

Application review of the laser scanning confocal microscope in quantitative analysis of microwears
Received date: 2020-04-24
Online published: 2020-11-26
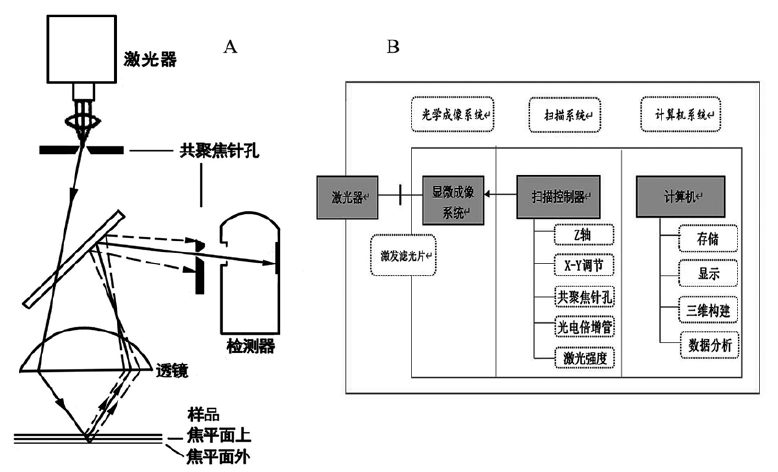
Microwear analysis is a common method for the study of crafts and functions of lithics, bone implements, teeth, etc. However, whether the high-power or low-power technique, it’s difficult to describe in-situ quantitative analysis limited by observation methods such as stereo optical microscope and SEM. So the quantification of microwear analysis is the key problem encountered by the academic circles at present. In recent years, the quantification of microwear analysis has obtained new practice and progress in Western academic with the application of laser scanning confocal(LSC) microscope. This article mainly introduces the principle of LSC microscope and its cases and prospects with new approach in the research of microwear, which expect to promote the further development of microwear analysis in China.
Key words: Microwear; Laser scanning confocal microscope; Roughness; Quantification
Tianxing CUI , Weiwei SONG . Application review of the laser scanning confocal microscope in quantitative analysis of microwears[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022 , 41(01) : 180 -192 . DOI: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0068
| [1] | 王小庆. 石器使用痕迹显微观察(高倍法)的研究[J]. 农业考古, 2005(1): 188-190 |
| [2] | 沈辰, 陈淳. 微痕研究(低倍法)的探索与实践——兼谈小长梁遗址石制品的微痕观察[J]. 考古, 2001(7): 62-73 |
| [3] | 高星, 沈辰. 石器微痕分析的考古学实验研究 [M]. 科学出版社, 2008: 1-22 |
| [4] | Gijn VAL. Science and interpretation in microwear studies[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2014, 48: 166-169 |
| [5] | Dumont J. The quantification of microwear traces: A new use for interferometry[J]. World Archaeology, 1982, 14(2): 206-217 |
| [6] | Kimball LR, Kimball JF, Allen PE. Microwear polishes as viewed through the atomic force microscope[J]. Lithic Technology, 1995: 6-28 |
| [7] | 陈耀文, 林月娟, 张海丹, 等. 扫描电子显微镜与原子力显微镜技术之比较[J]. 中国体视学与图像分析, 2006, 11(1): 53-58 |
| [8] | Stemp WJ, Stemp M. UBM laser profilometry and lithic use-wear analysis: a variable length scale investigation of surface topography[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2001, 28(1): 81-88 |
| [9] | Stemp WJ, Stemp M. Documenting stages of polish development on experimental stone tools: surface characterization by fractal geometry using UBM laser profilometry[J]. Journal of archaeological science, 2003, 30(3): 287-296 |
| [10] | Stemp WJ, Childs BE, Vionnet S, et al. Quantification and discrimination of lithic use-wear: surface profile measurements and length-scale fractal analysis[J]. Archaeometry, 2009, 51(3): 366-382 |
| [11] | Stemp WJ, Childs BE, Vionnet S. Laser profilometry and length-scale analysis of stone tools: second series experiment results[J]. Scanning, 2010, 32(4): 233-243 |
| [12] | Stemp WJ. A review of quantification of lithic use-wear using laser profilometry: a method based on metrology and fractal analysis[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2014, 48: 15-25 |
| [13] | 刘东武, 牟洪善. 激光扫描共聚焦显微镜技术在材料学研究中的应用[J]. 生命科学仪器, 2006(5): 11-14 |
| [14] | 李叶, 黄华平, 林培群, 等. 激光扫描共聚焦显微镜的基本原理及其使用技巧[J]. 电子显微学报, 2015(2): 86-93 |
| [15] | 张洪飞, 谈梦科, 及少勇, 等. 激光共聚焦扫描显微镜的光学设计[J]. 光学仪器, 2016(3): 37-41 |
| [16] | 霍霞, 吕建勋, 杨仁东, 等. 激光共聚焦显微镜与光学显微镜之比较[J]. 激光生物学报, 2001(1): 78-81 |
| [17] | 李楠, 王黎明, 杨军. 激光共聚焦显微镜的原理和应用[J]. 军医进修学院学报, 1996(03): 79-81 |
| [18] | Wright SJ, Centonze E, Stricker SA, et al. Introduction to confocal microscopy and three-dimensional reconstruction[M]. Methods in cell biology. Academic Press, 1993, 38: 1-45 |
| [19] | Farber E. A new method to achieve lithic use-wear discrimination using laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM)[D]. Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, FL, 2013. |
| [20] | Standard A. B46. 1-2009. Surface Texture (Surface Roughness, Waviness, and Lay)[S], ASME, New York : An American National Standard. American Society of Mechanical Engineers. |
| [21] | Evans AA, Macdonald D. Using metrology in early prehistoric stone tool research: further work and a brief instrument comparison[J]. Scanning, 2011, 33(5): 294-303 |
| [22] | Evans AA, Macdonald DA, Giusca CL, et al. New method development in prehistoric stone tool research: evaluating use duration and data analysis protocols[J]. Micron, 2014, 65: 69-75 |
| [23] | Stemp WJ, Watson AS, Evans AA. Surface analysis of stone and bone tools[J]. Surface Topography: Metrology and Properties, 2016(4): 013001 |
| [24] | Ungar PS, Brown CA, Bergstrom TS, et al. Quantification of dental microwear by tandem scanning confocal microscopy and scale-sensitive fractal analyses[J]. Scanning: The Journal of Scanning Microscopies, 2003, 25(4): 185-193 |
| [25] | Scott RS, Ungar PS, Bergstrom TS, et al. Dental microwear texture analysis: technical considerations[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2006, 51(4): 339-349 |
| [26] | 华李成, Peter S Ungar. 牙齿微痕研究在古食性重建中应用的简述[J]. 人类学学报, 2019(4): 1-16 |
| [27] | Ungar PS, Sponheimer M. The diets of early hominins[J]. Science, 2011, 334: 190-193 |
| [28] | Ungar PS. Mammalian dental function and wear: A review[J]. Biosurface and Biotribology, 2015, 1(1): 25-41. |
| [29] | Ungar PS. 进化的咬痕 [M]. 新世界出版社, 2019: 134-150 |
| [30] | Scott RS, Ungar PS, Bergstrom TS, et al. Dental microwear texture analysis shows within-species diet variability in fossil hominins[J]. Nature, 2005, 436(7051): 693-695 |
| [31] | Ungar PS, Grine FE, Teaford MF. Dental microwear and diet of the Plio-Pleistocene hominin Paranthropus boisei[J]. PLoS one, 2008, 3(4): 1-6 |
| [32] | Ungar PS, Krueger KL, Blumenschine RJ, et al. Dental microwear texture analysis of hominins recovered by the Olduvai Landscape Paleoanthropology Project,1995-2007[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2012, 63(2): 429-437 |
| [33] | Derndarsky M, Ocklind G. Some preliminary observations on subsurface damage on experimental and archaeological quartz tools using CLSM and dye[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2001, 28(11): 1149-1158 |
| [34] | Evans AA, Donahue RE. Laser scanning confocal microscopy: A potential technique for the study of lithic microwear[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2008, 35(8): 2223-2230 |
| [35] | Stemp WJ, Chung S. Discrimination of surface wear on obsidian tools using LSCM and RelA: pilot study results (area-scale analysis of obsidian tool surfaces)[J]. Scanning, 2011, 33(5): 279-293 |
| [36] | Stemp WJ, Lerner HJ, Kristant EH. Quantifying microwear on experimental Mistassini quartzite scrapers: preliminary results of exploratory research using LSCM and scale-sensitive fractal analysis[J]. Scanning: The Journal of Scanning Microscopies, 2013, 35(1): 28-39 |
| [37] | Stemp WJ, Lerner HJ, Kristant EH. LSCM and RelA for Quantifying Microwear: A Case Study[J]. Photonics Spectra, 2015, 49(2): 45-50 |
| [38] | Stemp WJ, Lerner HJ, Kristant EH. Testing Area-Scale Fractal Complexity (A sfc) and Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy (LSCM) to Document and Discriminate Microwear on Experimental Quartzite Scrapers[J]. Archaeometry, 2018, 60(4): 660-677 |
| [39] | Stemp WJ, Morozov M, Key AJM. Quantifying lithic microwear with load variation on experimental basalt flakes using LSCM and area-scale fractal complexity (Asfc)[J]. Surface Topography: Metrology and Properties, 2015, 3(3): 034006 |
| [40] | Key AJM, Stemp WJ, Morozov M, et al. Is loading a significantly influential factor in the development of lithic microwear? An experimental test using LSCM on basalt from Olduvai Gorge[J]. Journal of Archaeological Method and Theory, 2015, 22(4): 1193-1214 |
| [41] | Pfleging J, Iovita R, Buchli J. Influence of force and duration on stone tool wear: results from experiments with a force-controlled robot[J]. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 2019, 11(11): 5921-5935 |
| [42] | Ibáñez JJ, González-Urquijo JE, Gibaja J. Discriminating wild vs domestic cereal harvesting micropolish through laser confocal microscopy[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2014, 48: 96-103 |
| [43] | Ibáñez JJ, Anderson PC, Gonzalez-Urquijo JE, et al. Cereal cultivation and domestication as shown by microtexture analysis of sickle gloss through confocal microscopy[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2016, 73: 62-81 |
| [44] | Ibáñez JJ, Lazuen T, González-Urquijo J. Identifying experimental tool use through confocal microscopy[J]. Journal of Archaeological Method and Theory, 2019, 26(3): 1176-1215 |
| [45] | Caux S, Galland A, Queffelec A, et al. Aspects and characterization of chert alteration in an archaeological context: A qualitative to quantitative pilot study[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2018, 20: 210-219 |
| [46] | Galland A, Queffelec A, Caux S, et al. Quantifying lithic surface alterations using confocal microscopy and its relevance for exploring the Châtelperronian at La Roche-à-Pierrot (Saint-Césaire, France)[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2019, 104: 45-55 |
| [47] | Macdonald DA, Xie L, Gallo T. Here's the dirt: First applications of confocal microscopy for quantifying microwear on experimental ground stone earth working tools[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2019, 26: 101861 |
| [48] | 刘斌, 冯其波, 匡萃方. 表面粗糙度测量方法综述[J]. 光学仪器, 2004(26): 42-46 |
| [49] | 李伯奎, 刘远伟. 表面粗糙度理论发展研究[J]. 工具技术, 2003(38): 63-67 |
| [50] | 何宝凤, 魏翠娥, 刘柄显, 等. 三维表面粗糙度的表征和应用[J]. 光学精密工程, 2018, 26(8): 164-181 |
| [51] | Macdonald DA, Evans AA. Evaluating surface cleaning techniques of stone tools using laser scanning confocal microscopy[J]. Microscopy Today, 2014, 22(3): 22-27 |
| [52] | Brakenhoff GJ, Blom P, Barends P. Confocal scanning light microscopy with high aperture immersion lenses[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 1979, 117(2): 219-232 |
| [53] | 马亢, 周庆峰, 施传信, 等. 激光共聚焦显微镜技术进展[J]. 农学学报, 2016, 6(6): 30-35 |
| [54] | 李叶, 黄华平, 林培群, 等. 激光扫描共聚焦显微镜[J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2015(7): 272-275+279 |
| [55] | 奥林巴斯(北京)销售服务有限公司. OLS5000产品说明[Z]. 2020-04-06. https://www.olympus-ims.com.cn/en/metrology/ols5000/ |
| [56] | 崔天兴. 石器微痕分析中的印模材料及技术[N]. 中国文物报, 2017-08-25(007) |
| [57] | Stemp WJ, Macdonald DA, Gleason MA. Testing imaging confocal microscopy, laser scanning confocal microscopy,and focus variation microscopy for microscale measurement of edge cross-sections and calculation of edge curvature on stone tools: Preliminary results[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2019, 24: 513-525 |
| [58] | Stevens NE, Harro DR, Hicklin A. Practical quantitative lithic use-wear analysis using multiple classifiers[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2010, 37(10): 2671-2678 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |