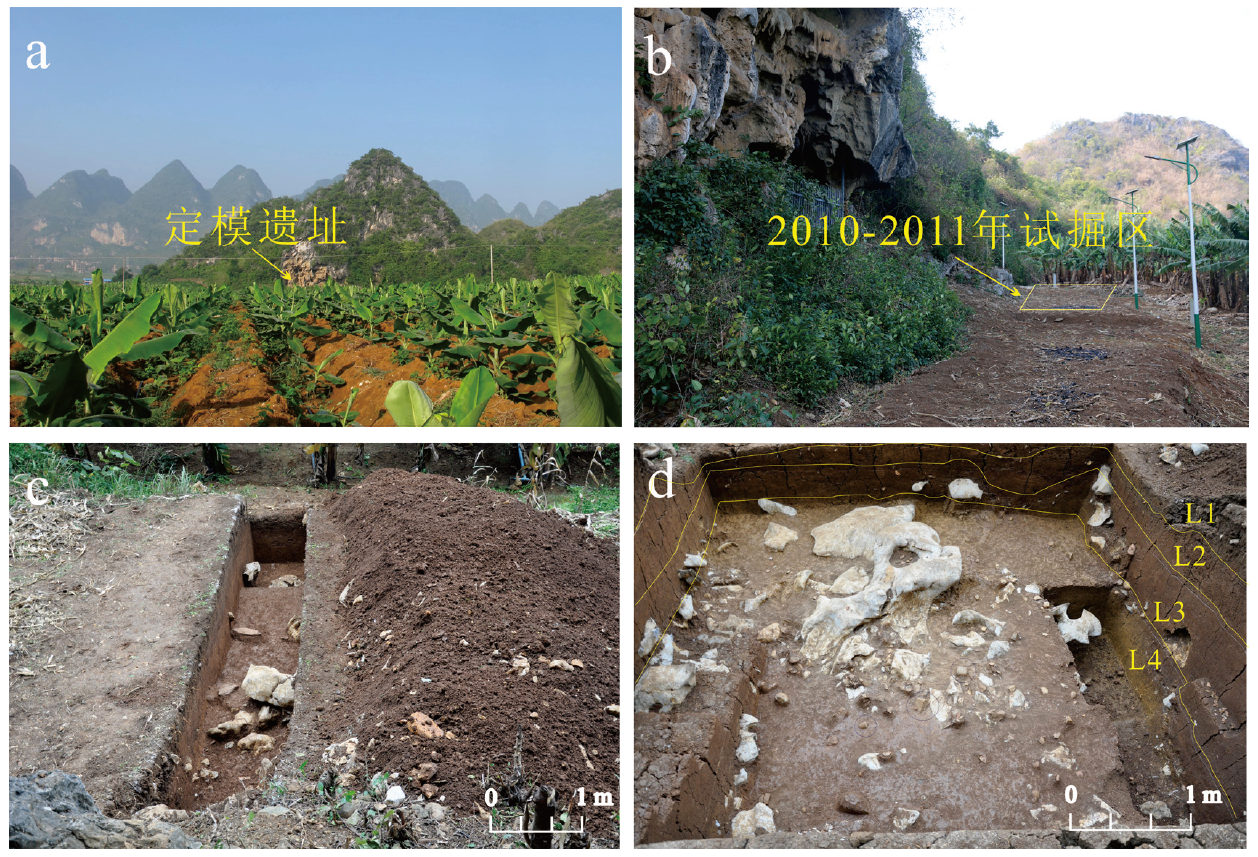
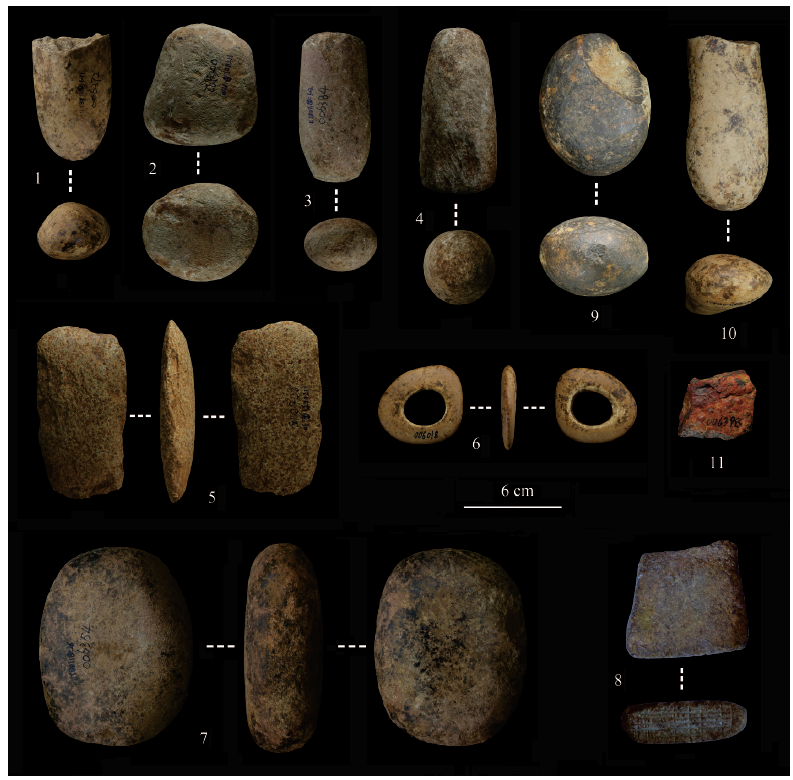
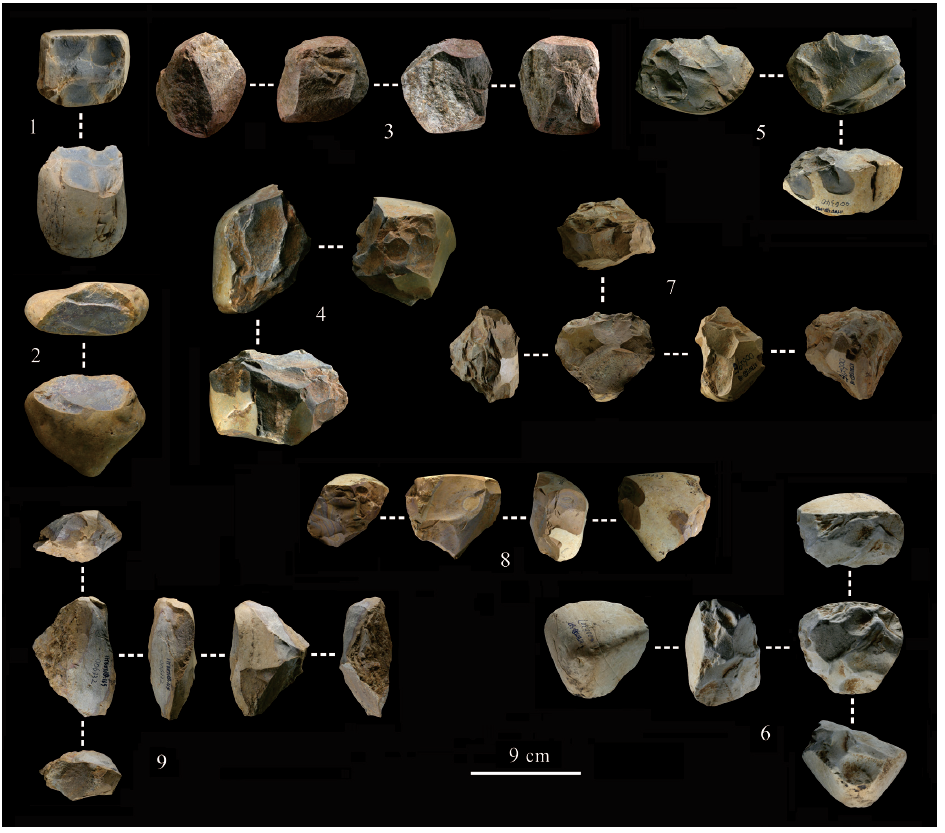
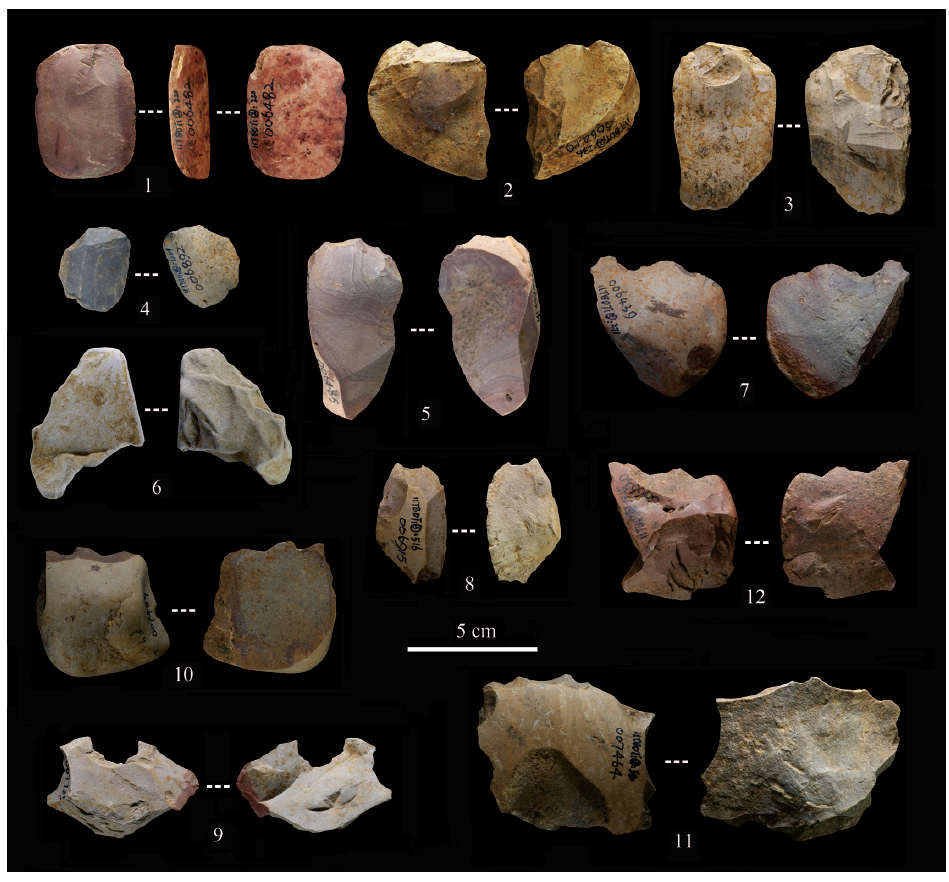
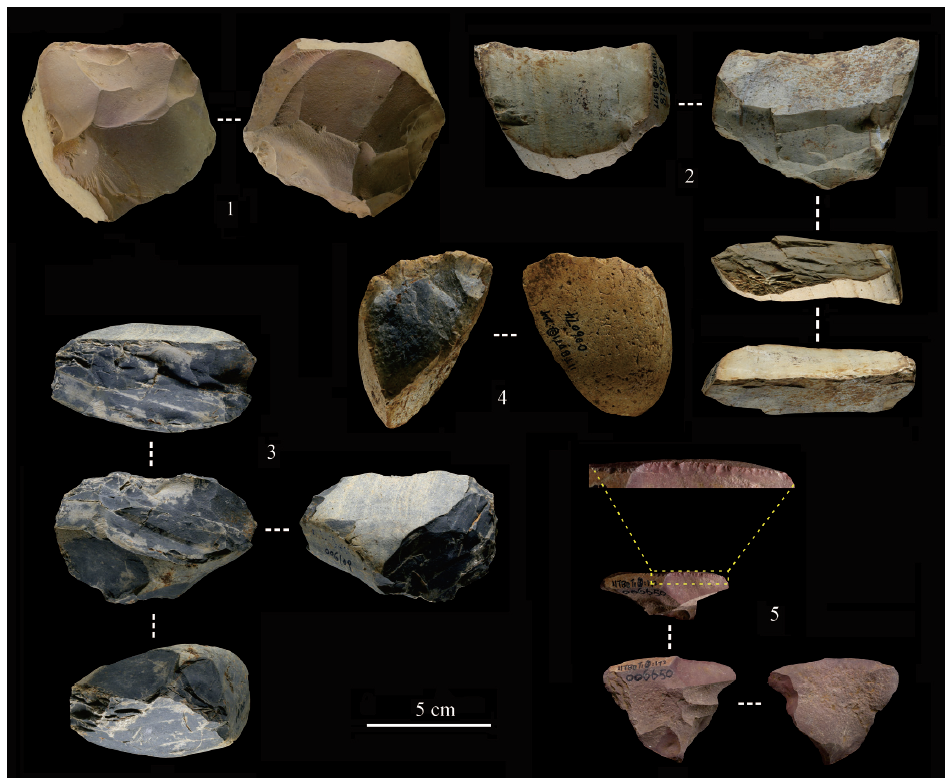
| [1] |
Liu W, Martinón-Torres M, Cai Y, et al. The earliest unequivocally modern humans in southern China[J]. Nature, 2015, 526: 696-699
doi: 10.1038/nature15696
|
| [2] |
Liu W, Jin CZ, Zhang YQ, et al. Human remains from Zhirendong, South China, and modern human emergence in East Asia[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010, 107(45): 19201-19206
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014386107
URL
|
| [3] |
Bae C, Wang W, Zhao J, et al. Modern human teeth from Late Pleistocene Luna Cave (Guangxi, China)[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 354: 169-183
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.06.051
URL
|
| [4] |
Yao YY, Liao W, Bae CJ, et al. New discovery of Late Pleistocene modern human teeth from Chongzuo, Guangxi, southern China[J]. Quaternary International, 2020, 563: 5-12
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2020.02.002
URL
|
| [5] |
Bai F, Zhang XL, Ji XP, et al. Paleolithic genetic link between Southern China and Mainland Southeast Asia revealed by ancient mitochondrial genomes[J]. Journal of Human Genetics, 2020, 65: 1125-1128
doi: 10.1038/s10038-020-0796-9
|
| [6] |
Wang TY, Wang W, Xie GM, et al. Human population history at the crossroads of East and Southeast Asia since 11,000 years ago[J]. Cell, 2021, 184: 3829-3841
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.018
pmid: 34171307
|
| [7] |
Chen XY, He AY, Sun XF, et al. Guomo open-air site (15-12 ka) in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, southern China: A new cobble-based industry for rethinking the definition of “Hoabinhian”[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2023, 49: 104033
doi: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2023.104033
URL
|
| [8] |
Zhou YD, Wei J, Wang R, et al. Between simplicity and complexity: The knapping flexibility on cobbles at the early Neolithic site of Zengpiyan Cave (12-7 ka), Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, southern China[J]. L’anthropologie, 2022, 126: 103098
|
| [9] |
王幼平. 华南晚更新世晚期人类行为复杂化的个案——江西万年吊桶环遗址的发现[J]. 人类学学报, 2016, 35(3): 397-406
|
| [10] |
Xie GM, Lin Q, Wu Y, et al. The Late Paleolithic industries of southern China (Lingnan region)[J]. Quaternary International, 2020, 535: 21-28
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.09.043
URL
|
| [11] |
Wang YP. Late Pleistocene Human Migrations in China[J]. Current Anthropology, 2017, 58: S504-S513
doi: 10.1086/693899
URL
|
| [12] |
何乃汉, 黄云忠, 刘文. 柳州市大龙潭鲤鱼嘴新石器时代贝丘遗址[J]. 考古, 1983, 9: 769-774+865
|
| [13] |
邓婉文, 刘锁强, 巫幼波, 等. 广东英德青塘遗址黄门岩2号洞地点2016年度的发掘[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(1): 64-73
|
| [14] |
广东省珠江文化研究会岭南考古研究专业委员会等编著. 英德牛栏洞遗址:稻作起源与环境综合研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.05
|
| [15] |
宋方义, 张镇洪, 邓增魁, 等. 广东封开黄岩洞1989年和1990年发掘简报[J]. 东南文化, 1992, 1: 148-156
|
| [16] |
广西柳州白莲洞洞穴科学博物馆编著. 柳州白莲洞[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009
|
| [17] |
广西文物保护与考古研究所, 隆安县文物管理所. 广西隆安娅怀洞遗址发掘取得重要收获[N]. 中国文物报,2018-01-19(004)
|
| [18] |
李意愿, 谭远辉, 罗希, 等. 湖南澧县十里岗旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 考古与文物, 2020, 1: 3-13
|
| [19] |
李意愿, 王轩, 陆翼捷, 等. 湖南澧县乌鸦山旧石器遗址2011年发掘简报[J]. 江汉考古, 2019, 6: 20-31+16
|
| [20] |
李意愿. 湖南临澧县条头岗旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2019, 3: 3-14+2
|
| [21] |
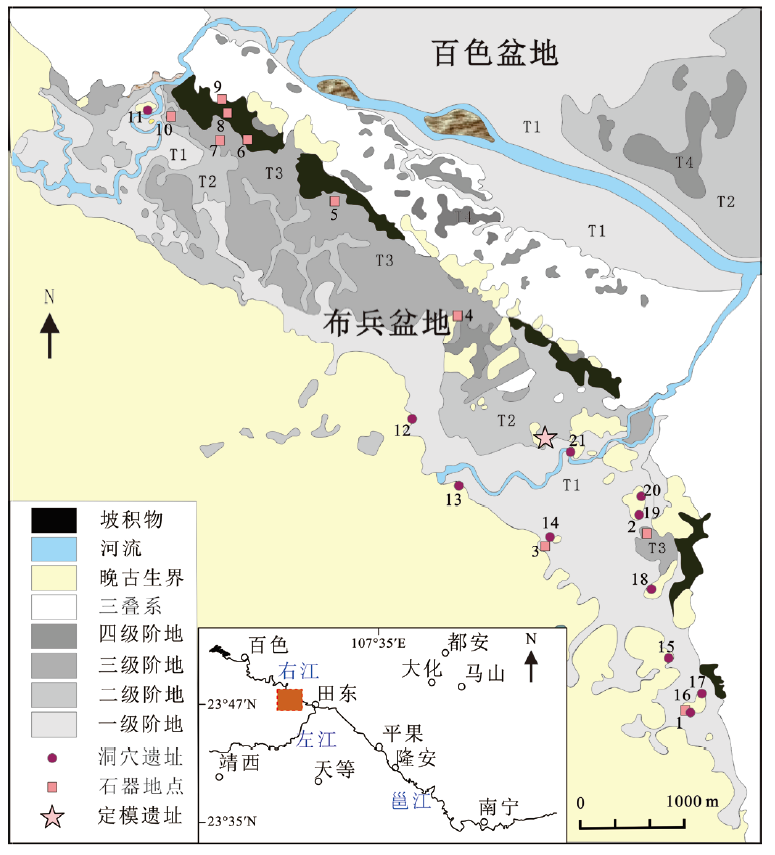
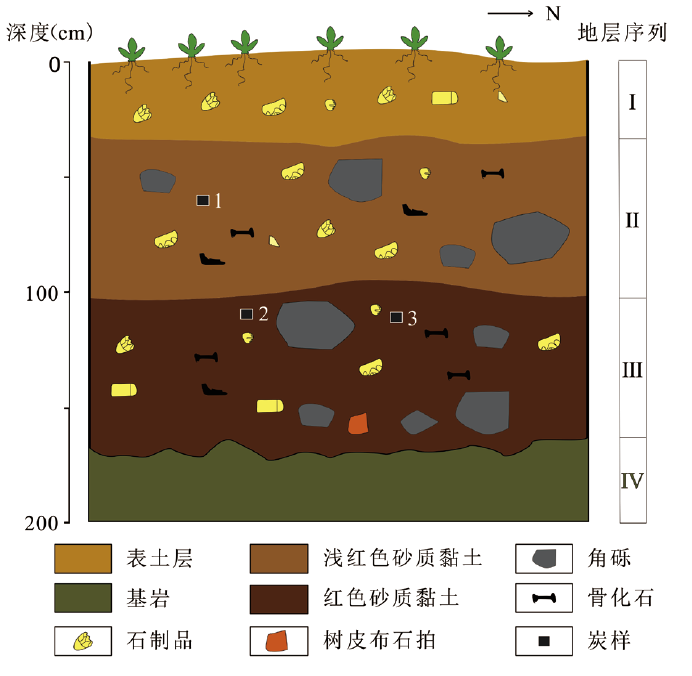
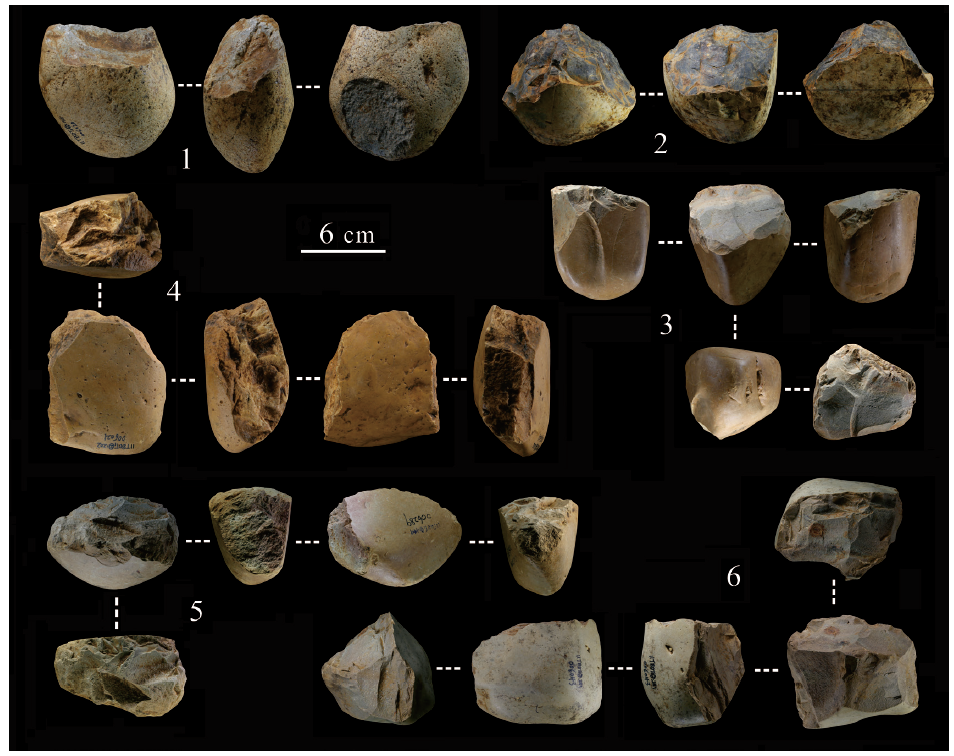
王頠. 广西布兵盆地河流阶地新发现的史前石器遗址[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(3: 270-284
|
| [22] |
Li D, Wang W, Tian F, et al. The oldest bark cloth beater in southern China (Dingmo, Bubing basin, Guangxi)[J]. Quaternary International. 2014, 354: 184-189
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.06.062
URL
|
| [23] |
田丰, 黄芬, 黄秋艳, 等. 广西布兵盆地第四纪地貌与地质发育历史[A].见:第十一届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008:221-228
|
| [24] |
王頠, Richard Potts, 侯亚梅, 等. 广西布兵盆地么会洞新发现的早更新世人类化石[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(17): 1879-1883
|
| [25] |
王頠. 广西田东么会洞早更新世遗址[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013
|
| [26] |
Wang W, Potts R, Yuan B, et al. Sequence of mammalian fossils, including hominoid teeth, from the Bubing Basin Caves, South China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2007, 52: 370-379
pmid: 17198721
|
| [27] |
Tian C, Liao W, Chen Q, et al. Human behavioral responses to the 8.2 ka BP climatic event: Archaeological evidence from the Zhongshandong Cave Site in Bubing basin, Guangxi, southern China[J]. Quaternary International, 2020, 563: 96-104
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2020.01.004
URL
|
| [28] |
Tian C, Liao W, Yao YY, et al. New lithic evidence from Terminal Pleistocene-Early Holocene Zhongshan Rockshelter, Guangxi, southern China[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2023, 49: 103916
doi: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2023.103916
URL
|
| [29] |
李有恒, 吴茂霖, 彭书琳, 等. 广西田东县祥周公社定模洞调查报告[J]. 人类学学报, 1985(02): 127-131
|
| [30] |
Bordes F. The old stone age[M]. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 1968
|
| [31] |
Debenath A, Dibble HL. Hand book of Paleolithic Typology: Lower and Middle Paleolithic of Europe[M]. University Museum,University of Pennsylvania, 1994
|
| [32] |
Wright K. A classification system for ground stone tools from the prehistoric Levant[J]. Paléorient, 1992, 2: 53-81
|
| [33] |
周玉端, 李英华, 韦军, 等. 广西桂林市甑皮岩遗址砾石工具的技术-功能分析及相关问题[J]. 考古, 2023, 1: 65-78
|
| [34] |
Thong PH. Con Moong Cave: A Noteworthy Archaeological Discovery in Vietnam[J]. Asian Perspectives, 1980, 23(1): 17-21
|
| [35] |
Anisyutkin NK, Timofeyev VI. The Paleolithic flake industry in Vietnam[J]. Archaeology, Ethnology & Anthropology of Eurasia, 2006, 27: 16-24
|
| [36] |
Wu Y, Qiu K, Luo Y, et al. Dedan Cave: Extending the evidence of the Hoabinhian technocomplex in southwest China[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2022, 44: 103524
doi: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2022.103524
URL
|
| [37] |
Ji X, Kuman K, Clarke RJ, et al. The oldest Hoabinhian technocomplex in Asia (43.5 ka) at Xiaodong rockshelter, Yunnan Province, southwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 1-9
|
| [38] |
Zhou Y, Forestier H, Wu Y, Jet al. Final Pleistocene-Early Holocene ( -40-8 ka) Lithic Industries in Southern China and Their Implications for Understanding the Prehistory of Mainland Southeast Asia[J]. Lithic Technology, 2023, 2247645
|
| [39] |
Zhou Y, Ji X, Li Y, et al. Tangzigou open-air site: A unique lithic assemblage during the Early Holocene in Yunnan Province, Southwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2020, 563: 105-118
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2019.11.011
URL
|
| [40] |
Zhou YD, Cai SF, Liu XD, et al. Cobbles during the final Pleistocene-early Holocene transition: An original lithic assemblage from Maomaodong rockshelter, Guizhou Province, southwest China[J]. Archaeological Research in Asia, 2022, 32: 100411
doi: 10.1016/j.ara.2022.100411
URL
|