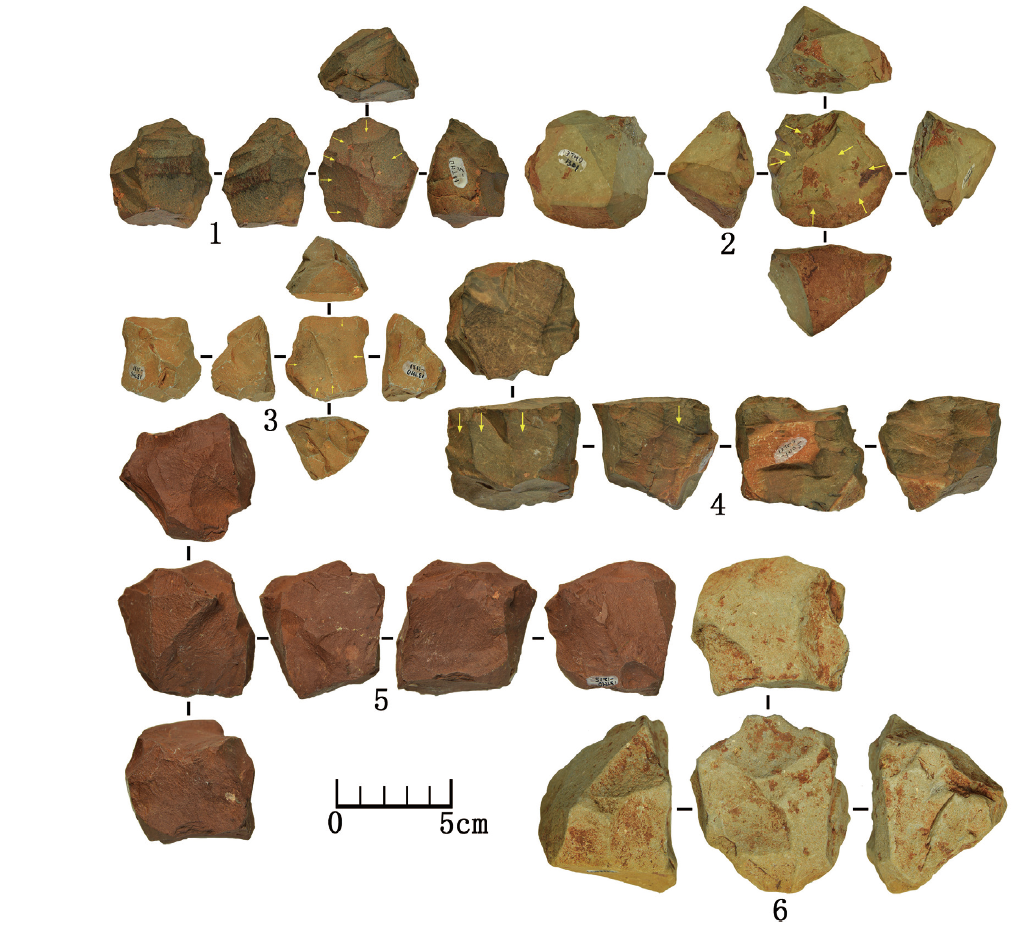
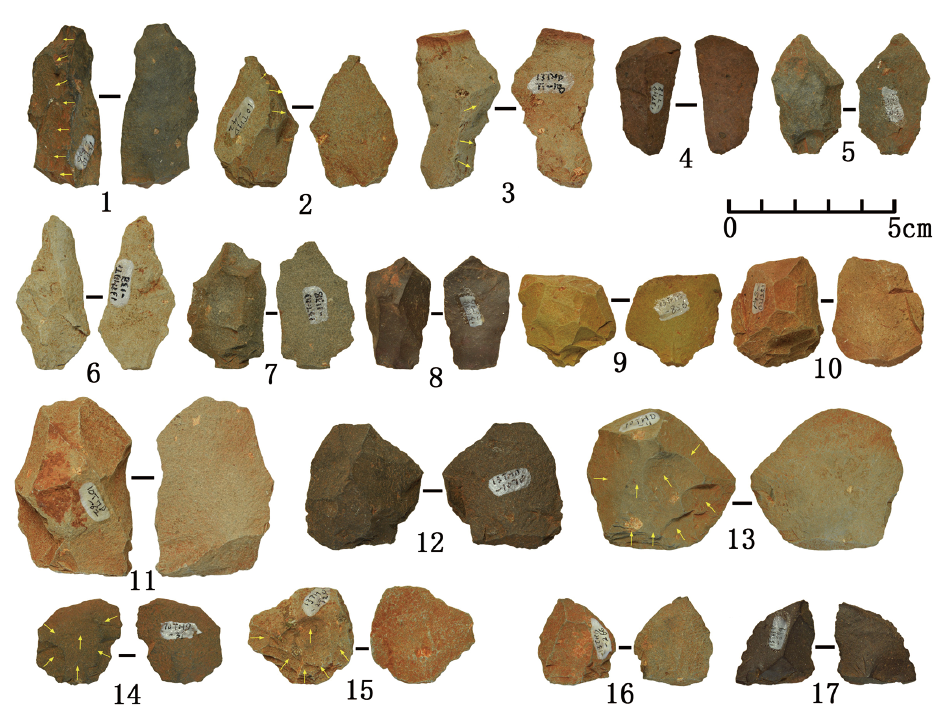
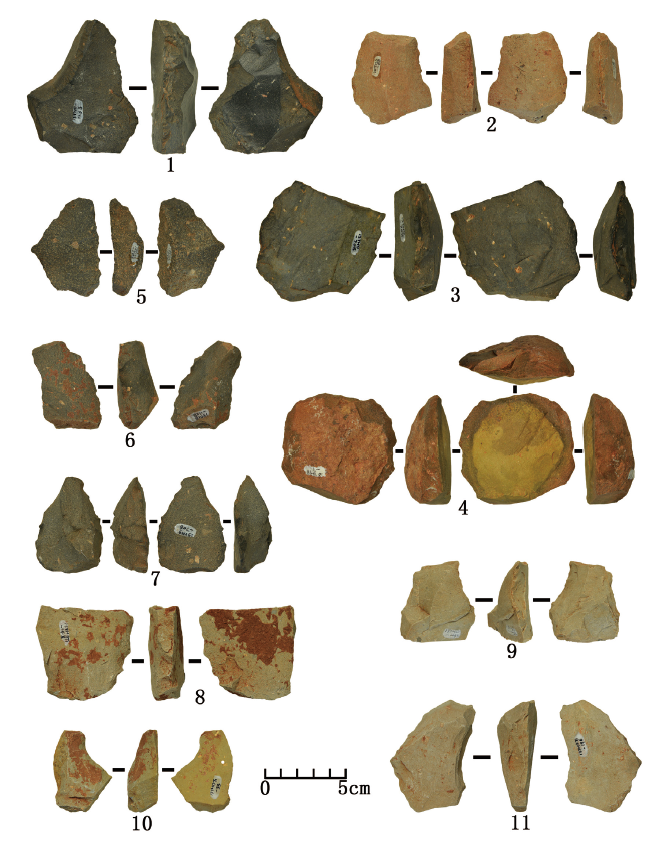
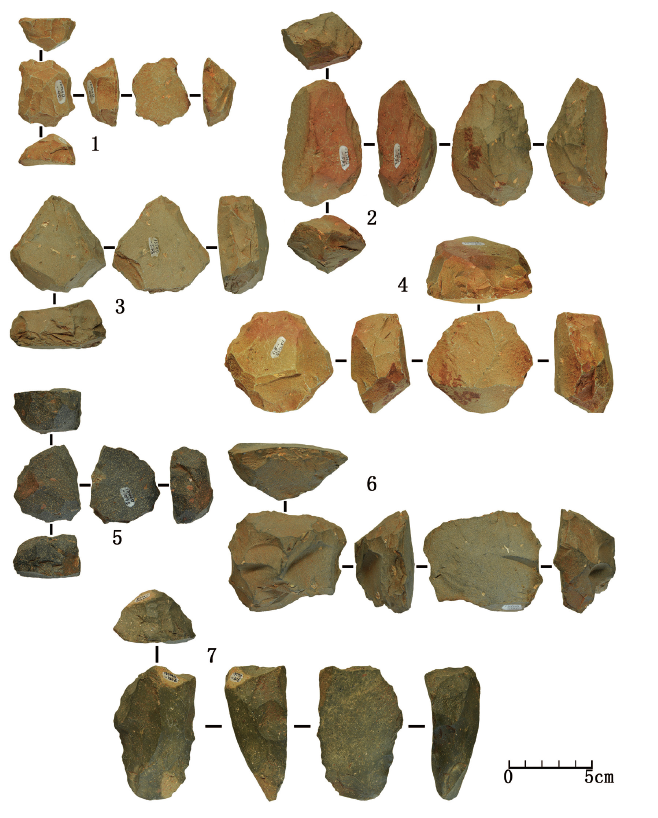
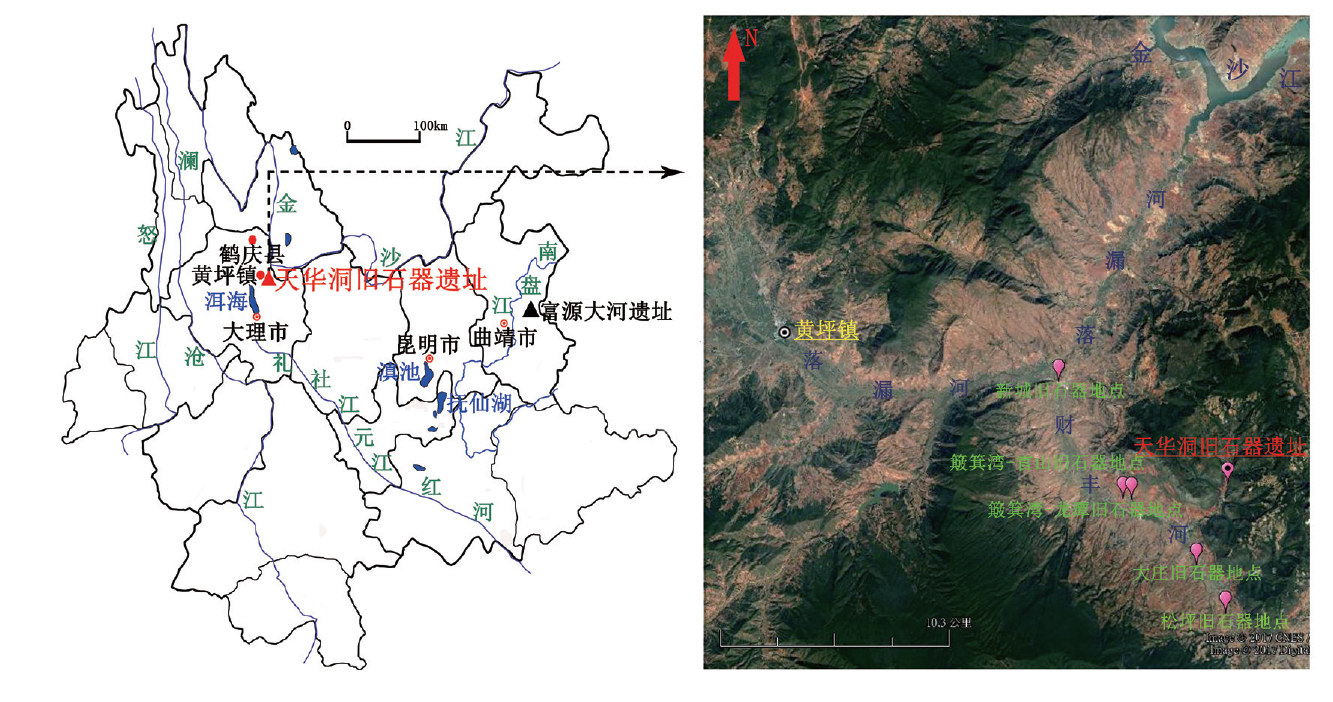
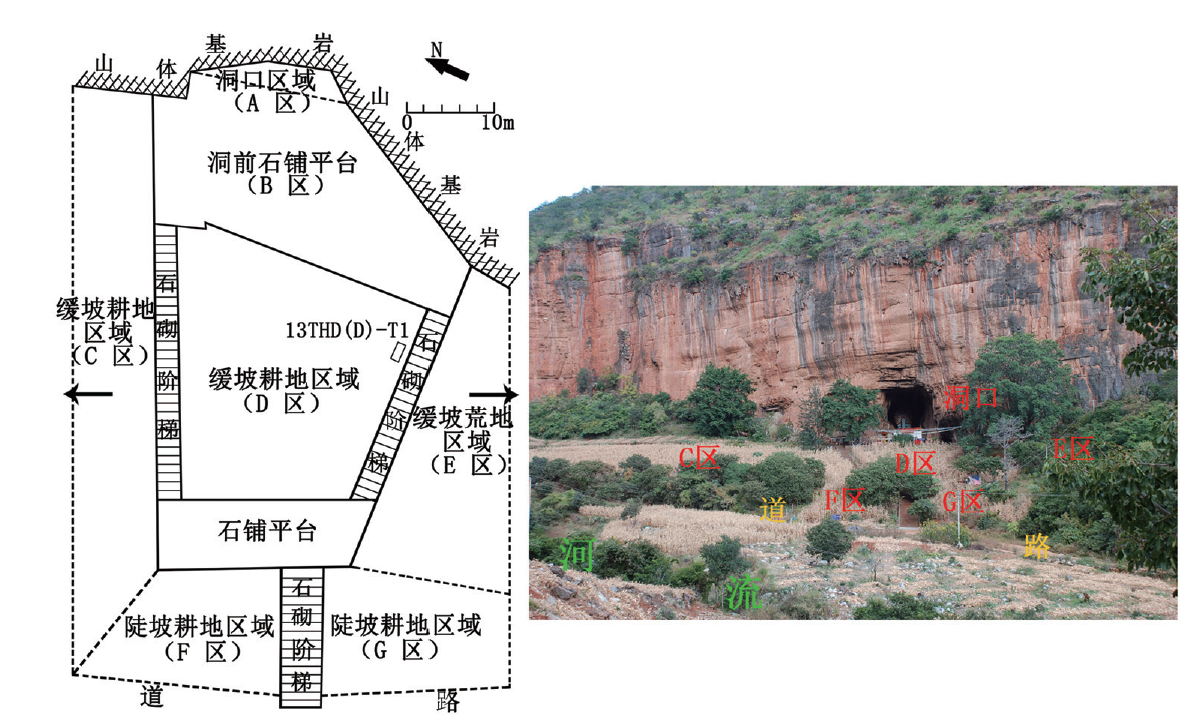
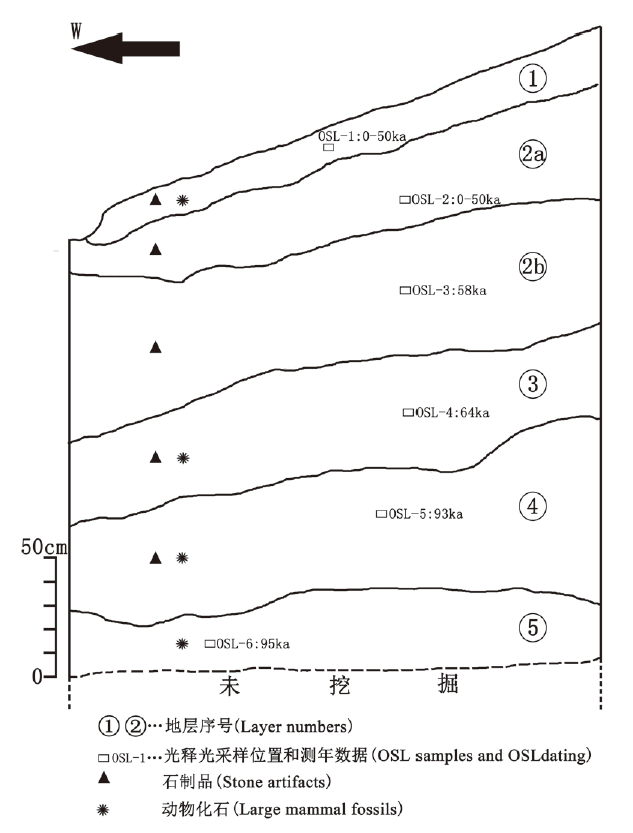
| [1] |
Richard GR, Zenobia J, Li B, et al. Optical dating in archaeology: thirty years in retrospect and grand challenges for the future[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015(56):41-60
|
| [2] |
Akhilesh K, Pappu S, Rajapara HM, et al. Early Middle Palaeolithic culture in India around 385-172 kareframes Out of Africa models[J]. Nature, 2018(554):97-101
|
| [3] |
Richter D, Grün R, Joannes-Boyau R, et al. The age of the hominin fossils from Jebel Irhoud, Morocco, and the origins of the Middle Stone Age[J]. Nature, 2017(546):293-296
|
| [4] |
Adler DS, Wilkinson KN, Blockley S, et al. Early Levallois technology and the Lower to Middle Paleolithic transition in the Southern Caucasus[J]. Science, 2014(345):1609-1613.
|
| [5] |
王幼平.石器研究: 旧石器时代考古方法初探[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2006,78
|
| [6] |
Van Peer P. The Levallois Reduction Strategy[M]. Madison: Prehistory Press, 1992
|
| [7] |
Boëda E. Le débitage discoïde et le débitage Levallois récurrent centripède[J]. Bulletin de la Société Préhistorique Française, 1993(90):392-404
|
| [8] |
Otte M. The nature of Levallois[A]. Dibble HL, Bar-Yosef O(eds). The Definition and Interpretation of Levallois Technology[C]. Madison : Prehistory Press, 1995: 117-143
|
| [9] |
Toth N. The Stone Technologies of Early Hominids at Koobi Fora, Kenya: An Experimental Approach.Dissertation[D]. For the degree of doctor of philosophy in the University of California, Berkeley, 1982
|
| [10] |
卫奇. 石制品观察格式讨论[A].见: 邓涛,王原.第八届中国古脊椎动物学术年会论文集[C].北京:海洋出版社, 2001, 209-218
|
| [11] |
Faivre JP, Gravina B, Bourguignon L, et al. Late Middle Palaeolithic lithic technocomplexes (MIS 5-3) in the northeastern Aquitaine Basin: Advances and challenges[J]. Quaternary International, 2017(433):116-131
|
| [12] |
Peter H, Turq A, Faivre J-Ph, et al. Quina procurement and tool production[A]. eds Adams B,Blades B: Lithic Materials and Paleolithic Societies [C]. West Sussex, 2009: 232-246
|
| [13] |
Faivre J-Ph, Discamps E, Gravina B, et al. The contribution of lithic production systems to the interpretation of Mousterian industrial variability in south-western France: The example of Combe-Grenal (Dordogne, France)[J]. Quaternary International, 2014 ( 350):227-240
|
| [14] |
李炎贤, 蔡回阳. 贵州白岩脚洞石器的第二步加工[J].江汉考古, 1986(2):56-64
|
| [15] |
云南省文物考古研究所. 探寻历史足迹,保护文化遗产——纪念云南省文物考古研究所成立50年[M]. 昆明: 云南教育出版社, 2009: 22-26
|
| [16] |
吉学平. 大河洞穴之魅——富源大河旧石器遗址揭秘[J]. 中国文化遗产, 2008,28(6):78-83
|
| [17] |
王志浩, 侯亚梅, 杨泽蒙, 等. 内蒙古鄂尔多斯市乌兰木伦旧石器时代中期遗址[J]. 考古, 2012,579(7):3-13
|
| [18] |
贾兰坡, 卫奇. 阳高许家窑旧石器时代文化遗址[J].考古学报, 1976(2):97-114
|
| [19] |
Li F, Kuhn SL, Chen FY, et al. The easternmost Middle Paleolithic (Mousterian) from Jinsitai Cave, North China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2018(114):76-84
|
| [20] |
Ji XP, Kuman K, Clarke RJ, et al. The oldest Hoabinhian technocomplex in Asia (43.5 ka) at Xiaodong rockshelter, Yunnan Province, Southwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2016(400):166-174
|
| [21] |
大理白族自治州文物管理所, 云南省文物考古研究所, 剑川县文物管理所. 剑川象鼻洞旧石器遗址研究[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2015: 108-115
|
| [22] |
高峰, 闵锐, 李秉涛, 等. 怒江首次考古发掘兰坪玉水坪遗址的重要意义[A], 见:张跃等:峡谷中的怒族社会[C].昆明:云南大学出版社, 2012: 387-402
|
| [23] |
朱之勇, 吉学平. 云南保山老虎洞旧石器遗址石器研究[J]. 边疆考古研究, 2011,9(4):1-8
|
| [24] |
邱中郎, 张银运, 胡绍锦. 昆明呈贡龙潭山第2地点的人化石和旧石器[J].人类学学报, 1985(3):233-242
|
| [25] |
Klein RG. Out of Africa and evolution of human behavior[J]. Evolutionary Anthropology, 2008(17):267-281
|
| [26] |
Oppenheimer S. The great arc of dispersal of modern humans: Africa to Australia[J]. Quaternary International, 2009(202):2-13
|
| [27] |
Bar-Yosef O, Belfer-Cohen A. Following Pleistocene road signs of human dispersals across Eurasia[J]. Quaternary International, 2013(285):30-43
|