ | 45 | 75 | 12% | 67 | 33% | 47 | 45% | 71 | 44% | 30 | 17% | |
| 南非South Africa[ | 46 | 370 | 30% | 392 | 46% | 362 | 19% | 385 | 27% | 298 | 18% | |
| 科伊桑Khoisan[ | 47 | 88 | 7% | 89 | 72% | 85 | 5% | 87 | 26% | 60 | 17% | |
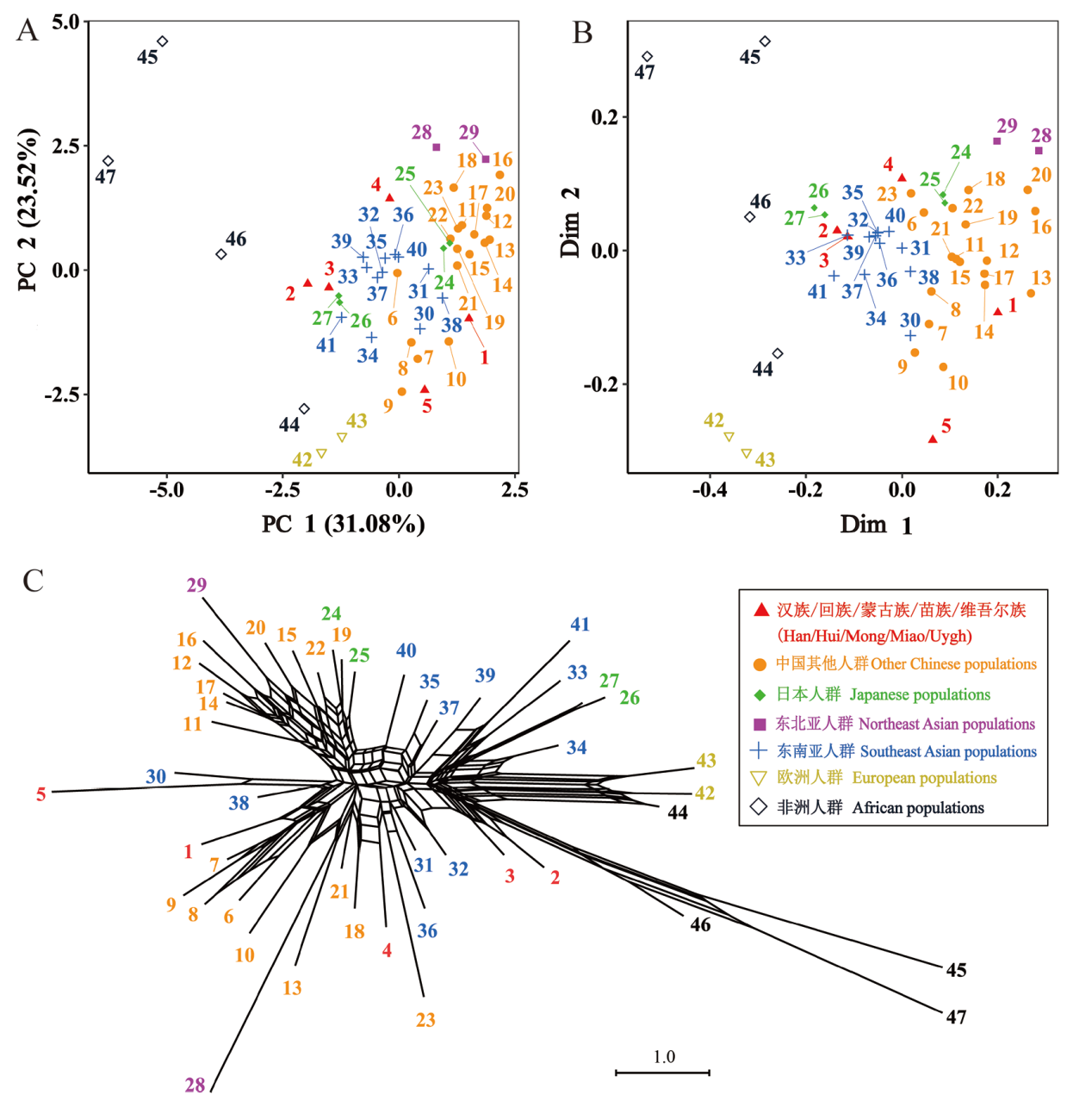
图2 5个目标人群与世界人群的牙齿形态特征群体关系图 A.主成分分析 Principal Component Analysis (PCA);B.多维尺度分析Multidimensional Scaling (MDS);C.邻接网络分析Neighbor-Net。本研究人群数据信息来源及人群序号与表1、表2一致The population data for this study and the population numbers are consistent with table 1 & table 2
Fig.2 Dental Morphological Traits Relationship of the Five Populations and the World Populations
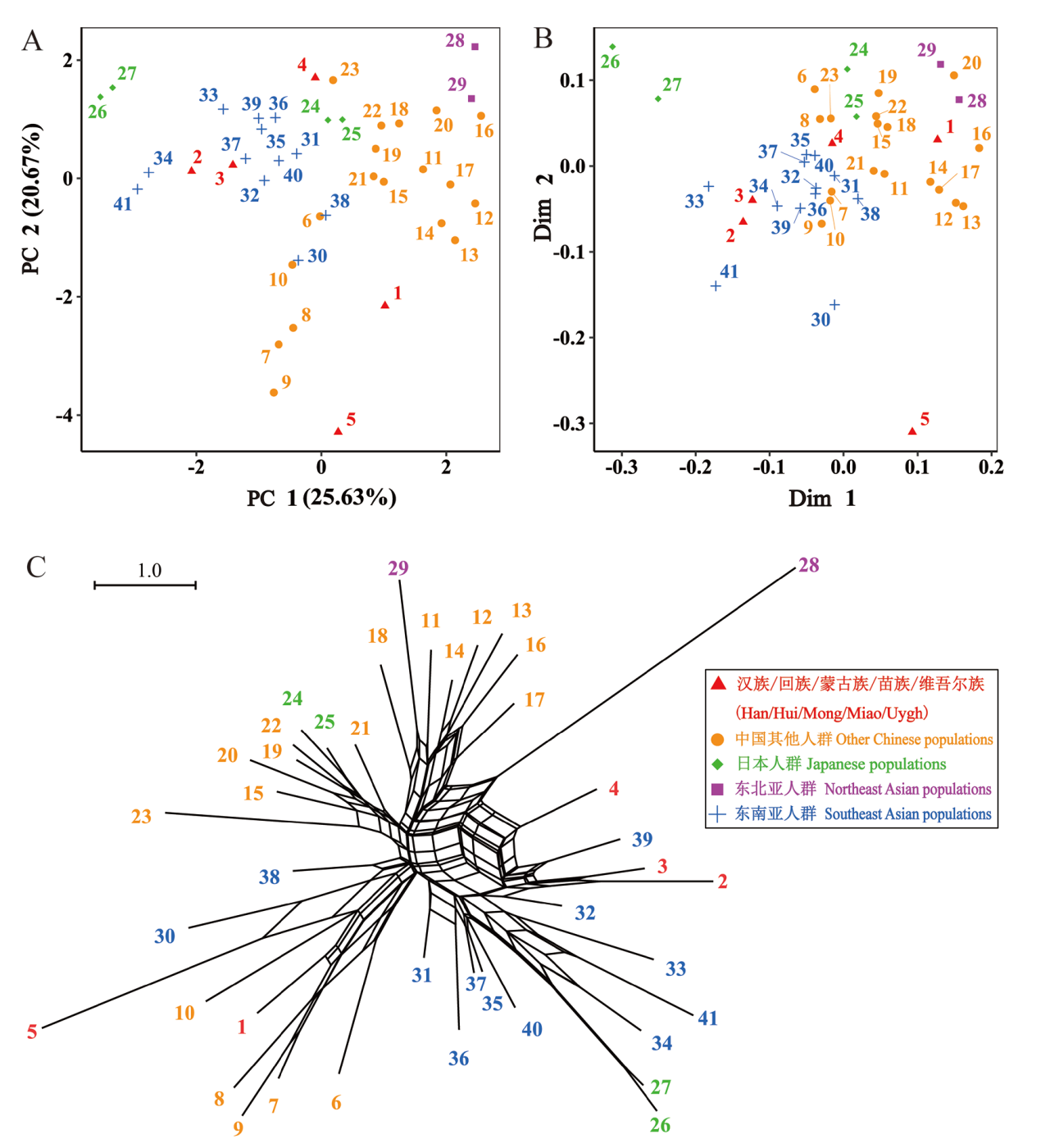
图3 5个目标人群与东亚人群的牙齿形态特征群体关系图 A.主成分分析 Principal Component Analysis (PCA);B.多维尺度分析 Multidimensional Scaling (MDS);C.邻接网络分析Neighbor-Net。本研究人群数据信息来源和人群序号与表1、表2一致The population data for this study and the population numbers are consistent with table 1 & table 2
Fig.3 Dental Morphological Traits Relationship of the Five Populations and the East Asia Populations
| [1] | Hanihara K. Mongoloid dental complex in the deciduous dentition with special reference to the dentition of the Ainu[J]. The Journal of Anthropological Society of Nippon, 1970, 78(1): 3-17 |
| [2] |
Turner CG II. Late Pleistocene and Holocene population history of East Asia based on dental variation[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1987, 73(3): 305-321
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330730304 pmid: 3303958 |
| [3] |
Turner CG II. Teeth and prehistory in Asia[J]. Scientific American, 1989, 260(2): 88-96
pmid: 2643828 |
| [4] |
Turner CG II. Major features of Sundadonty and Sinodonty, including suggestions about East Asian microevolution, population history, and late Pleistocene relationships with Australian aboriginals[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1990, 82(3): 295-317
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330820308 pmid: 2375382 |
| [5] | 刘武. 《牙齿人类学进展》评介[J]. 人类学学报, 1996, 15(1): 89-91 |
| [6] | Hrdlička A. Shovel-shaped teeth[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1920, 3(4): 429-465 |
| [7] | 李春芳, 皮昕, 陈国栋, 等. 卡氏尖名称的探讨[J]. 口腔医学纵横杂志, 1995, 11(4): 237-238 |
| [8] | Dietz VH. A common dental morphotropig factor the carabelli cusp[J]. The Journal of the American Dental Association, 1944, 31(11): 784-789 |
| [9] | Dahlberg AA. Materials for the establishment of standards for classification of tooth characters, attributes, and techniques in morphological studies of the dentition[D]. Chicago: Zollar Laboratory of Dental Anthropology, University of Chicago (mimeo), 1956, 34-681 |
| [10] | Turner CG II, Nichol CR, Scott GR. Scoring procedures for key morphological traits of the permanent dentition: the Arizona State University dental anthropology system[A]. In: Kelley M, Larsen CS(eds). Advances in Dental Anthropology[C]. New York: Wiley-Liss Inc, 1991, 13-31 |
| [11] | Scott GR, Turner CG II. The anthropology of modern human teeth[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2018: 23-52, 216-219, 253-262, 285-295 |
| [12] |
Turner CG II. Expression count: A method for calculating morphological dental trait frequencies by using adjustable weighting coefficients with standard ranked scales[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1985, 68(2): 263-267
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330680213 pmid: 4061615 |
| [13] | 金力, 席焕久, 谭婧泽. 中华民族体质表型调查方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2024, 151-168 |
| [14] | Jacob C. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences: differences between correlation coefficients[M]. Academic Press, 1977, 109-143 |
| [15] | Buda A, Jarynowski A. Life time of correlations and its applications[M]. ABRASCO - Associação Brasileira de Saúde Coletiva Press, 2010, 132-153 |
| [16] | 金泽英作, 佐竹隆, 佐佐木佳世子, 等. 中国云南省5个少数民族人群的牙齿性状[J]. 现代人类学通讯, 2009, 15: 77-84 |
| [17] | Chikushi S. Dental charasteristics in the Dafurs tribe of Inner Mongoria, China.[J]. The Journal of the Kyushu Dental Society, 2001, 55(3): 189-205 |
| [18] | Kiyosue T. Dental characteristics in the Hui of Liao-ning, China[J]. The Journal of the Kyushu Dental Society, 2000, 54(6): 510-520 |
| [19] | Jin H. Dental characteristics in the Chaoxian of Liao-ning province, China[J]. The Journal of the Kyushu Dental Society, 1999, 53(5): 529-537 |
| [20] | Fukunari F. Dental characteristics in the Manchu tribe of Xin-Bin, China[J]. The Journal of the Kyushu Dental Society, 1999, 53(1): 63-88 |
| [21] | Kikuti N. Dental characteristics in the Han of Liao-Ning, China[J]. The Journal of the Kyushu Dental Society, 1997, 51(1): 193-216 |
| [22] | Manabe Y, Rokutanda A, Kitagawa Y, et al. Genealogical position of native Taiwanese(Bunun Tribe) in East Asian populations based on tooth crown morphology[J]. The Journal of the Anthropological Society of Nippon, 1991, 99(1): 33-47 |
| [23] |
Manabe Y, Rokutanda A, Kitagawa Y. Nonmetric tooth crown traits in the Ami tribe, Taiwan aborigines: comparisons with other east Asian populations[J]. Human Biology, 1992, 64(5): 717-726
pmid: 1398612 |
| [24] | Yamaguchi Y. Dental characteristics in Balinese[J]. The Journal of the Kyushu Dental Society, 1996, 50(4): 663-680 |
| [25] |
Corruccini RS, Potter RHY. Developmental correlates of crown component asymmetry and occlusal discrepancy[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1981, 55: 21-31
pmid: 7196159 |
| [26] | Mizoguchi Y. Mirror imagery and genetic variability of lateral asymmetries in the mesiodistal crown diameters of permanent teeth[J]. Bulletin of the National Science Museum, 1987, 13: 11-19 |
| [27] |
Townsend GC, Brown T. Dental asymmetry in Australian aboriginals[J]. Human Biology, 1980, 52: 661-673
pmid: 7203440 |
| [28] |
Scott GR. Classification, Sex dimorphism, Association, and Population variation of the canine distal accessory ridge[J]. Human Biology, 1977, 49(3): 453-469
pmid: 892765 |
| [29] |
Townsend GC, Brown T. The Carabelli trait in Australian Aboriginal dentition[J]. Archives of Oral Biology, 1981, 26(10): 809-814
doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90177-1 pmid: 6949523 |
| [30] |
Scott GR. Population Variation of Carabelli’s Trait[J]. Human Biology, 1980, 52: 63-78
pmid: 7364428 |
| [31] | Tan J, Peng Q, Li J, et al. Characteristics of dental morphology in the Xinjiang Uyghurs and correlation with the EDARV370A variant[J]. Science in China: Life Sciences, 2014, 57(5): 510-518 |
| [32] | Matthew W. Tocheri. The Effects of Sexual Dimorphism, Asymmetry, and Inter-trait Association on the Distribution of Thirteen Deciduous Dental Nonmetric Traits in a Sample of Pima Amerindians[J]. Dental Anthropology Journal, 2002, 15 |
| [33] | Khamis M. Jane AT, Samsudin A. et al. Variation in dental crown morphology in Malaysian populations[J]. Dental Anthropology Journal, 2018, 19(2): 49-60 |
| [34] | Burnett SE, Irish JD, Fong MR. Wear’s the problem? Examining the effect of dental wear on studies of crown morphology. Anthropological Perspectives on Tooth Morphology[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2013, 535-554 |
| [35] |
Stojanowski CM, Johnson KM. Observer error, dental wear, and the inference of new world sundadonty[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2015, 156(3): 349-362
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.22653 pmid: 25363296 |
| [36] | Molnar S. Sex, age, and tooth position as factors in the production of tooth wear[J]. American Antiquity, 1971, 36(2): 182-188 |
| [37] |
Tomenchuk J, Mayhall JT. A correlation of tooth wear and age among modern Igloolik Eskimos[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1979, 51(1): 67-77
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330510109 pmid: 453346 |
| [38] | Wen B, Li H. Genetic evidence supports demic diffusion of Han culture[J]. Nature, 2004, 431(7006): 302-305 |
| [39] |
Xu S, Yin X, Li S, et al. Genomic dissection of population substructure of Han Chinese and its implication in association studies[J]. American Journal of Human Genetics, 2009, 85(6): 762-774
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.10.015 pmid: 19944404 |
| [40] | Qiao H, Tan JZ, Wen SQ, et al. De novo dissecting the three-dimensional facial morphology of 2379 Han Chinese individuals[J]. Phenomics, 2024, 4: 1-12 |
| [41] | 李紫君. 头面部观察类形态特征揭示现代汉族的多样性[D].硕士研究生学位论文, 上海: 复旦大学, 2020, 57-61 |
| [42] | 殷杏. 中国汉族头面部测量特征的南北差异性研究[D].硕士研究生学位论文, 上海: 复旦大学, 2020, 78-88 |
| [43] | 吴佳姿. 现代汉族人群体部测量表型的差异研究[D].硕士研究生学位论文, 上海: 复旦大学, 2021, 61-91 |
| [44] | 陆艳, 蔡晓云, 李辉. 苗瑶与孟高棉人群的遗传同源[J]. 现代人类学通讯, 2011, 5: 214-223 |
| [45] | 李辉, 金雯俐. 人类起源和迁徙之谜[M]. 上海: 上海科技教育出版社, 2020, 144-173 |
| [46] | Wang CC, Yan S, Qin ZD, et al. Late Neolithic expansion of ancient Chinese revealed by Y chromosome haplogroup O3a1c-002611[J]. J Syst Evol, 2013, 51 (3): 280-286 |
| [47] | 韦兰海. 东欧亚人群父系Y染色体谱系树的更新[D].博士研究生学位论文, 上海: 复旦大学, 2016, 60-62 |
| [48] |
Ma X, Yang W, Gao Y, et al. Genetic Origins and Sex-Biased Admixture of the Huis[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2021, 38(9): 3804-3819
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab158 pmid: 34021754 |
| [49] | 郑连斌, 陆舜华. 我国23个群体体质的聚类分析与主成分分析[J]. 人类学学报, 1997, 16(2): 151-158 |
| [50] | 张兴华, 张尚才, 宇克莉, 等. 山东、安徽汉族与我国19个族群体质特征的聚类分析与主成分分析[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 34(3): 76-80 |
| [51] | 祝海歌, 乔辉, 杨晨, 等. 中国5个人群的牙齿形态特征对比研究[J]. 复旦学报 (自然科学版), 2023, 62(6): 765-774 |
| [52] | Yu K, Li Y, Zhang X, et al. Physical characteristics of the Uyghurs: anthropometric data from Kashgar[J]. Science in China: Life Sciences, 2020, 50(9): 983-995 |
| [53] | Feng Q, Lu Y, Ni X, et al. Genetic History of Xinjiang’s Uyghurs Suggests Bronze Age Multiple-Way Contacts in Eurasia[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2017, 34(10): 2572-2582 |
| [54] |
陆九正, 乔辉, 孙畅, 等. 汉族、黎族、维吾尔族和藏族头面部测量特征比较[J]. 解剖学报, 2022, 53(4): 526-1356
doi: 10.16098/j.issn.0529-1356.2022.04.017 |
| [1] | 王旭, 万腾淑, 刘雪敏, 李孟思, 翟家淇, 赵春旺. 河南汉族儿童头面部的形态特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 813-827. |
| [2] | 吕婧祎, 肖瑶, 宇克莉, 程智, 聂浩波, 高新颖, 姚玥彤, 包金萍, 郑连斌, 张兴华. 中国黄衣佤族的体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(04): 549-560. |
| [3] | 张兴华, 肖瑶, 岩坎翁, 玉应香, 高雯芳, 包金萍, 程智, 高新颖, 姚玥彤, 刘鑫, 宇克莉. 中国曼咪人的体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(04): 561-573. |
| [4] | 宇克莉, 张兴华, 程智, 郑连斌. 中国不同人群的头面部特征及其差异[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(04): 574-585. |
| [5] | 李欣, 姜帅, 黄婷, 钟华, 温有锋. 内蒙古与新疆达斡尔族头面部特征比较[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(04): 586-596. |
| [6] | 李彦雷. 河北汉族成年男性身高与足迹的相关性[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(04): 657-667. |
| [7] | 汤挺兵, 叶先才, 张军, 陈光平, 范晓文, 叶晓鸥. 浙江汉族大学生指长比与心理状况的关系[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(04): 668-674. |
| [8] | 成芷菡, 种建荣, 孙战伟, 杨磊, 靖晓亭, 王继红, 何嘉宁. 人类股骨头颈处的非测量特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 415-426. |
| [9] | 曾浩然, 刘康康, 罗亚平. 指纹皱纹研究的现状及展望[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 518-528. |
| [10] | 许竞文, 浣发祥, 杨石霞. 旧石器时代考古中出土的赭石及相关遗物的研究方法[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(02): 331-343. |
| [11] | 张振, 王莹, 李月丛. 泥河湾盆地旧石器时代人类活动与环境关系的研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(01): 184-198. |
| [12] | 倪喜军. 人类起源研究中的哲学问题[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(06): 709-720. |
| [13] | 何嘉宁, 冉智宇. 中国史前人类的头骨变形[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(05): 575-589. |
| [14] | 孙蕾, 李彦桢, 武志江. 河南郑州站马屯遗址仰韶晚期人骨的颅面形态[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(03): 331-341. |
| [15] | 王邦彦, 王久存, 文少卿. 古代强直性脊柱炎的诊断标准及国内研究回顾[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(03): 422-434. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 395
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 784
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3