

A study of skull morphology of Yangshao Culture residents from the Sunzhuang site in Zhengzhou
Received date: 2019-05-07
Revised date: 2019-10-22
Online published: 2020-09-11
The Sunzhuang site, located in the south of Sunzhuang Village, Zhongyuan District, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, is a late Yangshao cultural site distributed in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. Through the measurement and observation of 10 cases of basically intact skulls unearthed from the site, the following conclusions are drawn: The craniofacial features of Sunzhuang group can be summarized as follows: high cranial type combined with narrow cranial type, moderate to large facial flatness, narrow frontal type, middle nasal type, low orbital type, middle facial angle belonging to flat jaw type, underdeveloped canine dentate fossa and nasal root fossa. Simple parietal suture. The morphological characteristics of the skulls of the ancient residents of the Sunzhuang formation belong to the Asian Mongolian nationality. The results of the multivariate statistical analysis of the morphological characteristics of the skull showed that the Sunzhuang formation is most closely related to the modern South China formation (R=1.26) of Asian Mongolians, and is estranged from the modern Mongolian group (R=1.80) and Tungus group (R=2.06). In comparison with Neolithic formation, the relationship between Sunzhuang male formation and Yangshao merge formation (R=1.00), Miaozigou formation (R=1.00), Xishan formation (R=1.07) and Dawenkou formation (R=1.13) is close. Sunzhuang female group is closest to Dawenkou group (Dij=3.10), Xubao group (Dij=4.58) and Xishan group (Dij=4.60). In summary, We can see that the middle and late Yangshao people distributed in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River have the same craniofacial characteristics and high homology, and should belong to the “ancient Central Plains type” residents.
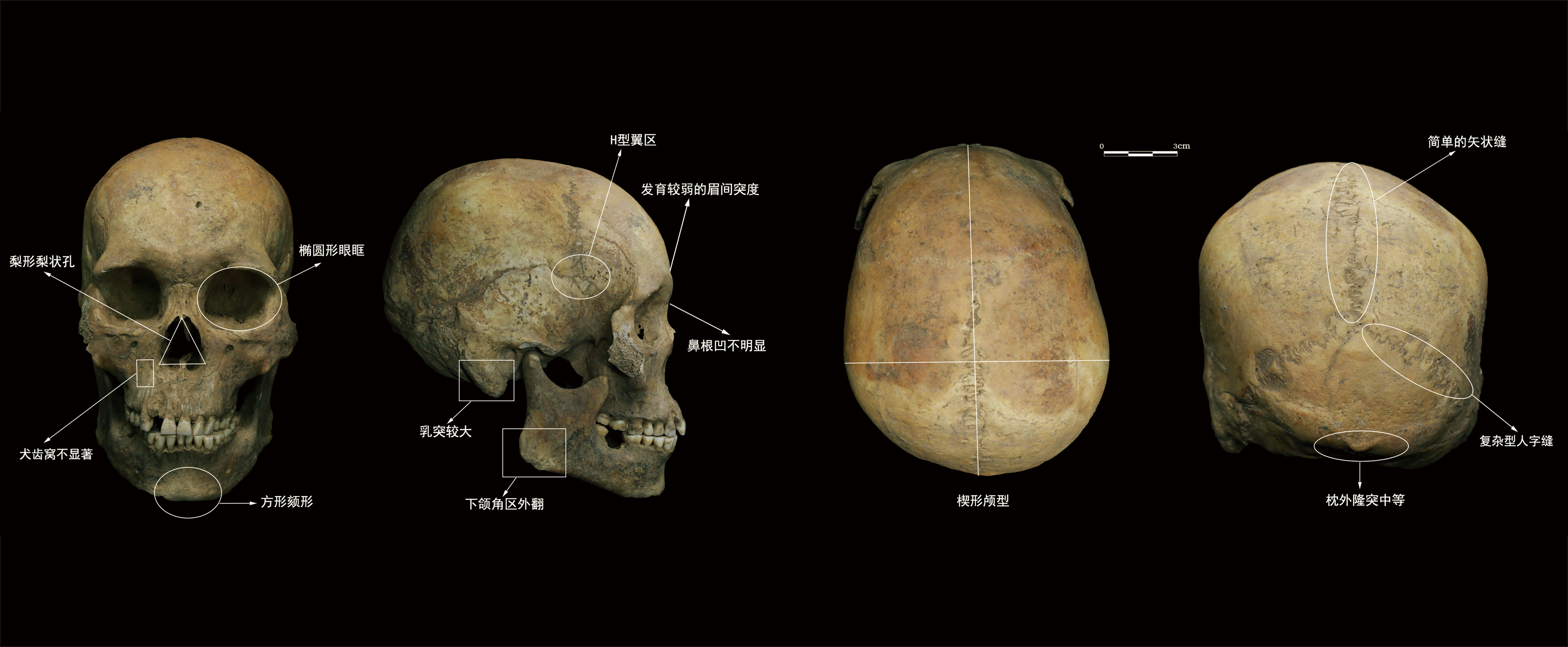
Key words: Skull; Race type; Yangshao culture; Sunzhuang site
Yawei ZHOU , Xiaoran ZHANG , Wanfa GU . A study of skull morphology of Yangshao Culture residents from the Sunzhuang site in Zhengzhou[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021 , 40(04) : 611 -627 . DOI: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0036
| [1] | Weidenreich F. Apes, giants and man[M]. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press, 1946 |
| [2] | 吴新智. 山顶洞人的种族问题[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1960(2):141-149 |
| [3] | 吴新智. 从中国晚期智人颅牙特征看中国现代人起源[J]. 人类学学报, 1998(4):276-280 |
| [4] | 吴汝康. 广西柳江发现的人类化石[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1959(3):97-104 |
| [5] | 颜誾. 从人类学上观察中国旧石器时代晚期与新石器时代的关系[J]. 考古, 1965(10):513-516 |
| [6] | 张振标, 王令红, 欧阳莲. 中国新石器时代居民体征类型初探[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1982(1):72-78 |
| [7] | 韩康信, 潘其风. 古代中国人种成分研究[J]. 考古学报, 1984(2):245-265 |
| [8] | 朱泓. 体质人类学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004: 321-353 |
| [9] | 荣焱. 中原腹地新石器时代中晚期房屋基址研究[D]. 开封:河南大学, 2017, 1-5 |
| [10] | 刘东兴. 郑州大河村遗址仰韶时期生产工具的初步研究[J]. 华夏文明, 2018(10):17-21 |
| [11] | 孙蕾. 渑池笃忠遗址仰韶文化晚期人骨研究[J]. 华夏考古, 2010(3):100-109 |
| [12] | 周亚威, 张晓冉, 顾万发. 郑州汪沟遗址仰韶文化居民的牙齿磨耗及口腔健康状况分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2019: 10-23 |
| [13] | 王建华. 黄河中下游地区史前人口研究[D]. 济南:山东大学, 2005 |
| [14] | 吴汝康, 吴新智, 张振标. 人体测量方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984: 14-15 |
| [15] | 邵象清. 人体测量手册[M]. 上海: 上海辞书出版社, 1985: 34-56 |
| [16] | 武松, 潘发明, 等. SPSS统计分析大全[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016: 326-329 |
| [17] | 薛薇. 统计分析与 SPSS 的应用[M]. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2015: 129-134 |
| [18] | 赵永生, 曾雯, 魏成敏, 等. 大汶口文化居民枕骨变形研究[J]. 东南文化, 2017(3):64-72 |
| [19] | 颜誾. 大汶口新石器时代人骨的研究报告[J]. 考古学报, 1972(1):91-122 |
| [20] | 韩康信. 山东诸城呈子新石器时代人骨[J]. 考古, 1990(7):644-654 |
| [21] | 韩康信. 山东兖州王因新石器时代人骨的鉴定报告[A].见:中国社会科学院考古研究所.山东王因[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000, 388-407 |
| [22] | 中桥孝博, 栾丰实. 丁公遗址出土的龙山文化人骨—头盖骨[A].见:栾丰实,宫本一夫.海岱地区早期农业和人类学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008, 187-198 |
| [23] | 朱泓. 山东济宁潘庙汉代墓葬人骨研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1990(3):260-264 |
| [24] | 魏东, 张桦, 朱泓. 郑州西山遗址出土人类遗骸研究[J]. 中原文物, 2015(2 ): 111-119 |
| [25] | 孙蕾. 河南渑池笃忠遗址仰韶晚期出土的人骨骨病研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2011(1):55-63 |
| [26] | 朱泓, 张全超. 内蒙古林西县井沟子遗址西区墓地人骨研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2007(2):98-106 |
| [27] | 肖晓鸣. 吉林大安后套木嘎遗址人骨研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2014, 3-160 |
| [28] | 考古研究所体质人类学组. 陕西华阴横阵的仰韶文化人骨[J]. 考古, 1977(4):247-250 |
| [29] | 颜誾, 刘昌芝, 顾玉珉. 宝鸡新石器时代人骨的研究报告[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1960(1):33-43 |
| [30] | 颜誾. 华县新石器时代人骨的研究[J]. 考古学报, 1962(2):85-104 |
| [31] | 朱泓. 内蒙古察右前旗庙子沟新石器时代颅骨的人类学特征[J]. 人类学学报, 1994(2):126-133 |
| [32] | 李法军. 河北阳原姜家梁新石器时代人骨研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 88-141 |
| [33] | 潘其风, 韩康信. 柳湾墓地的人骨研究[A].见:青海省文物管理处考古队,中国社会科学院考古研究所.青海柳湾[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1984, 261-303 |
| [34] | 韩康信. 青海民和阳山墓地人骨[A].见:青海省文物考古研究所.《民和阳山》附录一[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1990, 160-173 |
| [35] | 李法军, 王明辉, 冯孟钦, 等. 鲤鱼墩新石器时代居民头骨的形态学分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2013(3):32 |
| [36] | 赵欣. 辽西地区先秦时期居民的体质人类学与分子考古学研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2009 |
| [37] | 内蒙古文物考古研究所, 日本京都中国考古学研究会. 饮牛沟墓地1997年发掘报告[A].见:岱海考古(二)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001, 278-327 |
| [38] | 韩康信, 潘其凤. 安阳殷墟中小墓人骨的研究[A].见:中国社会科学院历史研究所,中国社会科学院考古研究所.安阳殷墟头骨研究[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1985 |
| [39] | 周亚威, 刘明明, 冯春燕, 等. 徐堡遗址龙山文化居民颅骨的形态学研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2018(1):18-28 |
| [40] | 颜誾. 西夏侯新石器时代人骨的研究报告[J]. 考古学报, 1973(2):91-125 |
| [41] | 中国社会科学院考古研究所编著. 中国考古学.新石器时代卷[M]. 北京: 中国社会科学出版社, 2010: 278-764 |
| [42] | 朱泓. 中原地区的古代种族.中国古代居民体质人类学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014: 35-43 |
| [43] | 安金槐. 试论河南地区龙山文化的社会性质[J]. 中原文物, 1989(1):20-24 |
| [44] | 中国科学院考古研究所. 庙底沟与三里桥[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1959: 118 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |