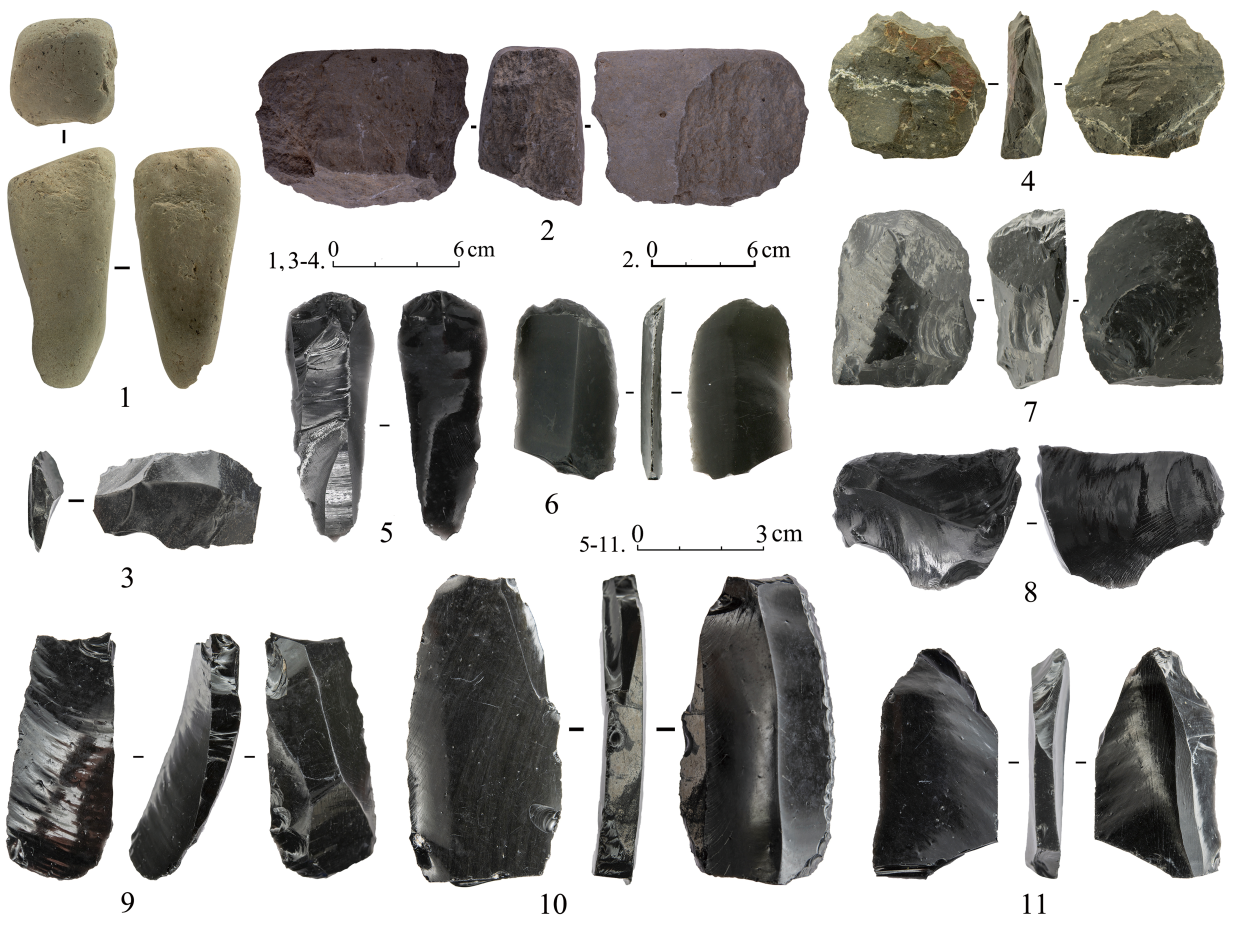
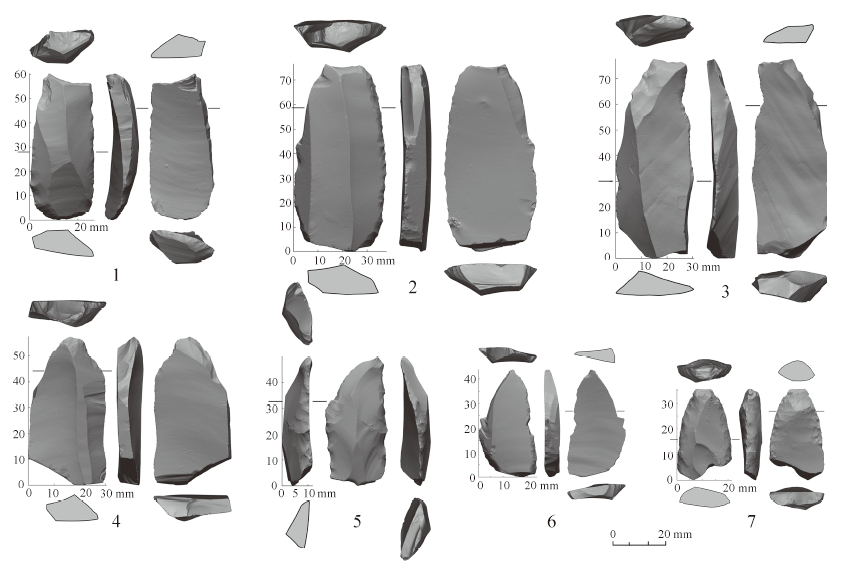
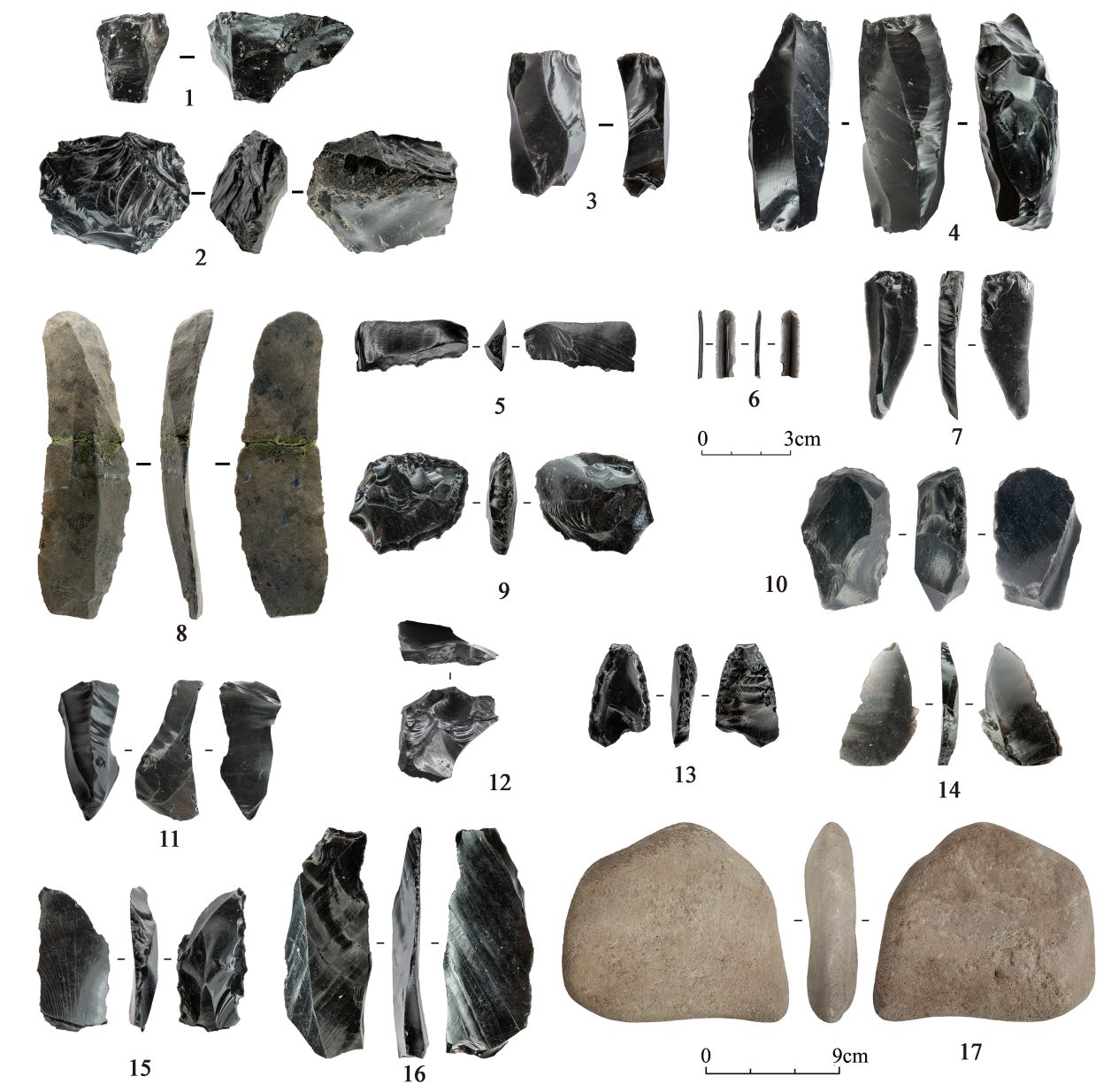
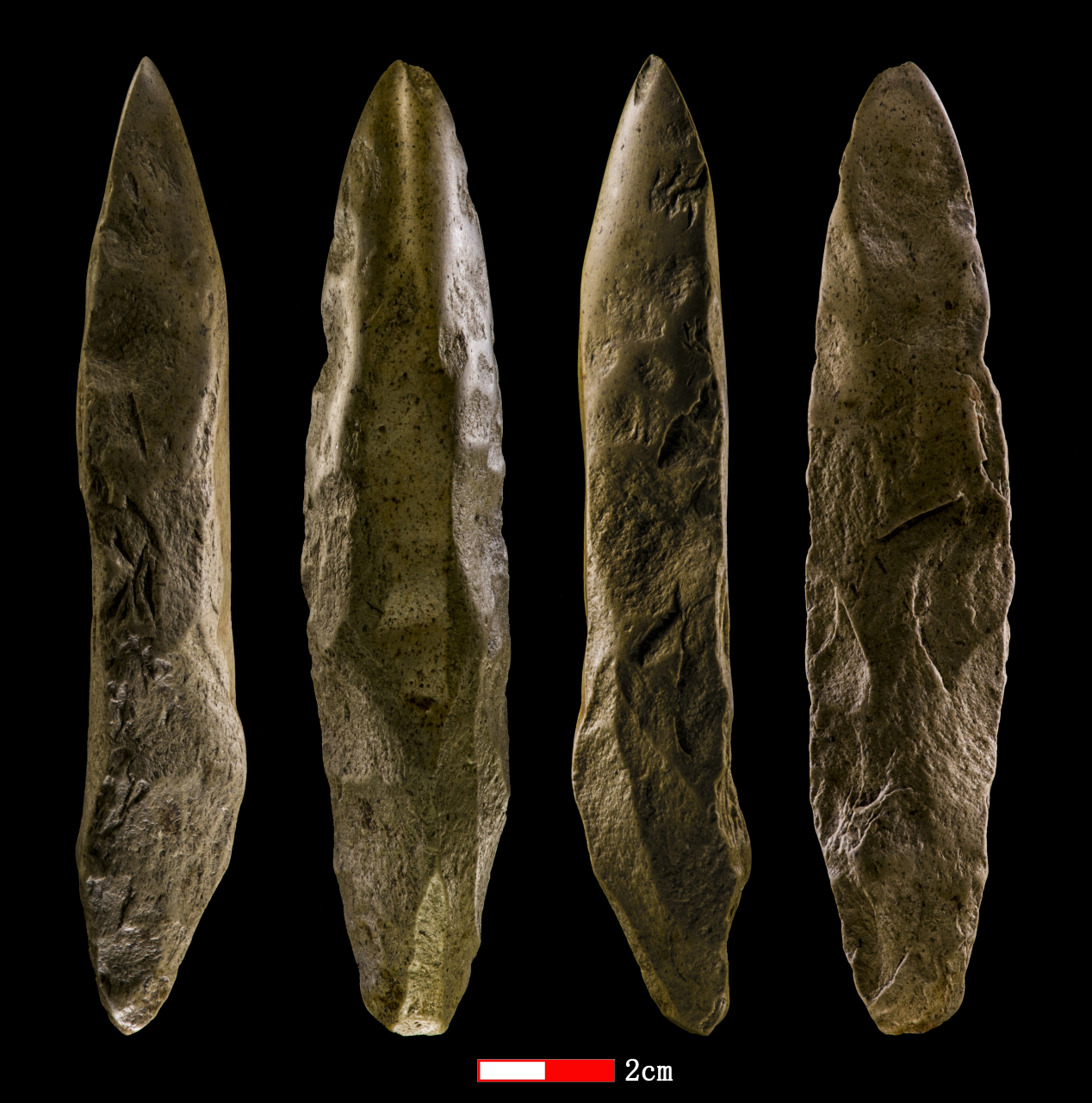
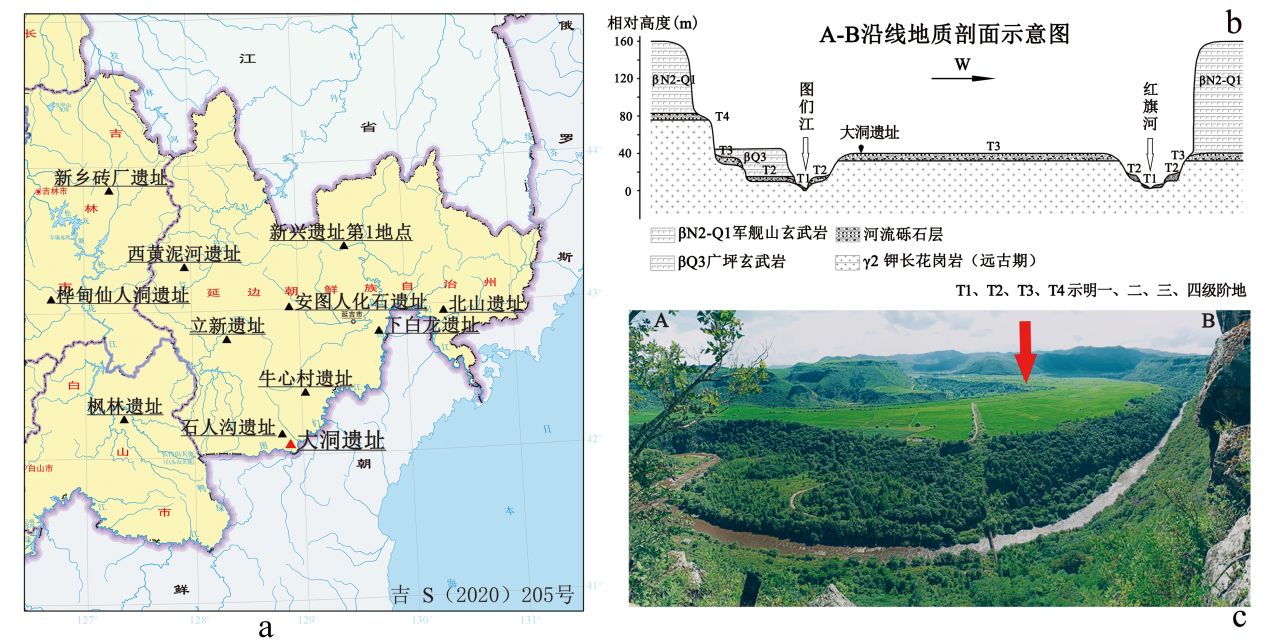
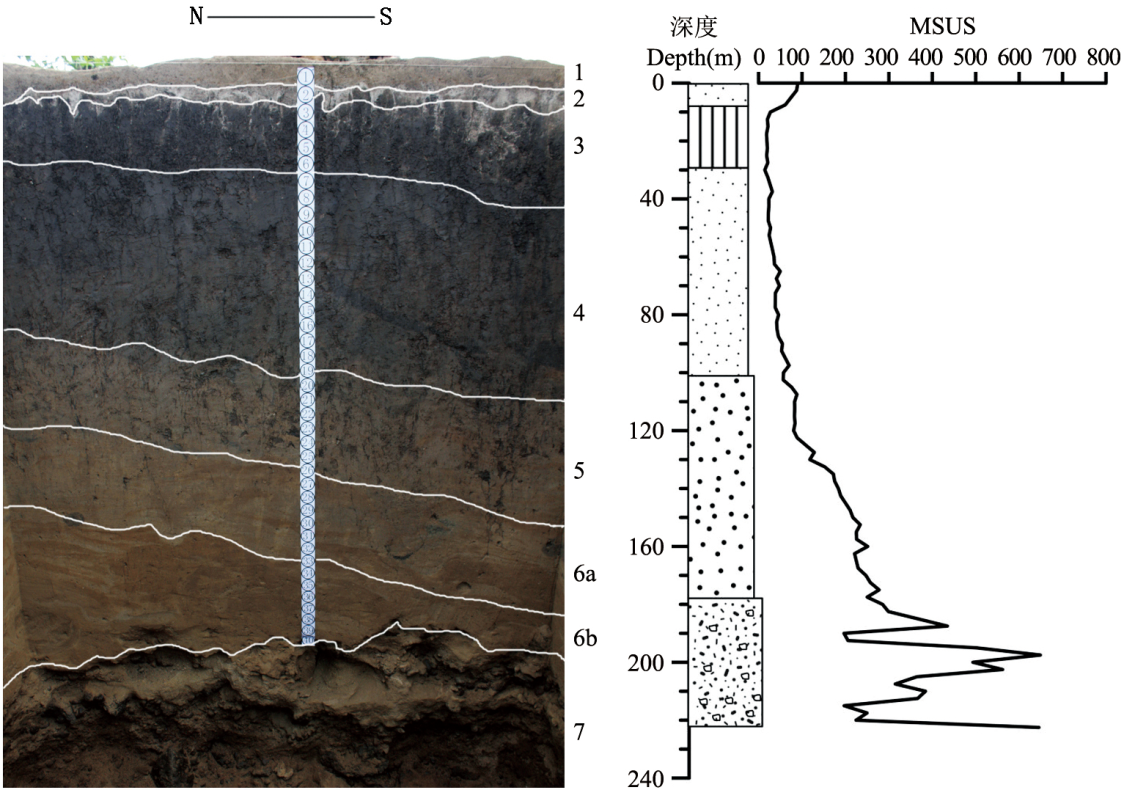
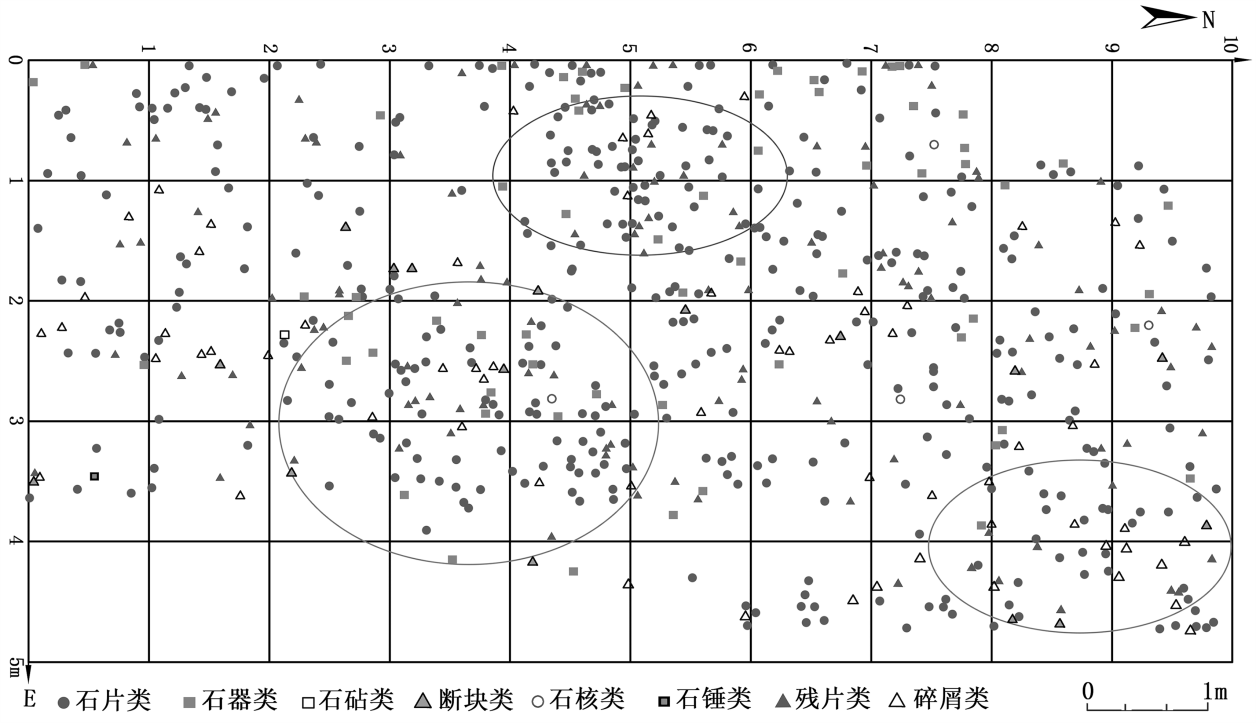
Organized by:Chinese Academy of Sciences
Sponsored by:Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology
Published:China Science Publishing & Media Ltd
Sponsored by:Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology
Published:China Science Publishing & Media Ltd