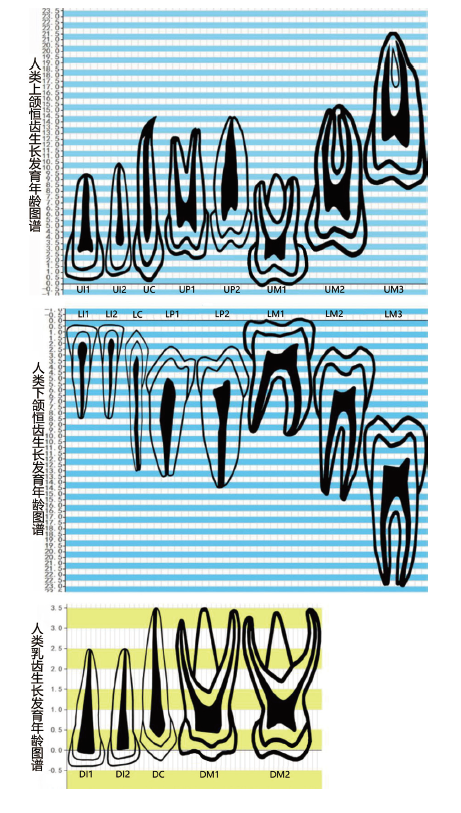
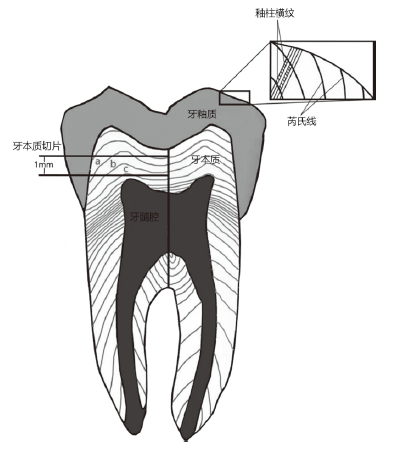
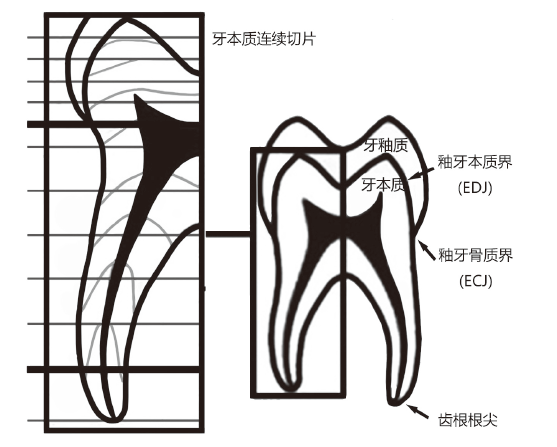
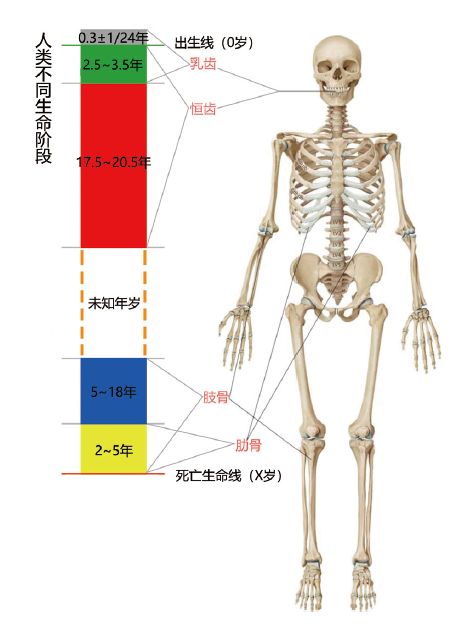
| [1] |
Roberts C, Manchester K. 疾病考古学(第三版)[M]. 译者:张桦. 济南: 山东画报出版社, 2010: 69-78
|
| [2] |
Gilbert RI, Mielke JH. Analysis of prehistoric diets[M]. London: London Academic Press, 1985: 201
|
| [3] |
Budd P, Millard A, Chenery C, et al. Investigating population movement by stable isotope analysis: a report from Britain[J]. Antiquity, 2004, 78(299): 127-141
doi: 10.1017/S0003598X0009298X
URL
|
| [4] |
Privat KL, Connell TC, Richards MP. Stable isotope analysis of human and faunal remains from the Anglo-Saxon cemetery at Berinsfield, Oxfordshire: dietary and social implications[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2002, 29(7): 779-790
doi: 10.1006/jasc.2001.0785
URL
|
| [5] |
张震康, 俞光岩. 实用口腔科学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2009
|
| [6] |
Scott GR, Tuner CG. Dental anthropology[J]. Annual review of Anthropology, 1988, 17(1): 99-126
doi: 10.1146/annurev.an.17.100188.000531
URL
|
| [7] |
Larson CS. Biological changes in human populations with agriculture[J]. Annual Review of Anthropology, 1995, 24: 185-213
doi: 10.1146/annurev.an.24.100195.001153
URL
|
| [8] |
Christy G, Turner II. Dental anthropological indications of agriculture among the Jomon people of central Japan[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1979, 51(4): 619-636
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330510413
URL
|
| [9] |
李明启, 杨晓燕, 王辉, 等. 甘肃临潭陈旗磨沟遗址人牙结石中淀粉粒反映的古人类植物性食物[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2010, 40(4): 486-492
|
| [10] |
Smith BH. Patterns of molar wear in hunter gatherers and agriculturalists[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1984, 63(1): 39-56
pmid: 6422767
|
| [11] |
Hinton RJ. Form and patterning of anterior tooth wear among aboriginal human groups[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1981, 54(4): 555-564
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330540409
pmid: 7234993
|
| [12] |
侯侃. 山西榆次高校园区先秦墓葬人骨研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017: 130-132
|
| [13] |
Goodman AH, Armelagos GJ, Rose JC. Enamel hypoplasias as indicators of stress in three prehistoric populations from Illinois[J]. Human Biology, 1980, 52(3): 515-528
pmid: 7005071
|
| [14] |
Starling AP, Stock JT. Dental indicators of health and stress in early Egyptian and Nubian agriculturists: a difficult transition and a gradual recovery[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2007, 134(4): 520-528
pmid: 17786997
|
| [15] |
Schmidt CW. On the Relationship of Dental Microwear to Dental Macrowear[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2010, 142(1): 67-73
|
| [16] |
Perez-Perez A. Lalueza C. Turbon D. Intraindividual and intragroup varibility of buccal tooth striation pattern[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1994, 94(2): 175-188
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330940203
URL
|
| [17] |
张全超, 韩涛, 张群. 新疆鄯善洋海墓地出土人骨的牙齿微磨耗痕迹研究[J]. 西域研究, 2018(3): 83-146
|
| [18] |
张雯欣. 新疆吐鲁番加依墓地青铜—早期铁器时代居民牙齿磨耗研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018: 24
|
| [19] |
Aufderheide AC. Chemical analysis of skeletal remains[A]. In: IscanMY, KennedyKAR(Eds.). Reconstruction of life from the skeleton[M]. New York: Alan R Liss Inc, 1989: 237-260
|
| [20] |
Ambrose SH, Norr L. On stable isotopic data and prehistoric subsistence in the Soconusco region[J]. Current Anthropol, 1992, 33(4): 401-404
doi: 10.1086/204088
URL
|
| [21] |
Humphrey LT, Dean MC, Jeffries TE, et al. Unlocking evidence of early diet from tooth enamel[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 2008, 105(19): 6834-6839
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711513105
URL
|
| [22] |
Burton JH, Price TD, Cahue L, et al. The use of barium and strontium abundances in human skeletal tissues to determine their geographic origins[J]. International Journal Osteoarchaeology, 2003, 13(1-2): 88-95
doi: 10.1002/oa.661
URL
|
| [23] |
Toots H, Voorhies MR. Strontium in fossil bones and the reconstruction of food chains[J]. Science, 1965, 149(3686): 854-855
pmid: 17737382
|
| [24] |
Burton JH, Price TD. The ratio of barium to strontium as a palaeodietary indicator of consumption of the marine resources[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1990, 17(5): 547-557
doi: 10.1016/0305-4403(90)90035-4
URL
|
| [25] |
孟勇. 陕西出土6000年和1000年前古人牙齿结构、组成及病理特征的对比研究[D]. 西安: 第四军医大学, 2011: 58
|
| [26] |
Nanci A. Ten Cate’s oral histology:development, structure, and function[M]. Missouri: Elsevier Mosby, 2013
|
| [27] |
张雪莲. 应用古人骨的元素、同位素分析研究其食物结构[J]. 人类学学报, 2003, 22(1): 75-85
|
| [28] |
Dupras TL, Tocheri MW. Reconstructing infant weaning histories at Roman period Kellis, Egypt using stable isotope analysis of dentition[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2007, 134(1): 63-74
pmid: 17568441
|
| [29] |
Howcroft R, Eriksson G, Liden K. Infant feeding practices at the Pitted Ware Culture site of Ajvide, Gotland[J]. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, 2014, 34: 42-53
doi: 10.1016/j.jaa.2014.01.001
URL
|
| [30] |
Hoogewerff J, Papesch W, Kralik M, et al. The last domicile of the iceman from hauslabjoch: A geochemical approach using Sr, C and O isotopes and trace element signatures[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2001, 28(9): 983-989
doi: 10.1006/jasc.2001.0659
URL
|
| [31] |
Tsutaya T, Yoneda M. Reconstruction of Breastfeeding and Weaning Practices Using Stable Isotope and Trace Element Analyses: A Review[J]. Yearbook of Physical Anthropology, 2015, 156(S59): 2-21
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.22657
URL
|
| [32] |
Beaumont J, Montgomery J. Oral histories: a simple method of assigning chronological age to isotopic values from human dentine collagen[J]. Annals of Human Biology, 2015, 42(4): 407-414
pmid: 26225904
|
| [33] |
Hillson S. Tooth Development in Human Evolution and Bioarchaeology[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014: 28-68
|
| [34] |
AlQahtani SJ, Hector MP, Liversidge HM. Brief co mmunication: the London Atlas of Human Tooth Development and Eruption[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2010, 142(3): 481-490
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.21258
pmid: 20310064
|
| [35] |
Dean MC, Liversidge HM, Elamin F. Combining radiographic and histological data for dental development to compare growth in the past and the present[J]. Annals Human Biology, 2014, 41(4): 336-347
doi: 10.3109/03014460.2014.922614
URL
|
| [36] |
White TD, Folkens PA. The Human Bone Manual[M]. Burlington: Elsevier Academic Press, 2005: 38
|
| [37] |
许复贞. 牙体解剖与雕刻技术[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2011: 21-53
|
| [38] |
孟勇. 陕西出土6000年和1000年前古人牙齿结构、组成及病理特征的对比研究[D]. 西安: 第四军医大学, 2011: 25
|
| [39] |
于世凤. 口腔组织病理学(第5版)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2006: 23-58
|
| [40] |
Newsome SD, Koch PL, Etnier MA, et al. Using carbon and nitrogen isotope values to investigate maternal strategies in northeast Pacifific Otariids[J]. Marine Ma mmal Science, 2006, 22(3): 556-572
|
| [41] |
Jelmer W, Ada G, Eric J, et al. Estimating weaning and early childhood diet from serial micro-samples of dentin collagen[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2011, 38(11): 3101-3111
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2011.07.010
URL
|
| [42] |
Rowena C. Henderson, Julia Lee-Thorp, et al. Early Life Histories of the London Poor Using δ13C and δ15N Stable Isotope Incremental Dentine Sampling[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2014, 154(4): 585-593
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.22554
pmid: 24898314
|
| [43] |
易冰, 刘翔宇, 原海兵, 等. 四川大邑县高山古城遗址宝墩文化先民牙本质序列的碳氮稳定同位素分析[J]. 四川文物, 2020(1): 95-106
|
| [44] |
Beaumont J, Gledhill A. Childhood diet: a closer examination of the evidence from dental tissues using stable isotope analysis of incremental human dentine[J]. Archaeometry, 2012, 55(2): 277-295
doi: 10.1111/j.1475-4754.2012.00682.x
URL
|
| [45] |
Austin C, Smith TM, Bradman A, et al. Barium distributions in teeth reveal early-life dietary transitions in primates[J]. Nature, 2013, 498: 216-219
doi: 10.1038/nature12169
URL
|
| [46] |
郭光文, 王序. 人体解剖彩色图谱(第二版)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017: 3
|
| [47] |
Lessen R, Kavanagh K. Position of the academy of nutrition and dietetics: promoting and supporting breastfeeding[J]. Journal of the Academy Nutrition and Dietetics, 2015, 115(3): 444-449
doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2014.12.014
URL
|
| [48] |
Valeggia C, Ellison PT. Interactions between metabolic and reproductive functions in the resumption of postpartum fecundity[J]. Annals Human Biology, 2009, 21(4): 559-566
|
| [49] |
Sellen DW. Comparison of infant feeding patterns reported for nonindustrial populations with current recom mendations[J]. Journal of Nutrition, 2001, 131(10): 2707-2715
pmid: 11584094
|
| [50] |
Bourbou C, Fuller BT, Garvie-Lok SJ, et al. Nursing mothers and feeding bottles: reconstructing breastfeeding and weaning patterns in Greek Byzantine populations (6th-15th centuries AD) using carbon and nitrogen stable isotope Ratios[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2013, 40(11): 3903-3913
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2013.04.020
URL
|
| [51] |
Xia Y, Zhang JL, Yu F. et al. Breastfeeding, weaning, and dietary practices during the Western Zhou Dynasty (1122-771 BC) at Boyangcheng, Anhui Province, China[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2018, 165(2): 343-352
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.23358
URL
|
| [52] |
唐孙思邈. 千金方[M]. 北京: 华夏出版社, 1993
|
| [53] |
Dunne J, Rebay-Salisbury K, Salisbury RB, et al. Milk of ruminants in ceramic baby bottles from prehistoric child graves[J]. Nature, 2019, 574: 246-248
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1572-x
URL
|
| [54] |
Stevens EE, Patrick TE, Pickler R. A history of infant feeding[J]. Journal Perinatal Education, 2009, 18(2): 32-39
|
| [55] |
Fuller BT, Fuller JL, Harris DA, et al. Detection of breastfeeding and weaning in modern human infants with carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2006, 129(2): 279-293
pmid: 16261548
|
| [56] |
Richards MP, Mays S, Fuller BT. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope values of bone and teeth reflect weaning age at the Medieval Wharram Percy site, Yorkshire, UK[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2002, 119(3): 205-210
pmid: 12365032
|
| [57] |
李岩. 中国古代尊老养老问题研究[M]. 北京: 中国社会科学出版社, 2016: 27
|
| [58] |
清阮元校刻. 十三经注疏[M]. 北京: 中华书局, 1986: 1347-2768
|
| [59] |
杨宽. 西周史[M]. 上海: 人民出版社, 1999: 752
|
| [60] |
Manolagas SC. Birth and death of bone cells: Basic regulatory mechanisms and implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoporosis[J]. Endocrine Reviews, 2000, 21(2): 115-137
pmid: 10782361
|
| [61] |
Hedges REM, Reynard LM. Nitrogen isotopes and the trophic level of humans in archaeology[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2007, 34: 1240-1251
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2006.10.015
URL
|