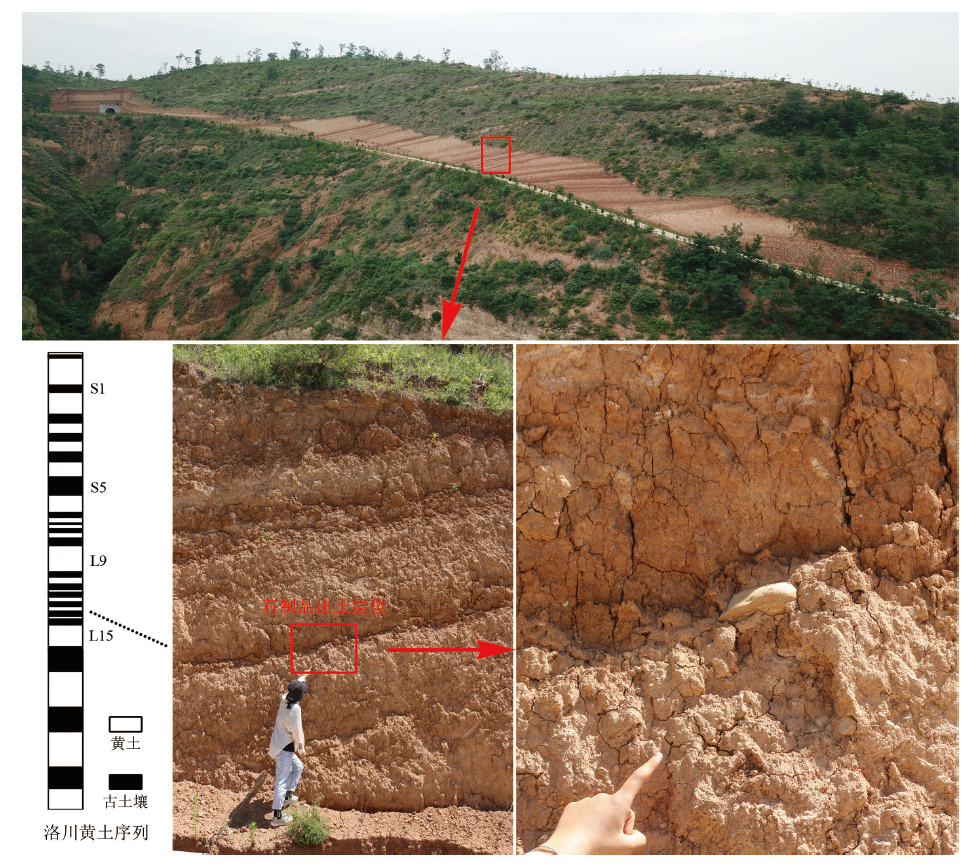
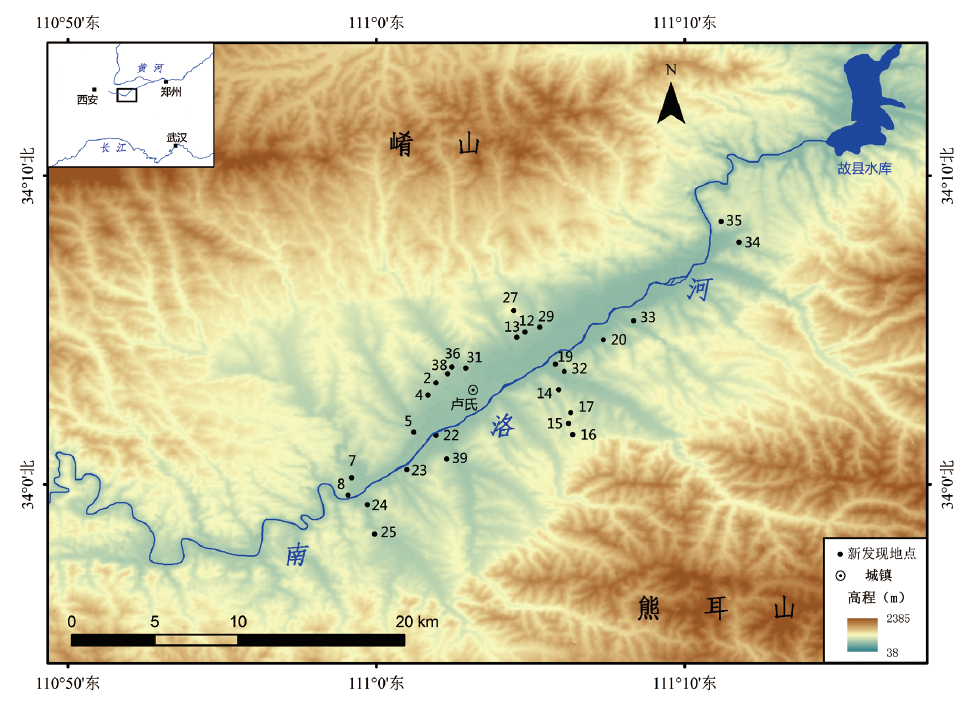
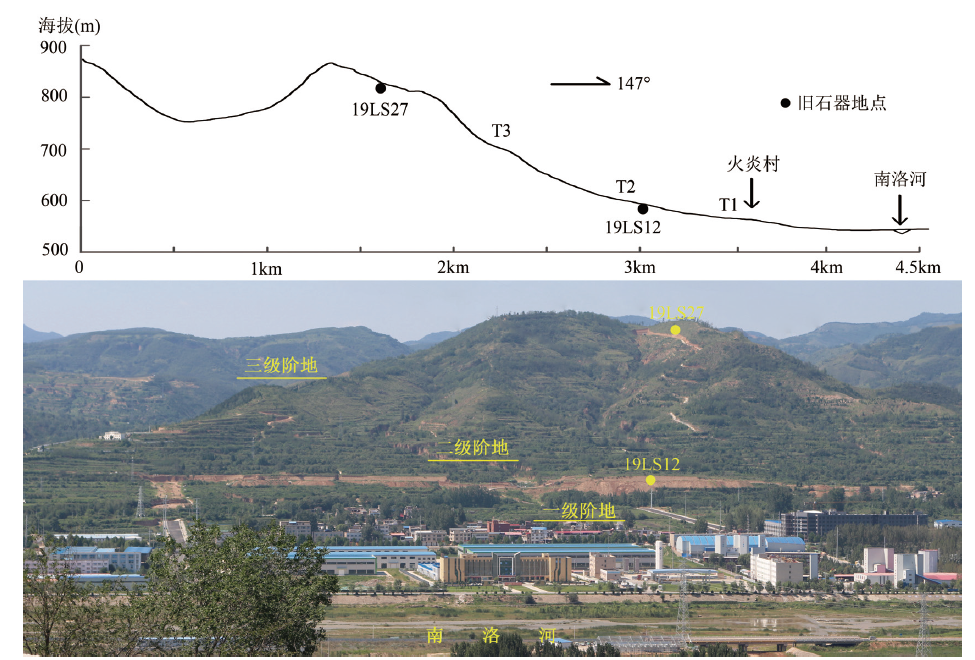
| [1] |
季楠, 牛树森. 河南省卢氏县发现人类化石[J]. 人类学学报, 1983, 2(4): 399
|
| [2] |
李占扬. 卢氏县段家窑旧石器地点[A].见:中国考古学会(编).中国考古学年鉴 1996[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1998: 163
|
| [3] |
吕遵谔. 从巩义和洛南之行浅谈砾石石器工业[J]. 考古与文物, 1999, 1: 27-35
|
| [4] |
王社江, 鹿化煜, 张红艳, 等. 东秦岭南洛河中游地区发现的旧石器和黄土堆积[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(6): 988-999
|
| [5] |
杜水生, 刘富良, 朱世伟, 等. 河南卢氏发现黄土旧石器[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(6): 1000-1006
|
| [6] |
Lu HY, Sun XF, Wang SJ, et al. Ages for hominin occupation in Lushi Basin, middle of South Luo River, central China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2011, 60 (5): 612-617
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2010.12.009
URL
|
| [7] |
鹿化煜, 张红艳, 孙雪峰, 等. 中国中部南洛河流域地貌、黄土堆积与更新世古人类生存环境[J]. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32(2): 167-177
|
| [8] |
Zhang HY, Lu HY, Jiang SY, et al. Provenance of loess deposits in the Eastern Qinling Mountains (central China) and their implications for the paleoenvironment[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 43: 94-102
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.04.010
URL
|
| [9] |
王社江, 鹿化煜. 秦岭地区更新世黄土地层中的旧石器埋藏与环境[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2016, 46(7): 881-890
|
| [10] |
Sun XF, Lu HY, Wang SJ, et al. Hominin distribution in glacial-interglacial environmental changes in the Qinling Mountains range, central China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 198: 37-55
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.08.012
URL
|
| [11] |
Lu HY, Zhuo HX, Zhang WC, et al. Earth surface processes and their effects on human behavior in monsoonal China during the Pleistocene-Holocene epochs[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2017, 27(11): 1311-1324
doi: 10.1007/s11442-017-1437-x
URL
|
| [12] |
鹿化煜, 张红艳, 王社江, 等. 东秦岭南洛河上游黄土地层年代的初步研究及其在旧石器考古中的意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(4): 559-567
|
| [13] |
丁伯涛, 徐廷, 赵莹, 等. 奥维互动地图浏览器在旧石器考古调查中的应用—以吉林省汪清县专项调查为例[N]. 中国文物报, 2018-7-13(7)
|
| [14] |
杜水生, 刘富良, 朱世伟, 等. 洛宁县发现黄土石器工业[J]. 考古与文物, 2010, 2: 14-17+59
|
| [15] |
河南省文物研究所, 灵宝县文管会. 河南灵宝营里旧石器地点调查简报[J]. 华夏考古, 1990, 2: 1-8
|
| [16] |
陕西省考古研究院, 商洛地区文管会,洛南县博物馆. 花石浪(I):洛南盆地旷野类型旧石器地点群研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 1-248
|
| [17] |
邢路达, 王社江, 张改课, 等. 陕西洛南盆地夜塬地点发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(1): 1-13
|
| [18] |
于青瑶, 王社江, Shen C, 等. 洛南盆地槐树坪地点2013年出土的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(2): 154-164
|
| [19] |
王社江, 张小兵, 鹿化煜, 等. 丹江上游商丹盆地新发现的旧石器及其埋藏黄土地层[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(4): 421-431
|
| [20] |
王社江, 孙雪峰, 鹿化煜, 等. 汉水上游汉中盆地新发现的旧石器及其年代[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(2): 125-136
|
| [21] |
别婧婧, 王社江, 夏楠, 等. 陕西汉中洋县金水河口旧石器遗址出土石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(3): 344-361
|