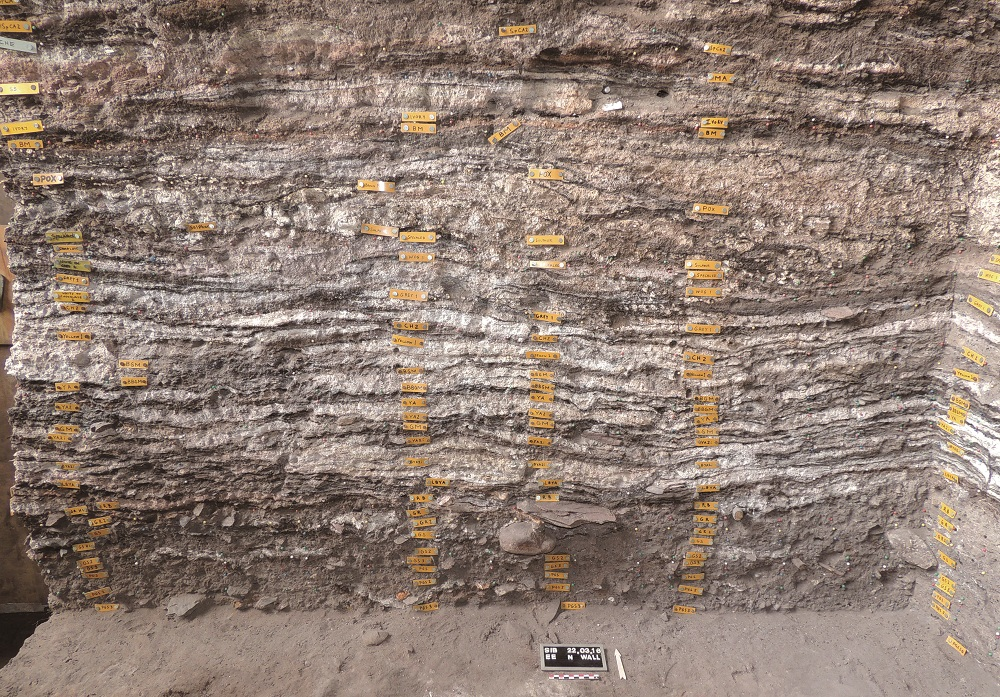
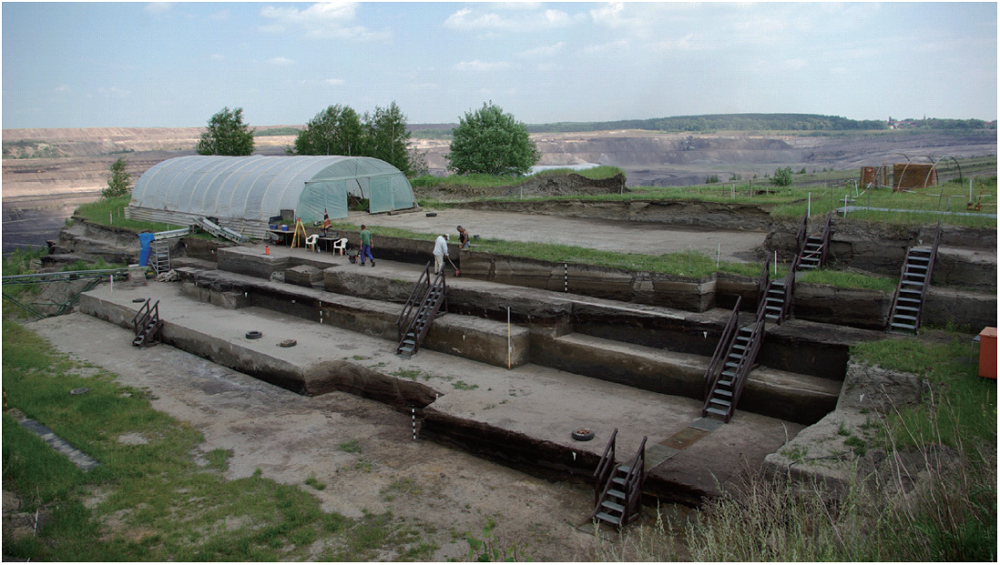
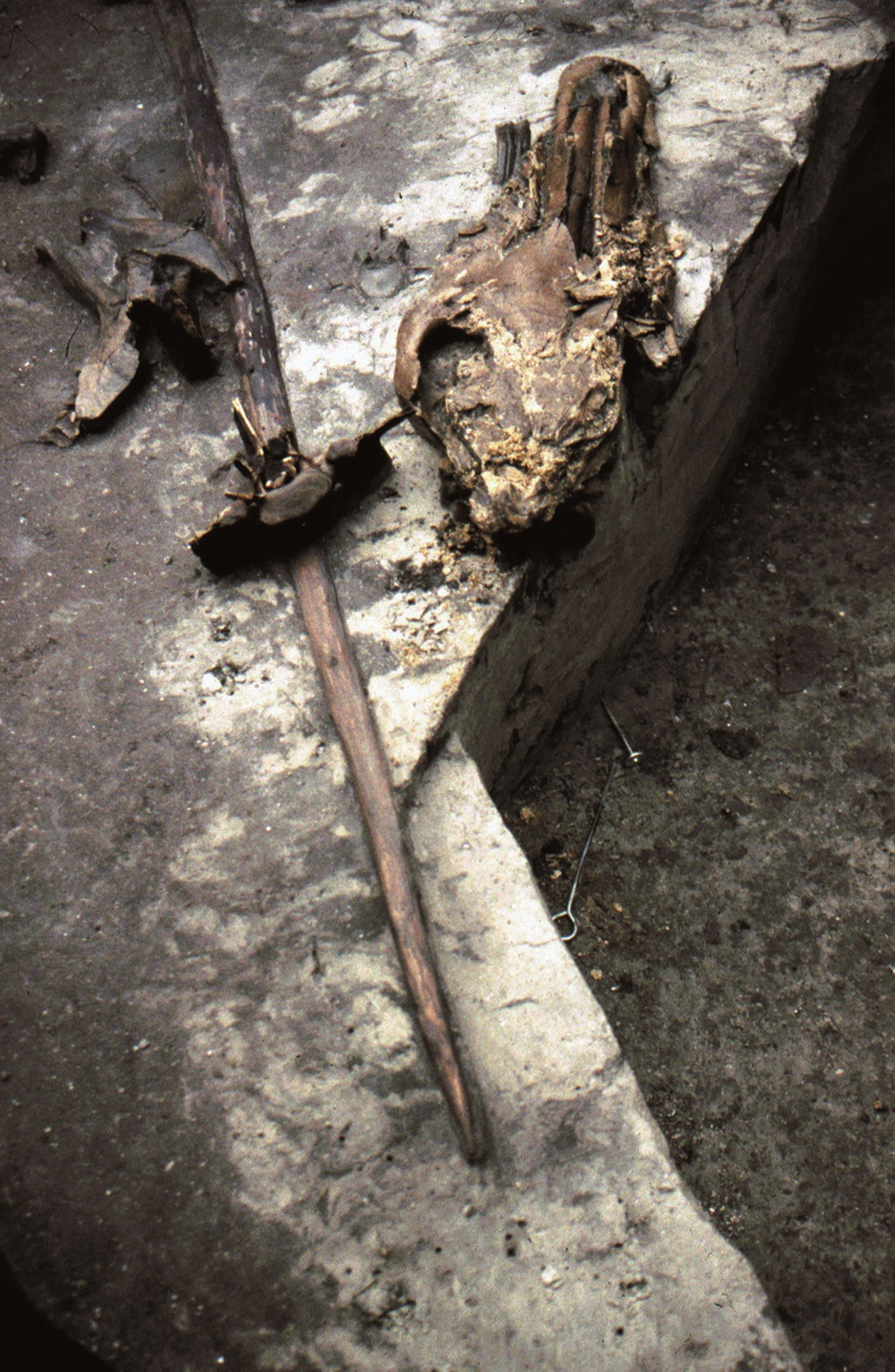
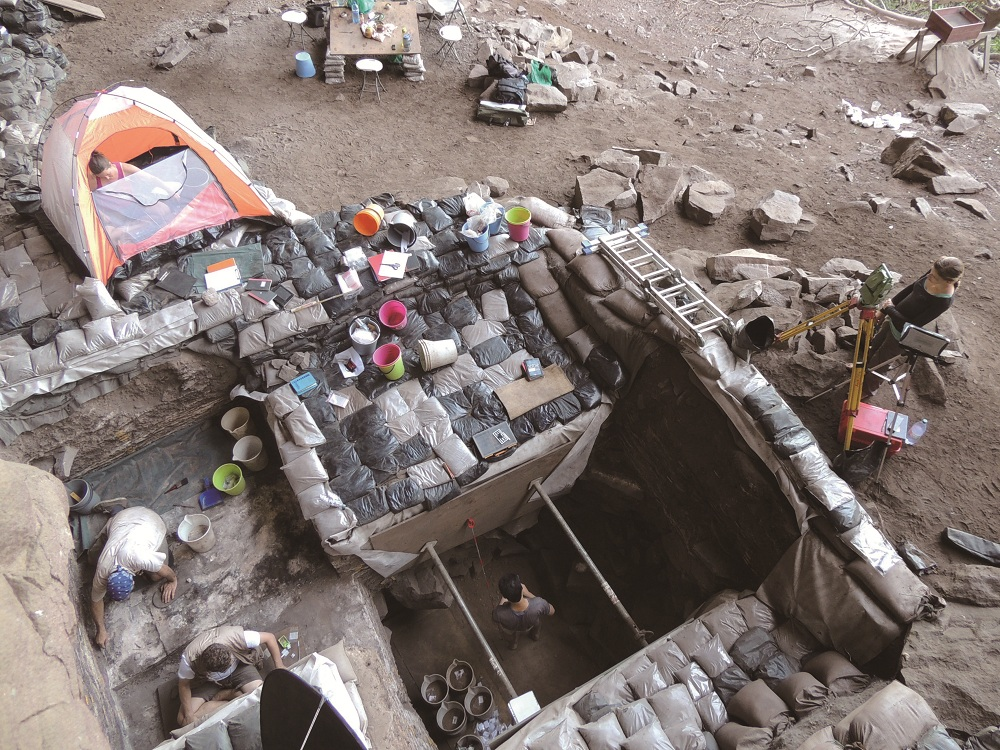
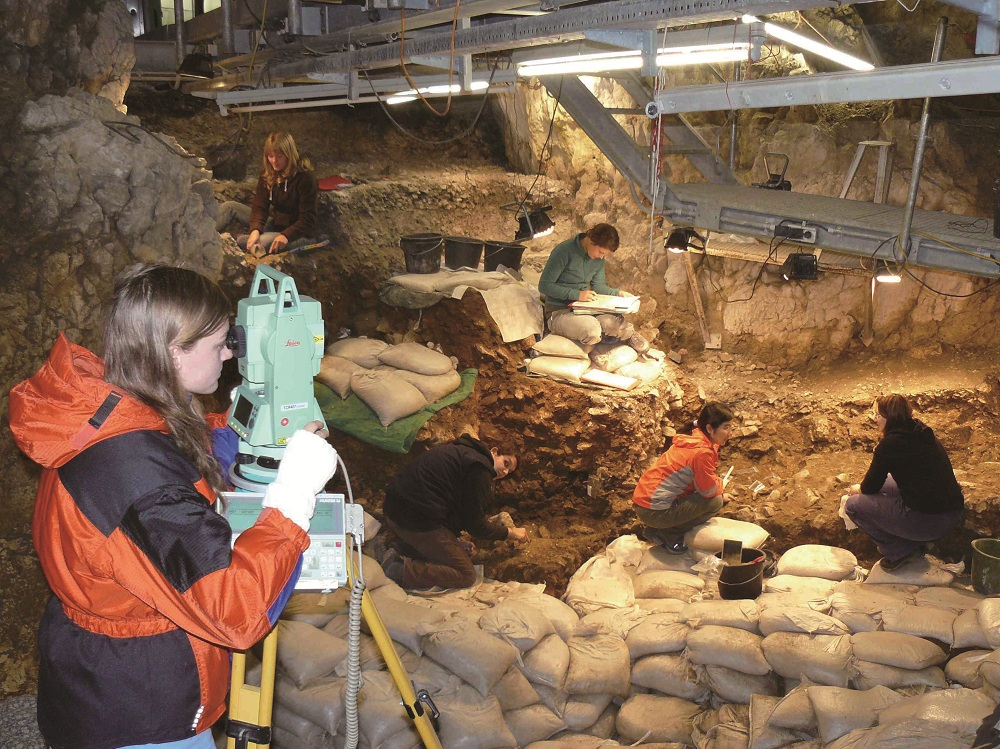
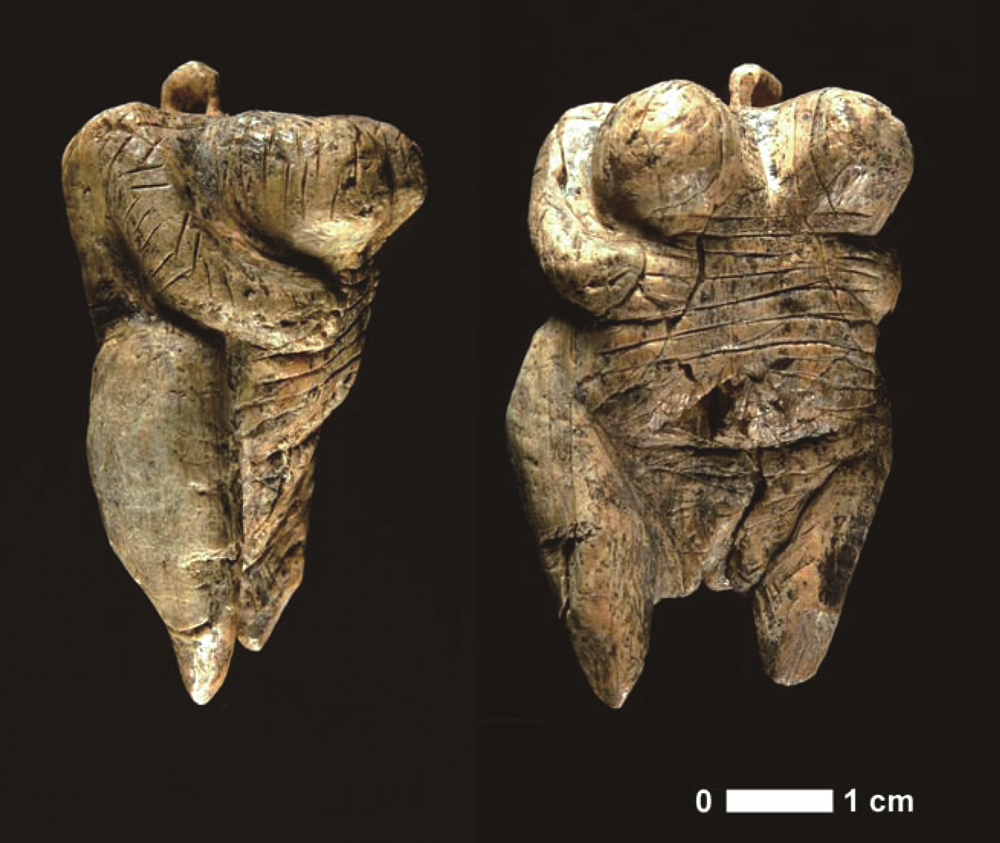
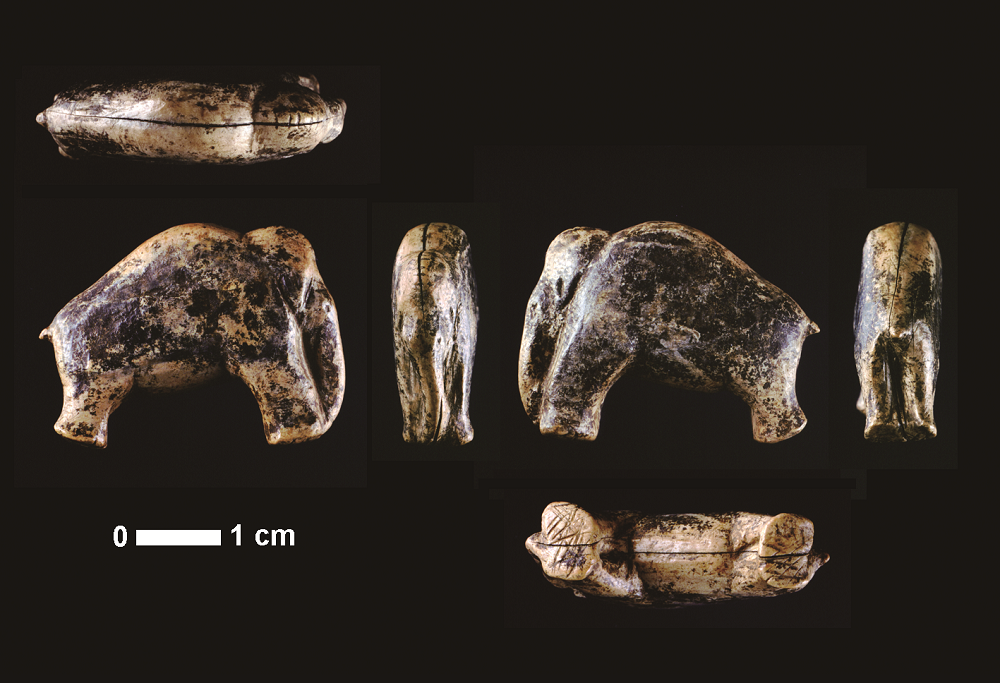
| [1] |
Dibble HL and McPherron SP. A Multimedia Companion to the Middle Paleolithic site of Combe-Capelle Bas(France)[M]. CD-ROM. University of Pennsylvania, 1996
|
| [2] |
Thieme H. Lower Palaeolithic hunting weapons from Schöningen, Germany: The oldest spears in the world[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2000(19):140-147
|
| [3] |
Conard NJ, Miller CE, Serangeli J, et al(Eds). Special Issue of Journal of Human Evolution[M]. Excavations at Schöningen: New Insights into Middle Pleistocene Lifeways in Northern Europe, 2015
|
| [4] |
Conard NJ, Serangeli J, Böhner U, et al. Excavations at Schöningen and paradigm shifts in human evolution[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2015(89):1-17
|
| [5] |
Binford LR. Bones: Ancient Men and Modern Myths[M]. Academic Press, New York, 2015
|
| [6] |
Binford LR. Human ancestors: Changing views of their behavior[J]. Journal of Anthropological Archaeolgy, 1989(4):292-327
|
| [7] |
Gamble C. Man the shoveler: alternative models for Middle Pleistocene colonization and occupation of northern latitudes[M]. In: Soffer O(Ed). The Pleistocene Old World New. Plenum Press, 1987, 81-98
|
| [8] |
Bräuer G. The ‘Afro-European Sapiens Hypojournal’ and Hominid Evolution in East Asia during the Late Middle and Upper Pleistocene[J]. Cour. Forsch. -Inst. Senckenberg, 1984(69):145-165
|
| [9] |
Bräuer G. Africa’s Place in the Evolution of Homo sapiens[M]. Continuity or Replacement. Controversies in Homo Sapiens Evolution, ed. by Bräuer G and Smith FH, 1992, 83-98
|
| [10] |
Stringer C, Andrews P. Genetic and Fossil Evidence for the Origins of Modern Humans. Science, 1988(239):1263-1268
|
| [11] |
Kandel AW, Conard NJ. Settlement patterns during the Earlier and Middle Stone Age around Langebaan Lagoon, Western Cape(South Africa)[J]. Quaternary International, 2012(270):15-29
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2011.06.038
URL
|
| [12] |
Parkington JE. Coastal diet, encephalization, and innovative behaviors in the late Middle Stone Age of southern Africa[M]. In: Cunnane SC, Stewart KM(Eds. ), Human Brain Evolution-The Influence of Freshwater and Marine Food Resources Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken, 2010, 189-203
|
| [13] |
Will M, Parkington J, Kandel AW, et al. Coastal adaptations and the Middle Stone Age lithic assemblages from Hoedjiespunt 1 in the western Cape, South Africa[J]. Journal of Human Evolultion, 2013(64):518-537
|
| [14] |
Wadley L, Jacobs Z. Sibudu Cave: Background to the excavations, stratigraphy and dating[J]. South Afr Humanit, 2006(18):1-26
|
| [15] |
Jacobs Z, Roberts RG, Galbraith RF, et al. Ages for the Middle Stone Age of southern Africa: implications for human behavior and dispersal[J]. Science, 2008(322):733-735
|
| [16] |
Henshilwood CS. Late Pleistocene techno-traditions in southern Africa: A review of the Still Bay and Howiesons Poort, c.75-59 ka[J]. Journal of World Prehistory, 2012(25):205-237
doi: 10.1007/s10963-012-9060-3
URL
|
| [17] |
Conard NJ. A critical view of the evidence for a southern African origin of behavioral modernity. South African Archaeological[J]. Society Goodwin Series. 2008(10):175-179
|
| [18] |
Conard NJ. Cultural Evolution during the Middle and Late Pleistocene in Africa and Eurasia. In Handbook of Paleoanthropology 2nd Edition[M]. Edited by Henke W and Tattersall I. Springer: Berlin, 2015: 2465-2508
|
| [19] |
Conard NJ, Will M. Examining the causes and consequences of short-term behavioral change during the Middle Stone Age at Sibudu, South Africa[J]. PLoS One, 2015,10(6): DOI 10. 1371/journal. pone. 0130001
URL
pmid: 26126109
|
| [20] |
Conard NJ, Porraz G, Wadley L. What is in a name? Characterising the ‘Post-Howieson’s Poort’ at Sibudu[J]. South African Archaeological Bulletin, 2012(67):180-199
|
| [21] |
Bretzke K, Marks AE, Conard NJ. Projektiltechnologie und kulturelle evolution in Ostafrika[J]. Mitteilungen Gesellschaft Urgeschichte, 2006(15):63-81
|
| [22] |
Will M, Conard NJ. Assemblage variability and bifacial points in the lowermost Sibudan layers at Sibudu, South Africa[J]. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 2016, DOI 10.1007/s12520-016-0361-9
doi: 10.1007/s12520-016-0446-5
URL
pmid: 30294383
|
| [23] |
Bader GD, Cable C, Lentfer C, et al. Umbeli Belli Rock Shelter, a forgotten piece fromthe puzzle of the Middle Stone Age in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2016(9):608-622
|
| [24] |
Lombard M, Parsons I. What happened to the human mind after the Howiesons Poort?[J] Antiquity, 2011(85):1-11
|
| [25] |
Kandel AW, Bolus M, Bretzke K, et al. Increasing Behavioral Flexibility? An Integrative Macro-Scale Approach to Understanding the Middle Stone Age of Southern Africa[M]. Journal of Archaeological Method and Theory, 2015, DOI 10.1007/s10816-015-9254-y
|
| [26] |
Conard NJ. Tönchesberg and its Position in the Paleolithic Prehistory of Northern Europe[M]. Monograph 20, Römisch-Germanisches Zentralmuseum Series. Habelt Bonn, 1992
|
| [27] |
Conard NJ, Prindiville TJ. Middle Paleolithic Hunting Economies in the Rhineland[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2000(10):286-309
|
| [28] |
Conard NJ, River Terraces Volcanic Craters and the Middle Paleolithic of the Rhineland[M]. In Settlement Dynamics of the Middle Paleolithic and Middle Stone Age. Edited by Conard NJ. Tübingen Publications in Prehistory 1. Tübingen: Kerns Verlag, 2001, 221-250
|
| [29] |
Adler DS, Prindiville TJ, Conard NJ. Patterns of Spatial Organization and Land Use during the Eemian Interglacial in the Rhineland: New Data from Wallertheim[J]. Germany Eurasian Prehistory 1, 2003(2):25-78
|
| [30] |
Conard NJ, Adler DS. Lithic Reduction and Hominid Behavior in the Middle Paleolithic of the Rheinland[J]. Journal of Anthropological Research, 1997(53):147-176
|
| [31] |
Zilhão J, d’Errico F. The Chronology and Taphonomy of the Earliest Aurignacien and Its Implications for the Understanding of Neandertal Extinction[J]. Journal of World Prehistory, 1999(13):1-68
|
| [32] |
Zilhão J, d’Errico F. The chronology of the Aurignacian and Transitional technocomplexes. Where do we stand[M]? In Zilhão J & d’Errico F(Eds. ), The chronology of the Aurignacian and of thetransitional technocomplexes. Dating, stratigraphies, culturalm implications(Trabalhos de Arqueologia. 2003(33):313-349
|
| [33] |
d’Errico F. The Invisible Frontier. A Multiple Species Model for the Origin of Behavioral Modernity[J]. Evolutionary Anthropology, 2003(12):188-202
|
| [34] |
Mann A. The origins of spoken language in human evolution.From Tools to Symbols,From Early Hominids to Modern Humans. International Round Table, Abstracts.Johannesburg 16th-18th March, 2003
|
| [35] |
Henshilwood CS, d’Errico F, Yates R, et al. The emergence of modern human behavior: Middle Stone Age engravings from South Africa[J]. Science, 2002(295):1278-1280
|
| [36] |
Texier PJ, Guillaume P, Parkington J. A Howiesons Poort tradition of engraved ostrich eggshell containters dated to 60,000 years ago at Diepkloof Rock Shelter, South Africa[M]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010(107):6180-6185
|
| [37] |
Conard NJ, Floss H, Barth M, et al(Eds). Eiszeit-Kunst und Kultur[M]. Jan Thorbecke Verlag: Ostfildern, 2009
|
| [38] |
Vogelsang R. Middle Stone Age Fundstellen in Südwest-Namibia. Africa Praehistorica 11. Heinrich-Barth-Institute: Cologne, 1998
|
| [39] |
Wolf S. Schmuckstücke: Die Elfenbeinbearbeitung im Schwäbischen Aurignacien[M]. Kerns Verlag: Tübingen, 2015
|
| [40] |
Conard NJ, Kind CJ. Als der Mensch die Kunst erfand: Eiszeithöhlen der Schwäbischen Alb[M]. Theiss Verlag: Stuttgart, 2017
|
| [41] |
Williams LD. The Mind in the Cave. Consciousness and the Origins of Art[M]. London: Thames & Hudson, 2002
|
| [42] |
Conard NJ, Bolus M. Radiocarbon Dating the Appearance of Modern Humans and Timing of Cultural Innovations in Europe: New Results and new Challenges[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2003(44):333-373
|
| [43] |
Gourhan M. A Pre´histoire de l’art occidental. Éditions d’art Lucien Mazenod[M]. Paris, 1965
|
| [44] |
Bosinski G. Die Kunst der Eiszeit in Deutschland und der Schweiz[M]. RGZM: Bonn, 1982
|
| [45] |
Conard NJ. The Demise of the Neanderthal Cultural Niche and the Beginning of the Upper Paleolithic in Southwestern Germany[M]. In: Neanderthal Lifeways, Subsistence and Technology: One Hundred Fifty Years of Neanderthal Study Edited by Conard NJ and Richter J. Springer Verlag: Heidelberg, 2011: 223-240
|
| [46] |
Conard NJ. The evolution of modern behavior in East Asia. In Human origin sites and the World Heritage Convention in Asia[M]. Edited by Sanz N. UNESCO: Paris, 2014: 16-23
|