

A preliminary report on the Paleolithic survey in Jinghe River basin, Shaanxi Province in 2019
Received date: 2019-07-18
Revised date: 2019-09-09
Online published: 2021-02-25
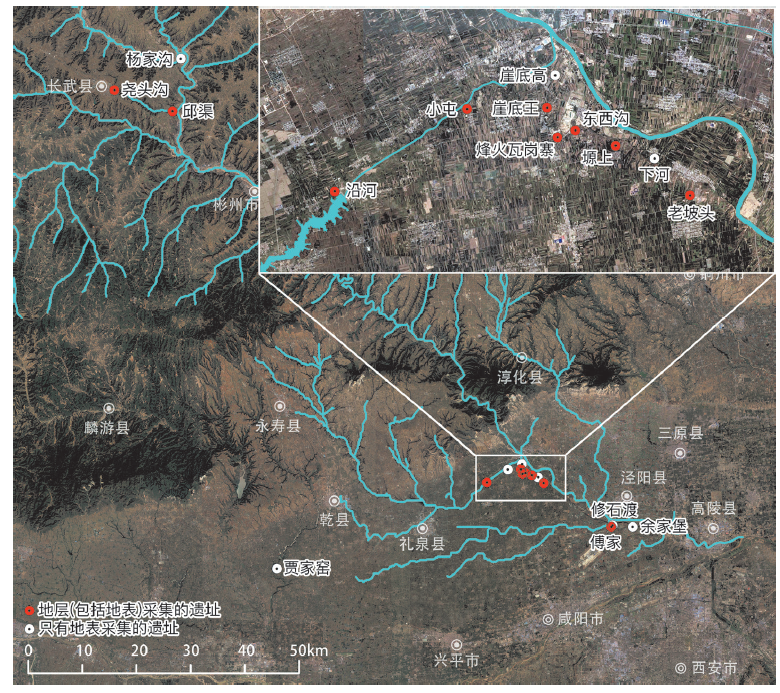
Jinghe River system is one of the important areas on the study of human occupied patterns in Northwest China. In 1920, some stone artifacts were recovered from loess deposit by French Archaeologist E. Licent in Zhaojiacha and Xinjiagou, which marked the beginning milestone of Chinese Paleolithic Archaeology. In the past century, many Paleolithic localities such as Niujiaogou, Shigoukou, Loufangzi from Qingyang and Pingliang of Gansu, Yaotougou and Dabeigou from Changwu and Qianxian of Shannxi, which enriched the early human adapted data in the Jinghe River system. However, all the discoveries are buried in the Upper and Middle Jinghe River system, and the investigations were carried out several decades ago, while few information was gotten in the lower Jinghe River system. The new findings of this Paleolithic survey fill in gaps in the Lower Jinghe River system to some extent. Sixteen localities were discovered which centralized in the second terrace of the Middle to Lower Jinghe River system, and sixty-three stone artifacts were recovered from the loess deposit. The new discovered lithic artifacts include cores, flakes and scrapers, which can be assigned to the Flake Tool Tradition in North China. Judging from the artifact layers and comparison among the geomorphology and stratigraphy in Jinghe River system, the age of the artifact layers can be deduced to Late Pleistocene.
Key words: Survey; Jinghe river; Stone artifacts; Loess; Late Pleistocene
Shijia ZHAN , Zhe DONG , Yaopeng QIAN . A preliminary report on the Paleolithic survey in Jinghe River basin, Shaanxi Province in 2019[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021 , 40(01) : 157 -164 . DOI: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2019.0076
| [1] | 陕西师大地理系. 咸阳市地理志[M]. 西安: 陕西人民出版社, 1991: 35-86 |
| [2] | 李瑜琴. 泾河流域全新世环境演变及特大洪水水文学研究[D]. 西安:陕西师范大学, 2009: 34-46 |
| [3] | 冉大川, 吴永红. 泾河流域水土保持生态环境建设与治理方略刍议[J]. 水土保持研究, 2003, 10(2): 58-60 |
| [4] | 刘玉林, 黄慰文, 林一璞. 甘肃泾川发现的人类化石和旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 1984(1): 11-18 |
| [5] | 黄万波, 郑绍华. 记陕西长武晚更新世人牙及共生哺乳动物化石[J]. 人类学学报, 1982, 1(1): 14-17 |
| [6] | 陈恩志(主编). 中国化石古人类和旧石器文化考古发现与研究(1901-1990)·西北地区卷[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 1992: 477-482 |
| [7] | 刘玉林. 甘肃泾川大岭上发现的旧石器[J]. 史前研究, 1987(1): 37-42 |
| [8] | 张宏彦. 泾水上游旧石器时代遗存的年代与分期研究[J]. 西北大学学报:哲学社会科学版, 2005(1): 87-94 |
| [9] | 盖培, 黄万波. 陕西长武发现的旧石器时代中期文化遗物[J]. 人类学学报, 1982(1): 18-29 |
| [10] | 谢骏义. 甘肃环县刘家岔旧石器时代遗址[J]. 考古学报, 1982(1): 35-48 |
| [11] | 薛祥煦. 甘肃环县楼房子晚更新世哺乳动物化石及古文化遗物[A].见:西北大学编.黄土与第四纪地质[M]. 西安: 陕西人民出版社, 1982: 108-115 |
| [12] | 邱中郎. 陕西乾县的旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 1984(3): 212-214 |
| [13] | Toth N. The Stone Technologies of Early Hominids at Koobi Fora: An Experimental Approach[D]. Berkeley: University of California, 1982: 48-101 |
| [14] | 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985: 44-112 |
| [15] | 黄万波, 郑绍华. 记陕西长武晚更新世人牙及共生哺乳动物化石[J]. 人类学学报, 1982, 1(1): 14-17 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |