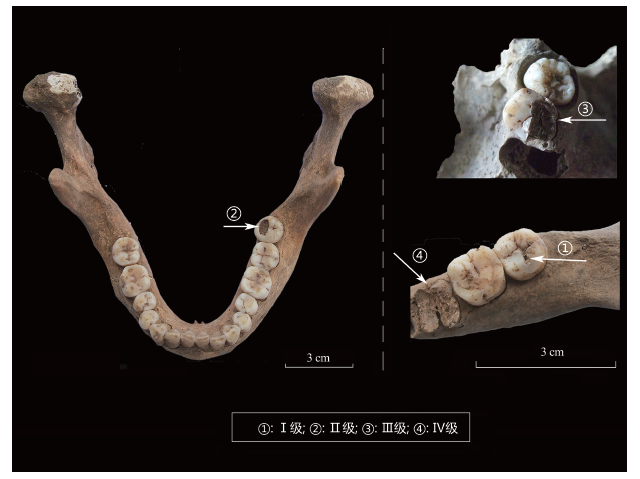
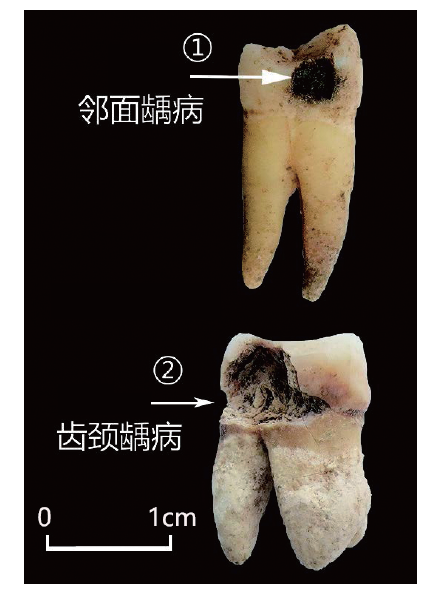
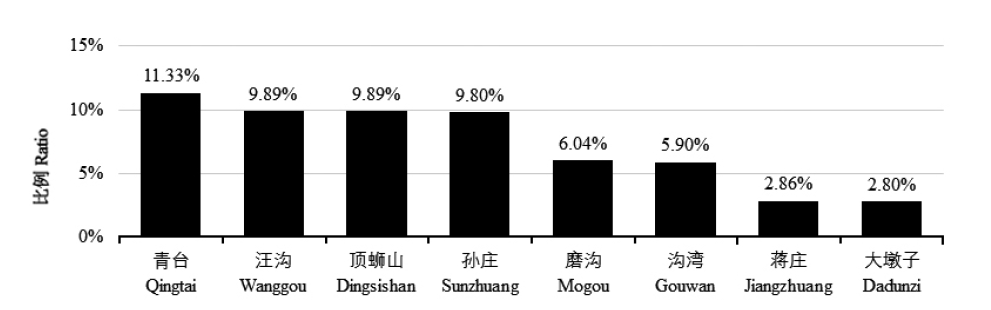
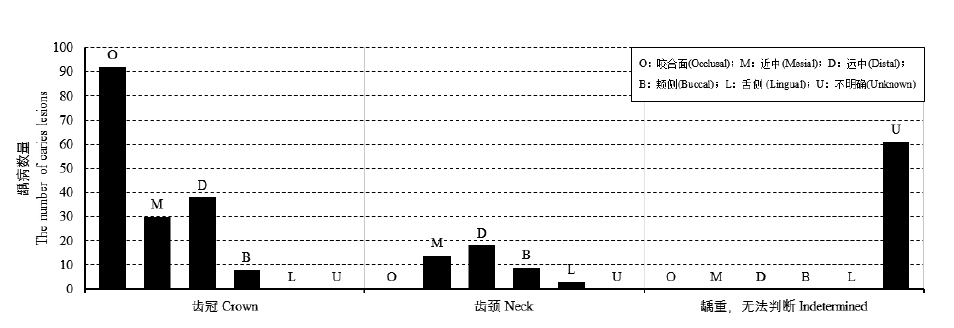
| [1] |
Hillson S. Tooth Development in Human Evolution and Bioarchaeology[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014
|
| [2] |
Halvorsrud K, Lewney J, Craig D, et al. Effects of starch on oral health: Systematic review to inform WHO guideline[J]. Journal of Dental Research, 2018(1):46-53
|
| [3] |
Giacaman RA. Sugars and beyond. The role of sugars and the other nutrients and their potential impact on caries[J]. Oral Disease, 2017(7):1185-1197
|
| [4] |
Bradshaw DJ, Lynch RJM. Diet and the microbial aetiology of dental caries: new paradigms[J]. International Dental Journal, 2013: 64-72
|
| [5] |
Tayles N, Domett K, Nelsen K. Agriculture and dental caries? The case of rice in prehistoric Southeast Asia[J]. World Archaeology, 2000, 32(1):68-83
pmid: 16475298
|
| [6] |
Sivamaruthi BS, Kesika P, Chaiyasut C. A review of the role of probiotic supplementation in dental caries[J]. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins, 2020(4):1300-1309
|
| [7] |
Albino J, Tiwari T. Behavior change for caries prevention: Understanding inconsistent results[J]. JDR Clinical and Translational Research, 2019(1):6-9
|
| [8] |
Lukacs JR, Largaespada LL. Explaining sex differences in dental caries prevalence: Saliva, hormones, and “life-history” etiologies[J]. American Journal of Human Biology, 2006, 18(4):540-555
pmid: 16788889
|
| [9] |
Sheiham A, James WPT. Diet and dental caries: The pivotal role of free sugars reemphasized[J]. Journal of Dental Research, 2015(10):7-13
|
| [10] |
郑州市文物考古研究所. 荥阳青台遗址出土纺织物的报告[J]. 中原文物, 1999(3):4-9
|
| [11] |
夏鼐. 河南成皋廣武區考古紀略[J]. 科学通报, 1951(7):724-729
|
| [12] |
张松林, 赵清. 青台仰韶文化遗址1981年上半年发掘简报[J]. 中原文物, 1987(1):3-9
|
| [13] |
杜百廉, 臧卫东, 景润峰, 等. 对河南考古出土人骨骨病的研究[A].见:周光召(编).面向21世纪的科技进步与社会经济发展(下册)[C]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 1999: 33-34
|
| [14] |
朱泓. 体质人类学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004: 92-106
|
| [15] |
张璇, 韩迎星, 邵金陵. 古代人类口腔疾病流行概况[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2005(8):467-470
|
| [16] |
樊明文. 牙髓牙体病学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008: 31-39
|
| [17] |
Metress JF, Conway T. Standardized system for recording dental caries in prehistoric skeletons[J]. Journal of Dental Research, 1975, 54(4):908
pmid: 1099138
|
| [18] |
侯侃. 山西榆次高校园区先秦墓葬人骨研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2017: 138-139
|
| [19] |
Lukacs JR. The ‘caries correction factor’: A new method of calibrating dental caries rates to compensate for antemortem loss of teeth[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 1995, 5:151-156
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1212
URL
|
| [20] |
Lukacs JR. Fertility and agriculture accentuate sex differences in dental caries rates[J]. Current Anthropology, 2008, 49(5):901-914
doi: 10.1086/592111
URL
|
| [21] |
李瑞玉, 黄金芳, 韩陆. 下王岗新石器时代人类的牙病[J]. 人类学学报, 1991(3):200-205.
|
| [22] |
张璇. 六千年前半坡人口腔流行病学研究[D]. 西安:第四军医大学, 2006: 30
|
| [23] |
韩康信, 陆庆伍, 张振标. 江苏邳县大墩子新石器时代人骨的研究[J]. 考古学报, 1974(2): 125-141, 192-195
|
| [24] |
周亚威, 张晓冉, 顾万发. 郑州汪沟遗址仰韶文化居民的牙齿磨耗及口腔健康状况[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(1):49-62
|
| [25] |
周亚威, 白倩, 顾万发, 等. 郑州孙庄遗址仰韶文化人群的龋病[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(2):282-291
|
| [26] |
张佩琪, 李法军, 王明辉. 广西顶蛳山遗址人骨的龋齿病理观察[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(3):393-405
|
| [27] |
赵永生, 曾雯, 毛瑞林, 等. 甘肃临潭磨沟墓地人骨的牙齿健康状况[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(4):483-496
|
| [28] |
王一如. 沟湾遗址新石器时代人骨研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2015: 42-46
|
| [29] |
朱晓汀. 江苏兴化蒋庄良渚文化墓葬人骨研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2018: 87-97
|
| [30] |
周大成. 河南成皋广武镇出土新石器时代人骨的口腔情况[J]. 中华口腔科杂志, 1959, 7(5):285-288
|
| [31] |
Pechenkina EA, Benfer RA, Zhijun W. Diet and health changes at the end of the Chinese neolithic: the Yangshao/Longshan transition in Shaanxi province[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2002(1):15-36
pmid: 11748560
|
| [32] |
中国社会科学院考古研究所, 河南省文物考古研究所. 灵宝西坡墓地[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2010: 197-228
|
| [33] |
孙蕾. 河南渑池笃忠遗址仰韶晚期出土的人骨骨病研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2011, 30(1):55-63
|
| [34] |
陈伟驹, 李法军. 鲤鱼墩遗址出土人牙的牙齿磨耗和龋齿[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(1):45-51
|
| [35] |
朱芳武, 卢为善. 桂林甑皮岩新石器时代遗址居民的龋病[J]. 人类学学报, 1997(4):18-20
|
| [36] |
原海兵, 朱泓. 牛河梁红山文化人群龋齿的统计与分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(1):60-70
|
| [37] |
Naoliko I, Qifeng P, Peiko S, et al. Tooth and Facial Morphology of Ancient Chinese Skulls[M]. Tokyo: Therapeia Publishing Co, 1997: 221-231
|
| [38] |
Turner CG. Dental anthropological indications of agriculture among the Jomon people of central Japan. X. Peopling of the Pacific[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 51(4):619-635
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-8644
URL
|
| [39] |
孙亚男. 郑州地区仰韶至青铜时代先民植物资源利用与陶器功能的淀粉粒分析[D]. 合肥:中国科学技术大学, 2018
|
| [40] |
赵志军. 仰韶文化时期农耕生产的发展和农业社会的建立——鱼化寨遗址浮选结果的分析[J]. 江汉考古, 2017, 153(6):98-108
|
| [41] |
赵志军. 新石器时代植物考古与农业起源研究[J]. 中国农史, 2020, 39(3):3-13
|
| [42] |
赵志军. 新石器时代植物考古与农业起源研究(续)[J]. 中国农史, 2020, 39(4):3-9
|
| [43] |
中国科学院考古研究所, 陕西省西安半坡博物馆. 西安半坡[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 963:61-70
|
| [44] |
西安半坡博物馆, 陕西省考古研究所, 临潼县博物馆. 姜寨[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1988
|
| [45] |
中国社会科学院考古研究所. 宝鸡北首岭[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1983: 31-70
|
| [46] |
陕西省考古研究所. 龙岗寺[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1990: 16-47
|
| [47] |
中国科学院考古研究所. 庙底沟与三里桥[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1959: 24-64
|
| [48] |
黄其煦. “灰像法”在考古学中的应用[J]. 考古, 1982(4):418-420, 460
|
| [49] |
吕鹏, 袁靖. 交流与转化——黄河上游地区先秦时期生业方式初探(下篇)[J]. 南方文物, 2019(1):113-121
|
| [50] |
佟伟华. 磁山遗址的原始农业遗存及其相关的问题[J]. 农业考古, 1984(1): 2, 194-207
|
| [51] |
魏京武, 杨亚长. 从考古资料看陕西古代农业的发展[J]. 农业考古, 1986(1):91-100
|
| [52] |
陈全家. 郑州西山遗址出土动物遗存研究[J]. 考古学报, 2006, 162(3): 385-418, 435-438
|
| [53] |
袁靖. 中国新石器时代至先秦时期生业初探[J]. 南方文物, 2019(5):200-209
|
| [54] |
马萧林. 河南灵宝西坡遗址动物群及相关问题[J]. 中原文物, 2007, 136(4):48-61
|
| [55] |
杨苗苗, 武志江, 侯彦峰. 河南渑池县笃忠遗址出土动物遗存分析[J]. 中原文物, 2009, 146(2):29-36
|
| [56] |
郭怡, 胡耀武, 高强, 等. 姜寨遗址先民食谱分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2011, 30(2):149-157
|
| [57] |
郭怡, 俞博雅, 夏阳, 等. 史前时期社会性质初探——以北刘遗址先民食物结构稳定同位素分析为例[J]. 华夏考古, 2017, 119(1):45-53
|
| [58] |
张雪莲, 仇士华, 钟建, 等. 中原地区几处仰韶文化时期考古遗址的人类食物状况分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(2):197-207
|
| [59] |
Tao DW, Zhang J, Zheng WQ, et al. Starch grain analysis of human dental calculus to investigate Neolithic consumption of plants in the middle Yellow River Valley, China: A case study on Gouwan site[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2015: 485-491
|
| [60] |
赵志军. 中国农业起源概述[J]. 遗产与保护研究, 2019, 4(1):1-7
|
| [61] |
Tayles N, Domett K, Halcrow S. Can dental caries be interpreted as evidence of farming? The Asian experience[J]. Front Oral Biology, 2009, 13:162-166
|
| [62] |
Newton JS, Domett KM, O’reilly DJW, et al. Dental health in Iron Age Cambodia: Temporal variations with rice agriculture[J]. International Journal of Paleopathology, 2013(1):1-10
doi: S1879-9817(13)00019-3
pmid: 29539354
|
| [63] |
石兴邦. 中国大百科全书·考古卷[M]. 北京: 中国大百科全书出版社, 1986: 595-602
|
| [64] |
严文明. 仰韶文化研究[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1989
|
| [65] |
张居中. 仰韶时代文化刍议[J]. 中原文物, 1986, 特刊
|
| [66] |
张宏彦. 关于仰韶文化时空范围的界定问题[J]. 考古与文物, 2006(5):66-70
|