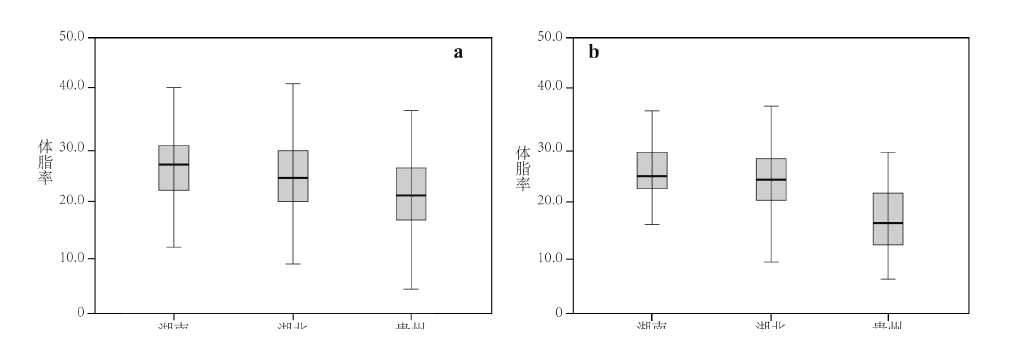
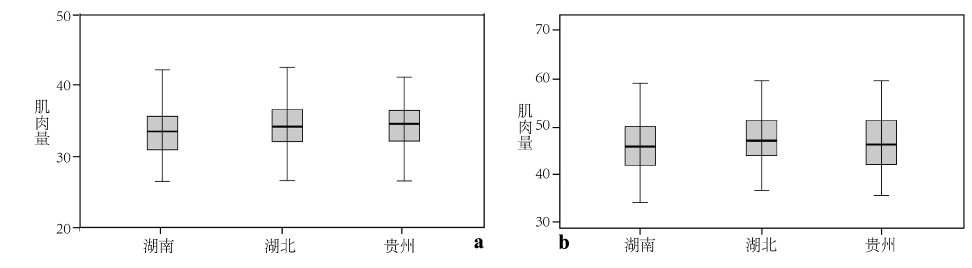
| [1] |
曹毅. 土家族族源再探[J]. 湖北民族学院学报:社会科学版, 1991(4): 34-38
|
| [2] |
周兴茂. 土家族的研究与发展[J]. 长江师范学院学报, 2008,24(5): 69-74
|
| [3] |
左娇蕾, 张倩, 刘爱玲, 等. 北京市儿童青少年体成分的分析[J]. 中国健康教育, 2011,27(6): 415-418
|
| [4] |
崔凯, 徐玉明. 大学生骨密度与身体成分相关分析研究[J]. 健康研究, 2012,32(4): 273-277
|
| [5] |
宇克莉, 王子善, 张兴华, 等. 尔苏人与木雅人身体成分分析[J]. 天津师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2018,38(1): 70-75
|
| [6] |
张兴华, 郑连斌, 宇克莉, 等. 山东寿光汉族体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2011,30(2): 206-217
|
| [7] |
曹芳, 温有锋, 席焕久, 等. 锦州汉族成人体成分与血脂的关系[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2014,37(1): 95-98
|
| [8] |
Mazess RB, Barden HS, Bisek JP, et al. Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry for total-body and regional bone-mineral and soft-tissue composition[J]. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 1990,51(6): 1106-1112
URL
pmid: 2349926
|
| [9] |
席焕久. 人体测量方法[M].科学出版社, 2010
|
| [10] |
闫丹, 阮祥燕. 人体成分测定方法的临床应用与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2011,15(24): 4499-4502
|
| [11] |
邴强, 王健. 人体体成分的模型及检测方法研究进展[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 2001,16(1): 51-55
|
| [12] |
Durnin JV, Womersley J. Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years[J]. British Journal of Nutrition, 1974,32(1): 77-97
|
| [13] |
孙玉梅. 高血压与超重、肥胖的相关性研究[D]. 南京:东南大学, 2009
|
| [14] |
中国肥胖问题工作组数据汇总分析协作组. 我国成人体重指数和腰围对相关疾病危险因素异常的预测价值:适宜体重指数和腰围切点的研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2002,23(1): 5-10
|
| [15] |
温潇潇, 麦劲壮, 高向民, 等. 成人中心性肥胖的腰围切点分析[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2015,43(9): 822-826
|
| [16] |
Altman DG, Bland JM. Measurement in medicine: The analysis of method comparison studies[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1983,32(3): 307-317
|
| [17] |
张国海. 运动对大学生骨密度和体成分的影响及相互关系的研究[J]. 中国体育科技, 2008,44(5): 56-62
|
| [18] |
刘继洪, 杨延斌, 曹海伟, 等. 成年人骨密度、骨量、体重、年龄、身高、脂肪含量相互关系的研究[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2002,18(2): 146-147
|
| [19] |
聂伟志, 隋显玉, 李立, 等. 骨量(骨密度)与体重、体成分的关系[J]. 中医正骨, 2004,16(10): 61-62
|
| [20] |
李继斌. 骨量影响因素研究进展[J]. 环境卫生学杂志, 2000(4): 213-217
|