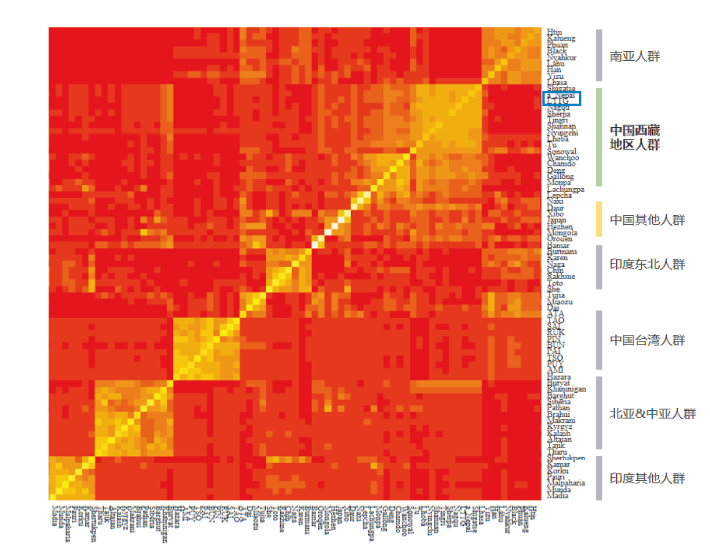
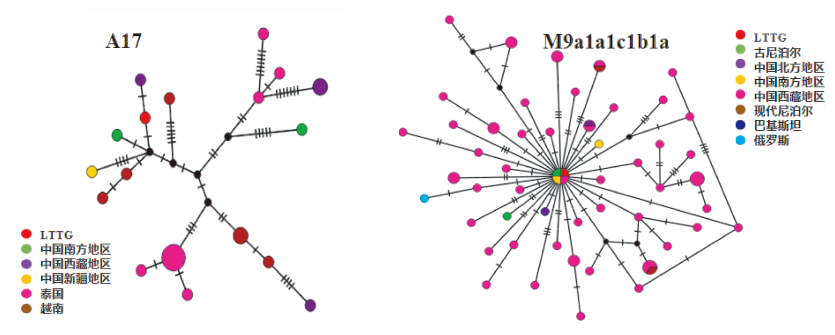
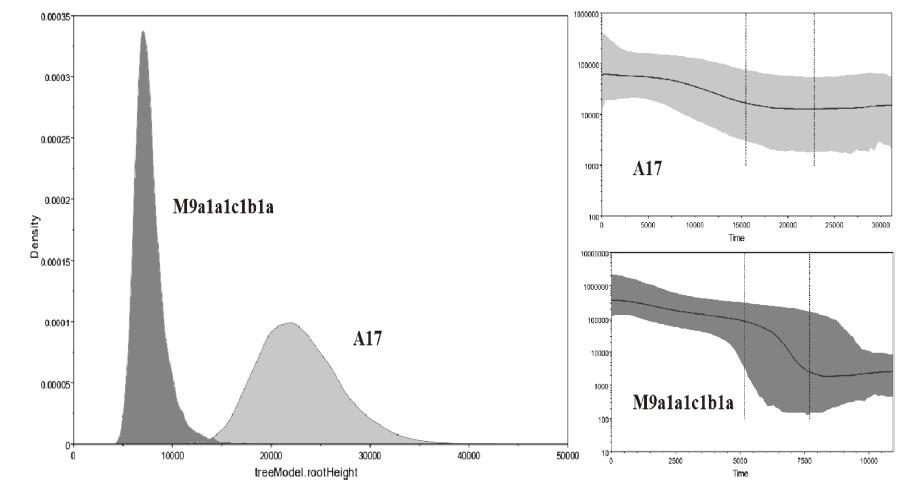
| [1] |
Zhang XL, Ha BB, Wang SJ, et al. The earliest human occupation of the high-altitude Tibetan Plateau 40 thousand to 30 thousand years ago[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6418): 1049-1051
doi: 10.1126/science.aat8824
URL
pmid: 30498126
|
| [2] |
Lu D, Lou H, Kai Y, et al. Ancestral origins and genetic history of Tibetan highlanders[J]. American Journal of Human Genetics, 2016, 99(3): 580-594
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.07.002
URL
pmid: 27569548
|
| [3] |
Li J, Zeng W, Zhang Y, et al. Ancient DNA reveals genetic connections between early Di-Qiang and Han Chinese[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 2017, 17(1): 239
doi: 10.1186/s12862-017-1082-0
URL
pmid: 29202706
|
| [4] |
Yong-Bin Z, Hong-Jie L, Sheng-Nan L, et al. Ancient DNA evidence supports the contribution of Di-Qiang people to the Han Chinese gene pool[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2011, 144(2): 258-268
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.21399
URL
pmid: 20872743
|
| [5] |
Handt O, Krings M, Ward RH, et al. The retrieval of ancient human DNA sequences[J]. American Journal of Human Genetics, 1996, 59(2): 368-76
URL
pmid: 8755923
|
| [6] |
Jeong C, Ozga AT, Witonsky DB, et al. Long-term genetic stability and a high-altitude East Asian origin for the peoples of the high valleys of the Himalayan arc[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(27): 7485
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1520844113
URL
|
| [7] |
Duong NT, Macholdt E, Ton ND, et al. Complete human mtDNA genome sequences from Vietnam and the phylogeography of Mainland Southeast Asia[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 11651.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29989-0
URL
pmid: 30076323
|
| [8] |
Lippold S, Xu H, Ko A, et al. Human paternal and maternal demographic histories: Insights from high-resolution Y chromosome and mtDNA sequences[J]. Investigative Genetics, 2014, 5(1): 13.
doi: 10.1186/2041-2223-5-13
URL
|
| [9] |
Zhendong Q, Yajun Y, Longli K, et al. A mitochondrial revelation of early human migrations to the Tibetan Plateau before and after the last glacial maximum[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2010, 143(4): 555-569
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.21350
URL
pmid: 20623602
|
| [10] |
Mian Z, Qing-Peng K, Hua-Wei W, et al. Mitochondrial genome evidence reveals successful Late Paleolithic settlement on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2009, 106(50): 21230-5
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907844106
URL
|
| [11] |
Peng MS, Palanichamy MG, Yao YG, et al. Inland post-glacial dispersal in East Asia revealed by mitochondrial haplogroup M9a’b[J]. BMC Biology, 2011, 9(1): 2.
doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-9-2
URL
|
| [12] |
Peng MS, Xu W, Song JJ, et al. Mitochondrial genomes uncover the maternal history of the Pamir populations[J]. European Journal of Human Genetics, 2017.
doi: 10.1038/s41431-020-00807-4
URL
pmid: 33495594
|
| [13] |
Kang L, Zheng HX, Zhang M, et al. MtDNA analysis reveals enriched pathogenic mutations in Tibetan highlanders[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 31083
doi: 10.1038/srep31083
URL
|
| [14] |
Li YC, Wang HW, Tian JY, et al. Ancient inland human dispersals from Myanmar into interior East Asia since the Late Pleistocene[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:9473
doi: 10.1038/srep09473
URL
pmid: 25826227
|
| [15] |
Adimoolam C, Satish K, Jwalapuram S, et al. Updating phylogeny of mitochondrial DNA macrohaplogroup m in India: Dispersal of modern human in South Asian corridor[J]. Plos One, 2009, 4(10): e7447
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007447
URL
pmid: 19823670
|
| [16] |
Summerer M, Horst J, Erhart G, et al. Large-scale mitochondrial DNA analysis in southeast Asia reveals evolutionary effects of cultural isolation in the multi-ethnic population of Myanmar[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 2014, 14(1): 17
doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-14-17
URL
|
| [17] |
Wang HW, Li YC, Sun F, et al. Revisiting the role of the Himalayas in peopling Nepal: Insights from mitochondrial genomes[J]. Journal of Human Genetics, 2012, 57(4): 228
doi: 10.1038/jhg.2012.8
URL
|
| [18] |
Bhandari S, Zhang X, Cui C, et al. Genetic evidence of a recent Tibetan ancestry to Sherpas in the Himalayan region[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:16249
doi: 10.1038/srep16249
URL
pmid: 26538459
|
| [19] |
Fornarino S, Pala M, Battaglia V, et al. Mitochondrial and Y-chromosome diversity of the Tharus (Nepal): A reservoir of genetic variation[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 2009, 9(1): 154
doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-9-154
URL
|
| [20] |
Derenko M, Malyarchuk B, Denisova G, et al. Western Eurasian ancestry in modern Siberians based on mitogenomic data[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 2014, 14(1): 217
doi: 10.1186/s12862-014-0217-9
URL
|
| [21] |
Albert Min-Shan K, Chung-Yu C, Qiaomei F, et al. Early Austronesians: into and out of Taiwan[J]. American Journal of Human Genetics, 2014, 94(3): 426-36
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.02.003
URL
|
| [22] |
Kutanan W, Kampuansai J, Srikummool M, et al. Complete mitochondrial genomes of Thai and Lao populations indicate an ancient origin of Austroasiatic groups and demic diffusion in the spread of TaifKadai languages[J]. Human Genetics, 2017, 136(1): 85-98
doi: 10.1007/s00439-016-1742-y
URL
pmid: 27837350
|
| [23] |
Dabney J, Knapp M, Glocke I, et al. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence of a Middle Pleistocene cave bear reconstructed from ultrashort DNA fragments[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(39): 15758-63
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1314445110
URL
|
| [24] |
Rohland N, Harney E, Mallick S, et al. Partial uracil-DNA-glycosylase treatment for screening of ancient DNA[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 2015, 370(1660): 20130624
doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0624
URL
pmid: 25487342
|
| [25] |
Jesse D, Matthias M. Length and GC-biases during sequencing library amplification: A comparison of various polymerase-buffer systems with ancient and modern DNA sequencing libraries[J]. Biotechniques, 2012, 52(2): 87-94
doi: 10.2144/000113809
URL
|
| [26] |
Kircher M, Sawyer S, Meyer M. Double indexing overcomes inaccuracies in multiplex sequencing on the Illumina platform[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40(1): e3
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr771
URL
pmid: 22021376
|
| [27] |
Fu Q, Meyer M, Gao X, et al. DNA analysis of an early modern human from Tianyuan Cave, China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(6): 2223
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221359110
URL
|
| [28] |
Gabriel R, Udo S, Janet K. LeeHom: Adaptor trimming and merging for Illumina sequencing reads[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(18): e141
doi: 10.1093/nar/gku699
URL
pmid: 25100869
|
| [29] |
Gabriel R, Udo S, Tomislav M, et al. DeML: Robust demultiplexing of Illumina sequences using a likelihood-based approach[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 31(5): 770-2
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu719
URL
pmid: 25359895
|
| [30] |
Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(14): 1754-60
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
URL
pmid: 19451168
|
| [31] |
Anita KBT, Dominic P, Sebastian SN, et al. HaploGrep: A fast and reliable algorithm for automatic classification of mitochondrial DNA haplogroups[J]. Human Mutation, 2011, 32(1): 25-32
doi: 10.1002/humu.21382
URL
|
| [32] |
Oven MV. PhyloTree Build 17: Growing the human mitochondrial DNA tree[J]. Forensic Science International, Genetics Supplement, 2015.
|
| [33] |
Kutanan W, et al. New insights from Thailand into the maternal genetic history of mainland southeast Asia. Eur J Hum Genet, 2018, 26(6): 898-911
doi: 10.1038/s41431-018-0113-7
URL
pmid: 29483671
|
| [34] |
Edgar RC. Muscle: Multiple sequence alignment with improved accuracy and speed[A]// Proceedings of the Computational Systems Bioinformatics Conference[C], IEEE, 2004.
|
| [35] |
Edgar RC. Muscle: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2004, 5:113
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-113
URL
pmid: 15318951
|
| [36] |
Bandelt HJ, Forster P. HLA. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1999, 16(1): 37-48
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026036
URL
pmid: 10331250
|
| [37] |
Leigh JW, Bryant D, Nakagawa S. Popart: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2015, 6(9): 1110-1116
doi: 10.1111/mee3.2015.6.issue-9
URL
|
| [38] |
Suchard MA, Lemey P, Baele G, Ayres DL, Drummond AJ, Rambaut A. Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10[J]. Virus Evolution, 2018, 4(1).
doi: 10.1093/ve/vex043
URL
pmid: 29340211
|
| [39] |
Excoffier L, Lischer H. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2010, 10(3): 564-567
doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02847.x
URL
pmid: 21565059
|
| [40] |
Hodges E, Xuan Z, Balija V, et al. Genome-wide in situ exon capture for selective resequencing[J]. Nature Genetics, 2007, 39(12): 1522-1527
doi: 10.1038/ng.2007.42
URL
pmid: 17982454
|
| [41] |
Sawyer S, Renaud G, Viola B, et al. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequences from two Denisovan individuals[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(51): 15696
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1519905112
URL
pmid: 26630009
|
| [42] |
Patterson N, Moorjani P, Luo Y, et al. Ancient admixture in human history[J]. Genetics, 2012, 192(3): 1065
doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.145037
URL
|
| [43] |
David P. jModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging[J]. Molecular Biology & Evolution, 2008, 25(7): 1253-1256
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msn083
URL
pmid: 18397919
|
| [44] |
Jose Manuel S, Diego D, Taboada GL, et al. jmodeltest.org: Selection of nucleotide substitution models on the cloud[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(9): 1310-1311
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu032
URL
|
| [45] |
Meyer MC, et al. Permanent human occupation of the central Tibetan Plateau in the early Holocene[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6320): 64-67
doi: 10.1126/science.aag0357
URL
pmid: 28059763
|
| [46] |
Brantingham PJ, Xing G, Madsen DB, et al. Late occupation of the high-elevation northern Tibetan plateau based on cosmogenic, luminescence, and radiocarbon ages[J]. Geoarchaeology, 2013, 28(5): 413-431
doi: 10.1002/gea.2013.28.issue-5
URL
|
| [47] |
Chen FH, et al. , Agriculture facilitated permanent human occupation of the Tibetan Plateau after 3600 B.P[J]. Science, 2015, 347(6219): 248-250
doi: 10.1126/science.1259172
URL
pmid: 25593179
|
| [48] |
Lu H. Colonization of the Tibetan plateau, permanent settlement, and the spread of agriculture: Reflection on current debates on the prehistoric archeology of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Archaeological Research in Asia, 2016, 5:12-15
doi: 10.1016/j.ara.2016.02.010
URL
|
| [49] |
Qi X, Cui C, Peng Y, et al. Genetic evidence of Paleolithic colonization and Neolithic expansion of modern humans on the Tibetan plateau[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2013, 30(8): 1761-78
doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst093
URL
|