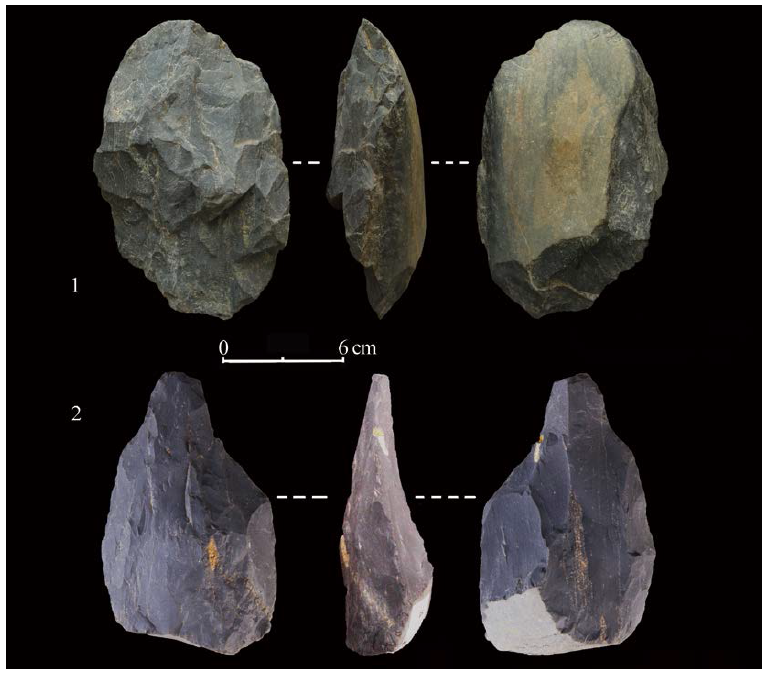
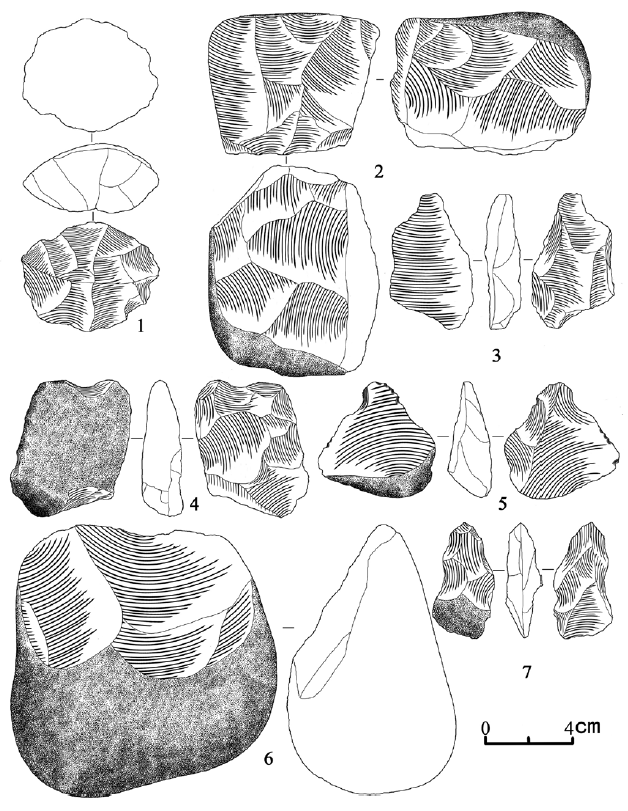
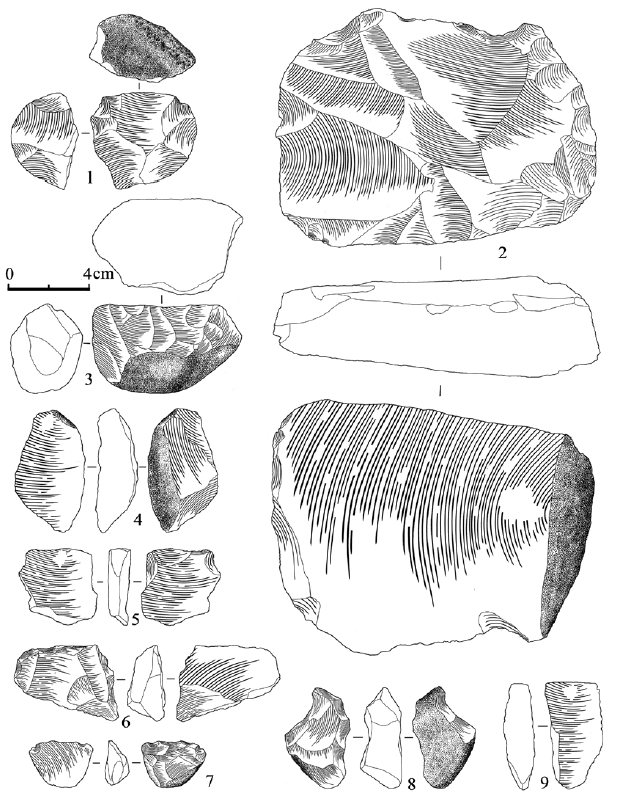
| [1] |
李超荣, 冯兴无, 李浩. 1994年丹江口库区调查发现的石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(4): 337-354
|
| [2] |
李浩, 李超荣, 冯兴无. 2004 年丹江口库区调查发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(2): 113-126
|
| [3] |
牛东伟, 马宁, 裴树文, 等. 丹江口库区宋湾旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(1): 11-23
|
| [4] |
卫奇. 《西侯度》石制品之浅见[J]. 人类学学报, 2000, 19(2): 85-96
|
| [5] |
Toth N. The Oldowan reassessed: a close look at early stone artifacts[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1985, 12: 101-120
doi: 10.1016/0305-4403(85)90056-1
URL
|
| [6] |
李英华. 湖北郧县后房遗址石器工业的年代、操作链及其意义[J]. 江汉考古, 2018, 155(2): 36-47
|
| [7] |
北京联合大学应用文理学院,湖北省文物局,郧阳区文物局. 湖北省郧县滴水岩旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 华夏考古, 2018(6): 43-57
|
| [8] |
黄学诗, 郑绍华, 李超荣, 等. 丹江库区脊椎动物化石和旧石器的发现与意义[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1996, 34(3): 228-233
|
| [9] |
Li H, Li CR, Kuman K. Rethinking the “Acheulean” in East Asia: Evidence from Recent Investigations in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region, Central China[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 347: 163-175
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.03.059
URL
|
| [10] |
张森水. 管窥新中国旧石器考古学的重大发展[J]. 人类学学报, 1998, 18(3): 193-214
|
| [11] |
张森水. 近20年来中国旧石器考古学的进展与思考[J]. 第四纪研究, 2002, 22(1): 11-19
|
| [12] |
牛东伟, 彭菲, 裴树文, 等. 丹江口水库淹没区白渡滩旧石器地点[A].见:中国古生物学会古脊椎动物学分会、第四纪古人类-旧石器专业委员会.第十三届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2012: 171-178
|
| [13] |
牛东伟, 裴树文, 仪明洁, 等. 丹江口库区贾湾1号地点发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(2): 97-112
|
| [14] |
Pei SW, Niu DW, Guan Y, et al. Middle pleistocene hominin occupation in the danjiangkou reservoir region, central china: studies of formation processes and stone technology of maling 2A site[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015, 53: 391-407
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2014.10.022
URL
|
| [15] |
中国科学院大学考古学与人类学系,河南省文物考古研究院. 河南淅川坑南遗址北区2016-2017年度发掘简报[J]. 华夏考古, 2019(3): 3-13
|
| [16] |
中国科学院大学考古学与人类学系,河南省文物考古研究院. 河南淅川坑南旧石器时代遗址TG05发掘简报[J]. 中原文物, 2020(3): 4-14
|
| [17] |
李英华, 孙雪峰. 湖北郧县后房旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 江汉考古, 2013, 126(1): 6-15
|
| [18] |
陈全家, 陈晓颖, 方启. 丹江口库区水牛洼旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(1): 27-38
|
| [19] |
裴树文, 关莹, 高星. 丹江口库区彭家河旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(2): 95-109
|
| [20] |
周振宇, 王春雪, 高星. 丹江口北泰山庙旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 29(3): 246-261
|
| [21] |
李浩, 李超荣, Kuman K. 丹江口库区果茶场II 旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(2): 144-154
|
| [22] |
李意愿, 高成林, 向开旺. 丹江口库区舒家岭旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(2): 149-165
|
| [23] |
陈胜前, 陈慧, 董哲, 等. 湖北郧县余嘴2号旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(1): 39-50
|