

Skull sex identification using improved convolution neural network and least squares method
Received date: 2017-08-01
Revised date: 2018-02-22
Online published: 2020-09-10
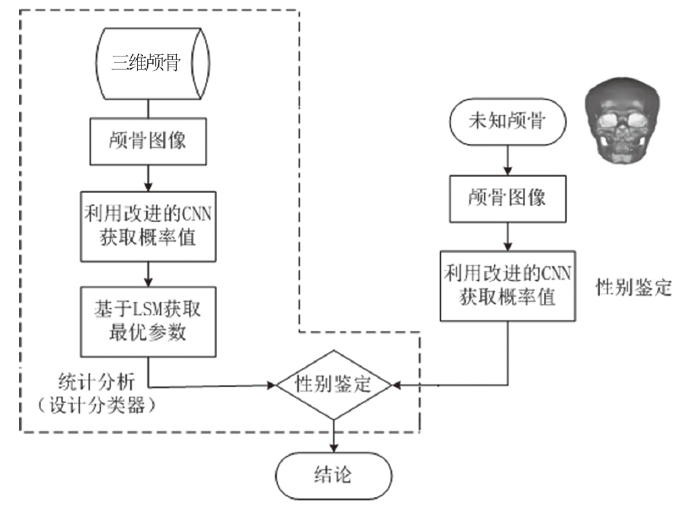
Skull sex identification has significant research and applied value in forensic anthropology and skull reconstruction. The traditional skull sex determination methods need expert participation and to some extent, is not objective, because computer-aided methods require to marking landmarks the feature points manually. We present a novel sex determination method based on improved Convolution Neural Network and Least Square. Firstly, obtain multi-angle skull images of three-dimensional skull model, and calculate the probability of each image belongs to male or female. Secondly, the weight of each image is calculated using the Least Squares method based on the probability mean. Lastly, the sex determination function is constructed by using the optimal parameters obtained through the above steps. This method does not need to mark the feature points or do the measurement. Experiments show that the proposed method can get quite a reliable performance with an accuracy of 94.4% for the the complete skull and 87.5% for the incomplete skull.
Wen YANG , Xiaoning LIU , Xiongle LIU , Lipin ZHU . Skull sex identification using improved convolution neural network and least squares method[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2019 , 38(02) : 265 -275 . DOI: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2018.0030
| [1] | Guyomarc’H P, Bruzek J. Accuracy and reliability in sex determination from skulls: a comparison of Fordisc? 3.0 and the discriminant function analysis[J]. Forensic Science International, 2011, 208(1): 180.e1-180.e6 |
| [2] | Stewart TD. Medico-legal aspects of the skeleton;sex,age,race and stature[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1948,6(3):315-321 |
| [3] | Iscan MY, Maryna S. The Human Skeleton in Forensic Medicine[M]. Royal Society of Medicine Press, 2013, 56(2): A-48 |
| [4] | Keen JA. A study of the differences between male and female skull[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1997,116(2):118-124 |
| [5] | 张亚盟, 魏偏偏, 吴秀杰. 现代人头骨断面轮廓的性别鉴定——基于几何形态测量的研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2016,35(2):172-180 |
| [6] | Ogawa Y, Imaizumi K, Miyasaka S, et al. Discriminant functions for sex estimation ofmodern Japanese skulls[J]. Journal of Forensic & Legal Medicine, 2013,20(4):234-238 |
| [7] | Kanchan J, Gupta A, Krishan K. Estimation of sex from mastoid trsiangle-A craniometric analysis[J]. Journal of Forensic & Legal Medicine, 2013,20(7):855-860 |
| [8] | 税午阳, 殷荣超, 周明全, 等. 中国汉族人颅骨数字模型的性别判别方法[J]. 中国法医学杂志, 2013,286(6):461-464 |
| [9] | Twisha S, Patel MN, Nath S, et al. Determination of sex using cephalo-facial dimensions by discriminant function and logistic regression equations[J]. Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences, 2016,6(2):114-119 |
| [10] | Santos F, Guyomarc’h P, Bruzek J. Comparison of linear discriminant analysis, logistic regression, support vector machines[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2014, 245(204): el-e8 |
| [11] | Alunni V, Jardin PD, Nogueira L, et al. Comparing discriminant analysis and neural network for the determination of sex using femur head measurements[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2015,253:81-87 |
| [12] | Afrianty I, Nasien D, Kadir MRA, et al. Back-Propagation neural network for gender determination in forensic anthropology[J]. Studies in Computational Intelligence, 2015,575:255-281 |
| [13] | Luo L, Wang M, Tian Y, et al. Automatic Sex Determination of Skulls Based on a Statistical Shape Model[J], Computational and mathematical methods in medicine, 2013,2013(1):251628 |
| [14] | Janarthanan R, Asha J. Supraorbital Margins for Identification of Sexual Dimorphism and Age Detection from Human Skull Using Wavelets[J]. Asian Journal of Applied Science and Technology, 2017,1(2):279-282 |
| [15] | 任荣荣, 周明全, 耿国华, 等. 三维颅骨形态量化表示与非线性性别判定[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2017,53(1):19-23 |
| [16] | Pham DV. Online handwriting recognition using multi-convolution neural network[J]. International Conference on Simulated Evolution & Learning, 2012,7673:310-319 |
| [17] | Lawrence S, Giles CL, Tsoi AC, et al. Face recognition: a convolutional neural-network approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Network, 1997,8(1):98-113 |
| [18] | Hu B, Lu Z, Li H, et al. Convolutional Neural Network Architectures for Matching Natural Language Sentences[J]. International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014,3:2042-2050 |
| [19] | Bouvrie J. Notes on Convolutional Neural Networks[J]. Neural Nets, 2006: 38-44 |
| [20] | Herreragomez A, Porter RM. Mixed linear-nonlinear least squares regression[J]. Mathematics, 2017: 49-65 |
| [21] | Barham RH, Wanzer D. An Algorithm for Least Squares Estimation of Nonlinear Parameters When Some of the Parameters are linear[J]. Technometrics, 1972,14(3):757-766 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |