| [1] |
Yuan J, Rowan F. Pig domestication in ancient China[J]. Antiquity, 2002, 76(293): 724-732
|
| [2] |
罗运兵.中国古代猪类驯化、 饲养与仪式性使用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012, 112-185
|
| [3] |
Cai DW, Zhu SQ, Gong M, et al. Radiocarbon and genomic evidence for the survival of Equus Sussemionus until the late Holocene[J]. eLife, 2022, 11: 1-22
|
| [4] |
王华, 王炜林, 胡松梅. 仰韶时代人类狩猎梅花鹿的策略:以铜川瓦窑沟遗址为案例[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(1): 90-100
|
| [5] |
Zhang NF, Liang QY, Shao XY, et al. Ancient cattle DNA provides novel insight into the subsistence mode transition from the late Neolithic to Bronze Age in the Nenjiang River Basin[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2023, 51: 1-8
|
| [6] |
陈全家, 赵海龙, 王法岗, 等. 桦甸仙人洞遗址出土的动物化石与孢粉[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(1): 52-62
|
| [7] |
张哲. 后套木嘎遗址(2011-2012)新石器时代动物遗存研究[D].硕士学位论文, 长春: 吉林大学, 2015,5-24
|
| [8] |
汤卓炜, 王立新, 段天璟, 等. 吉林白城双塔新石器时代遗址的动物遗存及其环境[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(4): 537-552
|
| [9] |
吕鹏, 贾笑冰, 金英熙. 人类行为还是环境变迁:小珠山贝丘遗址动物考古学研究新思考[J]. 南方文物, 2017, 1: 136-141
|
| [10] |
黄蕴平. 牛河梁遗址出土动物骨骼鉴定报告[A]. 见:辽宁省文物考古研究所(主编).牛河梁:红山文化遗址发掘报告(1983-2003年度)·中册[C]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2012, 507-510
|
| [11] |
陈全家. 白金宝遗址(1986年)出土的动物遗存研究[J]. 北方文物, 2004, 4: 111-112
|
| [12] |
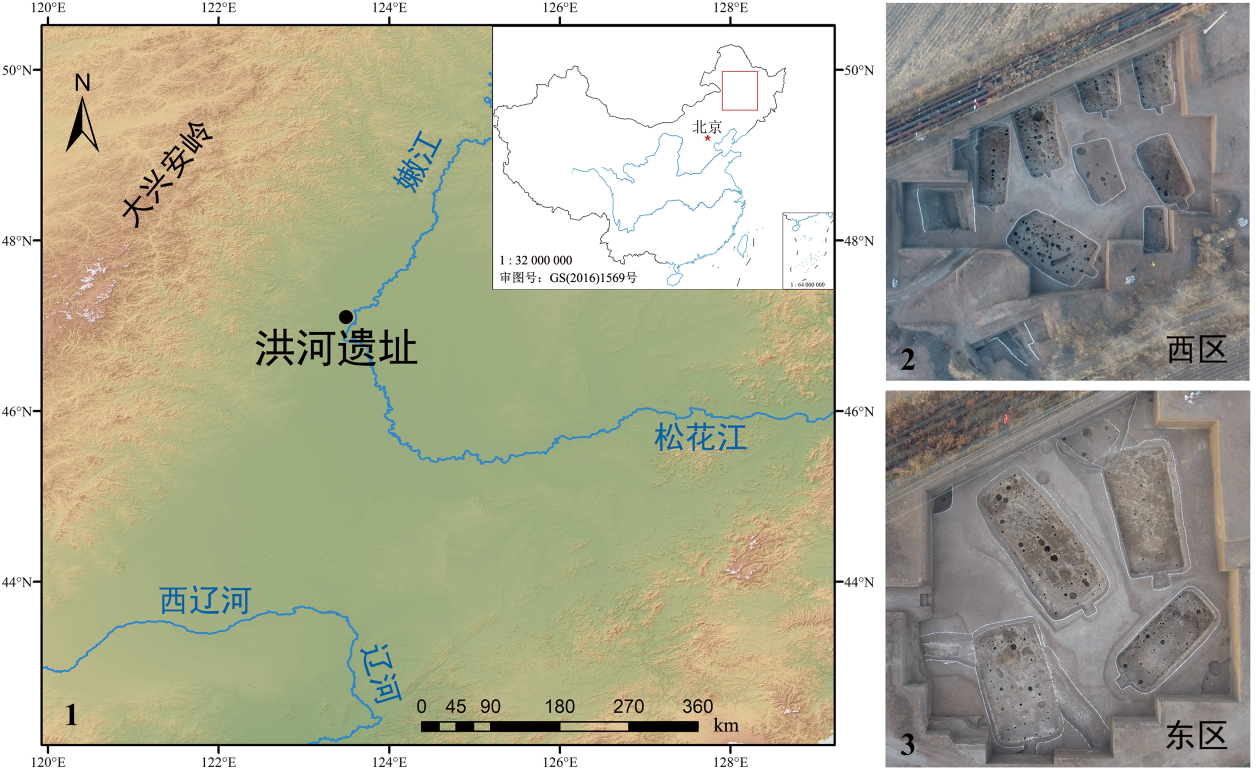
张伟, 田禾, 李有骞, 等. 黑龙江齐齐哈尔市洪河遗址[J]. 考古, 2020, 7: 20-33
|
| [13] |
Leng CC, Jie DM, Zhang C, et al. Quantitative climatic reconstruction and prehistoric human subsistence strategy evolution since the mid-Holocene in Nenjiang river Basin, Northeastern China[J]. Quaternary International, 2023, 649: 1-9
|
| [14] |
Liang QY, Chen QJ, Zhang NF, et al. Subsistence strategies in the Late Neolithic and Bronze Age in Nenjiang River Basin: A zooarchaeological and stable isotope analysis of faunal remains at Honghe site, Northeast China[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2023, 33(2): 271-284
|
| [15] |
Deng MX, Xiao B, Yuan JX, et al. Ancient Mitogenomes Suggest Stable Mitochondrial Clades of the Siberian Roe Deer[J]. Genes, 2022, 13(1): 1-14
|
| [16] |
Behrensmeyer AK. Taphonomic and ecologic information from bone weathering[J]. Paleobiology, 1978, 4(2): 150-162
|
| [17] |
Todd LC. Taphonomy of the Horner II bone bed[A]. In: Frison GC, Todd LC(Eds). The Horner Site: The Type Site of the Cody Cultural Complex[C]. London: Academic Press, 1987, 107-198
|
| [18] |
Linares-Matás GL, Ruiz NF, Uriarte MH, et al. Hyaenas and early humans in the latest Early Pleistocene of South-Western Europe[J]. Scientific reports, 2021, 11(1): 1-18
|
| [19] |
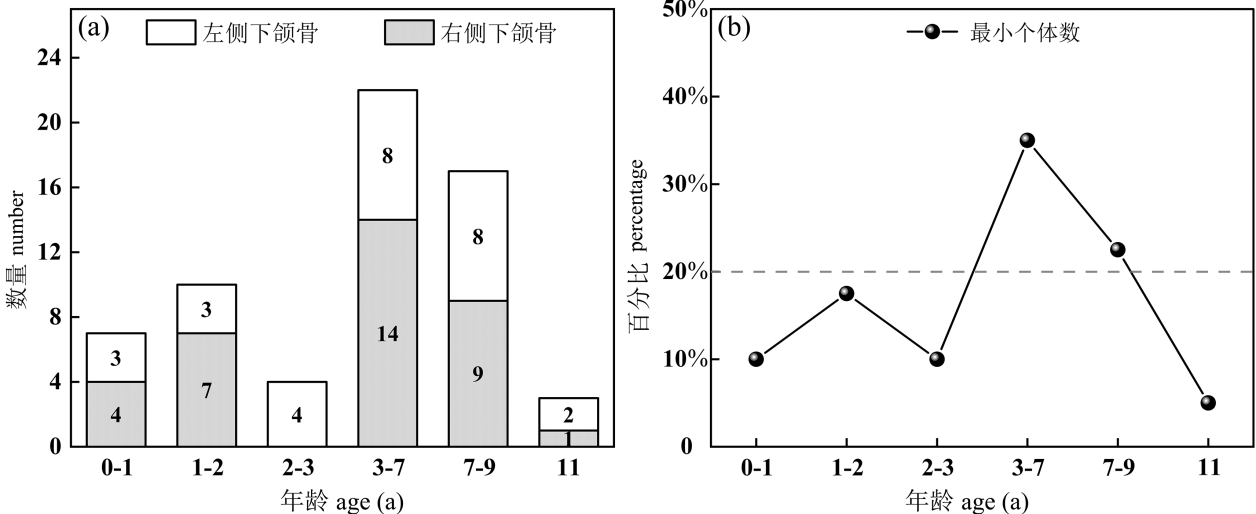
Tomé C, Vigne JD. Roe deer (capreolus capreolus) age at death estimates: New methods and modern reference data for tooth eruption and wear, and for epiphyseal fusion[J]. Archaeofauna, 2003, 12(2): 157-173
|
| [20] |
盛和林. 中国鹿科动物[M]. 上海: 华东师范大学出版社, 1992, 20-65
|
| [21] |
李长生, 马丽娟, 周会敏, 等. 狍的生物学特性[J]. 动物科学与动物医学, 2002, 4: 54-57
|
| [22] |
Reitz EJ, Wing ES. Zooarchaeology[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2008, 32-65
|
| [23] |
Binford LR. Nunamiut Ethnoarchaeology[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1978, 5-34
|
| [24] |
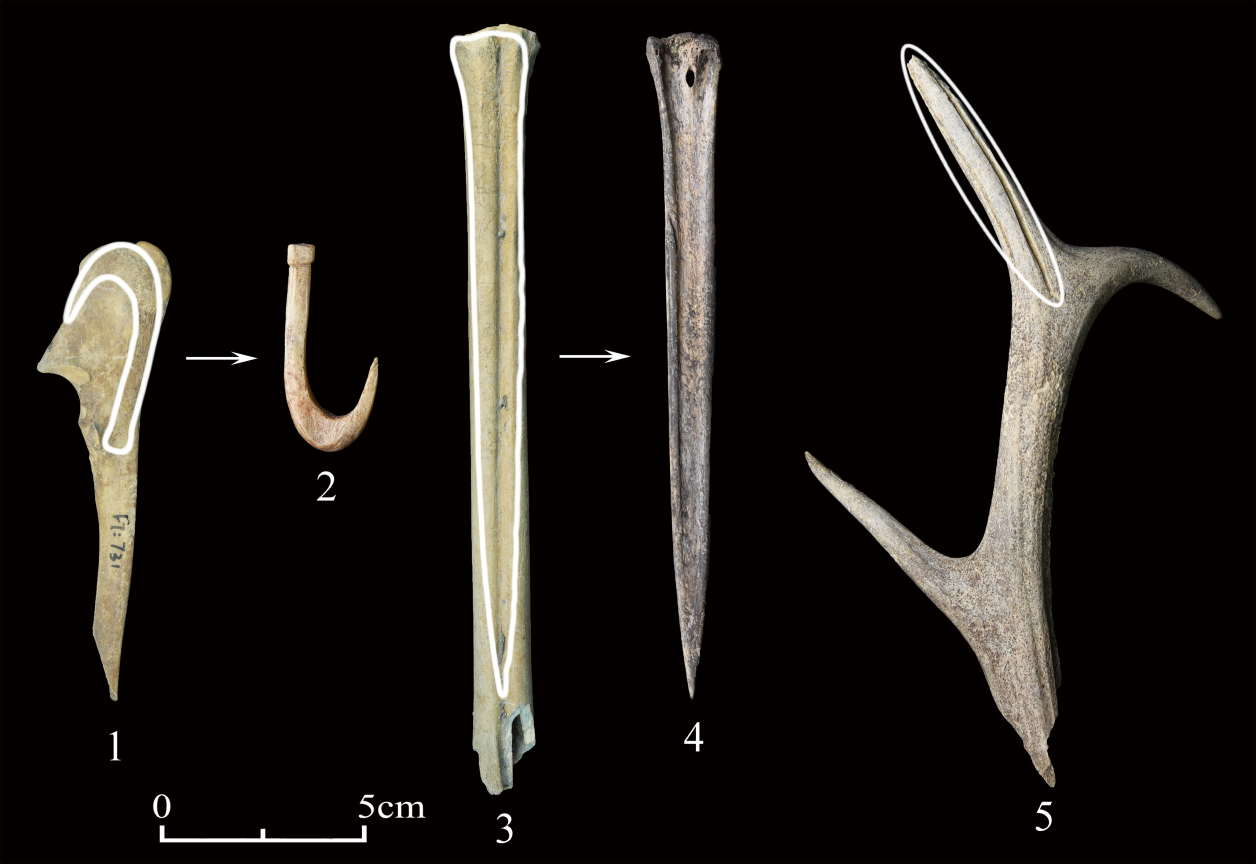
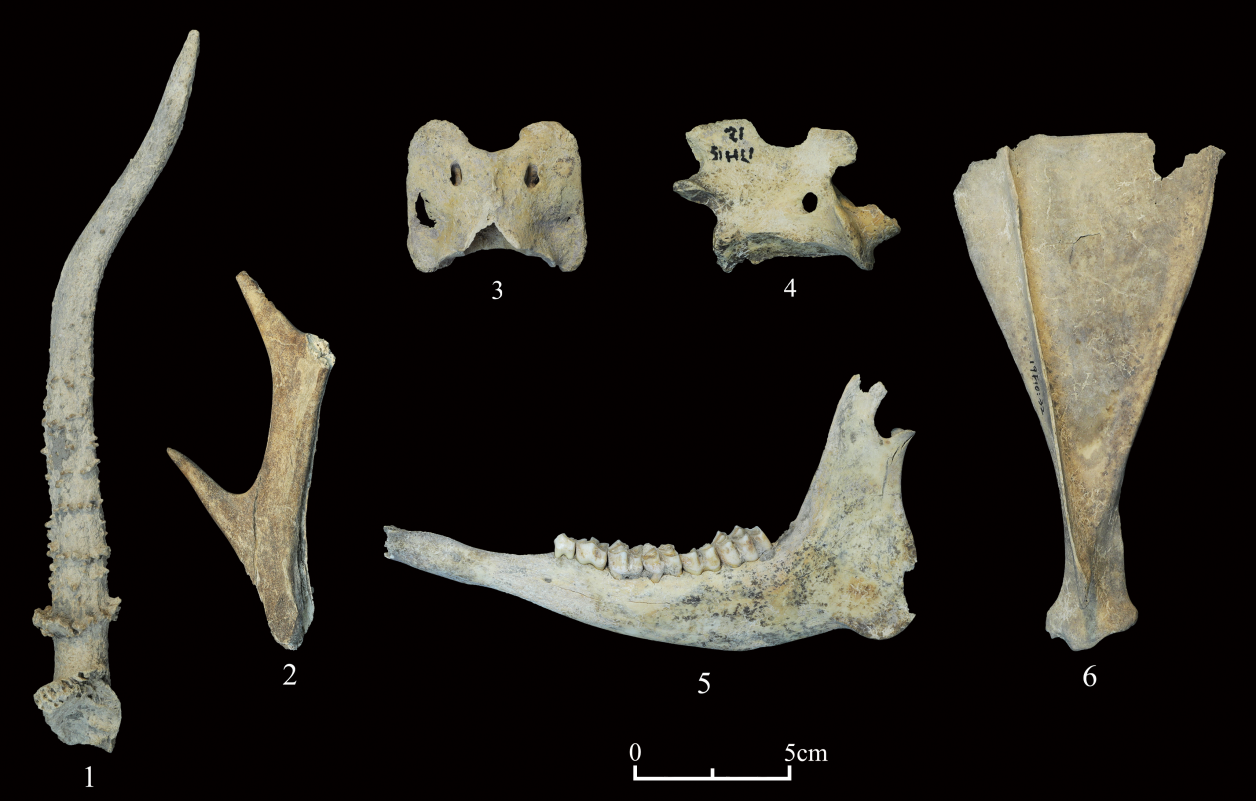
梁琪瑶, 张伟, 陈全家, 等. 黑龙江齐齐哈尔洪河遗址出土的骨器[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(5): 751-763
|
| [25] |
内蒙古自治区编辑组. 鄂伦春族社会历史调查[M]. 北京: 民族出版社, 2009, 18-76
|
| [26] |
朱洪敏. 鄂伦春族风俗琐谈[J]. 黑龙江史志, 2010, 24: 43-44
|
| [27] |
Chase PG. The hunters of Combe Grenal: Approaches to Middle Paleolithic subsistence in Europe[M]. Oxford: British Archaeological Reports Oxford Ltd, 1986, 28-59
|
| [28] |
Campana DV, Crabtree P. Evidence for skinning and craft activities from the Middle Paleolithic of Shanidar Cave, Iraq[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2019, 25: 7-14
|
| [29] |
Zhang SQ, Zhang Y, Li JS, et al. The broad-spectrum adaptations of hominins in the later period of Late Pleistocene of China: Perspectives from the zooarchaeological studies[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(8): 1529-1539
|
| [30] |
赵宾福. 嫩江流域新石器时代生业方式研究[J]. 考古, 2007, 11: 55-61
|
| [31] |
刘晓溪. 嫩江流域新石器至早期铁器时代聚落考古研究[D].博士学位毕业论文, 长春: 吉林大学, 2020, 95-108
|