

百色盆地六林岭旧石器遗址试掘报告
收稿日期: 2019-07-29
网络出版日期: 2022-02-15
基金资助
中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(B类: XDB26000000);国家自然科学基金项目(41977379)
A report of the trial excavation of the Liulinling Paleolithic site in the Bose Basin
Received date: 2019-07-29
Online published: 2022-02-15
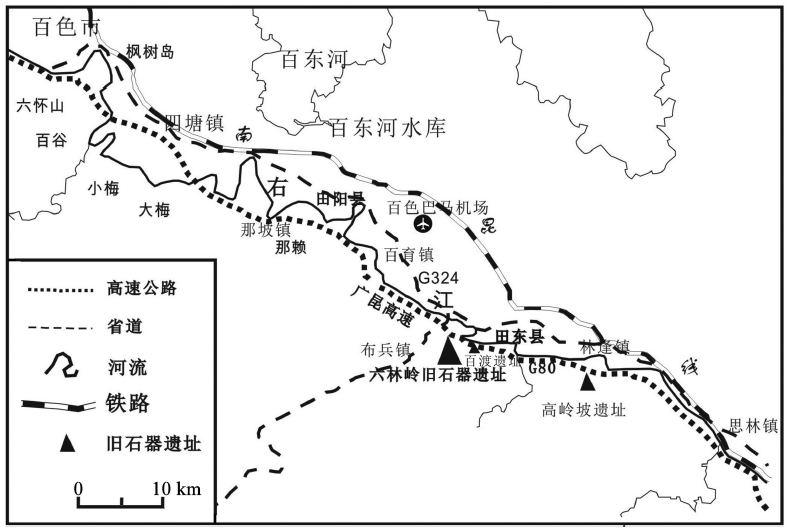
本文是对2018年广西百色六林岭旧石器遗址试掘结果的报道。试掘共开7个探方(面积28 m2)和1条探沟,可见9层堆积,从两个层位共获得石制品182件(其中地层出土40件,采集142件)。虽然两个文化层石制品在埋藏和保存状况上存在明显差异,但属于同一个技术传统。石制品分为备料、石锤、石核、石片、断块和石器;石器包括砍砸器、手镐和刮削器。在第一文化层发现了与石制品伴生的玻璃陨石碎片,初步推测其年代为803 kaBP,尚不排除二次堆积的可能;第二文化层在第一文化层之下,年代要早于第一文化层,表明古人类在百色盆地持续活动了相当长的一段时间;两个文化层显示出不同的沉积环境,表明古人类在百色盆地生存环境的复杂性和多样性。
高立红 , 侯亚梅 , 黄秋艳 , 李金燕 , 陆正勤 , 黄德奖 . 百色盆地六林岭旧石器遗址试掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2022 , 41(01) : 135 -147 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0024
This paper is a preliminary report of one test excavation and study of stone artifacts from work at the Liulinling Paleolithic site of Bose Basin in 2018. Liulinling Site (23°36′53′′N, 107°01′5′′E) is located in the Baidu village, Tiandong county, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. The excavation revealed an area of 28 m2 (excluding trenches), and 9 stratigraphic layers were identified. Totally 182 stone artifacts were obtained, of which 40 were unearthed from two culture layers. The stone artifacts include manuports, cores, stone hammers, flakes, tools and fragments. The flaking technique was direct hard hammer percussion. Tool types include choppers, picks and scrapers. In the first cultural layer, a piece of tektite fragment was uncovered along with the stone artifacts. It still need more work to confirm that if it belongs to deposit in situ. The second cultural layer is below the first one, its age can be primarily estimated as 803 kaBP at latest. This suggests that the time when ancient human appeared in the Bose basin is as early as 803 kaBP and lived here for a longer time. The different depositional environments of the two cultural layers indicates the complexity and diversity of adaptation of ancient human here.

Key words: Bose basin; Liulinling; Stone artifacts; Early Paleolithic
| [1] | 谢光茂, 林强, 黄鑫. 百色田东百渡旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(4): 355-371 |
| [2] | Bordes F. The old stone age[M]. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. 1968, 1-256 |
| [3] | Debenath A, Dibble HL. Hand book of Paleolithic Typology: Lower and Middle Paleolithic of Europe[M]. Univ Museum Pubns, 1994, 1-256 |
| [4] | 黄启善. 百色旧石器[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2003, 1-180 |
| [5] | 黄慰文, 何乃汉, 佐川正敏. 百色旧石器——中国广西百色遗址群发现的手斧对比研究[J]. 2001, 1-71 |
| [6] | 卫奇. 《西侯度》石制品之浅见[J]. 人类学学报, 2000, 19(2): 99-102 |
| [7] | Toth N. The Oldowan reassessed: a close look at early stone artifacts[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1985, 12(2): 101-120 |
| [8] | 李炎贤, 尤玉柱. 广西百色发现的旧石器[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1975, 13(4): 225-228 |
| [9] | Huang SM, Wang W, Bae CJ, et al. Recent Paleolithic field investigations in Bose Basin (Guangxi, China)[J]. Quaternary International, 2011, 1-5 |
| [10] | Wang W, Bae CJ. How old are the Bose (Baise) Basin (Guangxi, southern China) bifaces? The Australasian tektites question revisited[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2014, 1-4 |
| [11] | 黄慰文. 中国的手斧[J]. 人类学学报, 1987, 6(1): 61-68 |
| [12] | 黄慰文, 冷健, 员晓枫, 等. 对百色石器层位和时代的新认识[J]. 人类学学报, 1990, 9(2): 105-112 |
| [13] | Hou YM, Potts R, Yuan BY, et al. Mid-Pleistocene Acheulien-like stone technology of the Bose basin, South China[J]. Science, 2000, 287: 1622-1626 |
| [14] | 郭士伦, 郝秀红, 陈宝流, 等. 用裂变径迹法测定广西百色旧石器遗址的年代[J]. 人类学学报, 1996, 15(4): 347-350 |
| [15] | 谢光茂, 林强, 余明辉, 等. 广西百色盆地高岭坡遗址的地层及年代[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(1): 106-117 |
| [16] | 谢光茂, 林强, 韦江. 百色盆地旧石器时代考古发掘取得重大突破[N]. 中国文物报, 2007-05-04 |
| [17] | 廖卫, 李金燕, 李大伟, 等. 广西田阳县那赖旧石器遗址发现的石制品和玻璃陨石[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(4): 765-777 |
| [18] | 高立红, 袁俊杰, 侯亚梅. 百色盆地高岭坡遗址的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(2): 137-148 |
| [19] | 侯亚梅, 高立红, 黄慰文, 等. 百色高岭坡旧石器遗址1993年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2011, 30(1): 1-12 |
| [20] | Li H, Li CR, Kuman K. Rethinking the “Acheulean” in East Asia: Evidence from recent investigations in the Danjiankou Reservoir Region, central China[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 341(1): 163-175 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |