

收稿日期: 2018-09-25
修回日期: 2019-06-04
网络出版日期: 2021-04-13
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目资助(31671245)
Comparative analysis of body components of Tujian adults from Hunan, Hubei and Guizhou Provinces
Received date: 2018-09-25
Revised date: 2019-06-04
Online published: 2021-04-13
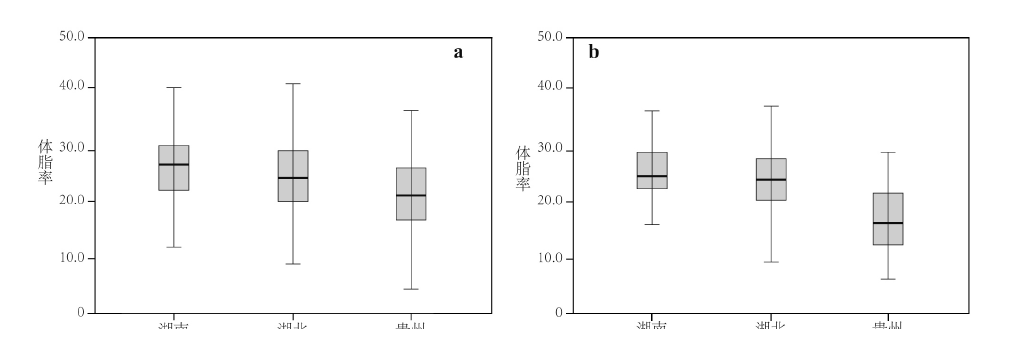
体成分指的是身体脂肪、蛋白质、肌肉、水等含量在体质量中所占的百分比。各成分之间的合理比例,对于维持机体的正常运行,十分重要。因此身体成分的研究一直是国内外研究的热点。体成分存在着人种和民族差异,因此它也是人类学研究的重要课题。目前的研究主要集中在中国青少年、大学生的体成分及体成分与其他身体指标的关系,而对于土家族的研究及不同地方间土家族的比较研究匮乏。本文采用生物电阻抗分析法,比较湖南、湖北、贵州土家族成人的体成分特点。旨在更全面的了解土家族的身体成分特点,探讨遗传、环境、饮食等因素对身体成分的影响。方法采取随机取样,测量湖北省、湖南省、贵州省959例(男性411例,平均年龄为53.7±14.2岁,女性548例,平均年龄为51.0±13.6岁)土家族成人19项身体成分指标,运用Excel 2007、SPSS 19.0对其各项指标进行方差分析(ANOVA)、Person相关分析及独立样本T检验分析。不同地区土家族男性身体成分的单因素方差分析结果显示,除总肌肉量、推定骨量、右上肢肌肉量、躯干肌肉量外,湖南、湖北和贵州土家族男性各项指标间差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05),不同地区的土家族女性中,除体质量、推定骨量、总能量代谢、右上肢肌肉量、右下肢肌肉量、左下肢脂肪率外,其余13项指标间差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。根据体脂率标准显示,除湖南土家族女性外,湖北、贵州及湖南土家族成人均属于正常范围,且其肥胖多属于中心性肥胖,脂肪多堆积于腹部,患慢性疾病的可能性较大,这与湖南地区人民生活水平较高有关。三个地区中,湖北省成人的肌肉较发达,湖南、湖北地区成人及贵州地区的女性,都呈现右肢肌肉量略高于左肢肌肉量的趋势,贵州男性左右下肢肌肉量相近;贵州地区推定骨量含量高,其骨骼更强壮。
李珊 , 王文佳 , 宇克莉 , 郑连斌 . 湖南、湖北、贵州土家族成人的体成分比较[J]. 人类学学报, 2021 , 40(02) : 272 -280 . DOI: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2019.0052
Body composition refers to the percentage of body fat, protein, muscle, water, etc. in body weight. A reasonable ratio between these components is important to maintain normal body operations, and with ethnic differences in body composition, this topic is key in anthropological research. Our current research focuses on the relationship between body composition of Chinese adolescents and college students with other physical indicators; in particular there is a lack of comparative research on the Tujia nationality. In this paper, the bioelectrical impedance analysis method was used to compare body composition characteristics of Tujia adults in Hunan, Hubei and Guizhou in order to explore the effects of genetics, environment, diet etc. on body composition. A random sample of 959 (411 males, average age 53.7±14.2 years; 548 females, average age 51.0±13.6 years) was studied. Excel 2007 and SPSS 19.0 were used to conduct ANOVA, Person correlation and independent sample T test analyses. ANOVA results indicated that except for total muscle mass, estimated bone mass, right upper limb muscle mass, and trunk muscle mass, Tujia males from the three regions showed statistically significant (P<0.05) differences among various indicators. Among Tujia women from the three regions, except for body weight, estimated bone mass, total energy metabolism, right upper limb muscle mass, right lower limb muscle mass, and left lower limb fat rate there were statistically significant (P<0.05) differences. According to standardized body fat percentages it was noted that Hubei, Guizhou and Hunan Tujia adults are in the normal range, and that Hunan Tujia women carry their obesity around abdomen, and therefore are more likely to suffer from chronic diseases. This result is related to the high standard of living of the Hunan people. Among the three regions, muscle mass in Hubei adults were more developed, with adults in Hunan and Hubei and Guizhou women having a tendency for slightly higher muscle mass in the right limb compred to the left. Guizhou men had similar muscle mass in the lower limbs, and thus it was assumed that bone mass would be higher and bones stronger.

Key words: Biological anthropology; Tujia nationality; Statistics; Body composition
| [1] | 曹毅. 土家族族源再探[J]. 湖北民族学院学报:社会科学版, 1991(4): 34-38 |
| [2] | 周兴茂. 土家族的研究与发展[J]. 长江师范学院学报, 2008,24(5): 69-74 |
| [3] | 左娇蕾, 张倩, 刘爱玲, 等. 北京市儿童青少年体成分的分析[J]. 中国健康教育, 2011,27(6): 415-418 |
| [4] | 崔凯, 徐玉明. 大学生骨密度与身体成分相关分析研究[J]. 健康研究, 2012,32(4): 273-277 |
| [5] | 宇克莉, 王子善, 张兴华, 等. 尔苏人与木雅人身体成分分析[J]. 天津师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2018,38(1): 70-75 |
| [6] | 张兴华, 郑连斌, 宇克莉, 等. 山东寿光汉族体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2011,30(2): 206-217 |
| [7] | 曹芳, 温有锋, 席焕久, 等. 锦州汉族成人体成分与血脂的关系[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2014,37(1): 95-98 |
| [8] | Mazess RB, Barden HS, Bisek JP, et al. Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry for total-body and regional bone-mineral and soft-tissue composition[J]. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 1990,51(6): 1106-1112 |
| [9] | 席焕久. 人体测量方法[M].科学出版社, 2010 |
| [10] | 闫丹, 阮祥燕. 人体成分测定方法的临床应用与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2011,15(24): 4499-4502 |
| [11] | 邴强, 王健. 人体体成分的模型及检测方法研究进展[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 2001,16(1): 51-55 |
| [12] | Durnin JV, Womersley J. Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years[J]. British Journal of Nutrition, 1974,32(1): 77-97 |
| [13] | 孙玉梅. 高血压与超重、肥胖的相关性研究[D]. 南京:东南大学, 2009 |
| [14] | 中国肥胖问题工作组数据汇总分析协作组. 我国成人体重指数和腰围对相关疾病危险因素异常的预测价值:适宜体重指数和腰围切点的研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2002,23(1): 5-10 |
| [15] | 温潇潇, 麦劲壮, 高向民, 等. 成人中心性肥胖的腰围切点分析[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2015,43(9): 822-826 |
| [16] | Altman DG, Bland JM. Measurement in medicine: The analysis of method comparison studies[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1983,32(3): 307-317 |
| [17] | 张国海. 运动对大学生骨密度和体成分的影响及相互关系的研究[J]. 中国体育科技, 2008,44(5): 56-62 |
| [18] | 刘继洪, 杨延斌, 曹海伟, 等. 成年人骨密度、骨量、体重、年龄、身高、脂肪含量相互关系的研究[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2002,18(2): 146-147 |
| [19] | 聂伟志, 隋显玉, 李立, 等. 骨量(骨密度)与体重、体成分的关系[J]. 中医正骨, 2004,16(10): 61-62 |
| [20] | 李继斌. 骨量影响因素研究进展[J]. 环境卫生学杂志, 2000(4): 213-217 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |