

新疆吐鲁番胜金店墓地人骨的牙齿微磨耗
收稿日期: 2020-11-26
修回日期: 2021-01-06
网络出版日期: 2022-04-13
基金资助
霍英东教育基金会高等院校青年教师基金基础性研究课题项目(141111);国家留学基金资助(202106170051)
Dental microwear analysis of human teeth in Shengjindian cemetery, Turpan, Xinjiang
Received date: 2020-11-26
Revised date: 2021-01-06
Online published: 2022-04-13
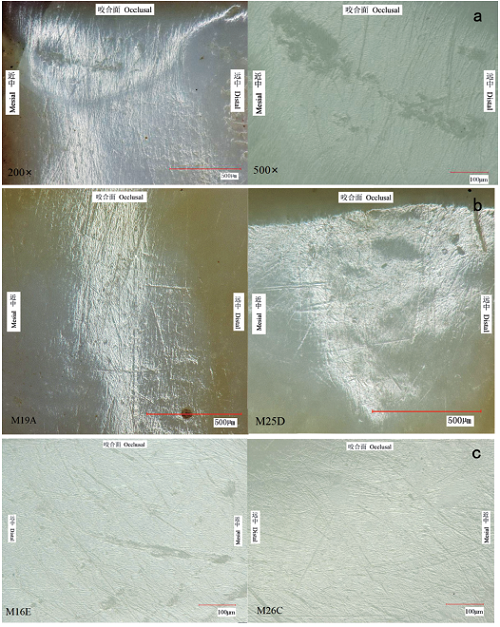
本文使用不同倍率的超景深电子显微镜,对新疆吐鲁番胜金店墓地中出土的13例臼齿的颊侧微磨耗形态进行了观察和研究。通过对臼齿颊侧表面凹坑和条痕形态微磨耗的测量和统计,计算出每例牙齿的微痕数量、均长、均宽、凹坑百分比和Lh/Lv比值,按照性别和年龄分组进行人群内的数据对比分析。研究结果表明,该人群中年龄较大的个体摄入更高比例的植物类食物;两性的食物结构不存在显著性差异,男性摄入植物类食物比例略高,女性的食物结构在不同的年龄阶段有所差异。将胜金店墓地人群与不同生计方式人群的Lh/Lv比值进行人群间的差异性分析,并结合胜金店墓地的随葬品特点推测,胜金店墓地人群的食物结构以肉类食物为主,其生计模式以游牧业为主,兼营种植类经济。
杨诗雨 , 张群 , 王龙 , 张全超 . 新疆吐鲁番胜金店墓地人骨的牙齿微磨耗[J]. 人类学学报, 2022 , 41(02) : 218 -225 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0029
In this study, based on the human teeth yielded from Shengjindian cemetery, the buccal surfaces of 13 molars were observed under different magnifications with hyper-filed 3D electron microscope. The statistics and comparative analysis on the scratches and pits of the molar buccal surfaces in terms of the gender and age suggested that the older individuals and male ingested a higher proportion of plant food and female tend to ingested less meat with age increasing. In addition, there was no significant difference in dietary composition between male and female. It could be inferred from the comparative analysis of Lh/Lv among the different populations(Shengjindian people, modern humans and other Chinese ancient populations) and the characteristics of the funerary objects that the main subsistence pattern of the population of Shengjindian was nomadic herding and the animal products was the dominant food in their daily dietary. Meanwhile, there also existed some proportion of agriculture.

| [1] | Ungar PS. Dental evidence for diet in primates[J]. Anthropologiai Közlemények, 1992, 34:141-155 |
| [2] | Ungar PS, Spencer MA. Incisor microwear, diet, and tooth use in three Amerindian populations[J]. American journal of physical anthropology, 1999, 109(3):387-396 |
| [3] | Romero A, Juan JD. Intra- and interpopulation human buccal tooth surface microwear analysis: Inferences about diet and formation processes[J]. L Anthropologie, 2007, 45:61-70 |
| [4] | El-Zaatari S. Occlusal molar microwear and the diets of the ipiutak and tigara populations (point hope) with comparisons to the aleut and arikara[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2008, 35(9):2517-2522 |
| [5] | Pérez-Pérez A, Lalueza C, Turbón D. Intraindividual and intragroup variability of buccal tooth striation pattern[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1994, 94(2):175-187 |
| [6] | 张全超, 李墨岑, 张群, 等. 内蒙古哈民忙哈遗址史前居民牙齿微磨耗形态观察与研究[J]. 边疆考古研究, 2017(2):357-366 |
| [7] | Homes Hogue S, Melsheimer R. Integrating dental microwear and isotopic analyses to understand dietary change in east-central Mississippi[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science. 2008, 35(2):228-238 |
| [8] | Mahoney P. Dental microwear from natufian hunter-gatherers and early neolithic farmers: Comparisons within and between samples[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2006, 130(3):308-319 |
| [9] | Puech P, Albertini H, Serratrice C. Tooth Microwear and Dietary Patterns in Early Hominids from Laetoli, Hadar and Olduvai[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 1983, 12:721-729 |
| [10] | Lalueza C, Pérez-Pérez A, Turbon D. Dietary Inferences through Buccal Microwear Analysis of Middle and Upper Pleistocene Human Fossils[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1996, 100(3):367-387 |
| [11] | 李肖, 张永兵, 祖力皮亚, 等. 新疆吐鲁番胜金店墓地2号墓发掘简报[J]. 文物, 2013(3):20-24 |
| [12] | 李志丹. 新疆吐鲁番胜金店墓地人骨研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2015 |
| [13] | 【东汉】 班固. 汉书·西域传[M]. 北京:中华书局, 1999: 2855-2857 |
| [14] | 吐鲁番学研究院. 新疆吐鲁番市胜金店墓地发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2013(02):29-55 |
| [15] | 张雯欣. 新疆吐鲁番加依墓地青铜——早期铁器时代居民牙齿磨耗研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2018 |
| [16] | 张全超, 韩涛, 张群. 新疆鄯善洋海墓地出土人骨的牙齿微磨耗痕迹研究[J]. 西域研究, 2018(3):83-88+145-146 |
| [17] | 蒋洪恩. 吐鲁番洋海墓地植物遗存与古洋海人及环境之间的关系[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学, 2006 |
| [18] | 支禄. 见证吐鲁番农业从游牧走向农耕[N]. 吐鲁番日报(汉), 2014-04-24 (004) |
| [19] | 李亚, 李肖, 曹洪勇, 等. 新疆吐鲁番考古遗址中出土的粮食作物及其农业发展[J]. 科学通报, 2013(S1):40-45 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |