

收稿日期: 2019-06-24
修回日期: 2019-08-06
网络出版日期: 2020-09-10
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(41472026);中国科学院战略性先导科技专项“关键地史时期生物与环境演变过程及其机制”(XDPB05)
Lithic artifacts excavated from the Jinshuihekou site in the Hanzhong Basin, Shaanxi Province, China
Received date: 2019-06-24
Revised date: 2019-08-06
Online published: 2020-09-10
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41472026);Macroevolutionary Processes and Paleoenvironments of Major Historical Biota(XDPB05)
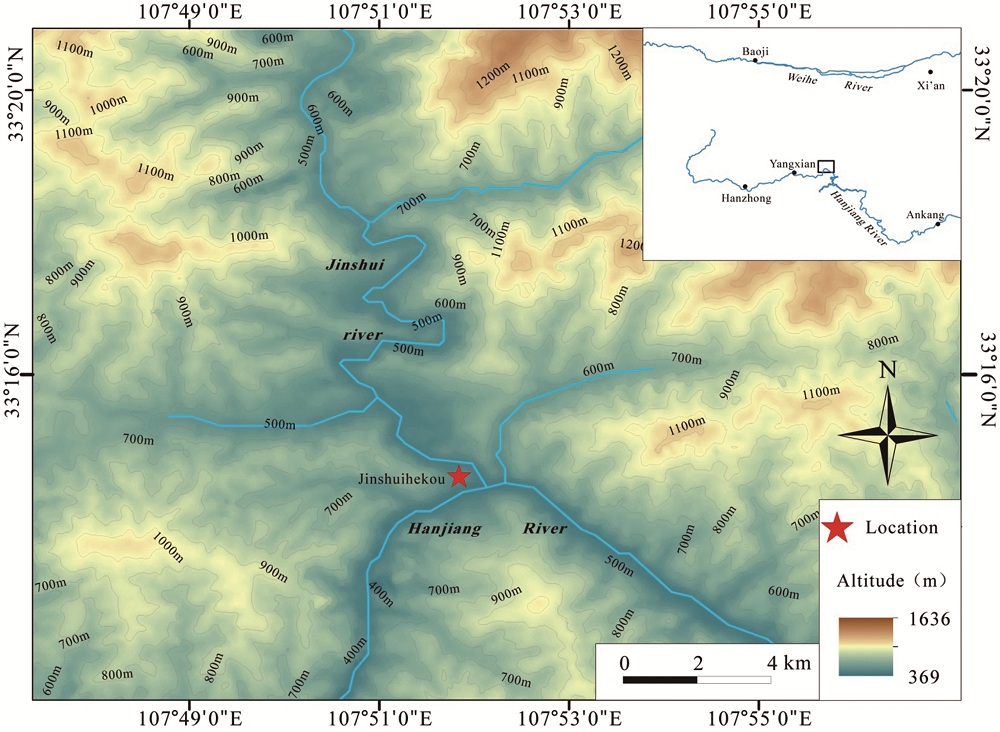
位于汉水左岸一级支流金水河第四级阶地的金水河口遗址是汉水流域发现较早的一处旧石器遗址。2014年6月~2015年2月,为了配合国家重点建设工程——南水北调西线“引汉济渭”项目的实施,我们对金水流域金水镇附近的3个旧石器遗址进行了正式发掘,金水河口遗址即为其中之一。该遗址发掘面积370m2,出土不同类型石制品1210件。研究显示在金水河口遗址生活的古人类主要选取附近河滩砾石为原料进行剥片及工具加工。石制品的岩性以石英和石英岩为主,硅质灰岩次之,并少量使用了石英砂岩和花岗岩原料。古人类主要使用锤击法剥片。遗址中石核的利用效率较低,近半数石片有直接使用的痕迹。加工工具的毛坯以石片为主。工具类型除了刮削器、凹缺器、石锥等小型工具之外,还有砍砸器、手镐、重型刮削器等重型工具。遗址中碎屑数量很少。石制品组合以刮削器等小型工具为主,也包含少量重型工具。相较于汉中盆地已发现的遗址,金水河口遗址的文化面貌与洛南盆地中更新世的龙牙洞遗址更相似,但是重型工具的比例更高。由于遗址堆积物已超出了钾长石红外后释光测年法(post-IR IRSL)的测年范畴,目前只能给出遗址的埋藏时间下限,即埋藏石制品地层的年代不晚于150 ka。作为汉中盆地有明确测年的中更新世晚期遗址,金水河口遗址为我们系统了解汉江支流金水河流域和秦岭地区的石器工业特点、遗址地层堆积及年代等提供了新的、丰富的材料。
别婧婧 , 王社江 , 夏楠 , 鹿化煜 , 王先彦 , 弋双文 , 夏文婷 , 张改课 , Mathew L. FOX , 张红艳 , 卓海昕 , 张文超 . 陕西汉中洋县金水河口旧石器遗址出土石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2019 , 38(03) : 344 -361 . DOI: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2019.0040
The Jinshuihekou site, discovered in the 1980s, is located in the southern piedmont of the Qinling Mountains. This site is on the fourth terrace of the Jinshui River, a left tributary of the Hanjiang River in central China. From June 2014 to February 2015, three Paleolithic localities, including the Jinshuihekou site, were excavated near Jinshui town as part of the national key construction project: the Western Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, also known as the “Hanjiang River to Weihe River Water Diversion Project”. An area of 370m2 was excavated yielding 1210 stone artifacts. The early hominins at this site mainly selected cobbles/pebbles from fluvial gravels for tool knapping; predominately made from quartz and quartzite, followed by siliceous limestone, quartzite sandstone and granite. The principal flake knapping method is hard hammer percussion, and considerable components of the artifacts still retain features of its original use without the need for modification. Analyses of the lithic assemblage indicate that the retouched tools are comprised of small tools made on small flakes such as scrapers, notches, awls, and heavy-duty tools such as choppers, picks, and heavy-duty scrapers. The characteristics of the lithic assemblage resemble the Longyadong Middle Pleistocene cave site in the Luonan Basin in the southern Qinling Mountains but with higher proportion of heavy-duty tools. Based on the post-IR elevated temperature IRSL(pIRIR 290°C) dating method, the layer which buried stone artifacts at Jinshuihekou is earlier than 150 ka. The Jinshuihekou site restore the missing part of the Paleolithic cultural sequence in the Hanzhong Basin and provides new materials for studying the behavior and Paleolithic technology of hominins in the catchment of the Jinshui River and the Qinling Mountains region.

| [1] | Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research. Geographical survey of Hanjiang river valley[M]. Science press, 1957(in Chinese) |
| [2] | Bureau of Shaanxi hydrological and water resources survey. Hydrology of Shaanxi province[M]. China Water Power Press, 2007(in Chinese) |
| [3] | Local Chronicles Compilation Committee of Yangxian County. Annals of Yangxian county[M]. Xi'an: Sanqin press, 1996(in Chinese) |
| [4] | Yan JQ. Newly investigation of Paleolithic artifacts in Liangshan Mountain, Hanzhong Basin, Shaanxi province[J]. Archaeology and Cultural Relics, 1981(2):1-5(in Chinese) |
| [5] | Archaeology team of Hanshui River at of Shaanxi Provincial Institute of Archaeology. Paleolithic artifacts found in Longgangsi site, Nanzheng county, Shaanxi province[J]. Archaeology and Cultural Relics, 1985(6):1-12(in Chinese) |
| [6] | Tang YJ, Zong GF, Lei YL. A new discovery of Paleolithic artifacts in the upper reaches of the Hanjiang River[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 1987,6(1):55-60(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Huang WW, Qi GQ. Preliminary observation on the Paleolithic artifacts in Liangshan Mountain[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 1987,6(3):236-244(in Chinese) |
| [8] | Lu N, Huang WW, Yin SP, et al. Re-study on Paleolithic artifacts at Liangshan Mountain[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2006,25(2):143-152(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Lu N, Hou YM. Analysis and comparative study on the manufacturing model of Paleolithic materials from Liangshan Mountain[A]. In: Dong W, eds. Proceedings of the 10th annual conference of vertebrate paleontology[C]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2006: 163-183(in Chinese) |
| [10] | Yan JQ. The firstly discovery of Paleolithic artifacts at Longgangsi site in Hanzhong Basin, Shaanxi province. Archaeology and Cultural Relics[J]. Archaeology and Cultural Relics, 1980(4):1-5(in Chinese) |
| [11] | Yan JQ, Wei JW. Paleolithic studies in Liangshan Mountain, Shaanxi province[J]. Prehistorical Studies, 1983(1):51-56(in Chinese) |
| [12] | Hou JL, Wang ZH, Yang YC, et al. Paleolithic artifacts and animal fossils newly unearthed from Longgangsi site, Nanzheng county, Shaanxi province[J]. Prehistorical Studies, 1986(Z2):46-56(in Chinese) |
| [13] | Yan JQ. The first discovery and preliminary study of paleolithic stone in Liangshan Mountain, Hanzhong Basin, Shaanxi province[J]. Journal of Xi 'an Mining College, 1981(1):56-67(in Chinese) |
| [14] | Yang X, Wang X, Wang S, et al. Fluvial terrace formation and its impacts on early human settlement in the Hanzhong basin, Qinling Mountains, central China[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2019,178:1-14. |
| [15] | Wang SJ, Sun XF, Lu HY, et al. Newly discovered Paleolithic open-air sites in Hanzhong Basin in upper valley of Hanjiang River and their ages[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2014,33(2):125-136(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Xia WT, Wang SJ, Xia N, et al. Lithic artifacts excavated from Locality 3 of the Longgangsi site in Hanzhong Basin, Shaanxi province[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2018,37(4):529-541(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Wang SJ, Lu HY. Taphonomic and paleoenvironmental issues of the Pleistocene loessic Paleolithic sites in the Qinling Mountains Region, Central China[J]. Science China: Earth Series, 2016,46(7):881-890(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Wang SJ, Lu HY. Current perspectives on Paleolithic archaeology in the Upper Hanjiang River Valley, Qinling Mountains Region, Central China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2014,33(3):315-328(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Wang SJ. Jinshuihekou Paleolithic site in Yangxian County[Z]. In: Wang W, eds. Almanac of Chinese archaeology [R].China Social Science Press, 2015, 322-323(in Chinese) |
| [20] | Buylaert JP, Jain M, Murray A S, Thomsen K J, Thiel C, & Sohbati R. A robust feldspar luminescence dating method for Middle and Late Pleistocene sediments[J]. Boreas. 2012,41(3):435-451 |
| [21] | Thiel C, Buylaert J, Murray A S, Terhorst B, Hofer I, Tsukamoto S, & Frechen M. Luminescence dating of the Stratzing loess profile(Austria) - Testing the potential of an elevated temperature post-IR IRSL protocol[J]. Quaternary International, 2011,234(1):23-31 |
| [22] | Sun X, Lu HY, Wang SJ, et al. Ages of Liangshan Paleolithic sites in Hanzhong Basin, central China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2012,10:380-386 |
| [23] | Sun X, Lu HY, Wang SJ, et al. Early human settlements in the southern Qinling Mountains, central China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017,164:168-186 |
| [24] | Wang SJ, Lu HY, Zhang HY, et al. A preliminary survey of Paleolithic artifacts and loess deposition in the middle South Luohe River, eastern Qinling Mountains, central China[J]. Quaternary Science, 2008,28(6):988-999(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Lu HY, Zhang HY, Wang SJ, et al. A preliminary survey on loess deposit in Eastern Qinling Mountains(central China) and its implication for estimating age of the Pleistocene lithic artifacts[J]. Quaternary Science, 2007,27(4), 559-567(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Sun XF, Lu HY, Wang SJ, et al. Age of newly discovered Paleolithic assemblages at Liuwan site Luonan Basin[J]. Quaternary International, 2014. 347, 193-199 |
| [27] | Xiao JL, Jin CZ, Zhu YZ. Age of the fossil Dali Man in north-central China deduced from chronostratigraphy of the loessepaleosol sequence[J]. Quaternary Science Review, 2002,21, 2191-2198 |
| [28] | Lu HY, Sun XF, Wang SJ, et al. Ages for hominin occupation in Lushi Basin, middle of South Luo River, central China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2011,60(5):612-617 |
| [29] | Dai EJ, Ji HX. Discovery of Palaeoliths at Lantian, Shanxi[J]. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 1964. 8(2), 152-161(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Wang YY, Xue XX, Yue LP, et al. Discovery of the fossil Dali Man in Shaanxi Province and the preliminary study[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1979,24:303-306(in Chinese) |
| [31] | Lu HY, Zhang HY, Wang SJ. Multiphase timing of hominin occupations and the paleoenvironment in Luonan Basin, Central China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2011,76, 142-147 |
| [32] | An ZS, Ho CK. New magnetostratigraphic dates of Lantian Homo erectus[J]. Quaternary Research, 1989,32:213-221 |
| [33] | Li TY, Elter D.A. New Middle Pleistocene hominid crania from Yunxian in China[J]. Nature, 1992,357:404-407 |
| [34] | Wang SJ, Cosgrove R, Lu HY. New progress on Paleolithic archaeological studies in the Luonan Basin, China[A]. In: Kazuto, Matsufuji(ed.), Loesse Paleosol and Paleolithic Chronology in East Asia[C]. Yuzankaku, Tokyo, 2008: 145-161(in Japanese with English abstract) |
| [35] | Feng X. Technological characterization of China and Europe lower Paleolithic industry from 1 Ma to 400,000 years similarity and difference between the Yunxian Hominid culture and European Acheulean.[J]. L'anthropologie, 2008,112, 423-447 |
| [36] | Sun XF, Lu HY, Wang SJ, et al. TT-OSL dating of Longyadong Middle Paleolithic site and paleoenvironmental implications for hominin occupation in Luonan Basin(central China).[J]. Quaternary Research, 2013,79, 168-174 |
| [37] | Sun XF, Yi SW, Lu HY, et al. TT-OSL and post-IR IRSL dating of the Dali Man site in central China[J]. Quaternary International, 2017,434, 99-106 |
| [38] | Lü ZE. Some remarks on pebble tool industries afteer visiting Gongyi and Luonan[J]. Archaeology and Cultural Relics, 1999(1):29-37(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [39] | Wang SJ, Zhang XB, Lu HY, et al. New discovered paleolithic open-air sites at Shangdan Basin in the Upper Danjiang River valley, eastern Qinling Mountains, central China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2013,32(4):421-431(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [40] | Wang SJ, Hu SM. The Palaeolithic Sites from the Yaoshi Basin of the Upper Danjiang River Val ley, the Shangluo Region of Shaanxi Province[J]. Archaeology and Cultural Relics, 2000(4):36-42(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [41] | Lu HY, Zhang HY, Wang SJ, et al. A preliminary survey on loess deposit in eastern Qinling Mountains(central China) and its simplication foe estimating age of the pleistocene lithic artifacts[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007(4):559-567(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [42] | Wang SJ, Lu HY, Zhang HY, et al. A preliminary survey of Paleolithic artifacts and loess deposit in the middle south Luohe River, eastern Qinling Mountains, central China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2008(6):988-999(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [43] | Wang SJ, Liu SM. Two newly discovered paleolithic sites in Shangluo city and Shanyang county, eastern Qinling Mountains[J]. Archaeology and Cultural Relics, 2011(1):24-28(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [44] | Liu FL, Du SS. Two newly discovered paleolithic sites in Luoyang city, Henan Province[J]. Huaxia Archaeology, 2010(1):44-48(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [45] | Wang SJ. Huashilang(I)-The Palaeolithic open-air sites in the Luonan Basin, China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [46] | Wang SJ. Huashilang(II)- Longyadong Palaeolithic cave site in the Luonan Basin, China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [47] | Wang SJ. The refitting of lithic artefacts from the Longyadong Cave, Luonan Basin, China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2005(1):1-17(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [48] | Wang SJ, Zhang XB, Shen C. A study of lithic assemblages from 1995 excavation at Longyadong cave, Luonan Basin ,China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2004(2):93-110(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [49] | Wang SJ, Shen C, Hu SM. Lithic artefacts collected from open-air sites during 1995 and 1999 investigations in Luonan Basin, China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2005(2):87-103(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [50] | Wang SJ, Huang PH. Stratigraphy and TL dating of paleolithic sites in the Luonan Basin[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2001(3):229-237(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [51] | Liu FL, Du SS. Research on stone artifacts unearthed in 1998 from the Beiyao loessic Paleolithic site, Luoyang City[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2011,30(1):13-21(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [52] | Du SS, Yang LR, Liu FL, et al. Re-examination of the age of Beiyao site, Luoyang city[J]. Quaternary Research, 2011,31(1):16-21(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [53] | Wang SJ, Lu HY. Taphonomic and paleoenvironmental issues of the Pleistocene loessic Paleolithic sites in the Qinling Mountains region, central China[J]. Science China: Earth Series, 2016,46(7):881-890(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [54] | Wang SJ, Lu HY, Zhang HY, et al. Newly discovered Palaeolithic artefacts from loess deposits and their ages in Lantian, central China[J]. Chinese science bulletin, 2014,59(7):651-661 |
| [55] | Xing LD, Wang SJ, Zhang GK, et al. Newly discovered Paleolithic artifacts from the Yeyuan open-air site in the Luonan Basin, central China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2015,34(1):1-13(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [56] | Wang SJ, Zhang XB, Shen C, et al. An important breakthrough made in the excavation of Zhanghuokou Paleolithic site in Luonan Basin, Shaanxi province[N]. China heritage news, 2011: 11-4(in Chinese) |
| [57] | Wang SJ, Zhang XB. Excavation of Mengwa Paleolithic site, Luonan Basin, Shaanxi province[N]. China heritage news, 2011: 7-4(in Chinese) |
| [58] | Lu HY, Zhang HY, Sun XF, et al. Landform, loeess deposit and paleoenvironment changes in the south Luohe River(central China) during the hominin occupations[J]. Quaternary Science, 2012,32(2):167-177(in Chinese with English abstract) |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |