

新疆且末县加瓦艾日克墓地人骨研究
收稿日期: 2021-04-20
修回日期: 2021-06-16
网络出版日期: 2021-12-17
基金资助
中国社会科学院创新工程(2021KGYJ015)
A study of human bones from the Gavaerk cemetery in Qiemo county, Xinjiang
Received date: 2021-04-20
Revised date: 2021-06-16
Online published: 2021-12-17
本文通过对新疆且末县托乎拉克勒克乡加瓦艾日克村29座墓地出土的人骨标本进行了观察和分析。共鉴定出150例个体,其中男性73例、女性50例、性别不明者27例。男性、女性平均死亡年龄分别为36.3岁和35.6岁。形态学的分析指出且末人群更多地具有欧洲人种的特点,如鼻根凹陷深、鼻骨明显突起及犬齿窝深等。聚类分析结果显示且末人群与新疆古代人群焉布拉克C组、察吾呼四号组、多岗等人群较为接近。文章还根据线粒体DNA的分析结果讨论了且末古代人群的种族属性,古DNA的分析揭示出且末人群存在欧亚大陆东、西部人群的基因交流,并进一步指出其西部类型的成分来源极有可能来自西伯利亚,其东部成分可能来自西伯利亚或中国甘肃,只是东西方人群的基因融合规模小而且处于初级阶段,所以并未在颅面部形态特征上有大规模明显的改变。此外,本文从考古学文化、体质人类学研究以及古DNA等几个方面探讨了新疆地区古代人群的种族成分来源。本文还对且末人群的身高进行了推算,对一例变形颅骨以及骨骼上的创伤作了简要描述。
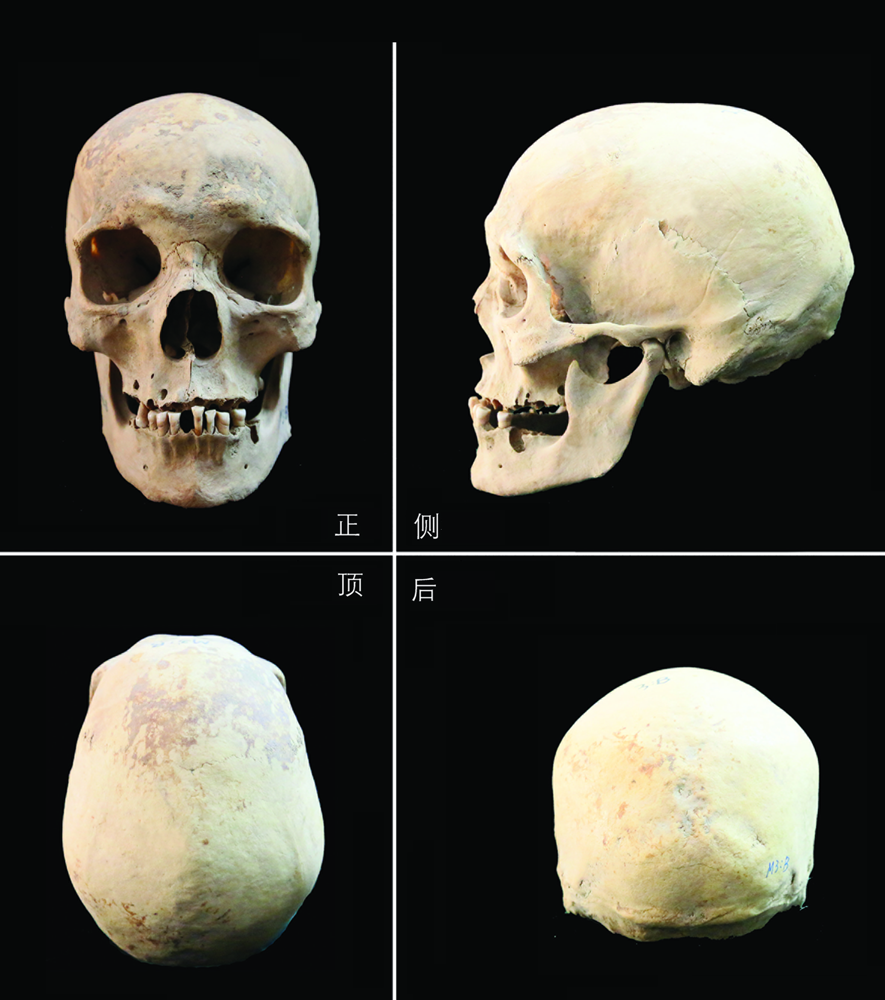
张雅军 , 张旭 . 新疆且末县加瓦艾日克墓地人骨研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2021 , 40(06) : 981 -992 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0074
The present study summarizes a combined biological and cultural assessment of human skeletal remains from Gavaerk cemetery at Qiemo County, Xinjiang, to decipher trends related to population variation, health, and lifestyle in this region. The skeletal assemblage of Qiemo was unearthed from 29 burials, consisting of 150 individuals (MNI; 73 males, 50 females, and 27 undetermined). Males had an average age at death of 36.3 years, while females had 35.6 years. Cranial osteometric results largely indicate that Qiemo people appear to have considerable phenetic similarities with European groups, namely, depressed nasion, highly arched nasals, and deep canine fossa. Cluster analysis also suggests that Qiemo people have a close morphological affinity to ancient populations in Xinjiang, such as Yanbulaq group C, Charwighul group IV, and Duogang. Even though very limited “Mongolian” phenetic characteristics have been captured from Qiemo people, integrated with ancient mitochondrial DNA, material culture, and cranial morphological analyses, this paper reveals a genetic admixture with populations from Eurasia, suggesting a possible dual ancestry stemming from two different areas: one, most likely from Siberia; the other from Gansu, China. Nevertheless, the genetic interactions between ancient groups may have been at an early stage, so that the patterns observed in craniofacial morphology of the Qiemo people are not congruent with their genetic structure. In addition, this paper preliminarily examined the stature, trauma, and cranial pathology (cranial deformation of one individual) in this sample.

Key words: Xinjiang; Qiemo; Human skeleton; Spring and Autumn Period; Warring State
| [1] | 韩康信. 新疆古代居民种族研究[A].见:韩康信.丝绸之路古代居民种族人类学研究[M]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆人民出版社, 2009: 1-22 |
| [2] | 中国社会科学院考古研究所新疆队, 新疆巴音郭楞蒙古自治州文管所. 新疆且末县加瓦艾日克墓地的发掘[J]. 考古, 1997(9):21-32 |
| [3] | Jane EB, Douglas HU. Standards for data collection from human skeletal remains[M]. AR: Arkansas Archeological Survey, 1994: 15-38 |
| [4] | 吴汝康, 吴新智, 张振标. 人体测量方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984: 11-24 |
| [5] | 邵象清. 人体测量手册[M]. 上海: 上海辞书出版社, 1985: 57-110 |
| [6] | 雅·雅·罗金斯基, 马·格·列文. 人类学[M]. 译者:王培英,汪连星,史庆礼,等. 北京: 警官教育出版社, 1993: 525 |
| [7] | 张君. 新疆拜城县多岗墓地人骨的种系研究[J]. 边疆考古研究(第12辑), 2012(2):397-422 |
| [8] | 陈靓, 汪洋. 新疆拜城克孜尔墓地人骨的人种学研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2005, 24(3):188-197 |
| [9] | 邵兴周, 崔静, 杨振江, 等. 洛浦县山普拉出土颅骨的初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1988, 7(1):26-38 |
| [10] | 韩康信. 新疆孔雀河古墓沟墓地人骨研究[J]. 考古学报, 1986(3):361-384 |
| [11] | 韩康信. 新疆哈密焉布拉克古墓人骨种系成分研究[J]. 考古学报, 1990(3):371-390 |
| [12] | 魏东, 赵永生, 常喜恩, 等. 哈密天山北路墓地出土颅骨的测量性状[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(4):395-406 |
| [13] | 聂颖. 伊犁恰甫其海水库墓地出土颅骨人类学研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2014: 26-68 |
| [14] | 韩康信, 张君, 赵凌霞. 察吾呼三号、四号墓地人骨的体质人类学研究[A].见:新疆文物考古研究所.新疆察吾呼[M]. 北京: 东方出版社, 1999: 305-321 |
| [15] | 陈靓. 鄯善苏贝希青铜时代墓葬人骨的研究[A].见:吉林大学考古系(编).青果集——吉林大学考古系建系十周年纪念文集[C]. 北京: 知识出版社, 1998: 237-254 |
| [16] | 韩康信. 阿拉沟古代丛葬墓人骨研究[A].见:韩康信.丝绸之路古代居民种族人类学研究[M]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆人民出版社, 2009: 56-146 |
| [17] | 陈靓. 新疆察布查尔县索墩布拉克墓地出土人头骨研究[J]. 考古, 2003(7):87-98 |
| [18] | Trotter M, Gleser GC. A re-evaluation of estimation of stature based on measurements of stature taken during life and of long bones after death[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1958, 16(1):79-123 |
| [19] | Pearson K, Bell J. A study of the long bones of the English skeleton[M]. London: Cambridge University Press, 1917.转引自张君. 河南商丘潘庙古代人骨种系研究[A].见:中国社会科学院考古研究所.考古求知集—96考古研究所中青年学术讨论会文集[C].北京:中国社会科学出版社, 1997: 486-498 |
| [20] | 韩康信, 潘其风. 古代中国人种成分研究[J]. 考古学报, 1984(2):245-263 |
| [21] | 吕恩国. 论颅骨穿孔和变形[J]. 新疆文物, 1993(1):107-120 |
| [22] | 张林虎. 新疆伊犁吉林台库区墓葬人骨研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2010: 107-109 |
| [23] | 陈靓. 新疆尉犁县营盘墓地古人骨的研究[J]. 边疆考古研究, 2002: 323-341 |
| [24] | 韩康信. 察吾呼沟三、四号墓地人骨研究[A].见:韩康信.丝绸之路古代居民种族人类学研究[M]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆人民出版社, 2009: 318-355 |
| [25] | 从德新, 刘辉, 陈戈. 新疆和静县察吾乎沟口三号墓地发掘简报[J]. 考古, 1990(10):882-889 |
| [26] | 吕恩国. 吐鲁番洋海墓地出土游牧民器物研究[J]. 吐鲁番学研究, 2020(1):1-18 |
| [27] | 徐智. 中国西北地区古代人群的DNA研究[D]. 上海:复旦大学, 2008 |
| [28] | 崔银秋, 段然慧, 周慧, 等. 新疆古代居民的遗传结构分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2002, 23(12):2278-2280 |
| [29] | 高诗珠. 中国西北地区三个古代人群的线粒体DNA研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2009: 68 |
| [30] | 中国社会科学院考古研究所, 新疆维吾尔自治区阿克苏地区文物局, 拜城县文物局. 拜城多岗墓地[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2014: 275-280 |
| [31] | 水涛. 新疆青铜时代诸文化的比较研究[A].见: 水涛.中国西北地区青铜时代考古论集[C]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 95-116 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |