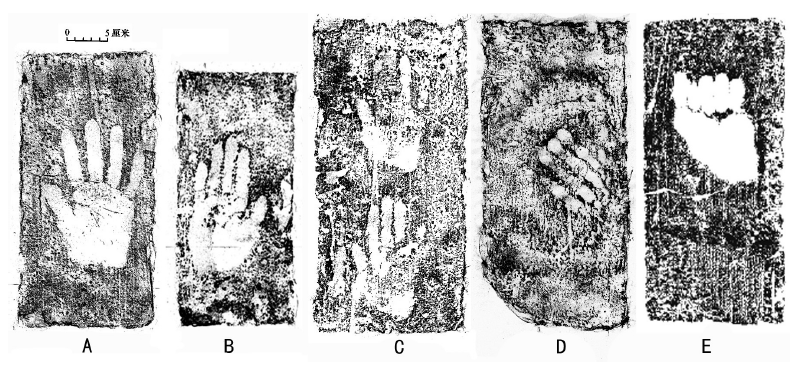
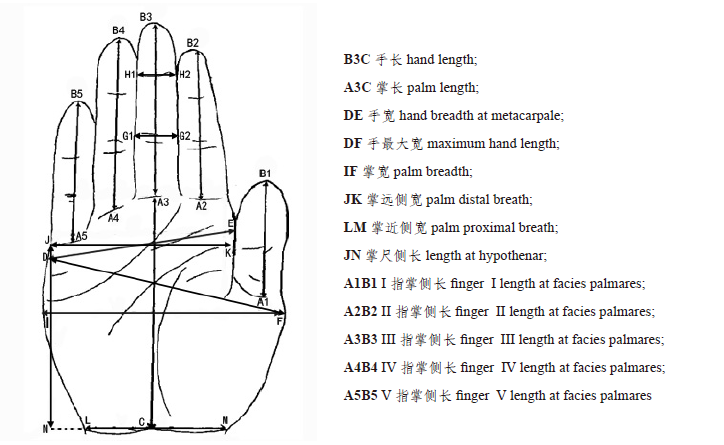
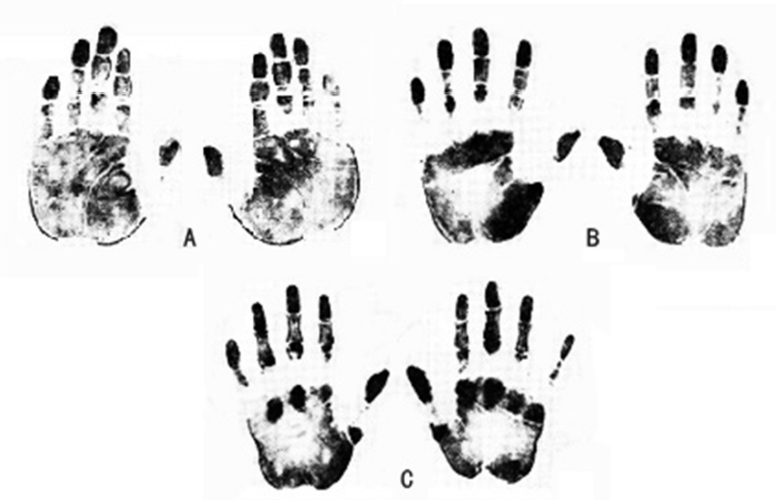
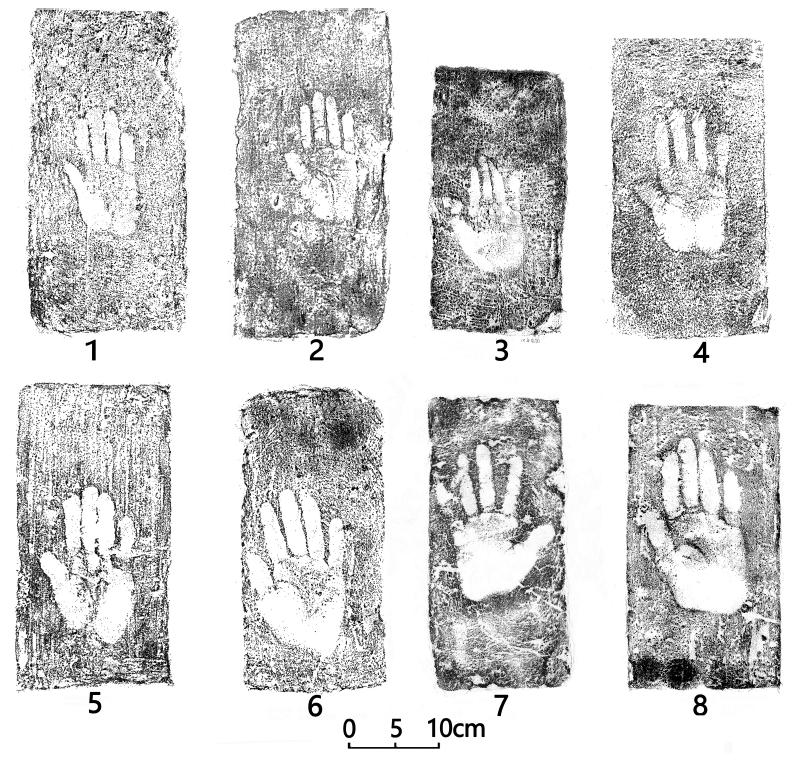
| [1] |
广东省文物考古研究所, 广州市番禺区文化局. 番禺汉墓[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006: 185-186
|
| [2] |
吴汝康. 今人类学[M]. 合肥: 安徽科学技术出版社, 1991: 158
|
| [3] |
南京市博物馆, 雨花台区文化广播电视局. 南京市雨花台区宁丹路东晋墓发掘简报[J]. 东南文化, 2014(6): 29-42+65-67
|
| [4] |
韦璇. 两广地区汉晋时期出土手印纹砖的体质人类学分析[D]. 桂林:广西师范大学, 2017
|
| [5] |
邵象清. 人体测量手册[M]. 上海: 上海辞书出版社, 1985
|
| [6] |
席焕久, 陈昭. 人体测量方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010
|
| [7] |
日本人类工效学会人体测量编委会编. 人体测量手册[Z]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1983
|
| [8] |
何光箎, 钟世旗, 刘正津. 手的活体测量[J]. 解剖学报, 1966, 9(2): 154-162
|
| [9] |
李英宏, 郎俊彦, 白彬. 四川广元、绵阳出土汉代画像砖掌印纹的痕检学分析[J]. 考古与文物, 2007(3): 64-75
|
| [10] |
刘少聪. 新指纹学[M]. 合肥: 安徽人民出版社, 1984
|
| [11] |
王俊. 中国古代赋税[M]. 北京: 中国商业出版社, 2015: 56
|
| [12] |
王子今. 两汉社会的“小男”“小女”[J]. 清华大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2008(1): 39-45
|
| [13] |
陈献跃. 根据人体的手部数据推断性别的研究[J]. 数理统计与管理, 2003(A1): 28-30
|
| [14] |
沈德立. 脑功能开发的理论与实践[M]. 北京: 教育科学出版社, 2001: 117
|
| [15] |
陈献跃. 利用人的手部数据推断身高的研究[J]. 数理统计与管理, 2004(1): 35-36
|
| [16] |
李力. 回归法推断手印和足迹与身高和体重的关系[J]. 法医学杂志, 2005, 21(4): 252-254
|
| [17] |
彭卫, 杨振红. 中国风俗通史·秦汉卷[M]. 上海: 上海文艺出版社, 2002: 354
|
| [18] |
【西汉】司马迁. 史记·卷一百四·田叔列传[M]. 北京:中华书局, 2006: 601-604
|
| [19] |
翦伯赞. 两汉时期的雇佣劳动[J]. 北京大学学报, 1959(1): 53-60
|
| [20] |
【南朝宋】范晔. 后汉书·卷四十四·胡广列传[M]. 北京:中华书局, 1965: 421-424
|
| [21] |
【东汉】班固. 汉书·卷七十六[M]. 北京:中华书局, 2005: 2409
|
| [22] |
顾丽华. 汉代妇女生活情态研究[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社, 2012: 148
|
| [23] |
【清】朱彬撰. 礼记训纂·卷十二[M]. 北京:中华书局, 1996: 434
|
| [24] |
赵东玉. 西周春秋妇女地位的式微——中国妇女地位变迁史研究之一[J]. 吉林大学社会科学学报, 1987(04): 36-39
|
| [25] |
王翠艳. 左利手及其形成机制:生理、病理及心理学的视角[J]. 心理学探新, 2012, 32(3): 272-276
|
| [26] |
张霭珠, 陈力君. 定量分析方法[G]. 上海: 复旦大学出版社, 2003
|
| [27] |
李济. 中国民族的形成[M]. 上海: 上海人民出版社, 2008: 39-40
|
| [28] |
广东省体育局. 2005年广东省国民体质监测报告[M]. 广州: 广东科技出版社, 2008: 90
|
| [29] |
广西壮族自治区体育局群体处, 广西国民体质监测中心. 2005年广西国民体质监测报告[G]. 南宁: 广西人民出版社, 2007: 26
|