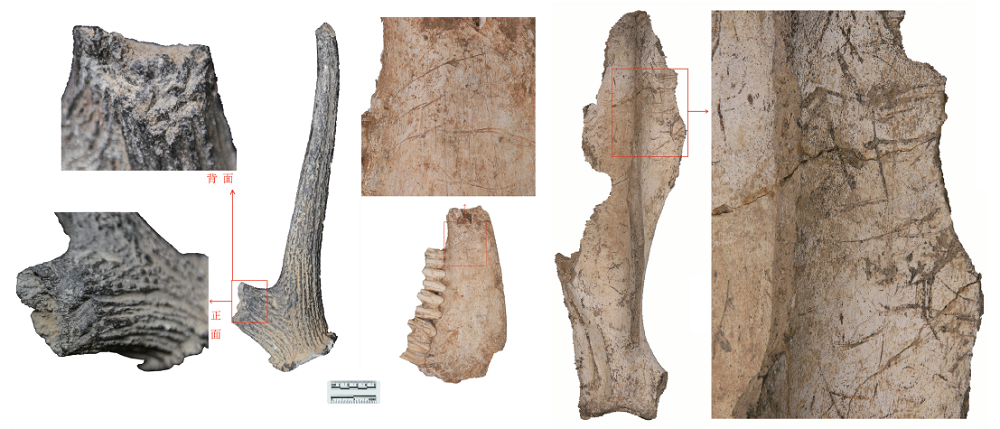
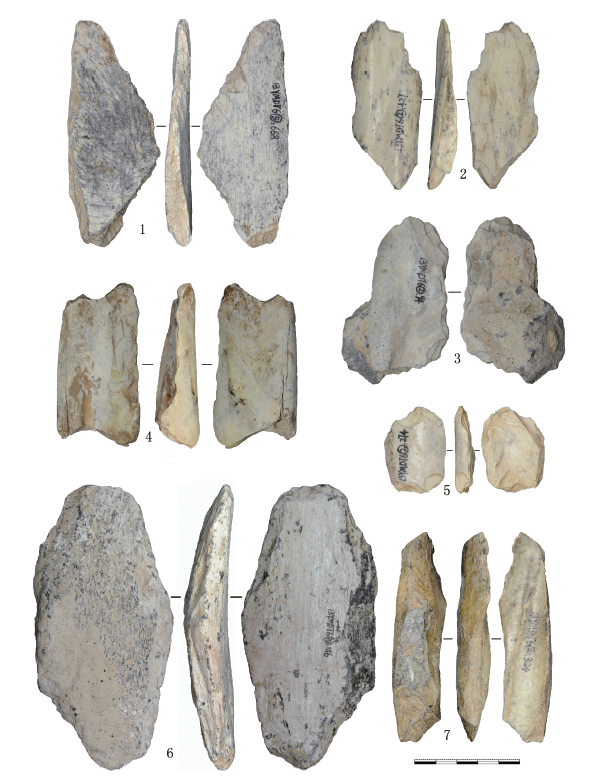
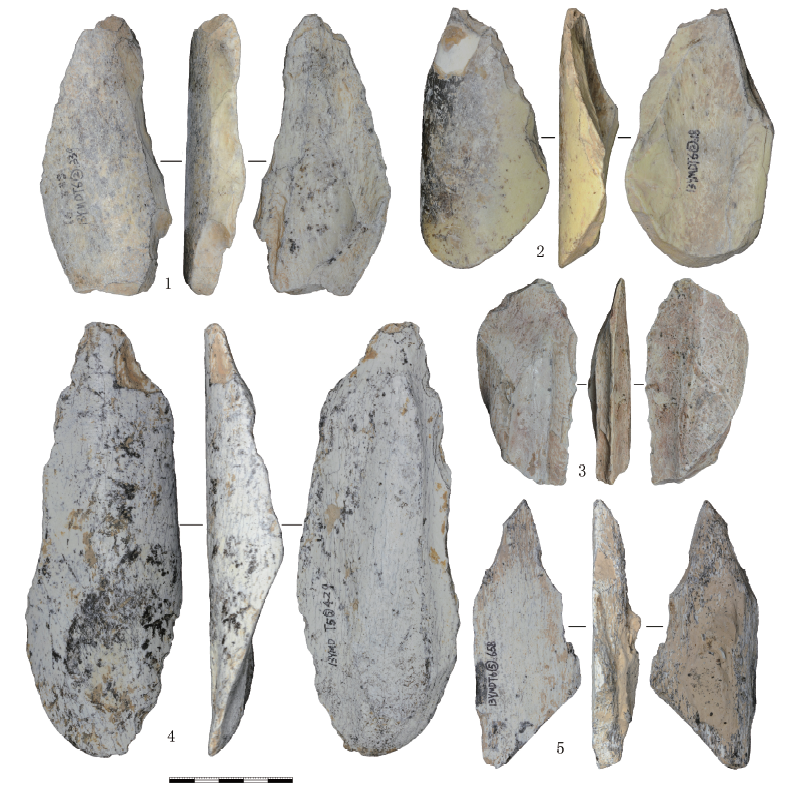
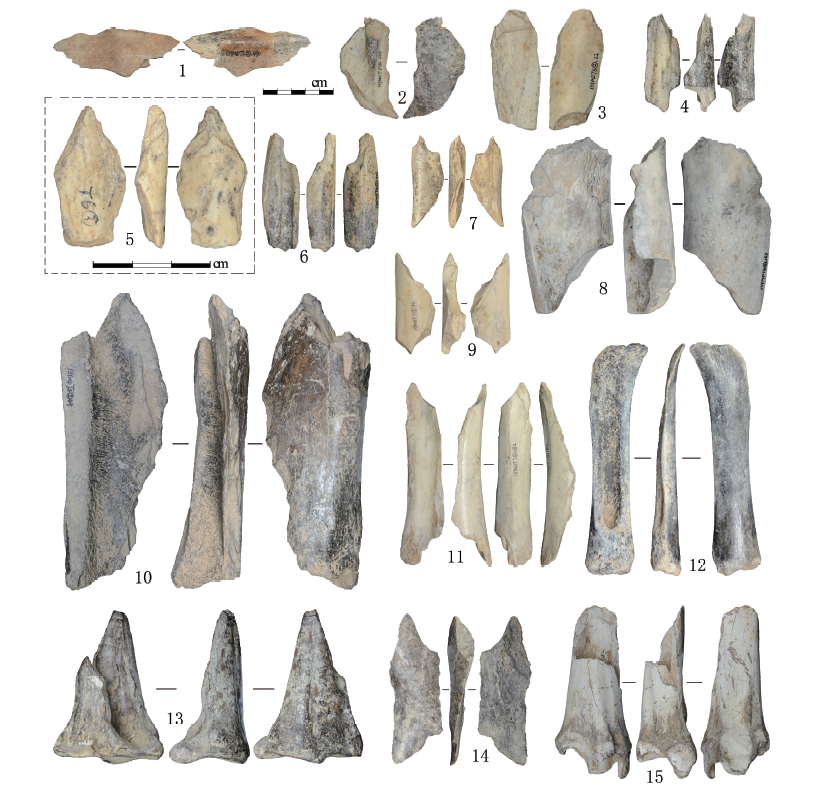
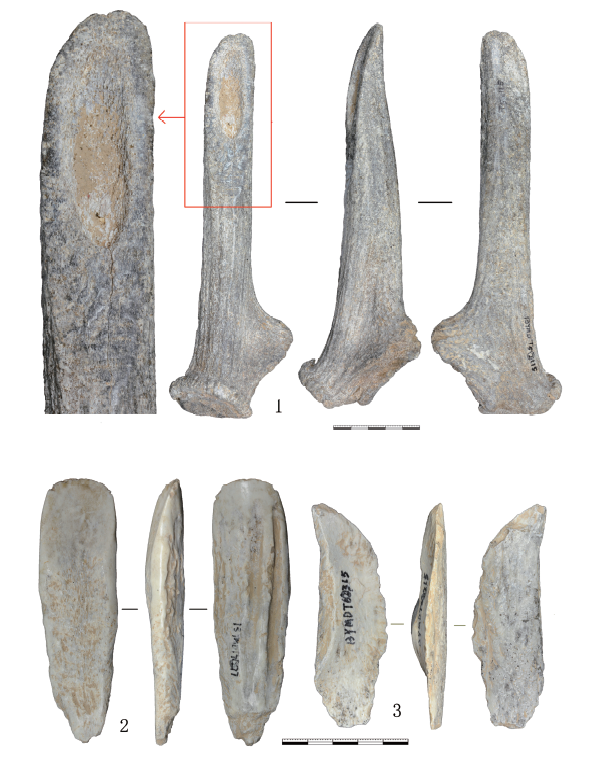
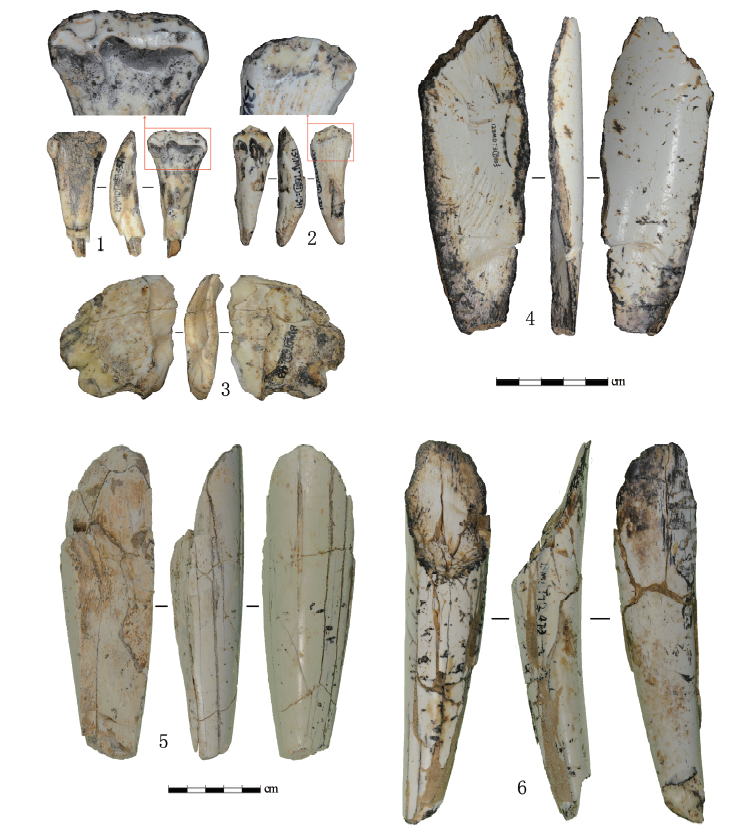
| [1] |
D'Errico F, Backwell L. Assessing the function of early hominin bone tools[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2009,36(8):1764-1773
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2009.04.005
URL
|
| [2] |
张森水. 中国旧石器文化[M]. 天津科学技术出版社, 1987: 78-80
|
| [3] |
Behrensmeyer AK. Taphonomic and Ecologic Information from Bone Weathering[J]. Paleobiology, 1978,4(2):150-162
doi: 10.1017/S0094837300005820
URL
|
| [4] |
吕遵谔, 黄蕴平. 大型肉食哺乳动物啃咬骨骼和敲骨取髓破碎骨片的特征[A].见: 北京大学考古学系编. 纪念北京大学考古专业三十周年论文集[C].北京:文物出版社, 1990: 4-39
|
| [5] |
张俊山. 峙峪遗址碎骨的研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1991,10(4):333-345
|
| [6] |
Zhang S, D'Errico F, Backwell LR, et al. Ma'anshan cave and the origin of bone tool technology in China[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2016,65:57-69
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2015.11.004
URL
|
| [7] |
Wei G, Huang W, Boëda E, et al. Recent discovery of a unique Paleolithic industry from the Yumidong Cave site in the Three Gorges region of Yangtze River, southwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2016
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2006.08.008
URL
pmid: 18591997
|
| [8] |
裴文中. 关于中国猿人骨器问题的说明和意见[J].考古学报, 1960(2):1-9
|
| [9] |
胡家瑞. 山西侯马市南梁旧石器遗址中的骨器[J].考古, 1961(1):20-21
|
| [10] |
曲彤丽, Nicholas JCONARD. 德国旧石器时代晚期骨角器研究及启示[J]. 人类学学报, 2013,32(2):169-181
|
| [11] |
黄蕴平. 小孤山骨针的制作和使用研究[J].考古, 1993(3):260-268
|
| [12] |
吕遵谔. 海城小孤山仙人洞鱼镖头的复制和使用研究[J].考古学报, 1995(1):1-17
|
| [13] |
林圣龙. 楔劈技术、沟裂技术和雕刻器[J]. 人类学学报, 1993,12(2):182-193
|
| [14] |
安家瑗. 小孤山发现的骨鱼镖——兼论与新石器时代骨鱼镖的关系[J]. 人类学学报, 1991,10(1):12-18
|
| [15] |
安家瑷. 华北地区旧石器时代的骨、角器[J]. 人类学学报, 2001,20(4):319-330
|
| [16] |
王尚尊, 郭志慧, 张丽黛. 河北泥河湾早更新世骨制品的初步观察[J]. 人类学学报, 1988,7(4):302-305.
|
| [17] |
冯兴无. 中国旧石器时代骨、角器研究的历史与现状[A].见: 董为主编. 第九届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C]. 北京:海洋出版社, 2004: 183-191
|
| [18] |
毛永琴, 曹泽田. 贵州穿洞遗址1979年发现的磨制骨器的初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2012,31(4):335-343
|
| [19] |
曹泽田. 猫猫洞的骨器和角器研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1982,1(1):36-41.
|
| [20] |
蔡回阳. 白岩脚洞的人化石和骨制品.见: 董为主编. 第十三届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C].北京:海洋出版社, 2012: 203-210
|
| [21] |
贺存定. 玉米洞遗址石器工业与人类行为[D]. 吉林大学, 2016: 12-15
|
| [22] |
Nowell A. Defining Behavioral Modernity in the Context of Neandertal and Anatomically Modern Human Populations[J]. Annual Review of Anthropology, 2010,39(1):437-452.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.anthro.012809.105113
URL
|
| [23] |
李锋. “文化传播”与“生态适应”——水洞沟遗址第2地点考古学观察[D]. 中国科学院大学, 2012: 125-127
|