

俄罗斯马特盖奇克遗址、卡缅内洛卡遗址试掘简报
收稿日期: 2019-07-16
网络出版日期: 2021-05-06
基金资助
中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(B类:XDB26030203)
A preliminary report on the investigation and excavation of Matkechik site and Kamennyy Log site in Russia
Received date: 2019-07-16
Online published: 2021-05-06
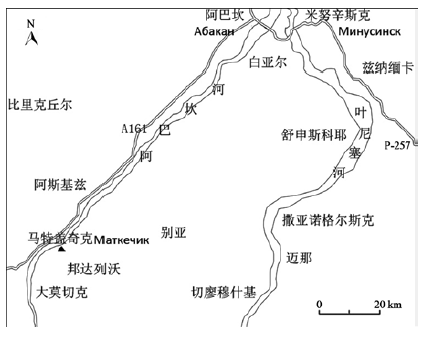
2017年8~9月,重庆市文化遗产研究院同俄罗斯科学院西伯利亚分院考古学与民族学研究所组成联合考古队,对西伯利亚两处旧石器时代遗址进行考古调查与试掘。通过调查与试掘,在叶尼塞河支流—阿巴坎河流域确认了一处旧石器时代晚期遗址—马特盖奇克遗址,该遗址石制品主要包括石核、石片和石器,原料主要是火山岩、燧石和石英岩。通过阶地比对,初步认为该遗址时代为旧石器时代晚期。另外,对库尔塔克卡缅内洛卡遗址的再次发掘出土了44件石制品,包含石核、石片和石器,原料主要是燧石、石英岩和火山岩。此次发掘进一步充实了该遗址的考古材料,也有利于进一步完善该遗址的考古年代学序列。
高磊 , 邹后曦 , 汪伟 , 代玉彪 , Nikolay Ivanovich DROZDVO . 俄罗斯马特盖奇克遗址、卡缅内洛卡遗址试掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2022 , 41(01) : 148 -156 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0022
In order to have a further understanding of paleolithic sites in Siberia, a joint archaeological team of Chongqing Institute of Cultural Heritage and Institute of Archaeology and Ethnography of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences was established in 2017. From August to September, two paleolithic sites in the Yenisei river were investigated and excavated, and a new paleolithic site named Matkechik in the valley of the Abakan River was surveyed. Matkechik site (near the village of Matkechik) is located in Abakan city, Republic of Khakassia. The artifacts excavated from the site include pebble cores, flakes and tools. The main raw material of the lithics are volcanics, chert and quartzite. Compared with other sites in the same terrace and similar burial context in the Yenisei River Basin, the age of the Matkechik site should be dated to the late Pleistocene.
Besides, an re-excavation was carried out in Kamennyy Log site, which is located in Kurtak geo-archaeological district. An area of 8 m2 was excavated, 44 pieces of artifacts excavated from Cultural Horizon 1 and a piece of stone artifacts was excavated from the profile surface of Cultural Horizon 2. The stone assemblage includes flak cores, flakes, chips and retouched tools, such as scrappers and drill. The raw material can be classified into 4 types, namely chert, vein quartz, quartzite and volcanics, while only chert and vein quartz were major raw materials. This excavation further enriched the archaeological materials of the site and was also conducive to further improving the archaeological chronology sequence of the site.

Key words: Siberia; Late Paleolithic; Matkechik site; Kamennyy Log site
| [1] | 高星. 周口店第15地点石器原料开发方略与经济形态研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2001, 20(3): 186-200 |
| [2] | 卫奇. 石制品观察格式探讨[A].见:第八届古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2001: 209-218 |
| [3] | Абрамова З.А. Палеолит Енисея[M]. Ленинград, 1991: 37-38 |
| [4] | Гурина ВИ. Мезолит и неолит на поселении Бирюса[J]. Этногенез народов Северной Азии. Новосибирск, 1969, Вып.1 |
| [5] | Акимова EB. Поздний палеолит красноярского водохранилища[J]. Иркутского Госудрственного Университета Серия Геоархеология, 2011, 10(7): 111-118 |
| [6] | Zander A, Frechen M, Zykina V, et al. Luminescence chronology of the Upper Pleistocene loess record at Kurtak in Middle Siberia[J]. Quaternary ence Reviews, 2003, 22(10): 999-1010 |
| [7] | Frechen M, et al. The loess record from the section at Kurtak in Middle Siberia[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2005, 228: 228-244 |
| [8] | Kuzmin YV, Orlova LA. Radiocarbon Chronology of the Siberian Paleolithic[J]. Journal of World Prehistory, 1998, 12(1): 1-53 |
| [9] | VasiI’ev SA. The Late Paleolithic of the Yenisei: A New Outline[J]. Journal of World Prehistory, 1992, 6(3): 1-47 |
| [10] | Derevianko AP, Shimkin DB, Powers WR. The Paleolithic of Siberia: new discoveries and interpretations[M]. Champaign: Illinois University Press, 1998 |
| [11] | Drozdov NI, Chekha VP, Laukhin SA, et al. Chronostratigraphy of Palaeolithic sites of Central Siberia (the Yenisei Basin)[A]. In: Chronostgratigraphy of Palaeolithic of Northern, Central and Eastern Asia, and America[C]. Novosibirsk, 1990, 7-64 |
| [12] | Cherkinskiy AE, Akimova EV, Bokarev AA, et al. Radiocarbon dating of Palaeolithic sites in the Yenisei River valley in the Eastern Sayan Foothills[A]. In: The Kurtak Archaeological Region: New Data on Chronostratigraphy of the Kurtak Archaeological Region (Palaeoecological Aspects)[C]. Krasnoyarsk, 1990, 10-18 |
| [13] | Orlova IL, Laukhin SA, Chekha VP. Radiocarbon dates of the Kurtak Pedocomplex[A]. In: Chronostgratigraphy of Palaeolithic of Northern, Central and Eastern Asia, and America[C]. Krasnoyarsk, 1990, 3-9 |
| [14] | Svezhentsev, Yu C, Lisitsin NF, et al. Radiocarbon chronology of the Yenisei Palaeolithic[A]. In: Chronostgratigraphy of Palaeolithic of Northern, Central and Eastern Asia, and America[C]. Novosibirsk, 1990, 57-64 |
| [15] | Chlachula J. Pleistocene climate change, natural environments and palaeolithic occupation of the upper Yenisei area, south-central Siberia[J]. Quaternary International, 2001, 80-81: 101-130 |
| [16] | Chlachula J. The Siberian loess record and its significance for reconstruction of Pleistocene climate change in north-central Asia[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003, 22: 1879-1906 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |