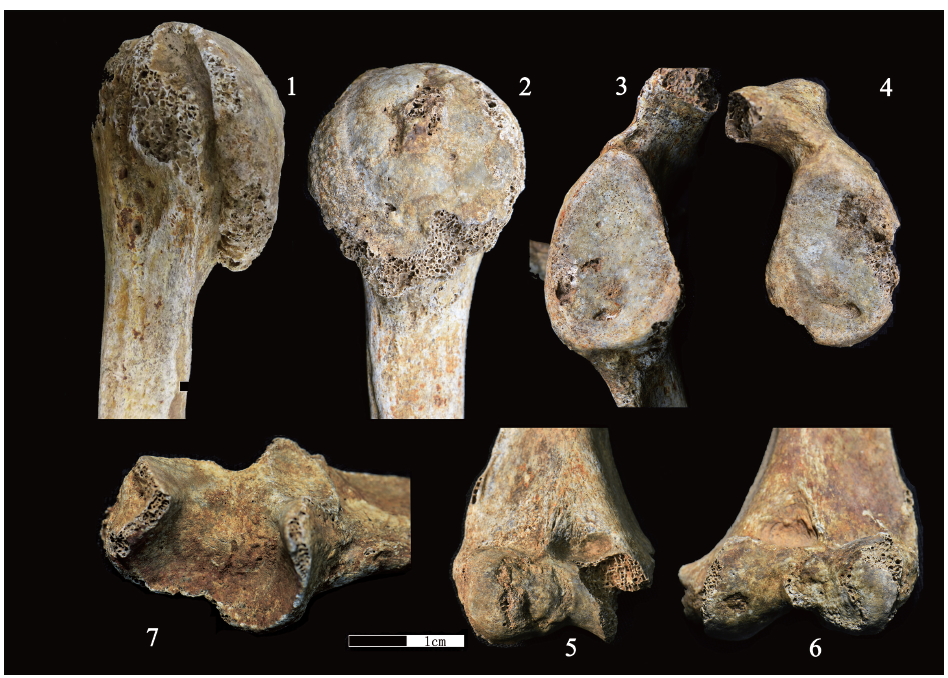
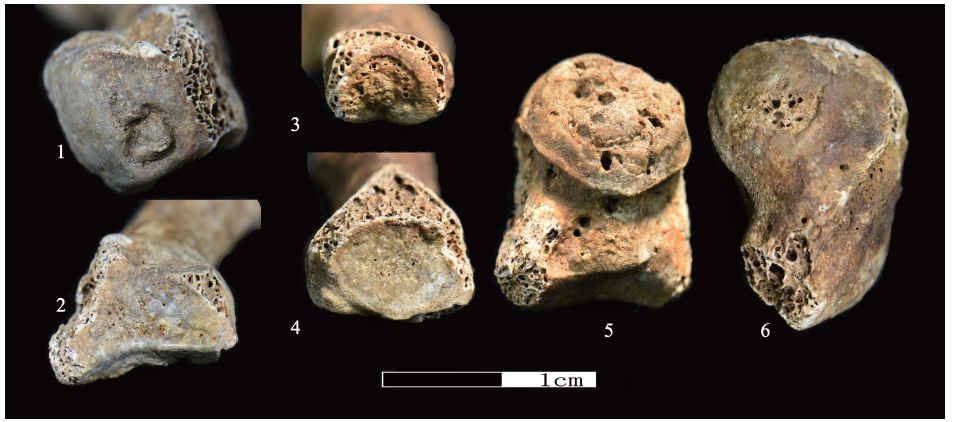
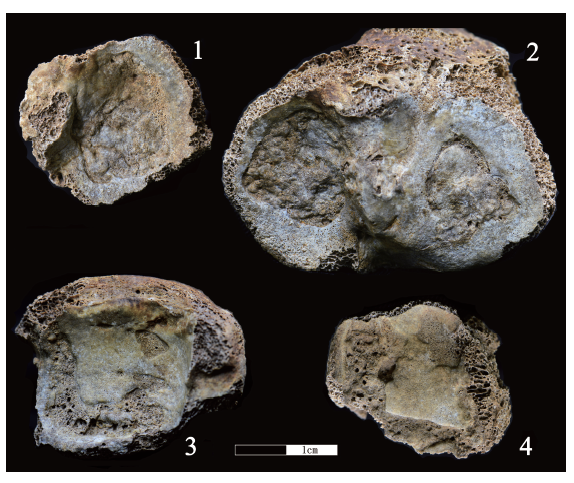
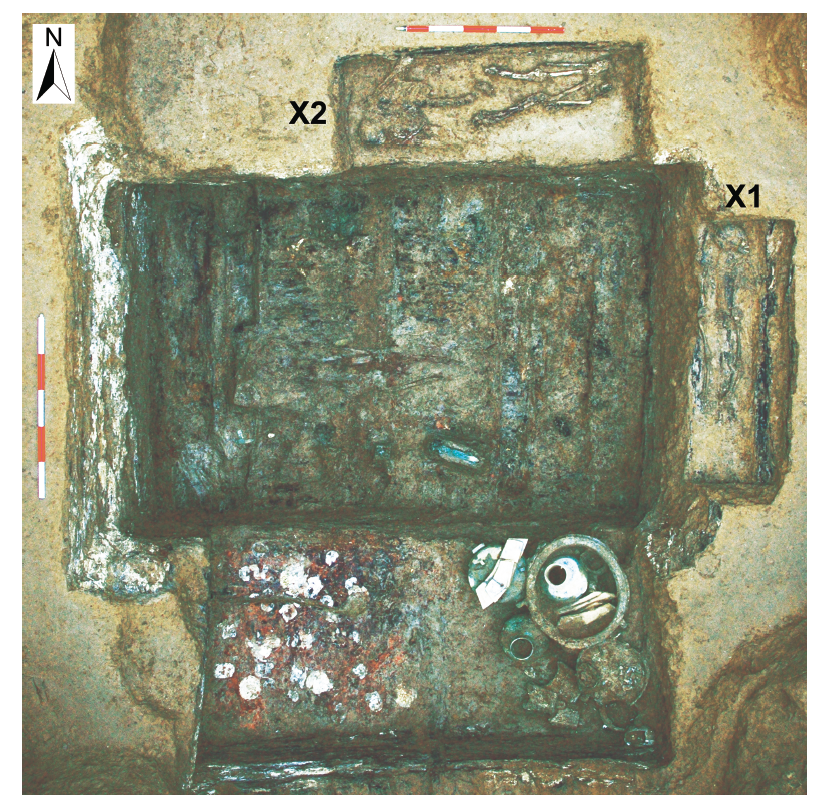
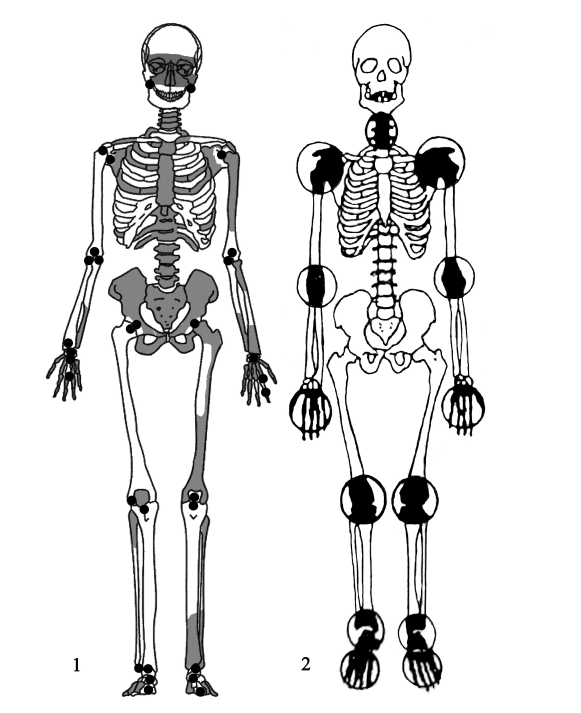
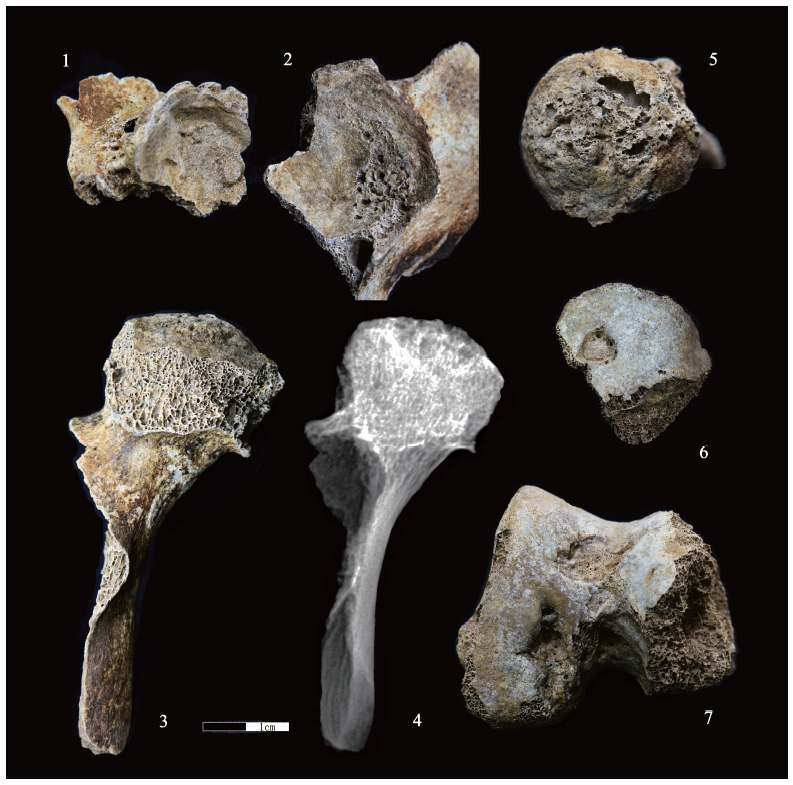
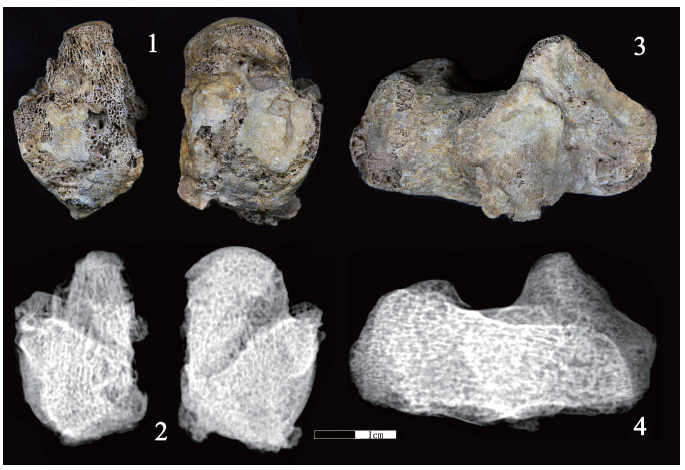
| [1] |
温博, 曾升平. 类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志, 2014, 9(9):1014-1019
|
| [2] |
中华医学会风湿病学分会. 类风湿关节炎诊断及治疗指南[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2010, 14(4):265-270
|
| [3] |
刘健. 风湿病中医临床思维[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2010, 22(9):753-761
|
| [4] |
倪立青. 类风湿关节炎[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2009: 3-61
|
| [5] |
潘远根, 旷惠桃. 类风湿性关节炎病机的再认识[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志, 1998, 5(1):11-14
|
| [6] |
Waldron T. Palaeopathology. Cambridge manuals in archaeology[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2009: 46-70
|
| [7] |
朱晓汀, 林留根, 朱泓. 江苏邳州梁王城遗址大汶口文化墓地出土人骨研究[J]. 东南文化, 2013, 4:53-64
|
| [8] |
Ortner DJ. Identification of pathological conditions in human skeletal remains (2nd edition)[M]. San Diego: Academic Press, 2003: 561-565
|
| [9] |
夏洛特•罗伯茨, 等. 疾病考古学[M].译者:张桦. 济南: 山东画报出版社, 2010: 145-183
|
| [10] |
Holly S. Patterns of molar wear in hunter-gatherers and agriculturalists[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1984, 63:39-56
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-8644
URL
|
| [11] |
邵象清. 人体测量手册[M]. 上海: 上海辞书出版社, 1985: 34-56
|
| [12] |
朱泓. 体质人类学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004: 92-106
|
| [13] |
陈世贤. 法医人类学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1998: 83-86
|
| [14] |
张继宗. 中国汉族女性长骨推算身高的研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2001, 20(4):302-307
|
| [15] |
中华医学会风湿病学分会. 类风湿关节炎诊治指南[J]. 现代实用医学, 2004, 16(3):184-188
|
| [16] |
Bernardo TA. Seronegative spondyloarthropathies and diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in ancient northern Chile[J]. American journal of physical anthropology, 1993, 91:263-278
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-8644
URL
|
| [17] |
吕芳, 李兴福. 2010年美国风湿病学会联合欧洲抗风湿病联盟的类风湿关节炎分类标椎解读[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2010, 9(4):307-310
|
| [18] |
Blondiaux JL, Cotton A, Fontaine C, et al. Two roman and medieval cases of symmetrical erosive polyarthropathy from normandy: anatomicopathological and radiological evidence for rheumatoid arthritis[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 1997, 7:451-466
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1212
URL
|
| [19] |
Leden I, Svensson B, Harding B, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) - an old or recent disease? More accurately defined criteria for paleopathological diagnosis of RA are expected to give the answer[J]. Paleopathology Newsletter, 2008, 142:30-32
|
| [20] |
Kilgore L. Possible case of rheumatoid arthritis from Sudanese Nubia[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1989, 79:177-183
pmid: 2662779
|
| [21] |
张晓盈, 郅新, 穆荣, 等. 侵蚀性手骨关节炎的临床及影像学特征分析[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2017, 21(7):455-460
|
| [22] |
Waldron T. The Health of the Adults[A]. In: Molleson T, Cox M(Eds.). The Spitalfields Project, Vol. 2, the anthropology: The middling sort[M]. CBA Research Report 86, York: Council for British Archaeology, 1993
|
| [23] |
吕厚山. 临床关节疾病图谱[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 59-77
|
| [24] |
漆强, 邹玉林, 余晖, 等. 痛风性关节炎的X线、CT和MRI诊断价值比较[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2015, 26(7):523-527
|
| [25] |
郭嘉隆, 毕黎琦. 血清阴性脊柱关节病概述[J]. 中国社区医师, 2002, 9:11-12
|
| [26] |
郭嘉隆, 章来晓. 放射学检查在血清阴性脊柱关节病中的应用[J]. 中国社区医师, 2002, 9:14-16
|
| [27] |
谢君艳, 王振刚. 反应性关节炎误诊为痛风性关节炎1例[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2018, 7(3):48-49
|
| [28] |
陈相佐, 周金伟, 季建松. 赖(Reiter)氏综合征的MRI与平片的诊断(附2例报告)[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2001, 17(1):636-637
|
| [29] |
彭晨星, 张晓岚. 炎性肠病关节炎发病机制新进展[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2012, 16(8):571-574
|
| [30] |
刘岳, 黄慈波. 炎性肠病性关节炎一例[J]. 临床内科杂志, 2015, 32(1):58
|
| [31] |
Resnick D, Niwayama G. Diagnosis of Bone and Joint Disorders[M]. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co. 1988
|
| [32] |
Rogers J, Waldron T, Dieppe P, et al. Arthropathies in palaeopathology: The basis of classification according to most probable cause[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1987, 14:179-193
doi: 10.1016/0305-4403(87)90005-7
URL
|
| [33] |
Leden I, Forslind K, Svensson B. Ankylosis of wrist and small joints of the hand occurs in rheumatoid arthritis: Diagnostic implication in paleopathology[J]. International Journal of Paleopathology, 2012, 2:249-251
doi: S1879-9817(12)00048-4
pmid: 29539374
|
| [34] |
Rothschild B, Woods R. Symmetrical erosive disease in Archaic Indians: the origin of rheumatoid arthritis in the new word?[J]. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 1990, 19:278-284
pmid: 2192458
|
| [35] |
Short CL. The antiquity of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 1974, 17:193-205
pmid: 4596668
|
| [36] |
Sturrock R, Sharma J, Buchanan W. Evidence of rheumatoid arthritis in ancient india[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 1977, 20(1):42-44
pmid: 319807
|
| [37] |
潘峥, 周彩云, 房定亚. 从风湿病的历史与现状谈辨证论治和辨病论治的关系[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2014, 3(1):68-71
|
| [38] |
Kacki S. Erosive polyarthropathy in a late Roman skeleton from northern France: A new case of rheumatoid arthritis from the pre-Columbian Old World?[J]. International Journal of Paleopathology, 2013, 3:59-63
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpp.2012.12.001
URL
|
| [39] |
Inoue K, Hukuda S, Nakai M, et al. Erosive peripheral polyarthritis in ancient Japanese skeletons: a possible case of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 1999, 9:1-7
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1212
URL
|
| [40] |
张晓英, 靳家扬, 何菁, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者风湿病家族史特征及临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(3):439-444
|
| [41] |
倪红燕. 类风湿关节炎危险因素的临床对照研究[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2011, 25(20):3160-3161
|
| [42] |
孙建. 河南省漯河地区中老年人群类风湿关节炎患病情况及影响因素[D]. 郑州:郑州大学, 2013: 70-88
|
| [43] |
Li R, Sun J, Ren LM, et al. Epidemiology of eight common rheumatic diseases in China: a large-scale cross-sectional survey in Beijing[J]. Oxford: Rheumatology, 2012, 51(4):721-729
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker370
URL
|
| [44] |
张凤山, 任潞雪. 我国北方高寒林区风湿病的流行病学调查[J]. 哈尔滨医科大学学报, 1991, 25(1):25-27
|
| [45] |
叶冬青, 李向培. 安徽准南潘地区类风湿性关节炎流行病学调查[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 1993, 28(1):3
|
| [46] |
汪太中, 万姜敏, 陈红, 等. 重庆市綦江区类风湿关节炎流行病学调查[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2018, 7(1):32-34+50
|
| [47] |
Mays S, Watt I, Loe L. An unusual erosive arthropathy from Medieval England[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2017, 27:693-699
doi: 10.1002/oa.v27.4
URL
|
| [48] |
刘健, 程华威, 郭雯, 等. 类风湿性关节炎生活质量调查[J]. 中国临床保健杂志, 2006, 9(2):106-108
|
| [49] |
叶伟胜, 张铁良. 类风湿关节炎流行病学进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2009, 30(3):144-146
|