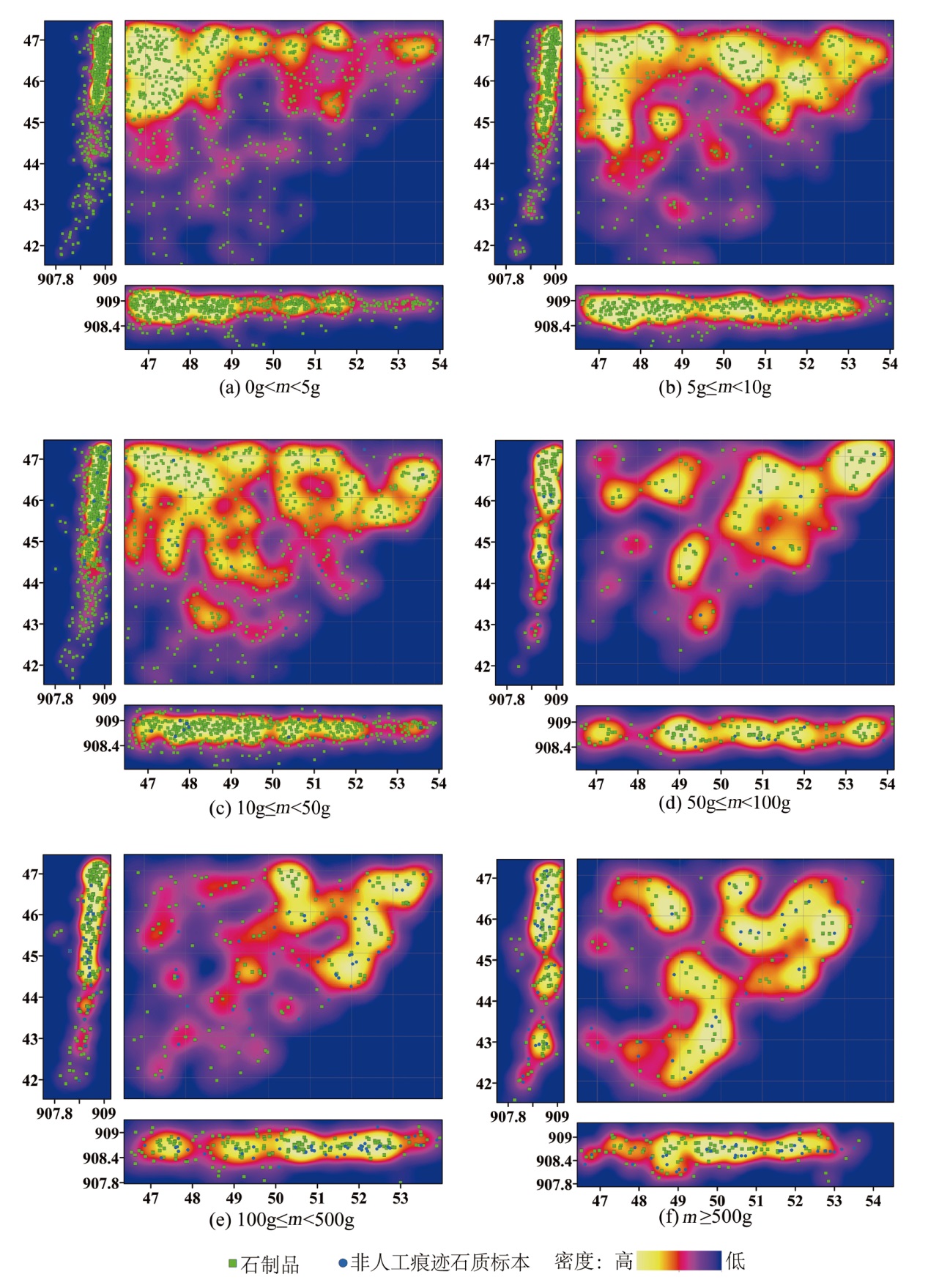
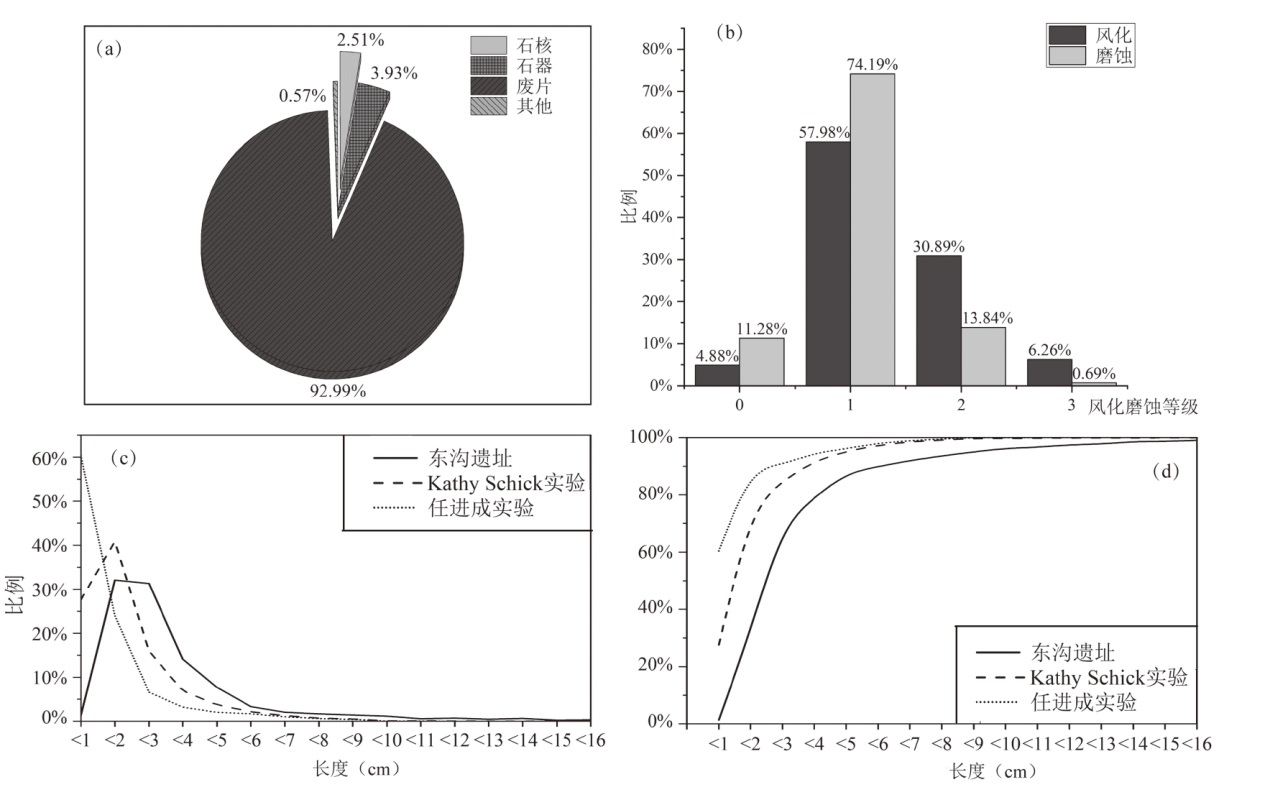
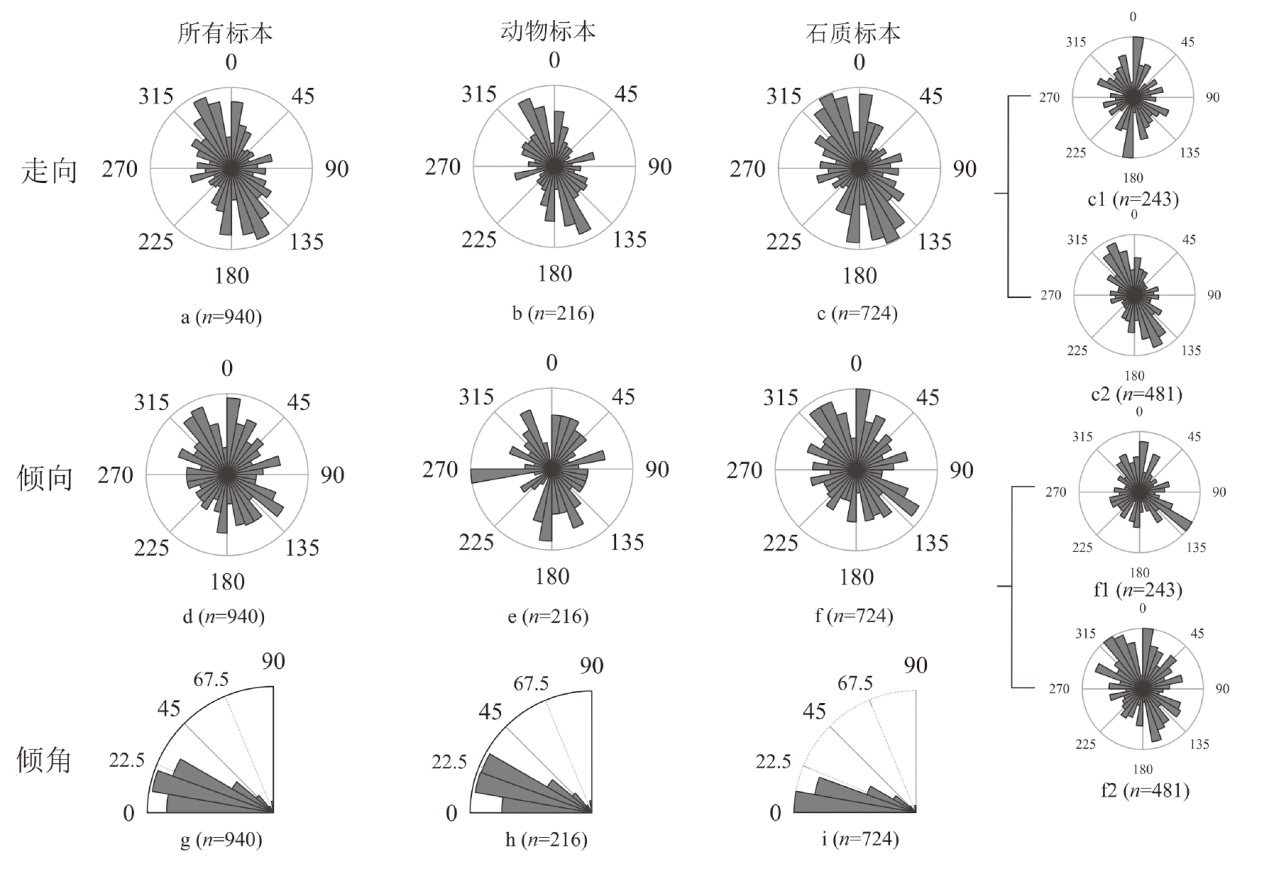
| [1] |
Rogers MJ, Semaw S. From nothing to something:The appearance and context of the earliest archaeological record[A]. In: CampsM, ChauhanP(eds). Sourcebook of Paleolithic Transitions[M]. S pringer Science+Business Media, 2009, 155-171
|
| [2] |
Zaidner Y, Frumkin A, Friesem D, et al. Landscapes, depositional environments and human occupation at Middle Paleolithic open-air sites in the southern Levant, with new insights from Nesher Ramla, Israel[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 138: 76-86
|
| [3] |
裴树文. 旧石器时代旷野遗址形成过程研究综述[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(1): 1-18
|
| [4] |
Aldeias V, Sandgathe D, McPherron SJP, et al. Site formation histories and context of human occupations at the Paleolithic site of La Ferrassie (Dordogne, France)[J]. Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology, 2023, 6: 30
|
| [5] |
Galili E, Ronen A, Mienis HK, et al. Beach deposits containing Middle Paleolithic archaeological remains from northern Israel[J]. Quaternary International, 2018, 464: 43-57
|
| [6] |
Hale JC, Benjamin J, Woo K, et al. Submerged landscapes, marine transgression and underwater shell middens: Comparative analysis of site formation and taphonomy in Europe and North America[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2021, 258: 106867
|
| [7] |
Hassan FA. Sediments in archaeology: methods and implications for palaeoenvironmental and cultural analysis[J]. Journal of Field Archaeology, 1978, 5(2): 197-213
|
| [8] |
Petraglia MD, Potts R. Water flow and the formation of Early Pleistocene artifact sites in Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania[J]. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, 1994, 13(3): 228-254
|
| [9] |
Bridgland DR, Antoine P, Limondin-Lozouet N, et al. The Palaeolithic occupation of Europe as revealed by evidence from the rivers: data from IGCP 449[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2006, 21(5): 437-455
|
| [10] |
裴树文. 中国古人类活动遗址形成过程研究的进展与思考[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(3): 349-362
|
| [11] |
Benito-Calvo A, de la Torre I. Analysis of orientation patterns in Olduvai Bed I assemblages using GIS techniques: Implications for site formation processes[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2011, 61(1): 50-60
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2011.02.011
pmid: 21470661
|
| [12] |
Pei S, Niu D, Guan Y, et al. Middle Pleistocene hominin occupation in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region, Central China: studies of formation processes and stone technology of Maling 2A site[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015, 53: 391-407
|
| [13] |
Schick K. Geoarchaeological analysis of an Acheulean site at Kalambo Falls, Zambia[J]. Geoarchaeology, 1992, 7(1): 1-26
|
| [14] |
Morton AGT. Archaeological site formation: Understanding lake margin contexts[M]. Oxford: BAR International Series 1211, 2004
|
| [15] |
谢飞. 泥河湾旧石器时代考古的回顾与展望[J]. 河北师范大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2018, 41(3): 5-11
|
| [16] |
裴树文, 贾真秀, 马东东, 等. 泥河湾盆地麻地沟E5旧石器地点的遗址成因与石器技术[J]. 人类学学报, 2016, 35(4): 493-508
|
| [17] |
Jia Z, Pei S, Benito-Calvo A, et al. Site formation processes at Donggutuo: A major Early Pleistocene site in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2019, 34(8): 621-632
|
| [18] |
Ma DD, Pei S, Xie F, et al. Site formation processes at Cenjiawan (Nihewan Basin, North China): A case study on the structure of the Early Pleistocene archaeological record in lakeshore environments[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2023, 38(4): 488-504
|
| [19] |
Pei S, Xie F, Deng C, et al. Early Pleistocene archaeological occurrences at the Feiliang site, and the archaeology of human origins in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. PLOS ONE, 2017, 12(11): e0187251
|
| [20] |
叶芷, 杜雨薇, 裴树文, 等. 蔚县盆地吉家庄旧石器遗址的形成过程[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(1): 46-60
|
| [21] |
Ao H, Liu CR, Roberts AP, et al. An updated age for the Xujiayao hominin from the Nihewan Basin, North China: implications for Middle Pleistocene human evolution in East Asia[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2017, 106: 54-65
doi: S0047-2484(17)30034-9
pmid: 28434540
|
| [22] |
任进成, 王法岗, 李锋, 等. 泥河湾盆地板井子旧石器时代遗址的形成过程[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(3): 378-392
|
| [23] |
Wang F, Guo Y, Xian Q, et al. Luminescence chronology for the Paleolithic site of Xinmiaozhuang Locality 1 (XMZ1) in the Nihewan Basin, northern China, and its paleoenvironmental and archaeological implications[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2021, 157: 103033
|
| [24] |
Wang FG, Yang SX, Ge JY, et al. Innovative ochre processing and tool use in China 40,000 years ago[J]. Nature, 2022, 603(7900): 284-289
|
| [25] |
周士航, 何湘栋, 徐静玥, 等. 蔚县盆地东沟遗址2017年度发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(1): 132-142
|
| [26] |
张亚光, 马梦玲, 周明兴, 等. 河北蔚县盆地晚上新世以来沉积古环境演化分析[J]. 地质论评, 2023, 69(S1): 37-39
|
| [27] |
夏正楷, 刘锡清. 泥河湾层古地理环境的初步认识[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1984, 3: 101-110
|
| [28] |
李潇丽. 泥河湾盆地吉家庄遗址地层易溶盐沉积记录的古气候信息[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(5): 149-159
|
| [29] |
李浩, 张玉柱, 李意愿, 等. 沉积物特征与旧石器遗址的形成过程[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(3): 363-377
|
| [30] |
Xiao JL, Fan JW, Zhou L, et al. A model for linking grain-size component to lake level status of a modern clastic lake[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 69: 149-158
|
| [31] |
Thompson R, Stober J, Turner G, et al. Environmental applications of magnetic measurements[J]. Science, 1980, 207(4430): 481-486
pmid: 17795619
|
| [32] |
Li H, Li ZY, Lotter MG, et al. Formation processes at the early Late Pleistocene archaic human site of Lingjing, China[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2018, 96: 73-84
|
| [33] |
Schick KD. Stone Age sites in the making: experiments in the formation and transformation of archaeological occurrences[M]. Oxford, England: BAR Series 319, 1986, https://doi.org/10.30861/9780860544074
|
| [34] |
de la Torre I. The Early Stone Age lithic assemblages of Gadeb(Ethiopia) and the Developed Oldowan/early Acheulean in East Africa[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2011, 60(6): 768-812
|
| [35] |
Boehner U, Serangeli J, Richter P. The Spear Horizon: first spatial analysis of the Schöningen site 13 II-4[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2015, 89: 202-213
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2015.10.001
pmid: 26626956
|
| [36] |
de la Torre I, Wehr K. Site formation processes of the early Acheulean assemblage at EF-HR (Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania)[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2018, 120: 298-328
doi: S0047-2484(17)30304-4
pmid: 28802723
|
| [37] |
Katsianis M, Tsipidis S, Kotsakis K, et al. A 3D digital workflow for archaeological intra-site research using GIS[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2008, 35(3): 655-667
|
| [38] |
de la Torre I, Mora R, 裴树文, 等. 旧石器时代早期石制品分析方案[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(4): 547-567
|
| [39] |
de la Torre I, Benito-Calvo A, Proffitt T. The impact of hydraulic processes in Olduvai Beds I and II, Tanzania, through a particle dimension analysis of stone tool assemblages[J]. Geoarchaeology, 2018, 33(2): 218-236
|
| [40] |
de la Torre I, Vanwezer N, Benito-Calvo A, et al. Spatial and orientation patterns of experimental stone tool refits[J]. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 2019, 11(9): 4569-4584
doi: 10.1007/s12520-018-0701-z
|
| [41] |
Bertran P, Hetu B, Texier JP, et al. Fabric characteristics of subaerial slope deposits[J]. Sedimentology, 1997, 44(1): 1-16
|
| [42] |
Bertran P, Texier JP. Fabric analysis: application to Paleolithic sites[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1995, 22(4): 521-535
|
| [43] |
Bertran P, Texier JP. Facies and microfacies of slope deposits[J]. Catena, 1999, 35(2-4): 99-121
|