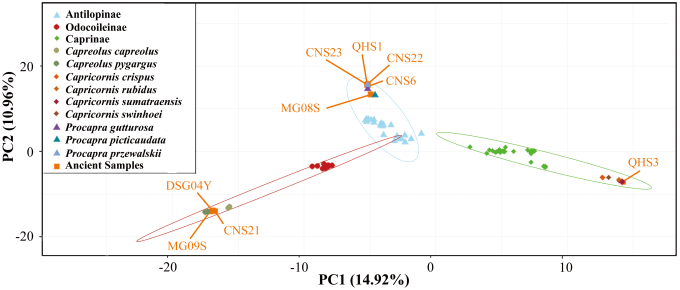
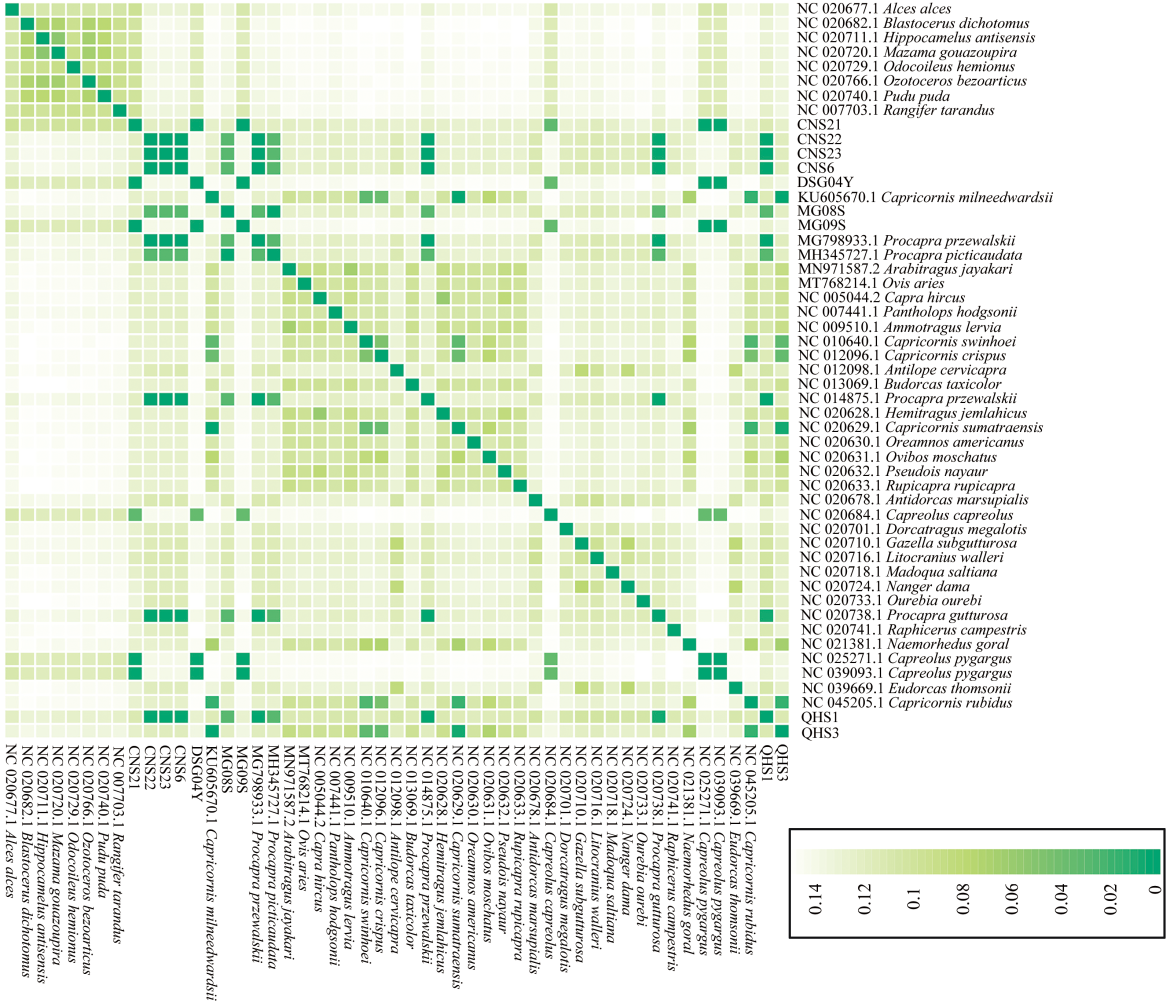
| [1] |
蔡大伟, 张乃凡, 赵欣. 中国山羊的起源与扩散研究[J]. 南方文物, 2021, 1: 191-200
|
| [2] |
郭雅琪. 新疆吉仁台沟口遗址出土古代盘羊的线粒体全基因组分析[D].硕士研究生毕业论文, 长春: 吉林大学, 2020, 1-2
|
| [3] |
韩璐. 内蒙古东周时期绵羊和山羊的线粒体DNA研究[D].博士研究生毕业论文, 长春: 吉林大学, 2010, 46-47
|
| [4] |
蔡大伟. 分子考古学导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008
|
| [5] |
Moore WS. Inferring phylogenies from mtDNA variation: mitochondrial gene trees versus nuclear gene trees[J]. Evolution, 1995, 49: 718-726
|
| [6] |
Meadows JRS, Hiendleder S, Kijas JW. Haplogroup relationships between domestic and wild sheep resolved using a mitogenome panel[J]. Heredity, 2011, 106: 700-706
doi: 10.1038/hdy.2010.122
pmid: 20940734
|
| [7] |
E. Dalym G, Torben CR, Nihan DD, et al. Green or white? Morphology, ancient DNA, and the identification of archaeological North American Pacific Coast sturgeon[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2021, 36: 102887
|
| [8] |
乌日嘎, 臧钰, 孙宏钰. 动物DNA分析技术及其法医学应用[J]. 中国法医学杂志, 2022, 37: 116-120
|
| [9] |
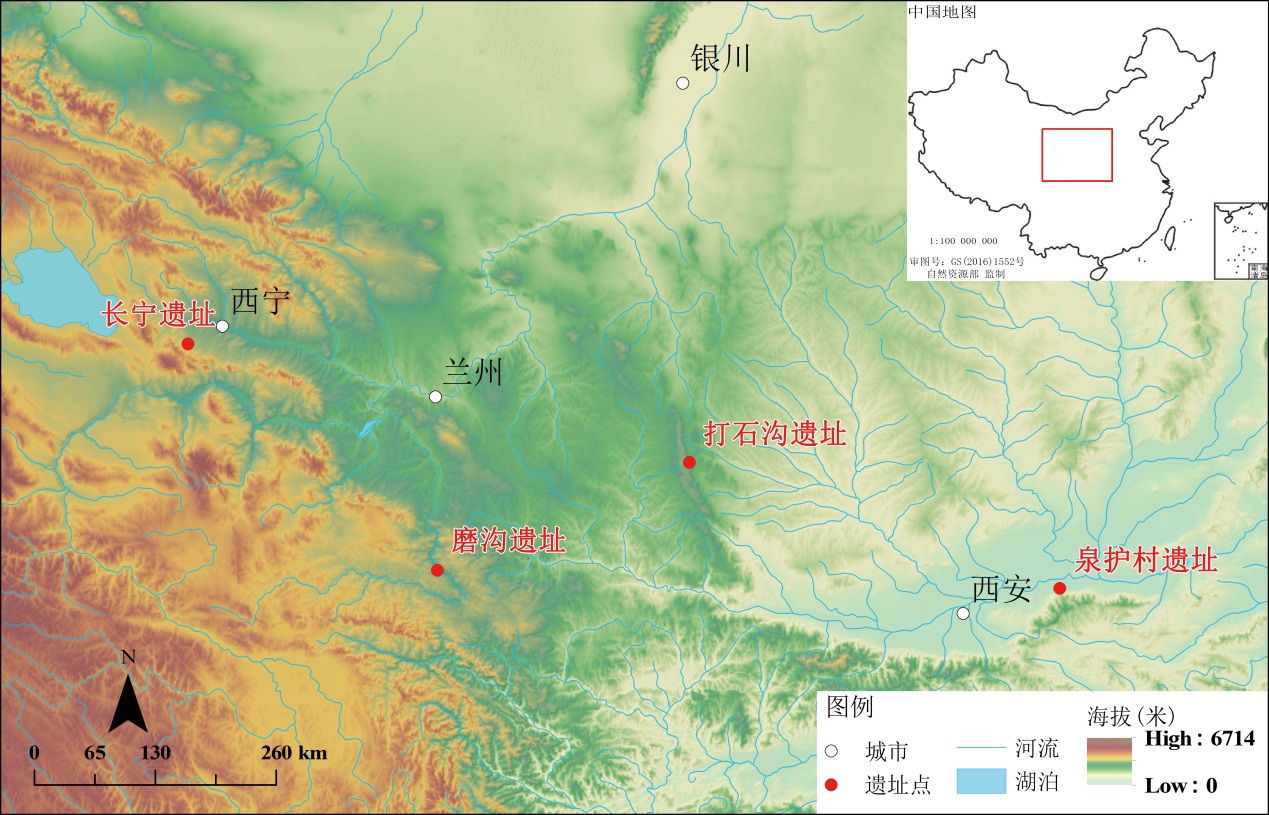
董广辉, 贾鑫, 安邦成, 等. 青海省长宁遗址沉积物元素对晚全新世人类活动和气候变化的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28: 115-119
|
| [10] |
李谅. 青海省长宁遗址的动物资源利用研究[D].硕士研究生毕业论文, 长春: 吉林大学, 2010, 4-6
|
| [11] |
王华, 毛瑞林, 周静. 甘肃临潭磨沟墓地仪式性随葬动物研究[J]. 考古与文物, 2022, 6: 118-125
|
| [12] |
陕西省考古研究院, 渭南市文物旅游局, 华县文物旅游局. 华县泉护村—1997年考古发掘报告[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2014
|
| [13] |
杨国宁. 彭阳历史文物[M]. 银川: 宁夏人民教育出版社, 2017
|
| [14] |
Yang DY, Eng BW, John S, et al. Improved DNA extraction from ancient bones using silica-based spin columns[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1998, 105: 539-543
pmid: 9584894
|
| [15] |
Schubert M, Ermini L, Sarkissian CD, et al. Characterization of ancient and modern genomes by SNP detection and phylogenomic and metagenomic analysis using PALEOMIX[J]. Nature Protocols, 2014, 9: 1056-1082
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.063
pmid: 24722405
|
| [16] |
Schubert M, Lindgreen S, Orlando L. AdapterRemoval v2: rapid adapter trimming, identification, and read merging[J]. BMC Research, 2016, 9: 88
|
| [17] |
Li H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM[CP]. URL: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1303.3997. Released on: 2013
|
| [18] |
Sacco J, Ruplin A, Skonieczny P, et al. Polymorphisms in the canine monoamine oxidase a (MAOA) gene: identification and variation among five broad dog breed groups[J]. Canine Genetics and Epidemiology, 2017, 4: 1
|
| [19] |
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data[J]. Genome Research, 2010, 20: 1297-1303
doi: 10.1101/gr.107524.110
pmid: 20644199
|
| [20] |
Okonechnikov K, Conesa A, García-Alcalde F. Qualimap 2: advanced multi-sample quality control for high-throughput sequencing data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2016, 32: 292-294
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv566
pmid: 26428292
|
| [21] |
Korneliussen TS, Albrechtsen A, Nielsen R. ANGSD: analysis of Next Generation Sequencing Data[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2014, 15: 356
doi: 10.1186/s12859-014-0356-4
pmid: 25420514
|
| [22] |
Samtools/htslib. lh3/htsbox: My experimental tools on top of htslib[CP]. URL: https://github.com/lh3/htsbox/
|
| [23] |
Renaud G, Slon V, Duggan AT, et al. Schmutzi: estimation of contamination and endogenous mitochondrial consensus calling for ancient DNA[J]. Genome Biology, 2015, 16: 224
doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0776-0
pmid: 26458810
|
| [24] |
Mpieva/mapping-iterative-assembler: Consensus calling (or “reference assisted assembly”), chiefly of ancient mitochondria[CP]. URL: https://github.com/mpieva/mapping-iterative-assembler/. Released on:2021-03-31
|
| [25] |
National Center for Biotechnology Information. BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool[DB]. URL: https://blastncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
|
| [26] |
Seguin-Orlando A, Gamba C, Sarkissian CD. Pros and cons of methylation-based enrichment methods for ancient DNA[J]. Scientific reports, 2015, 5: 11826
doi: 10.1038/srep11826
pmid: 26134828
|
| [27] |
Jónsson H, Ginolhac A, Schubert M, et al. mapDamage2.0: fast approximate Bayesian estimates of ancient DNA damage parameters[J]. Bioinformatics, 2013, 29: 1682-1684
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt193
pmid: 23613487
|
| [28] |
Briggs AW, Udo S, Johnson PLF, et al. Patterns of damage in genomic DNA sequences from a Neandertal[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2007, 104: 14616-14621
|
| [29] |
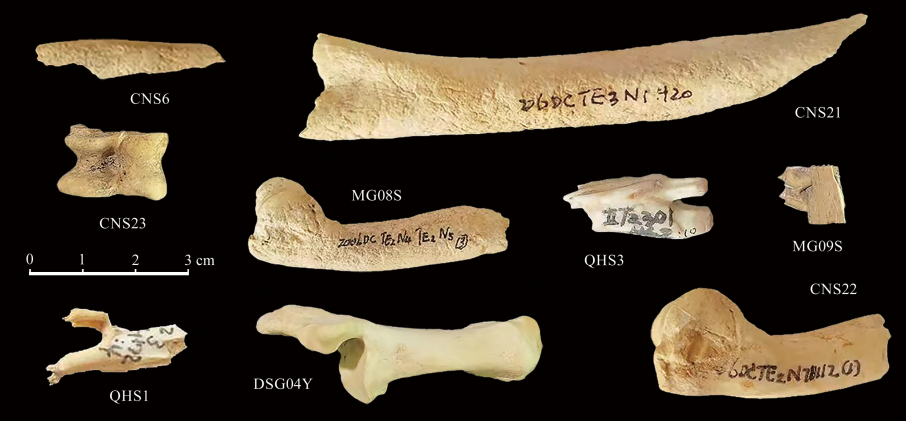
朱司褀. 中国北方三个遗址出土马属动物(Equus ovodovi) 的分子考古学研究[D].硕士研究生毕业论文, 长春: 吉林大学, 2020, 46-47
|
| [30] |
MikkelSchubert/paleomix. PALEOMIX 1.3.8 Documentation[CP]. URL: https://paleomix.readthedocs.io/en/stable/
|
| [31] |
Edgar RC. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32: 1792-1797
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh340
pmid: 15034147
|
| [32] |
Okonechnikov K, Golosova O, Fursov M. Unipro UGENE: a unified bioinformatics toolkit[J]. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28: 1166-1167
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts091
pmid: 22368248
|
| [33] |
Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2000, 17: 540-552
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026334
pmid: 10742046
|
| [34] |
Darriba D, Posada D, Kozlov AM, et al. ModelTest-NG: a new and scalable tool for the selection of DNA and protein evolutionary models[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2019, 37: 291-294
|
| [35] |
Kozlov AM, Darriba D, Flouri T, et al. RAxML-NG: a fast, scalable and user-friendly tool for maximum likelihood phylogenetic inference[J]. Bioinformatics, 2019, 35: 4453-4455
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz305
pmid: 31070718
|
| [36] |
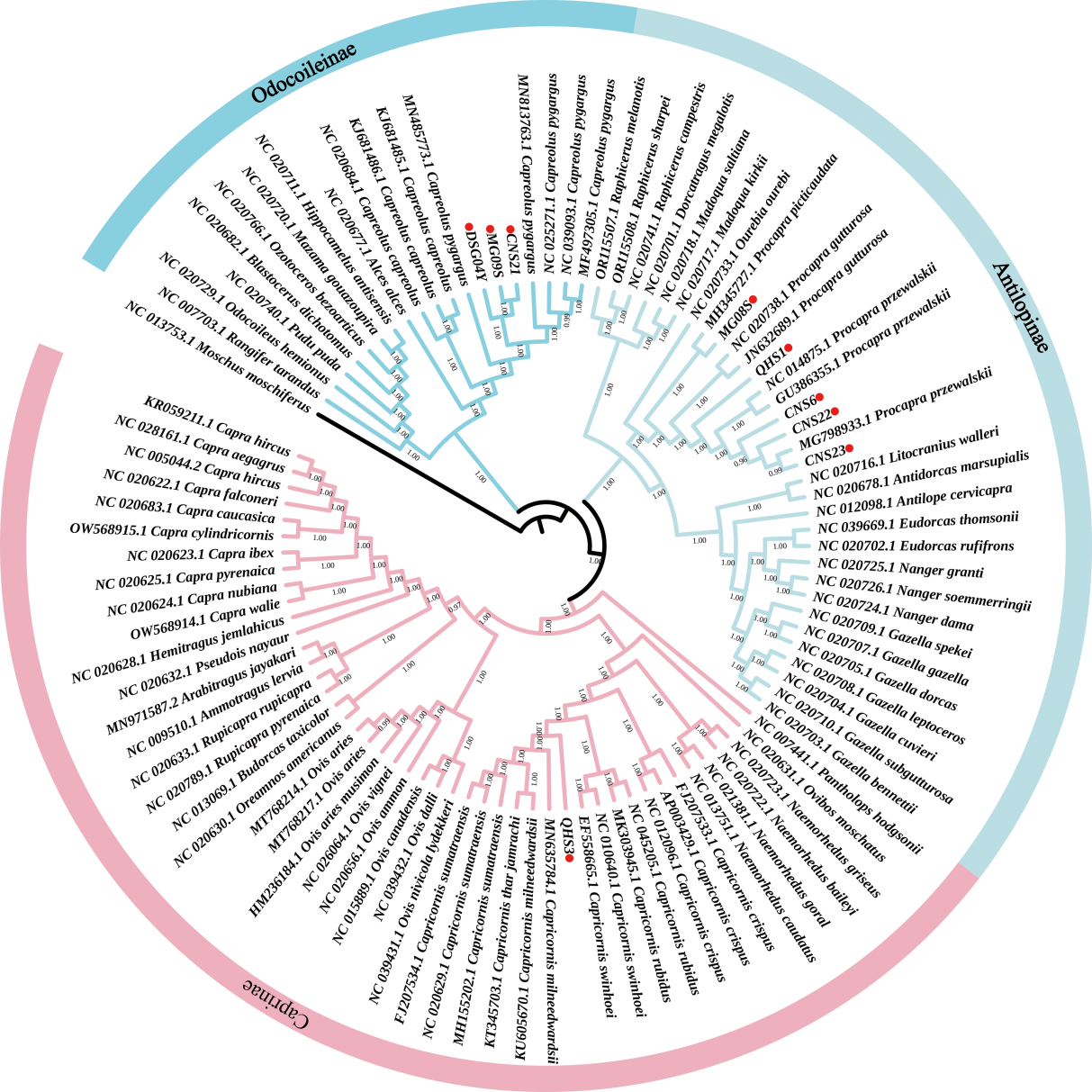
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A. BEAST: Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis by Sampling Trees[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 2007, 7: 214
pmid: 17996036
|
| [37] |
BEASTdoc. TreeAnnotator: a program to summarize the information from a sample of trees produced by BEAST onto a single “target” tree[CP]. URL: http://beast.community/treeannotator
|
| [38] |
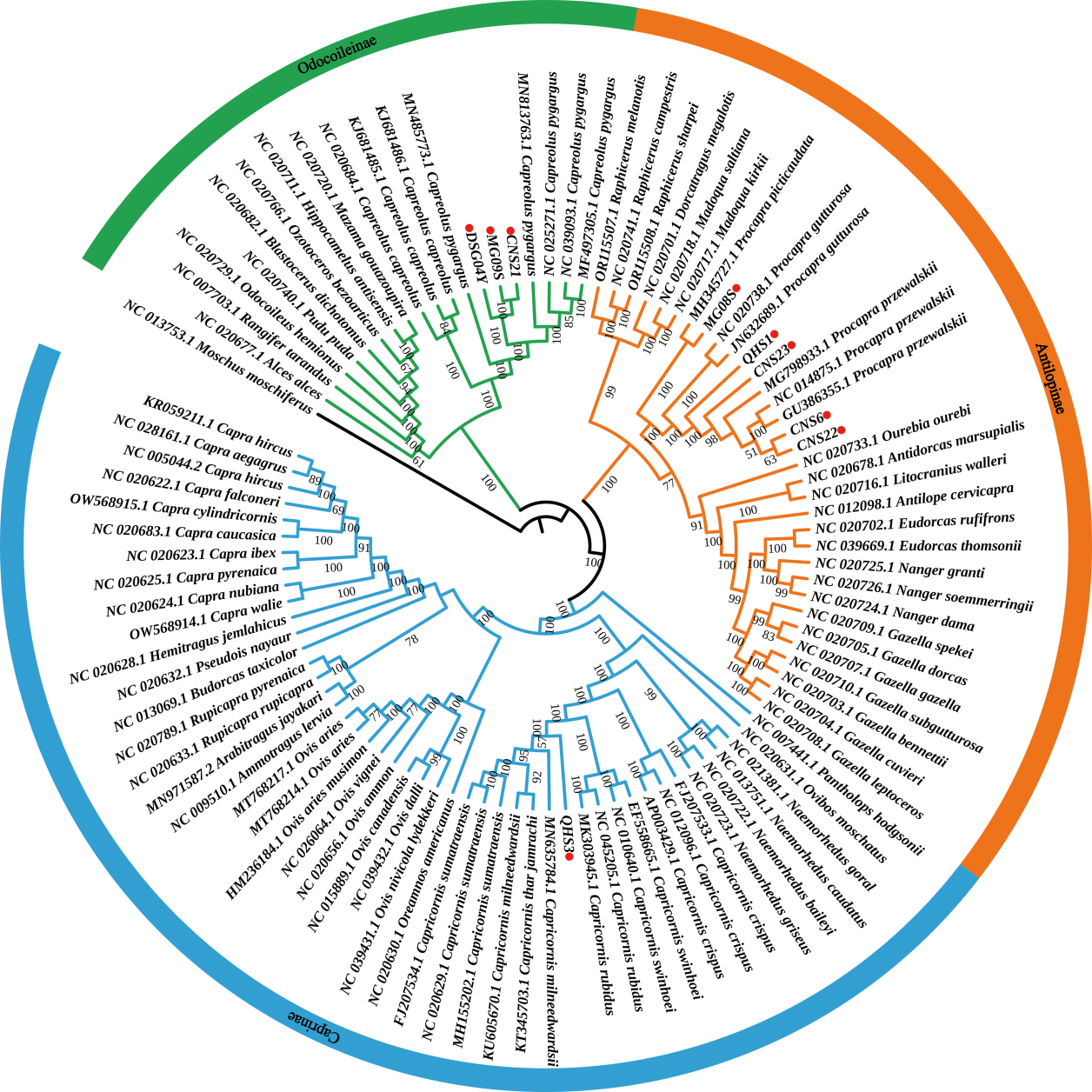
Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive tree of Life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49: W293-W296
|
| [39] |
Jombart T. adegenet: a R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers[J]. Bioinformatics, 2008, 24: 1403-14-05
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn129
pmid: 18397895
|
| [40] |
R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing[M]. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Austria, 2022
|
| [41] |
Wickham H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2016
|
| [42] |
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S. MEGA 11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2021, 37: 3022-3027
|
| [43] |
Kolde R. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R package version 1.0.12[CP]. URL: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap. Released on: 2019-01-04
|
| [44] |
Castelló JR. Bovids of the World:Antelopes, Gazelles, Cattle, Goats, Sheep, and Relatives[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2016
|
| [45] |
Smith AT. 中国兽类野外手册[M]. 长沙: 湖南教育出版社, 2009
|
| [46] |
蒋志刚. 中国的羊亚科和羚羊亚科动物[J]. 知识就是力量, 2003, 12: 34
|
| [47] |
Hewison AJM, Danilkin A. Evidence for separate specific status of European (Capreolus capreolus) and Siberian (C. pygargus) roe deer[J]. Mammalian Biology, 2001, 66: 13-21
|
| [48] |
Sheng H. The Deer in China[M]. Shanghai: East China Normal University Press, 1992, 1-251
|
| [49] |
王一如, 乔里斯·彼得斯. 中国西部羊亚科和羚羊亚科颅后骨形态鉴定标准和史前人-羊关系[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2023, 59: 526-542
|
| [50] |
Flad RK, Yuan J, Li S. Zooarcheological evidence for animal domestication in northwest China[J]. Developments in Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 9: 167-203
|
| [51] |
左豪瑞. 中国家羊的动物考古学研究综述和展望[J]. 南方文物, 2017, 1: 155-163
|
| [52] |
Taylor WTT, Pruvost M, Posth C, et al. Evidence for early dispersal of domestic sheep into Central Asia[J]. Nature Human Behaviour, 2021, 5: 1169-1179
doi: 10.1038/s41562-021-01083-y
pmid: 33833423
|
| [53] |
任乐乐. 青藏高原东北部及其周边地区新石器晚期至青铜时代先民利用动物资源的策略研究[D].硕士研究生毕业论文, 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017
|
| [54] |
包曙光. 中国北方地区夏至战国时期的殉牲研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021
|