

中国曼咪人的体质特征
收稿日期: 2023-10-08
修回日期: 2024-03-25
网络出版日期: 2024-08-13
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(32071185);天津市科学技术普及项目(23KPHDRC00160)
Physical characteristics of the Manmi people in China
Received date: 2023-10-08
Revised date: 2024-03-25
Online published: 2024-08-13
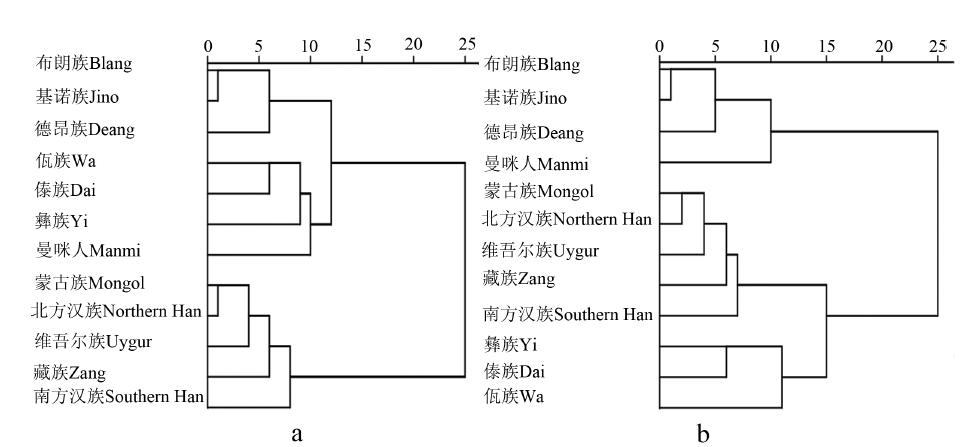
研究组在云南省西双版纳测量、调查了曼咪人121例成年人的61项体质指标、20项体质指数与13项观察指标,研究结果显示:曼咪人身高、头长等56项指标值性别间差异具有统计学意义;除女性大腿围大于男性外,其余55项指标值均男性大于女性。曼咪人男女性上眼睑皱褶出现率男性为94.3%,女性为85.3%;蒙古褶率男性为28.3%,女性为33.8%。曼咪人眼外角多高于眼内角,鼻背侧面观以直型为主,耳垂多为圆形。曼咪人男女性均以圆头型、高头型、超阔面型、中鼻型、宽胸型、宽肩型、宽骨盆型出现率最高。与国内族群比较,曼咪人男女体质特征与布朗族、基诺族接近,属于南方族群体质特征。与国外族群比较,曼咪人男性头面部特征与泰国人最为接近,女性则与越南人最为接近。
张兴华 , 肖瑶 , 岩坎翁 , 玉应香 , 高雯芳 , 包金萍 , 程智 , 高新颖 , 姚玥彤 , 刘鑫 , 宇克莉 . 中国曼咪人的体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2024 , 43(04) : 561 -573 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0051
A survey was conducted on 61 physical parameters, 20 body indices and 13 somatoscopic characteristics of 121 Manmi adults (53 males and 68 females) in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan Province. The results are as follows: The gender differences are statistically significant in 56 physical parameters such as stature, mass and head length. Except for the fact that the thigh circumference is greater in females than in males, the remaining 55 physical parameters are all greater in males than in females. There are statistically significant gender differences in the thickness of lips, opening height of eyeslits, nasal root height, nasal profile and hair occurrence rate of Manmi. Manmi mainly have lissotrichous, with 94.3% of males and 85.3% of females having eyefold of upper eyelid. Male mongoloid folds account for 28.3%, while female mongoloid folds account for 33.8%. The opening height of eyeslits is mainly medium, with the external angle of the eye being mostly higher than the internal angle. The nasal root height is mainly medium, and when the nasal profile is mainly straight. The nasal base is mostly upturned, and the maximal diameter of nostrils is mainly oblique.===The lobe types are mostly round, the chin is mostly straight, and the upper lip height is mainly medium. The physiognomic facial index, morphological facial index, transverse cephalo-fcaial index, vertical cephalo-fcaial index, manouvrier's skelic index and stature-shoulder breadth index of Manmi have statistically significant differences between genders, with male index values higher than females. The length-height index of head, stature-sitting height index, stature-crista iliaca index, stature-height of suprasteral notch above sitting plane index and acromio-cristal index of Manmi also have statistically significant differences between genders, with male index values being lower than females. According to the occurrence rate of index classification, Manmi adults have brachycephaly, hypsicephalic, hypereuryprosopy, mesorrhiny, wide chest, wide shoulder and wide crista iliaca. Compared with domestic ethnic groups, the Manmi physical characteristics are similar to those of the Blang and Jino, and belong to the physical characteristics of southern ethnic groups. The stature, sitting height, crista iliaca breadth, head breadth and morphological facial height of Manmi are relatively small, while the nose breadth, mouth breadth, lip height and nasal height are all relatively large. Compared with foreign ethnic groups, the male head and facial features of Manmi are closest to those of Thai people, while the female head and facial features of Manmi are closest to those of Vietnamese. The physical characteristics of Manmi are related to genetic factors, environmental factors and economic conditions.

Key words: Manmi; Anthropometry; Head and face; Physical characteristic; Cluster analysis
| [1] | 陈国庆. 克蔑语研究[M]. 北京: 民族出版社, 2005 |
| [2] | 李兴军. 文化主体性与创新乡村旅游发展基本理念:基于云南江头曼咪村旅游发展“停滞”现象的调查[J]. 北方民族大学学报, 2020, 3: 56-61 |
| [3] | 陈丽晖, 梁晓慧, 李科. 基于陆稻地方品种农家保护决策行为的支持系统研究:以云南省景洪市江头曼咪寨为例[J]. 云南地理环境研究, 2009, 21(2): 7-15 |
| [4] | 宇克莉, 杜慧敏, 贾亚兰, 等. 布朗族的体质特征[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2017, 40(5): 574-579+602 |
| [5] | 包金萍, 郑连斌, 宇克莉, 等. 基诺族体质特征及35年来体质的变化[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(2): 261-271 |
| [6] | 李咏兰, 郑连斌. 中国蒙古族体质人类学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018 |
| [7] | 郑连斌, 李咏兰, 席焕久, 等. 中国汉族体质人类学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017 |
| [8] | 李咏兰, 宇克莉, 张兴华, 等. 藏族的体质类型和人种学特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(4): 698-711 |
| [9] | 宇克莉, 董文静, 李咏兰, 等. 四川凉山彝族的人体测量学[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(3): 478-483 |
| [10] | 宇克莉, 李咏兰, 张兴华, 等. 维吾尔族体质类型:来自喀什的资料[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2020, 50(9): 983-995 |
| [11] | 宇克莉, 郑连斌, 李咏兰. 西双版纳傣族的人种学特点:来自人体测量学的数据[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(4): 553-560 |
| [12] | 席焕久, 陈昭. 人体测量方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010 |
| [13] | 金力, 席焕久, 郑连斌. 中华民族体质表型调查报告[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2024 |
| [14] | Farkas LG, Katic MJ, Forrest CR, et al. International Anthropometric Study of Facial Morphology in Various Ethnic Groups/Races[J]. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 2005, 16(4): 615-646 |
| [15] | 李祎, 赵雯婷, 李丹, 等. EDARV370A对新疆维吾尔族人群面部及耳朵形态的效应[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(11): 1024-1034 |
| [16] | Zhang M, Wu S, Du S, et al. Genetic variants underlying differences in facial morphology in East Asian and European populations[J]. Nature Genet, 2022, 54: 403-411 |
| [17] | 杜抱朴, 殷钰喆, 谭伊, 等. 中国现代人群两性身高差异分布及其影响因素[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(2): 191-200 |
| [18] | 刘祥君, 张兴华, 席焕久, 等. 中国汉族乡村成年人的身高与体质量的地理性分布[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(3): 484-495 |
| [19] | 赵钟鸣, 沈建华, 胡梅影, 等. 双生子的身高等形态指标的遗传度及身高的影响因素和预测的分析[J]. 中国优生与遗传杂志, 2007, 11: 110-113 |
| [20] | Marouli E, Graff M, Medina-Gomez C, et al. Rare and low-frequency coding variants alter human adult height[J]. Nature, 2017, 542(7640): 186-190 |
| [21] | Li Q, Chen J, Faux P, et al. Automatic landmarking identifies new loci associated with face morphology and implicates Neanderthal introgression in human nasal shape[J]. Commun Biol, 2023, 6(1):481 |
| [22] | Bonfante B, Faux P, Navarro N, et al. A GWAS in Latin Americans identifies novel face shape loci, implicating VPS13B and a Denisovan introgressed region in facial variation[J]. Sci Adv, 2021, 7(6): eabc6160 |
| [23] | Kun E, Javan EM, Smith O, et al. The genetic architecture and evolution of the human skeletal form[J]. Science, 2023, 381(6655): eadf8009 |
| [24] | Will M, Krapp M, Stock JT, et al. Different environmental variables predict body and brain size evolution in Homo[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12: 4116 |
| [25] | Serrat MA, King D, Lovejoy CO. Temperature regulates limb length in homeotherms by directly modulating cartilage growth[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2008, 105(49): 19348-19353 |
| [26] | Katzmarzyk PT, Leonard WR. Climatic influences on human body size and proportions: ecological adaptations and secular trends[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1998, 106(4): 483-503 |
| [27] | 杜抱朴, 杜靖. 从头面部测量性状分析中国现代人群体质类型及其成因[J]. 解剖学报, 2019, 50(6): 805-815 |
| [28] | 马立广, 曹彦荣, 徐玖瑾, 等. 中国102个人群的身高与地理环境相关性研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(3): 223-231 |
| [29] | 向小雪, 郑连斌, 宋晴阳, 等. 中国14个未识别群体的体部特征[J]. 解剖学报, 2020, 51(5): 802-808 |
| [30] | Wells JCK. Ecogeographical associations between climate and human body composition: Analyses based on anthropometry and skinfolds[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2012, 147(2): 169-186 |
| [31] | 字冉, 孔震, 朱原钦. 1959—2018年西双版纳热带雨林地区气候特征分析[J]. 农业灾害研究, 2019, 9(6): 61-66+114 |
| [32] | 李咏兰, 郑连斌. 中国人群的体部指数[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(5): 848-861 |
| [33] | 李咏兰, 张兴华, 孙泽阳, 等. 中国人的头面部形态特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(3): 450-462 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |