

Newly discovered lithic artifacts from the Shanxi-Shaanxi Gorge in the middle reaches of Yellow River, Longmen-Hukou of Shaanxi Province
Received date: 2020-09-24
Revised date: 2021-04-23
Online published: 2022-06-16
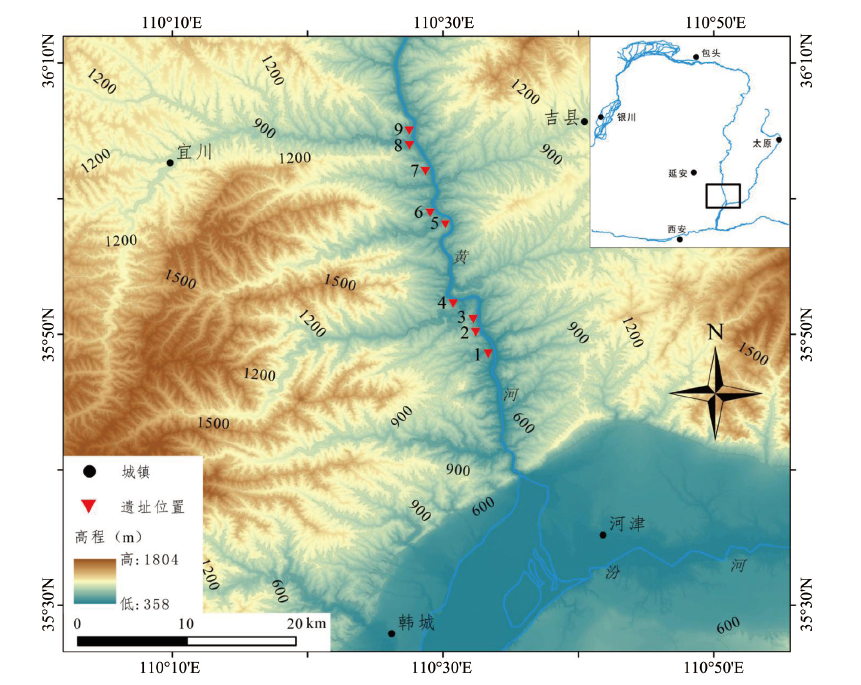
In 2019-2020, nine Paleolithic open-air sites were discovered in the Shanxi-Shaanxi Gorge in the middle reaches of the Yellow River, Longmen-Hukou (Shaanxi Province), Northern China. A total of 136 lithic artifacts were collected. Some of the lithic artifacts were directly collected from the exposed stratigraphic sections. In Kangjialing site, most of the lithic artifacts are buried in the fluvial clastic accumulation layer at the bottom of Malan loess, which may be in the early Late Pleistocene. In Sujialing site, only one lithic artifact from the fluvial clastic layer under the weak paleosol layer of MIS3 stage, most of the lithic artifacts are buried in Malan loess. The OSL age of the fluvial clastic layer is 72±7 kaBP. The rest of the buried strata are Malan loess layer, which can be temporarily placed in the middle and late stage of Late Pleistocene, and the OSL data of the loess layer in Liangquangou site is more than 50ka. The raw materials for processing lithic artifacts are mainly gravel, and the lithology is mainly quartzite, followed by quartz, in addition to a small amount of flint, fine sandstone and siliceous rock. The lithic artifacts include cores, flakes, retouched tools, chunks, which are mainly small (<50 mm) in size. The platforms of core and flake are dominated by cortical surface. Most of the lithic artifacts were knapped by direct hammer percussion, a few stone artifacts were knapped by bi-polar technique. The retouched tools include light-duty scrapers, notch, and choppers. The lithic industry show typical characters of the simple core-flake technology. These newly discovered Paleolithic site has further expanded the spatial and temporal distribution of Paleolithic remains in Shanxi-Shaanxi Gorge area of the Yellow River, which is conducive to the follow-up research work.
Key words: Yellow River; Loess; Lithic artifacts; Late Pleistocene; LithicTechnology
Gaike ZHANG , Xiaoning GUO , Shuangwen YI , Hongyan ZHANG , Hanqing ZHAO , Shejiang WANG . Newly discovered lithic artifacts from the Shanxi-Shaanxi Gorge in the middle reaches of Yellow River, Longmen-Hukou of Shaanxi Province[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022 , 41(03) : 470 -480 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0060
| [1] | 张改课, 王社江, 李钊, 等. 黄河中游晋陕峡谷延安段新发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(1): 86-105 |
| [2] | 陕西省考古研究院, 商洛地区文管会,洛南县博物馆. 花石浪(I)——洛南盆地旷野类型旧石器地点群研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007, 37-54 |
| [3] | 刘士莪, 张洲. 陕西韩城禹门口旧石器时代洞穴遗址[J]. 史前研究, 1984(1): 45-55 |
| [4] | 山西大学历史文化学院, 山西省考古研究所. 山西吉县柿子滩遗址S29地点发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2017(2): 35-51 |
| [5] | 王小庆. 石器解读—以龙王辿遗址第一地点为例[J]. 文博, 2017(6): 26-30 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |