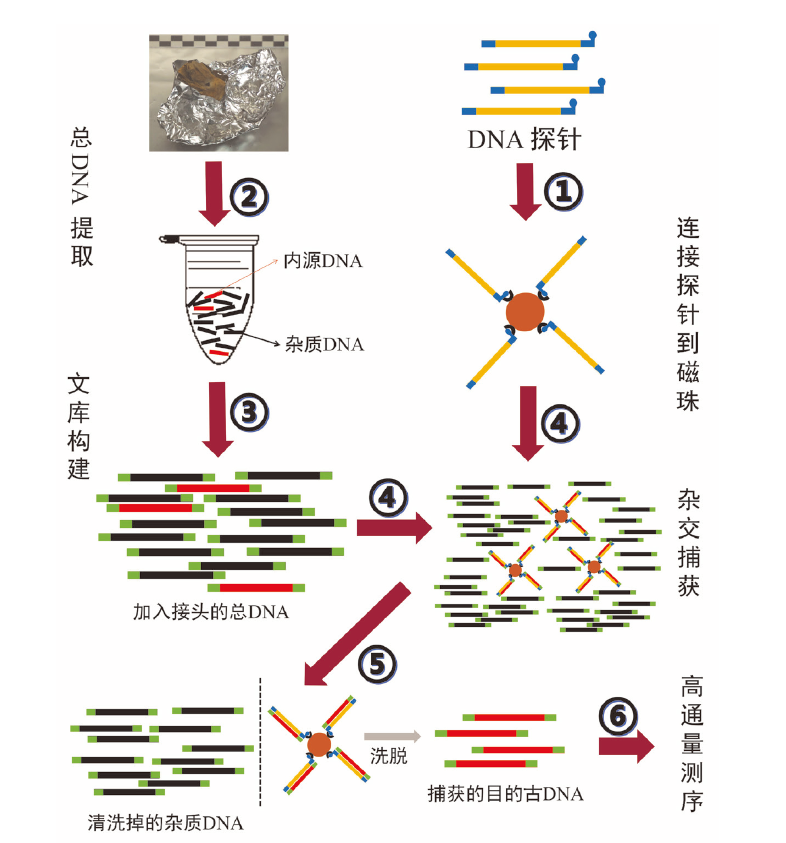
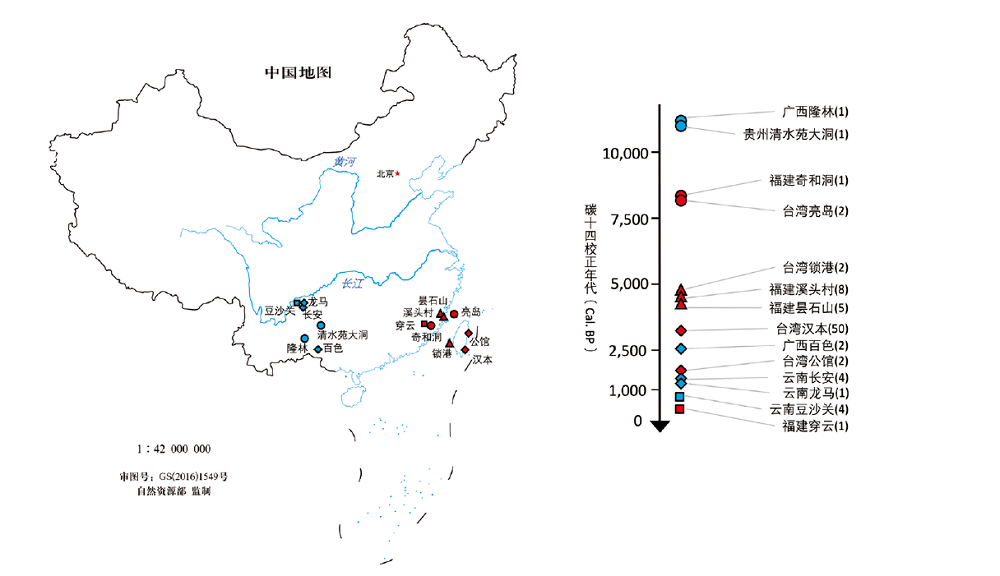
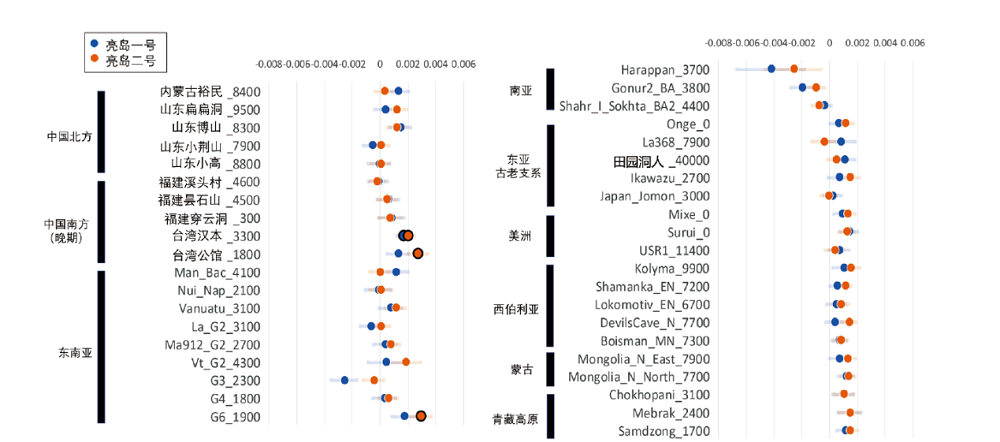
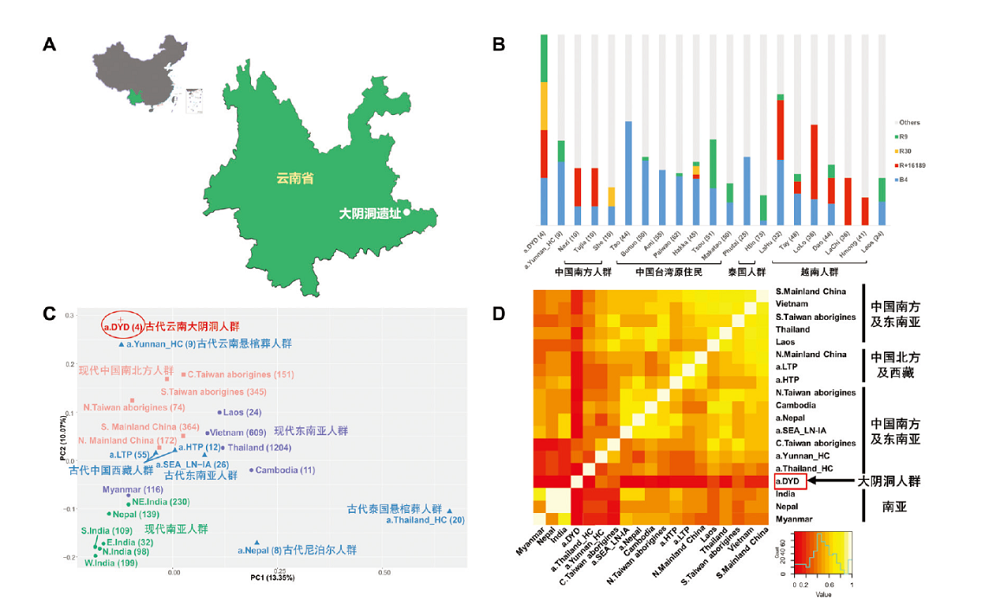
| [1] |
Yang MA, Fan X, Sun B, et al. Ancient DNA indicates human population shifts and admixture in northern and southern China[J]. Science, 2020,369(6501):282-288
URL
pmid: 32409524
|
| [2] |
Bai F, Zhang X, Ji X, et al. Paleolithic genetic link between Southern China and Mainland Southeast Asia revealed by ancient mitochondrial genomes[J]. Journal of Human Genetics, 2020: 1-4
doi: 10.1007/s100380050001
URL
pmid: 10697955
|
| [3] |
Ko AMS, Chen CY, Fu QM, et al. Early Austronesians: into and out of Taiwan[J]. American Journal of Human Genetics, 2014,94(3):426-436
|
| [4] |
Zhang X, Li C, Zhou Y, et al. A Matrilineal Genetic Perspective of Hanging Coffin Custom in Southern China and Northern Thailand[J]. iScience, 2020,23(4):101032
|
| [5] |
Wang CC, Yeh HY, Popov AN, et al. The Genomic Formation of Human Populations in East Asia[J]. bioRxiv, 2020
|
| [6] |
Yang MA, Gao X, Theunert C, et al. 40,000-year-old individual from Asia provides insight into early population structure in Eurasia[J]. Current Biology, 2017, 27(20): 3202-3208.e9
|
| [7] |
Ko AMS, Zhang Y, Yang MA, et al. Mitochondrial genome of a 22,000-year-old giant panda from southern China reveals a new panda lineage[J]. Current Biology, 2018,28(12):R693-R694
|
| [8] |
Slon V, Hopfe C, Weiss CL, et al. Neandertal and Denisovan DNA from Pleistocene sediments[J]. Science, 2017,356(6338):605-608
|
| [9] |
Burbano HA, Green RE, Maricic T, et al. Analysis of human accelerated DNA regions using archaic hominin genomes[J]. PloS one, 2012,7(3):e32877
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032877
URL
pmid: 22412940
|
| [10] |
Burbano HA, Hodges E, Green RE, et al. Targeted investigation of the Neandertal genome by array-based sequence capture[J]. Science, 2010,328(5979):723-725
|
| [11] |
Ávila-Arcos MC, Cappellini E, Romero-Navarro JA, et al. Application and comparison of large-scale solution-based DNA capture-enrichment methods on ancient DNA[J]. Scientific reports, 2011,1(1):1-5
|
| [12] |
Maricic T, Whitten M, Pääbo S. Multiplexed DNA sequence capture of mitochondrial genomes using PCR products[J]. PloS one, 2010,5(11):e14004
|
| [13] |
Sheng GL, Basler N, Ji XP, et al. Paleogenome reveals genetic contribution of extinct giant panda to extant populations[J]. Current Biology, 2019, 29(10): 1695-1700. e6
URL
pmid: 31080081
|
| [14] |
Fu QM, Meyer M, Gao X, et al. DNA analysis of an early modern human from Tianyuan Cave, China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013,110(6):2223-2227
|
| [15] |
Gnirke A, Melnikov A, Maguire J, et al. Solution hybrid selection with ultra-long oligonucleotides for massively parallel targeted sequencing[J]. Nature biotechnology, 2009,27(2):182-189
doi: 10.1038/nbt.1523
URL
pmid: 19182786
|
| [16] |
Fu QM, Hajdinjak M, Moldovan O T, et al. An early modern human from Romania with a recent Neanderthal ancestor[J]. Nature, 2015,524(7564):216-219
URL
pmid: 26098372
|
| [17] |
Fu QM, Li H, Moorjani P, et al. Genome sequence of a 45,000-year-old modern human from western Siberia[J]. Nature, 2014,514(7523):445-449
URL
pmid: 25341783
|
| [18] |
Fu QM, Posth C, Hajdinjak M, et al. The genetic history of ice age Europe[J]. Nature, 2016,534(7606):200-205
|
| [19] |
Kistler L, Ware R, Smith O, et al. A new model for ancient DNA decay based on paleogenomic meta-analysis[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017,45(11):6310-6320
|
| [20] |
Meyer M, Arsuaga JL, de Filippo C, et al. Nuclear DNA sequences from the Middle Pleistocene Sima de los Huesos hominins[J]. Nature, 2016,531(7595):504-507
doi: 10.1038/nature17405
URL
pmid: 26976447
|
| [21] |
Gansauge MT, Meyer M. Single-stranded DNA library preparation for the sequencing of ancient or damaged DNA[J]. Nature protocols, 2013,8(4):737-748
|
| [22] |
Glocke I, Meyer M. Extending the spectrum of DNA sequences retrieved from ancient bones and teeth[J]. Genome research, 2017,27(7):1230-1237
|
| [23] |
Meyer M, Kircher M, Gansauge MT, et al. A high-coverage genome sequence from an archaic Denisovan individual[J]. Science, 2012,338(6104):222-226
doi: 10.1126/science.1224344
URL
pmid: 22936568
|
| [24] |
Lipson M, Skoglund P, Spriggs M, et al. Population turnover in Remote Oceania shortly after initial settlement[J]. Current Biology, 2018, 28(7): 1157-1165.e7
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.051
URL
pmid: 29501328
|
| [25] |
McColl H, Racimo F, Vinner L, et al. The prehistoric peopling of Southeast Asia[J]. Science, 2018,361(6397):88-92
|
| [26] |
Zhang M, Sun G, Ren L, et al. Ancient DNA evidence from China reveals the expansion of Pacific dogs[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2020,37(5):1462-1469
|
| [27] |
de Barros Damgaard P, Marchi N, Rasmussen S, et al. 137 ancient human genomes from across the Eurasian steppes[J]. Nature, 2018,557(7705):369-374
URL
pmid: 29743675
|
| [28] |
de Barros Damgaard P, Martiniano R, Kamm J, et al. The first horse herders and the impact of early Bronze Age steppe expansions into Asia[J]. Science, 2018,360(6396)
doi: 10.1126/science.360.6396.1391
URL
pmid: 29954963
|
| [29] |
Ning C, Wang CC, Gao S, et al. Ancient genomes reveal Yamnaya-related ancestry and a potential source of indo-European speakers in iron age Tianshan[J]. Current Biology, 2019, 29(15): 2526-2532.e4
URL
pmid: 31353181
|
| [30] |
Sikora M, Pitulko VV, Sousa VC, et al. The population history of northeastern Siberia since the Pleistocene[J]. Nature, 2019,570(7760):182-188
URL
pmid: 31168093
|
| [31] |
Siska V, Jones ER, Jeon S, et al. Genome-wide data from two early Neolithic East Asian individuals dating to 7700 years ago[J]. Science Advances, 2017,3(2):e1601877
URL
pmid: 28164156
|
| [32] |
Wong EHM, Khrunin A, Nichols L, et al. Reconstructing genetic history of Siberian and Northeastern European populations[J]. Genome research, 2017,27(1):1-14
|
| [33] |
Pei S, Gao X, Wang H, et al. The Shuidonggou site complex: new excavations and implications for the earliest Late Paleolithic in North China[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2012,39(12):3610-3626
|
| [34] |
Wu X, Liu W, Wang Z. A human parietal fossil found at the Shuidonggou site, Ningxia, China[J]. Anthropological Science, 2004,112(1):83-89
|
| [35] |
Yang S X, Deng C L, Zhu R X, et al. The Paleolithic in the Nihewan Basin, China: Evolutionary history of an Early to Late Pleistocene record in Eastern Asia[J]. Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews, 2020,29(3):125-142
|
| [36] |
高星. 更新世东亚人群连续演化的考古证据及相关问题论述[J]. 人类学学报, 2014,33(3):237-253
|
| [37] |
Cai P, Huang Q, Zhang X, et al. Adsorption of DNA on clay minerals and various colloidal particles from an Alfisol[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2006,38(3):471-476
|
| [38] |
Ogram A, Sayler GS, Gustin D, et al. DNA adsorption to soils and sediments[J]. Environmental science & technology, 1988,22(8):982-984
|
| [39] |
Willerslev E, Hansen A J, Binladen J, et al. Diverse plant and animal genetic records from Holocene and Pleistocene sediments[J]. Science, 2003,300(5620):791-795
URL
pmid: 12702808
|
| [40] |
Nichols RV, Curd E, Heintzman PD, et al. Targeted Amplification and Sequencing of Ancient Environmental and Sedimentary DNA[J]. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ), 2019,1963:149-161
|
| [41] |
Pedersen MW, Ruter A, Schweger C, et al. Postglacial viability and colonization in North America’s ice-free corridor[J]. Nature, 2016,537(7618):45-49
URL
pmid: 27509852
|
| [42] |
Matsumura H, Hung H, Higham C, et al. Craniometrics reveal “two layers” of prehistoric human dispersal in eastern Eurasia[J]. Scientific reports, 2019,9(1):1-12
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37186-2
URL
pmid: 30626917
|
| [43] |
Westaway KE, Louys J, Awe RD, et al. An early modern human presence in Sumatra 73,000-63,000 years ago[J]. Nature, 2017,548(7667):322-325
URL
pmid: 28792933
|
| [44] |
Demeter F, Shackelford L, Westaway K, et al. Early modern humans from Tam Pà Ling, Laos: Fossil review and perspectives[J]. Current Anthropology, 2017,58(S17):S527-S538
|
| [45] |
Matsumura H, Oxenham M. Population dispersal from East Asia into Southeast Asia: Evidence from cranial and dental Morphology[A]. In: Bioarchaeology of East Asia: Movement, Contact, Health[M]. University Press of Florida, 2013: 179-209
|
| [46] |
Lipson M, Cheronet O, Mallick S, et al. Ancient genomes document multiple waves of migration in Southeast Asian prehistory[J]. Science, 2018,361(6397):92-95
doi: 10.1126/science.aat3188
URL
pmid: 29773666
|
| [47] |
焦天龙. 东南沿海的史前文化与南岛语族的扩散[J]. 中原文物, 2002 (2):13-16
|
| [48] |
Blust RA. The proto-Austronesian pronouns and Austronesian subgrouping[J]. Working Papers in Linguistics, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, 1977,9:1-15
|
| [49] |
Melton T, Peterson R, Redd AJ, et al. Polynesian genetic affinities with Southeast Asian populations as identified by mtDNA analysis[J]. American journal of human genetics, 1995,57(2):403-414
|
| [50] |
Raghavan M, Skoglund P, Graf KE, et al. Upper Palaeolithic Siberian genome reveals dual ancestry of Native Americans[J]. Nature, 2014,505(7481):87-91
doi: 10.1038/nature12736
URL
pmid: 24256729
|
| [51] |
Diamond JM. Express train to Polynesia[J]. Nature, 1988,336(6197):307-308
|
| [52] |
Jiao T. The Neolithic Archaeology of Southeast China[J]. A Companion to Chinese Archaeology, 2013: 597-611
|
| [53] |
张光直. 中国东南海岸考古与南岛语族起源问题[J]. 南方民族考古, 1987,1
|
| [54] |
Chang K. Prehistoric and early historic culture horizons and traditions in South China[J]. Current Anthropology, 1964,5(5):359-375
|
| [55] |
Chang K, Goodenough W H. Archaeology of southeastern coastal China and its bearing on the Austronesian homeland[J]. Transactions of the American philosophical society, 1996,86(5):36-56
|
| [56] |
Bellwood P. Austronesian prehistory in Southeast Asia: homeland, expansion and transformation[M]. Canberra: ANU E Press, 1995
|
| [57] |
刘益昌. 台湾史前史专论 [M]. 台北: 联经出版事业股份有限公司, 2016
|
| [58] |
赵志军. 中国农业起源概述[J]. 遗产与保护研究, 2019 (1):1
|
| [59] |
Crawford GW, Chen X, Luan F, et al. People and plant interaction at the Houli Culture Yuezhuang site in Shandong Province, China[J]. The Holocene, 2016,26(10):1594-1604
|
| [60] |
Deng Z, Hung H, Fan X, et al. The ancient dispersal of millets in southern China: New archaeological evidence[J]. The Holocene, 2018,28(1):34-43
|
| [61] |
Jeong C, Ozga AT, Witonsky DB, et al. Long-term genetic stability and a high-altitude East Asian origin for the peoples of the high valleys of the Himalayan arc[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016,113(27):7485-7490
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1520844113
URL
|
| [62] |
Moreno-Mayar JV, Potter BA, Vinner L, et al. Terminal Pleistocene Alaskan genome reveals first founding population of Native Americans[J]. Nature, 2018,553(7687):203-207
doi: 10.1038/nature25173
URL
pmid: 29323294
|
| [63] |
Shinde V, Narasimhan VM, Rohland N, et al. An ancient Harappan genome lacks ancestry from Steppe pastoralists or Iranian farmers[J]. Cell, 2019, 179(3): 729-735.e10
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.048
URL
pmid: 31495572
|
| [64] |
Ding M, Wang T, Ko AMS, et al. Ancient mitogenomes show plateau populations from last 5200 years partially contributed to present-day Tibetans[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 2020,287(1923):20192968
|
| [65] |
Bhandari S, Zhang X, Cui C, et al. Genetic evidence of a recent Tibetan ancestry to Sherpas in the Himalayan region[J]. Scientific reports, 2015,5:16249
doi: 10.1038/srep16249
URL
pmid: 26538459
|
| [66] |
Chandrasekar A, Kumar S, Sreenath J, et al. Updating phylogeny of mitochondrial DNA macrohaplogroup M in India: dispersal of modern human in South Asian corridor[J]. PloS one, 2009,4(10):e7447
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007447
URL
pmid: 19823670
|
| [67] |
Duong NT, Macholdt E, Ton ND, et al. Complete human mtDNA genome sequences from Vietnam and the phylogeography of Mainland Southeast Asia[J]. Scientific reports, 2018,8(1):1-13
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17765-5
URL
pmid: 29311619
|
| [68] |
Fornarino S, Pala M, Battaglia V, et al. Mitochondrial and Y-chromosome diversity of the Tharus (Nepal): a reservoir of genetic variation[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 2009,9(1):154
|
| [69] |
Kang L, Zheng H X, Zhang M, et al. MtDNA analysis reveals enriched pathogenic mutations in Tibetan highlanders[J]. Scientific reports, 2016,6(1):1-11
doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0001-8
URL
pmid: 28442746
|
| [70] |
Kutanan W, Kampuansai J, Srikummool M, et al. Complete mitochondrial genomes of Thai and Lao populations indicate an ancient origin of Austroasiatic groups and demic diffusion in the spread of Tai-Kadai languages[J]. Human genetics, 2017,136(1):85-98
doi: 10.1007/s00439-016-1742-y
URL
pmid: 27837350
|
| [71] |
Li YC, Wang HW, Tian JY, et al. Ancient inland human dispersals from Myanmar into interior East Asia since the Late Pleistocene[J]. Scientific reports, 2015,5:9473
doi: 10.1038/srep09473
URL
pmid: 25826227
|
| [72] |
Lippold S, Xu H, Ko A, et al. Human paternal and maternal demographic histories: insights from high-resolution Y chromosome and mtDNA sequences[J]. Investigative genetics, 2014,5(1):13
|
| [73] |
Peng MS, Palanichamy MG, Yao YG, et al. Inland post-glacial dispersal in East Asia revealed by mitochondrial haplogroup M9a'b[J]. BMC biology, 2011,9(1):2
|
| [74] |
Peng MS, Xu W, Song JJ, et al. Mitochondrial genomes uncover the maternal history of the Pamir populations[J]. European Journal of Human Genetics, 2018,26(1):124-136
doi: 10.1038/s41431-017-0028-8
URL
pmid: 29187735
|
| [75] |
Qin Z, Yang Y, Kang L, et al. A mitochondrial revelation of early human migrations to the Tibetan Plateau before and after the last glacial maximum[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2010,143(4):555-569
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.21350
URL
pmid: 20623602
|
| [76] |
Summerer M, Horst J, Erhart G, et al. Large-scale mitochondrial DNA analysis in Southeast Asia reveals evolutionary effects of cultural isolation in the multi-ethnic population of Myanmar[J]. BMC evolutionary biology, 2014,14(1):1-12
|
| [77] |
Wang HW, Li YC, Sun F, et al. Revisiting the role of the Himalayas in peopling Nepal: insights from mitochondrial genomes[J]. Journal of human genetics, 2012,57(4):228-234
doi: 10.1038/jhg.2012.8
URL
pmid: 22437208
|
| [78] |
Renaud G, Stenzel U, Kelso J. leeHom: adaptor trimming and merging for Illumina sequencing reads[J]. Nucleic acids research, 2014,42(18):e141-e141
doi: 10.1093/nar/gku699
URL
pmid: 25100869
|
| [79] |
Renaud G, Stenzel U, Maricic T, et al. deML: robust demultiplexing of Illumina sequences using a likelihood-based approach[J]. Bioinformatics, 2015,31(5):770-772
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu719
URL
pmid: 25359895
|
| [80] |
Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform[J]. bioinformatics, 2009,25(14):1754-1760
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
URL
pmid: 19451168
|
| [81] |
Andrews RM, Kubacka I, Chinnery PF, et al. Reanalysis and revision of the Cambridge reference sequence for human mitochondrial DNA[J]. Nature genetics, 1999,23(2):147
doi: 10.1038/13779
URL
pmid: 10508508
|
| [82] |
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009,25(16):2078-2079
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
URL
pmid: 19505943
|
| [83] |
Patterson N, Moorjani P, Luo Y, et al. Ancient admixture in human history[J]. Genetics, 2012,192(3):1065-1093
doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.145037
URL
pmid: 22960212
|
| [84] |
Fu QM, Mittnik A, Johnson PLF, et al. A revised timescale for human evolution based on ancient mitochondrial genomes[J]. Current biology, 2013,23(7):553-559
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.02.044
URL
pmid: 23523248
|
| [85] |
Edgar RC. MUSCLE: a multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity[J]. BMC bioinformatics, 2004,5(1):113
|
| [86] |
Kloss-Brandstätter A, Pacher D, Schönherr S, et al. HaploGrep: a fast and reliable algorithm for automatic classification of mitochondrial DNA haplogroups[J]. Human mutation, 2011,32(1):25-32
doi: 10.1002/humu.21382
URL
pmid: 20960467
|
| [87] |
Van Oven M. PhyloTree Build 17: Growing the human mitochondrial DNA tree[J]. Forensic Science International: Genetics Supplement Series, 2015,5:e392-e394
|
| [88] |
Van Oven M, Kayser M. Updated comprehensive phylogenetic tree of global human mitochondrial DNA variation[J]. Human mutation, 2009,30(2):E386-E394
doi: 10.1002/humu.20921
URL
pmid: 18853457
|
| [89] |
Bandelt H J, Forster P, Röhl A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies[J]. Molecular biology and evolution, 1999,16(1):37-48
URL
pmid: 10331250
|
| [90] |
Leigh JW, Bryant D, Nakagawa S. PopART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2015,6(9):1110-1116
|